RIYADH: For generations, historians and writers have unwittingly perpetuated the myth that the First Saudi State, forerunner of the modern-day Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, was founded in the year 1744.
In fact, as a new reappraisal of the origins of the Kingdom reveals, they were 17 years out.
There is no doubt that the events of 1744, the year in which Imam Mohammed ibn Saud of Diriyah offered sanctuary to the religious reformer Sheikh Mohammed ibn Abdulwahhab, were hugely significant.
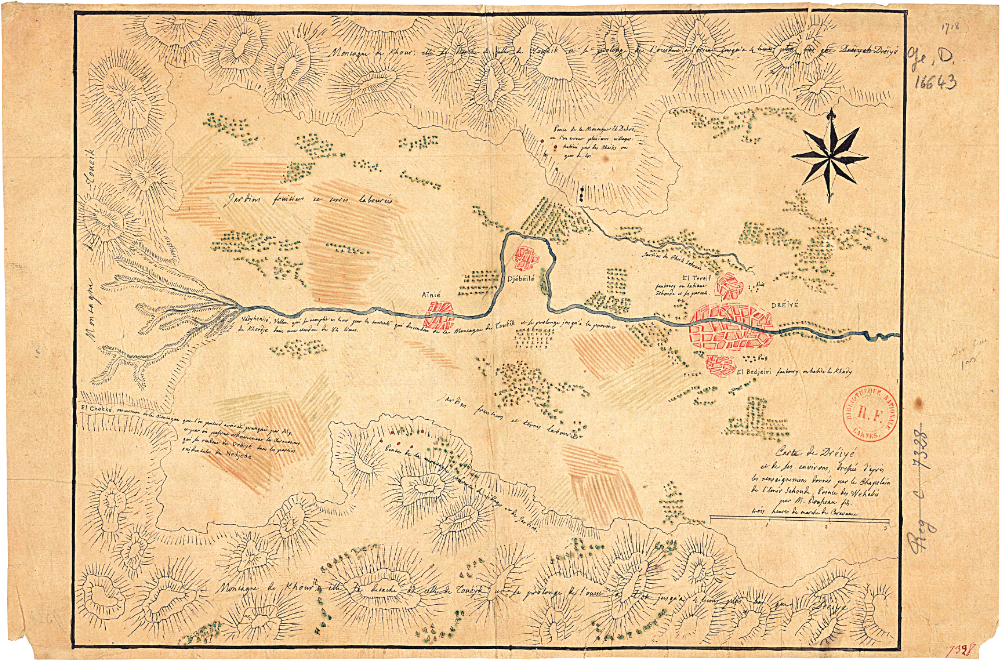
In this ‘Carte de Dreiye,’ the oldest-known map of Diriyah, drawn by a French diplomat in 1808, the historic UNESCO-listed district of At-Turaif on the Wadi Hanifah is recorded as ‘El Tereif.’
But over time the importance of that admittedly historic moment of common cause between state and faith came to obscure the far more complex and deeper-rooted origins of the First Saudi State.
It is to correct this neglect of the Kingdom’s crucial embryonic years that Founding Day has been created, to celebrate 1727 as the true moment of birth and to give Saudis a deeper appreciation of a past far richer than many realize.
