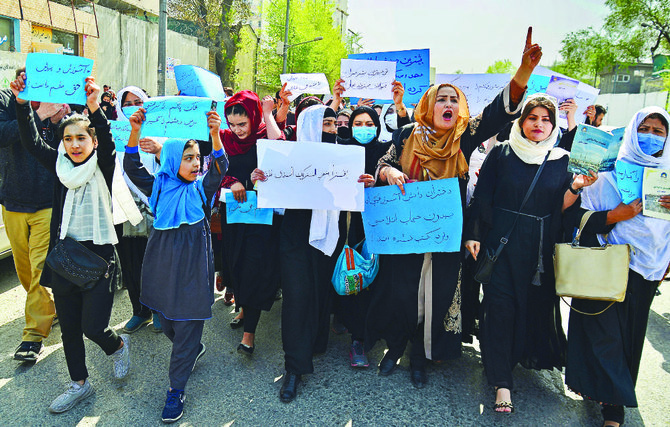
DUBAI: Every day, Nasima, 16, and Shakila, 17, eagerly await news that their school in Kabul, Lameha-e-Shaheed, will reopen so that they can resume their studies. They have waited one month now since the Taliban abruptly closed secondary schools for girls, reneging on a previous decision to grant women more freedom and access to education.
On the morning of March 23, more than 1 million girls of Nasima and Shakila’s age group had showed up at their schools across Afghanistan for the first time since the Taliban seized power in August last year, only to be turned away from the gates.
“Under the guidance of the leadership of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, schools for women from the sixth grade above are closed until further notice,” read a report by the pro-Taliban Bakhtar News Agency.
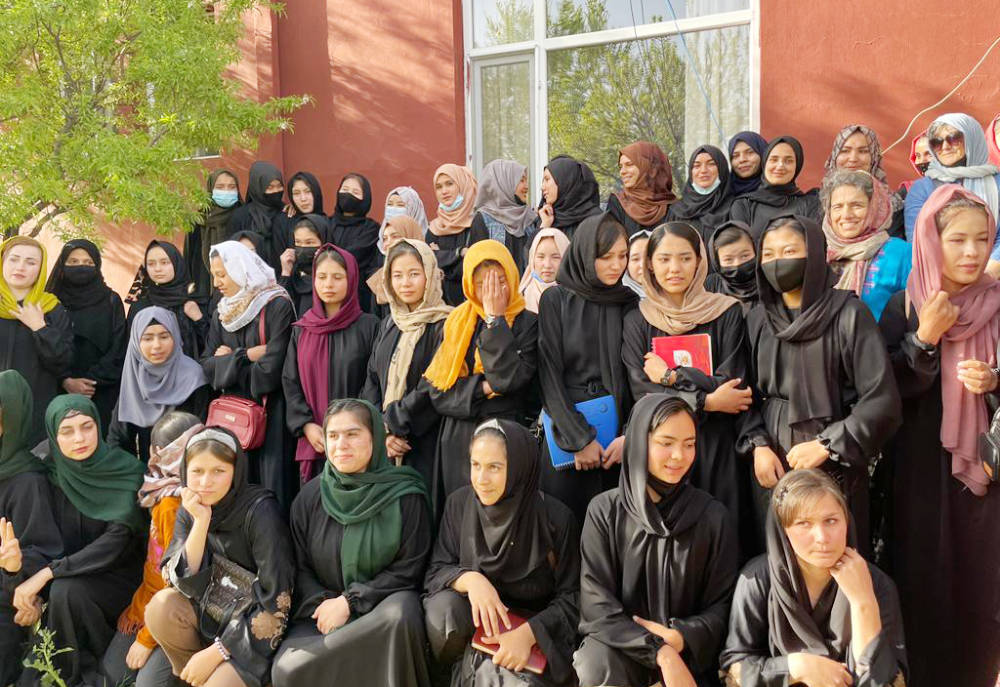