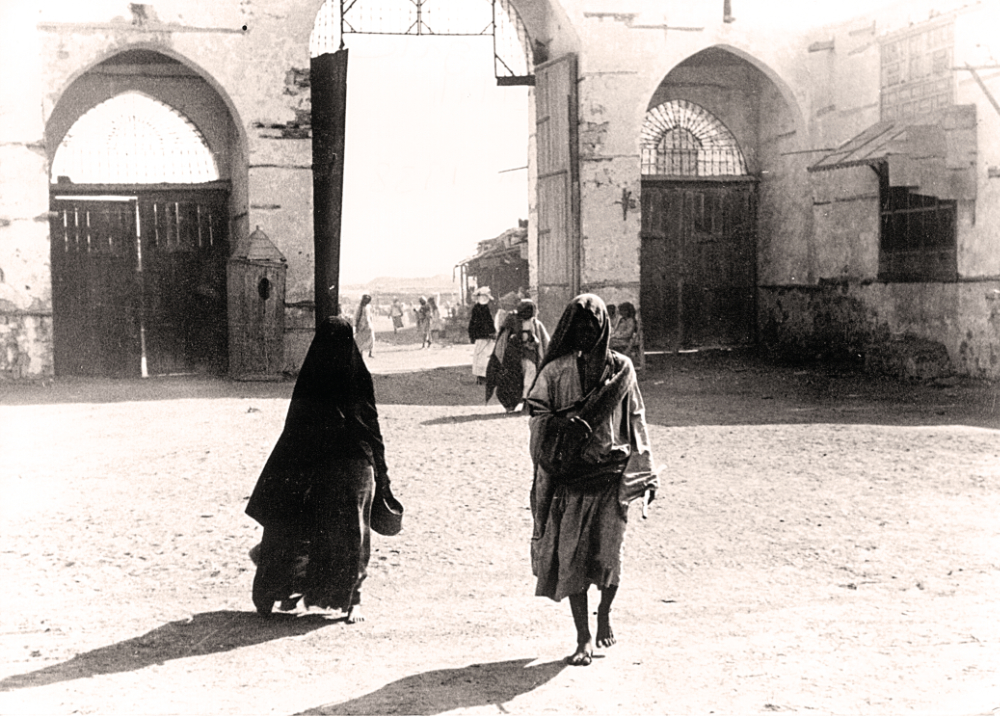

The original Makkah Gate in Jeddah.
It was in 1727 that Imam Mohammed ibn Saud came to the throne, carrying with him the dream of transforming the city state founded by his forebears three centuries earlier into the capital of a nation which, at its height, would bring peace and stability to most of the Arabian Peninsula.
This resetting of the clock from 1744 to 1727 is the outcome of extensive historical research that has been carried out studying the historical resources held by the new Saudi Historical School.
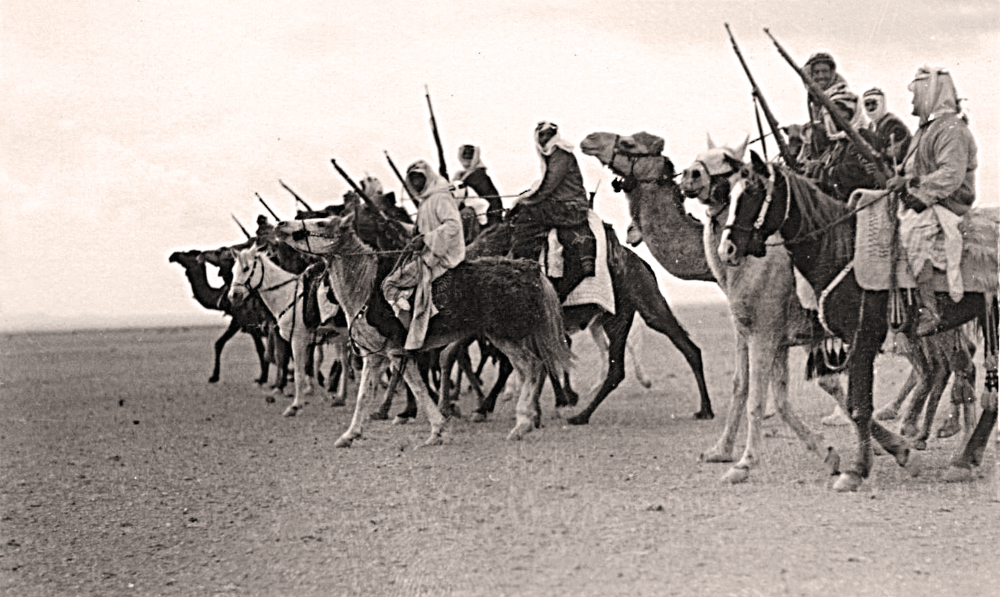

Ibn Saud’s warriors on the move in the early 20th century as the future founder of Saudi Arabia fought to bring the Najd and the Hejaz together.
“Many historians have linked the rise of the state to the arrival of Sheikh Mohammed ibn Abdul Wahab, and have neglected the initial period of Imam Mohammed ibn Saud’s rule and the preceding era, even though this was the foundational period of the state,” said Dr. Badran Al Honaihen, associate director of historical research and studies at Diriyah Gate Development Authority.
“The revision and reinterpretation of historical events is an intellectual phenomenon found in every part of the world. Previous writings can be considered judgments and opinions that do not prevent revisions or the reaching of new conclusions.”
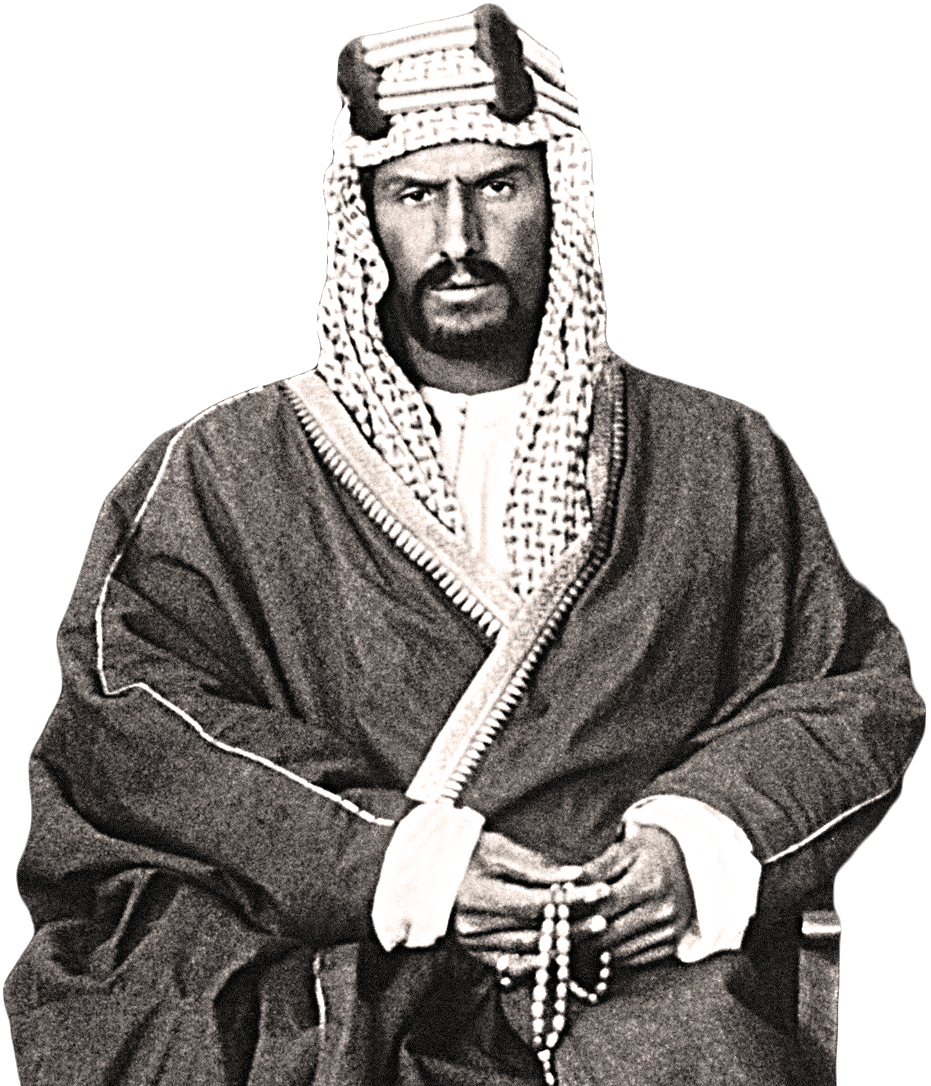

It was in 1727 that Imam Mohammed ibn Saud came to the throne, carrying with him the dream of transforming the city state founded by his forebears three centuries earlier into the capital of a nation which, at its height, would bring peace and stability to most of the Arabian Peninsula. (Supplied)
Today, no one can pinpoint exactly when the long journey toward statehood began. The first certain waypoint on the path is the year 430 when the Banu Hanifah tribe migrated to Al-Yamamah in the lower Najd from their home in the Hejaz on the Red Sea coast.
Here, at the junction of several important caravan routes, the tribe to which the ruling house of Al-Saud belongs settled and thrived, founding Hajr — modern-day Riyadh — trading, and growing crops in the fertile valley that in time would take their name — Wadi Hanifah.
With the coming of Islam the Banu Hanifah stepped on to the stage of world history for the first time.

It was in 1727 that Imam Mohammed ibn Saud came to the throne, carrying with him the dream of transforming the city state founded by his forebears three centuries earlier into the capital of a nation which, at its height, would bring peace and stability to most of the Arabian Peninsula. (Supplied)
In 628, six years after the hijra, the flight of Mohammed and his persecuted followers from Makkah to Madinah, the Prophet sent letters to various Arabian rulers, inviting them to embrace “Islam,” submission to the will of God.