“The truth is that the Taliban’s views on women’s rights, human rights and individual freedoms have not changed in the last 20 years,” Nilofar Akrami, a 30-year-old university lecturer who teaches women at Kabul University, told Arab News. (Supplied)
Although many Afghans were dismayed by the news, those familiar with the puritanical views and erratic policies of the Taliban during their 1996-2001 rule were not at all surprised.
Creeping ultraconservatism is evident in new rules that ban women without a hijab or male chaperone from traveling long distances, dismissal of women from jobs and positions of influence, and, most prominently, in the education policy U-turn of March 23.
FASTFACTS
• New ban on girls’ education exposes rifts in the Taliban leadership.
• Afghan teachers and girls hold out little hope of schools reopening.
• Female literacy rate more than doubled between 2000 and 2018.
“They kept telling us that they would reopen the schools and let everyone go back,” Lina Farzam, a primary school teacher in Kabul, told Arab News.
“Although we never trusted that the Taliban had changed, we had hope. We don’t know why the world trusted them and gave them another chance.”
The about-turn on secondary school education, which reportedly happened after a secret meeting of the group’s leadership in Kandahar, suggests that the ultraconservative wing still retains control over the regime’s ideological trajectory.
“What’s so cruel about this is the fact that they announced that girls can go back to school, then backtracked,” said Farzam. “Imagine those girls happily preparing for school the night before and waiting to go back to class.”
Primary school-aged girls in Afghanistan are permitted to receive schooling up until the sixth grade. Women are also allowed to attend university, albeit under robust gender segregation rules and only if they abide by a strictly enforced dress code.

The Taliban’s shift on girls’ schooling reportedly came after a secret meeting. (AFP)
Following the US-led coalition’s chaotic withdrawal from Afghanistan in August 2021, the resurgent Taliban insisted it had changed its ways and would allow women and girls to continue studying as they had under the UN-recognized government.
At a press conference in Kabul on Aug. 18, Taliban spokesman Zabihullah Mujahid promised that the new government would respect the rights of women.
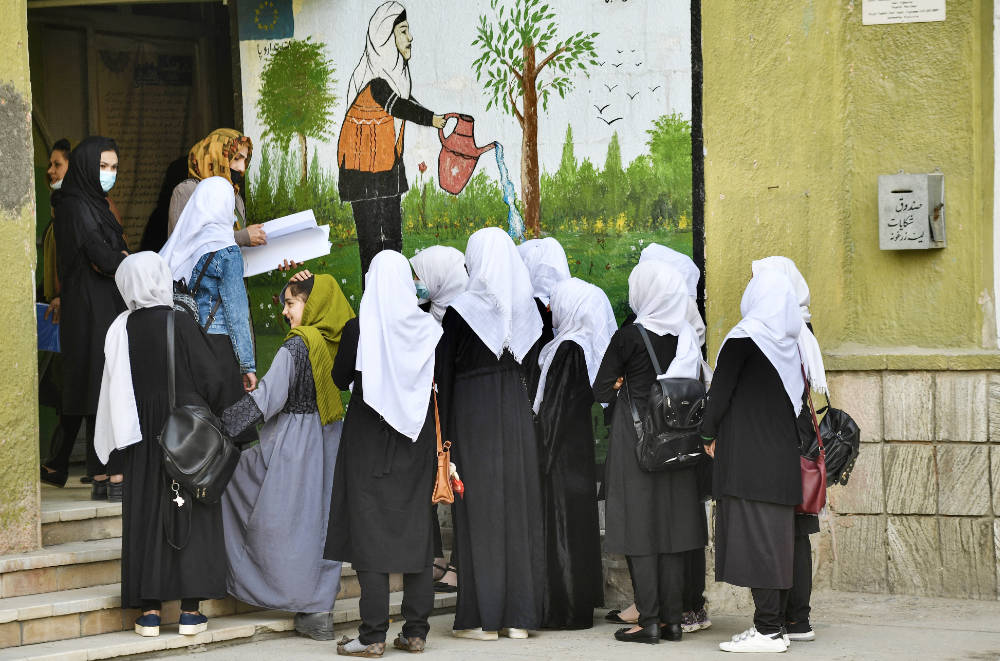

In this file photo taken on March 23, 2022, girls arrive at their school in Kabul. (AFP)
“The truth is that the Taliban’s views on women’s rights, human rights and individual freedoms have not changed in the last 20 years,” Nilofar Akrami, a 30-year-old university lecturer who teaches women at Kabul University, told Arab News.
“The Taliban are as brutal as they were in the 1990s, and, when it comes to women, they have gotten worse. Unfortunately, they have learned how to wear a good mask to deceive the world.
“They still think women should stay at home and women who leave their home to study or work are bad, and that they will corrupt society.”