The ruler of the Banu Hanifah at this time was Thumamah ibn Uthal, whose spiritual journey from initial rejection to heartfelt acceptance of Islam is celebrated in the Hadiths.
IMAM MOHAMMED IBN SAUD’S MOST SIGNIFICANT ACHIEVEMENTS
• Unified Diriyah under his rule and contributed to its stability.
• Managed internal affairs and strengthened Diriyah’s community.
• Ensured regional stability.
• Built the Diriyah wall to counter external attacks.
• Began unification campaigns.
• Political independence from any external influence.
• Organized the country’s resources.
• Unified the majority of Najd.
• Secured Hajj and trade routes.
In Hadith number 189, he is recorded as telling Mohammed: “There was no face on the face of the Earth that was more hateful to me than your face, but now your face has become the most beloved of all faces to me.”
In historical terms, Al-Yamamah would lay dormant for much of the next 800 years. This was a dark age of neglect and widespread emigration to escape the economic hardship endured under the oppressive Ukhaidhir dynasty, which rose to temporary prominence in the Najd in the ninth century.
Destiny, however, is a patient force, and by the 15th century the stage was finally set for the return to influence of the Banu Hanifah.
Generations earlier, part of the tribe had migrated eastwards to settle on the shores of the Arabian Gulf. But in 1446, Manaa’ Al-Muraide, leader of the Marada clan of the Al-Duru tribe of the Banu Hanifah, led his people back to the heart of Arabia, at the invitation of his cousin, Ibn Dira’, the ruler of Hajr.
The settlement they had founded on the coast they had named Diriyah after their tribal name, Al-Duru. Now they established a new Diriyah on the fertile banks of the Wadi Hanifah.
In the words of historian Dr. Badran Al-Honaihen, Al-Muraide’s arrival “laid the building blocks for the establishment of the greatest state in the history of the Arabian Peninsula, after the Prophetic State and the Rashidun Caliphate.”
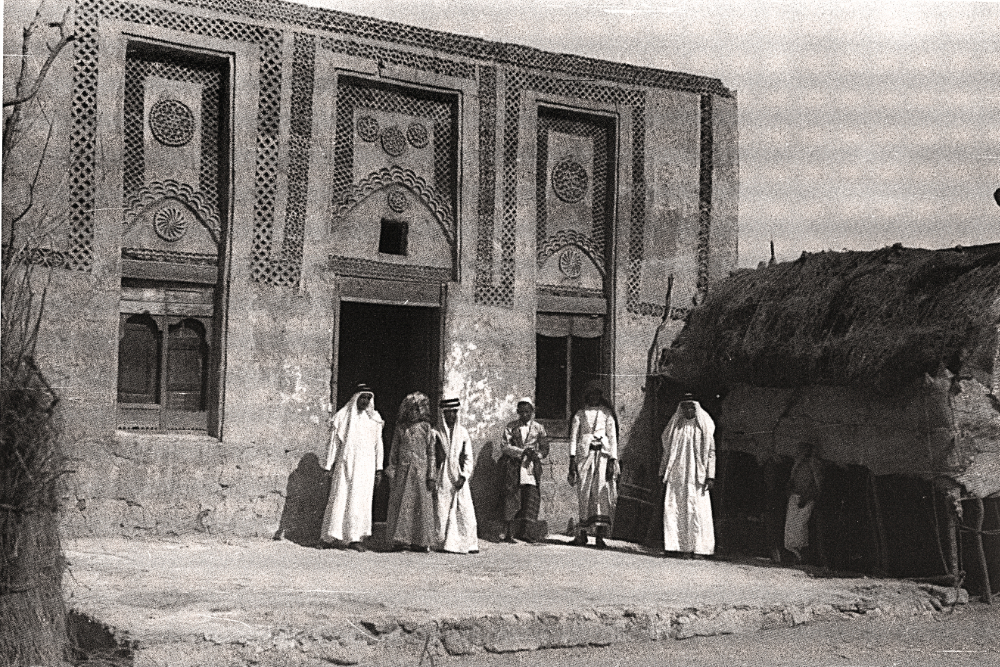

It was in 1727 that Imam Mohammed ibn Saud came to the throne, carrying with him the dream of transforming the city state founded by his forebears three centuries earlier into the capital of a nation which, at its height, would bring peace and stability to most of the Arabian Peninsula. (Supplied)
Another 300 years would pass before the next momentous steps were taken. In 1720, Saud ibn Mohammed assumed the leadership of Diriyah, who the Saudi Royal Family named after him.
Today, historians date the origin of the First Saudi State to 1727, when Saud’s son, Mohammed, became the ruler of the city state.
He had, said Al-Honaihen, “assumed power in exceptional circumstances.” Diriyah had been rent by internal divisions, and a plague that had spread throughout the Arabian Peninsula had claimed many lives in the Najd. Nevertheless, “Imam Mohammed was able to unite Diriyah under his rule, and to contribute to the spread of security and peace at the regional level and on the level of the Arabian Peninsula.
“The project of the first Saudi state began in 1727, and then his sons took it on after him. What we need to remember from this story is unity, security and peace after centuries of lack of unity.”

It was in 1727 that Imam Mohammed ibn Saud came to the throne, carrying with him the dream of transforming the city state founded by his forebears three centuries earlier into the capital of a nation which, at its height, would bring peace and stability to most of the Arabian Peninsula. (Supplied)
At last, here was a leader with a vision that extended beyond his immediate horizon, and who was determined to found a new state, based on education, culture and security and allegiance to the true faith of Islam.
It was to this dynamic and politically and economically increasingly powerful new state that the religious reformer Sheikh Mohammed ibn Abdul Wahab was drawn.
The sheikh, a religious scholar from the nearby village of Al-Uyayna, had become increasingly concerned that many in the Arab world were forsaking the teachings of the Prophet and returning to heretical pre-Islamic ways. His attempts to introduce reforms were met with hostility in Al-Uyayna, but he would find sanctuary in Diriyah.
“The migration to Diriyah of Sheikh Mohammed ibn Abdul Wahab came as a natural result of Imam Mohammed ibn Saud’s policies,” said Al-Honaihen. “The Imam was known to be religious, and his two brothers, Thunayan and Mishari, and his son Abdulaziz were among those in contact with Sheikh Mohammed ibn Abdulwahhab in Al-Uyayna.
“Sheikh Mohammed did not leave al-Uyayna until after Imam Mohammed invited him to come to Diriyah, and there was a state capable of protecting the Sheikh’s religious mission.”
For his part, “in supporting this reformist mission, Imam Mohammed saw that it was in agreement with the principles of the state he was working to establish, especially its religious aspect.”
In short, it was not the alliance of Sheikh and Imam that made possible the foundation of the First Saudi State, but rather it was the existence of that state, already politically and economically strong, that made possible the spread of the message of reform.

It was in 1727 that Imam Mohammed ibn Saud came to the throne, carrying with him the dream of transforming the city state founded by his forebears three centuries earlier into the capital of a nation which, at its height, would bring peace and stability to most of the Arabian Peninsula. (Supplied)
Al-Honaihen stressed that the decision to officially recognize 1727 as the year of founding should in no way be interpreted as undermining religion as the cornerstone of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
“That’s not correct,” he said. “The objective is merely to put a precise political date to the founding of the state, namely Imam Mohammed ibn Saud’s accession to power in Diriyah, since a number of erroneous policies and opinions had arisen concerning the rise and establishment of the state.
“Moreover, the state in its constitution stipulates that the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is an Arab Islamic state whose religion is Islam and whose constitution is the Book of God and the Sunna of His Prophet.”

It was in 1727 that Imam Mohammed ibn Saud came to the throne, carrying with him the dream of transforming the city state founded by his forebears three centuries earlier into the capital of a nation which, at its height, would bring peace and stability to most of the Arabian Peninsula. (Supplied)
He is also clear that Founding Day is not an alternative to National Day, celebrated on Sept. 23, but complementary to it.
“Founding Day is not intended to replace Saudi National Day, which celebrates the unification of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932, but rather to recognize the beginning of the Saudi state’s history with a new event that celebrates the deep historical roots of the Kingdom.”
Although there is no doubt about the year, 1727, the precise date of the start of Imam Mohammed’s reign is lost to history, according to Al-Honaihen.
Feb. 22 was selected as Founding Day simply because a number of important events are known to have taken place in the first months of Imam Mohammed’s reign, at the start of 1727.


