“I am disturbed because there is no justification for denying girls an education,” Daisy Khan, founder of the New York-based Women’s Islamic Initiative in Spirituality and Equality, told Arab News. (Supplied)
For Akrami, any hopes for women’s empowerment in Afghanistan have long been dashed. “As a woman who started her career at university to make a difference to the lives of women, I am sorry that my dreams and the dreams of hundreds of women like me have been ruined since the Taliban came to power,” she said.
Asma Faraz, who previously worked at the Afghan Embassy in Washington D.C., is likewise disheartened to see the freedoms and opportunities of the past 20 years snatched away.

Keeping women out of work costs Afghanistan up to $1 billion, or 5 percent of gross domestic product, according to the UN. (Supplied)
“My boss was a female ambassador,” she told Arab News, referring to Roya Rahmani, the first Afghan woman to serve as her country’s top diplomat in the US. “As a woman, I was so proud to see another enter the room and watch how everyone respected her.
“Women can also be ambassadors, women can be members of parliament, women can be journalists and doctors. But now in Kabul, women and girls will see how women cannot go to school and can only get married, and see their mothers only working at home.”
The Taliban leadership has sought to justify its ban on secondary education for Afghan girls on the grounds of religious principle — a view that Islamic scholars and civil society dispute.

At a press conference in Kabul on Aug. 18, Taliban spokesman Zabihullah Mujahid promised that the new government would respect the rights of women. (Supplied)
“I am disturbed because there is no justification for denying girls an education,” Daisy Khan, founder of the New York-based Women’s Islamic Initiative in Spirituality and Equality, told Arab News.
“In Islam, pursuit of knowledge is an obligation on all Muslims. Prophet Muhammad made no distinction between boys’ and girls’ education. He said: ‘The best of you is one who gives a good education to his children.’”
Conflicting messages from high-ranking officials could be indicative of a schism within the Taliban ranks between the hard line based in the movement’s Kandahar stronghold and the more moderate officials managing affairs from the capital.

Hibatullah Akhundzada, the Islamic Emirate’s supreme leader, has ignored repeated calls, even from many clerics, to reverse the decision on girls’ secondary education. (Supplied)
According to some reports, Hibatullah Akhundzada, the Islamic Emirate’s supreme leader, has ignored repeated calls, even from many clerics, to reverse the decision on girls’ secondary education.
“People keep talking about Hibatullah, but no one has seen him or knows where he is in Kandahar,” said Faraz. “Maybe he is living in a village where people don’t allow their daughters to go to school and he doesn’t know how living is outside the village.
“If we want to give the Taliban a chance, that’s fine, give them a chance, but they can’t rule over everyone else and bring what they think is right from their villages to the cities and to the capital where people used to go to school and work.”
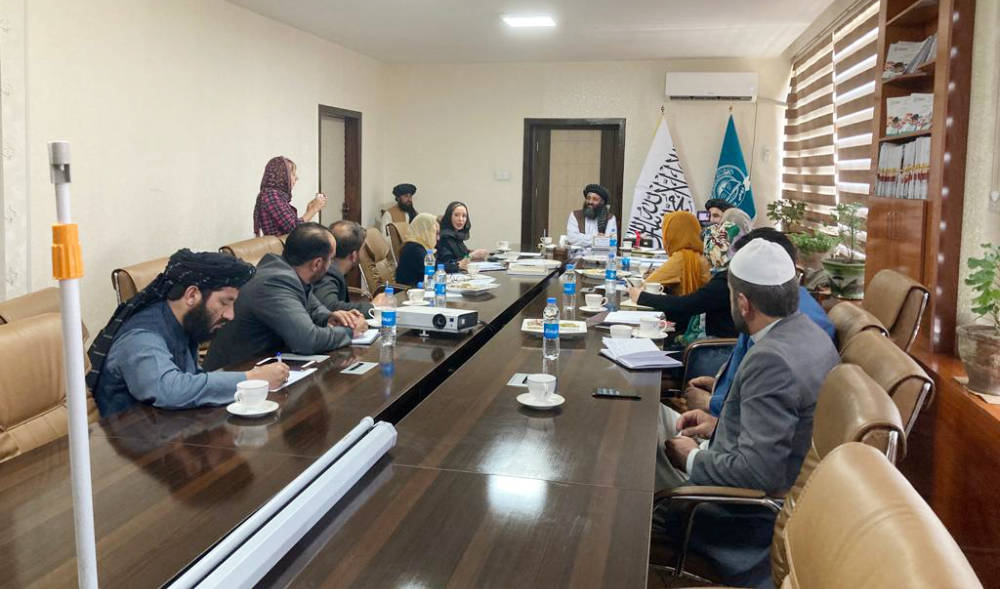

Eager to see the matter resolved quickly and the rights of Afghan women and girls preserved, education activists from the US traveled to Kabul at the end of March to meet with Taliban officials. (Supplied)
In contrast with the views emanating from the Kandahar camp, one senior official recently told NPR that the Taliban had not changed course on girls’ education but simply needed more time to decide on appropriate school uniforms.
“There is no issue of banning girls from schools,” Suhail Shaheen, the Taliban’s permanent ambassador-designate to the UN, told the news outlet. “It is only a technical issue of deciding on the form of school uniform for girls. We hope the uniform issue is resolved and finalized as soon as possible.”
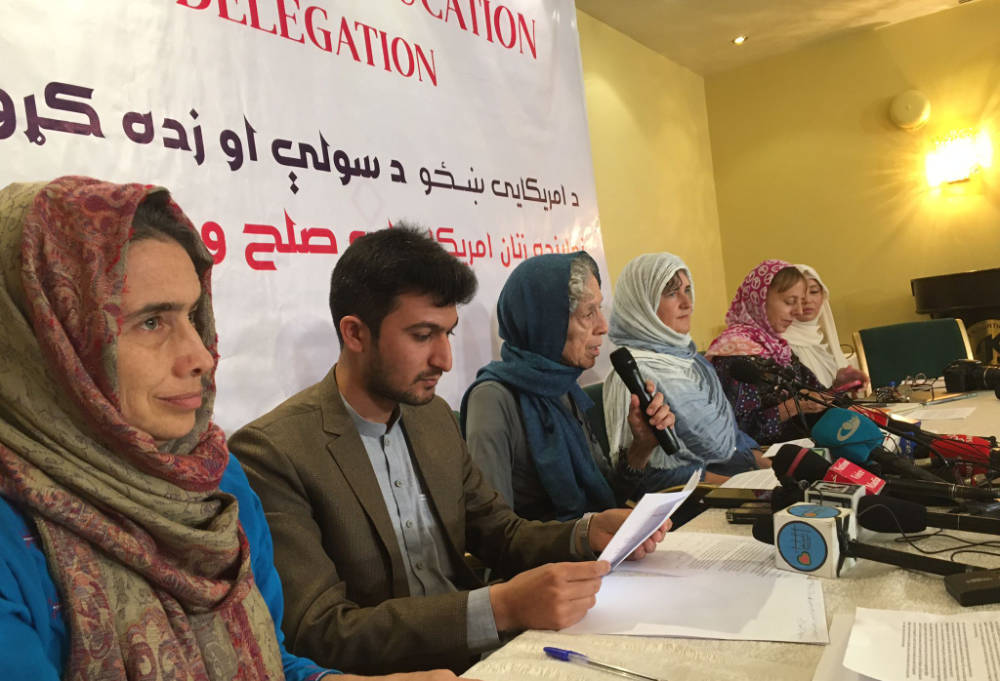

“There is no issue of banning girls from schools,” Suhail Shaheen, the Taliban’s permanent ambassador-designate to the UN, told NPR. (Supplied)
Eager to see the matter resolved quickly and the rights of Afghan women and girls preserved, education activists from the US traveled to Kabul at the end of March to meet with Taliban officials.
“While the world’s attention has turned to the crisis in Ukraine, it is extremely important that we not forget what is happening in Afghanistan, a country which is now experiencing one of its worst years in recorded history,” Masuda Sultan, an Afghan American entrepreneur and human rights advocate, who was part of the delegation, told Arab News.
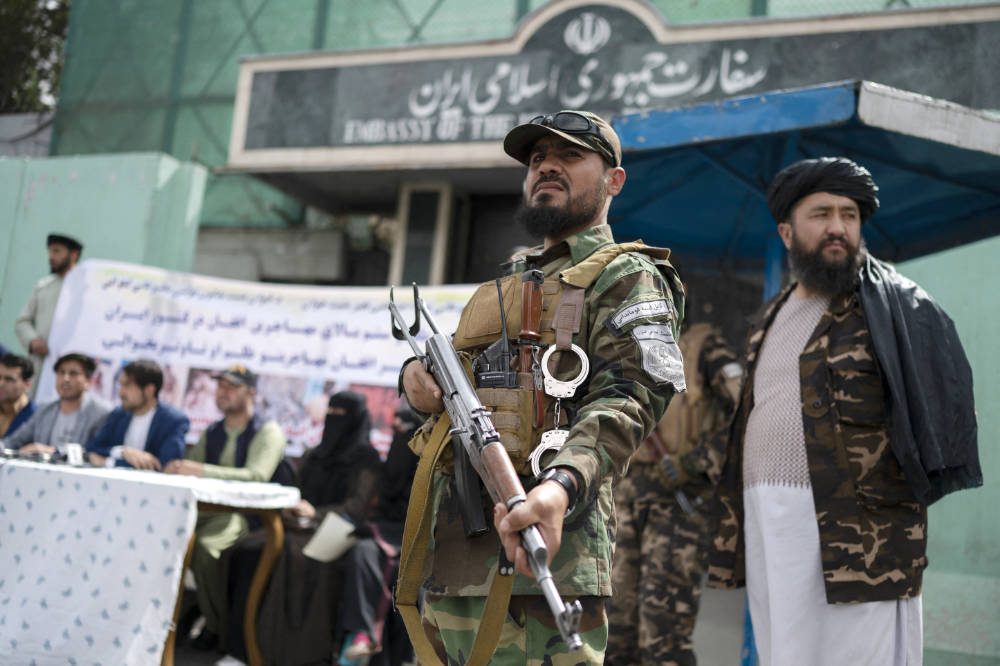

Taliban fighters stand guard as Afghan protestors take part in a protest against the alleged published reports of harassment of Afghan refugees in Iran, in front of the Iranian embassy in Kabul on April 11, 2022. (AFP)
“The continued economic strangulation of this nation may bring about consequences that will be far more costly to resolve if not addressed right away.”
Indeed, unless the Taliban shows it is willing to soften its hard-line approach, particularly on matters relating to women’s rights, the regime is unlikely to gain access to billions of dollars in desperately needed aid, loans and frozen assets held by the US, IMF and World Bank.

The Taliban leadership has sought to justify its ban on secondary education for Afghan girls on the grounds of religious principle. (Supplied)
Furthermore, keeping women out of work costs Afghanistan up to $1 billion, or 5 percent of gross domestic product, according to the UN. As The Economist noted in a recent article, “in the midst of an economic crisis, the country can ill afford the loss.”
For Farzam and her school pupils in Kabul, and indirectly even for the millions of Afghans in urgent need of economic assistance, the outcome of the apparent ideological tussle within the Taliban leadership could prove momentous, whether for better or worse.
“The girls are now sad because they can’t continue their education,” she told Arab News. “They are eagerly waiting for the reopening of their schools.”






















