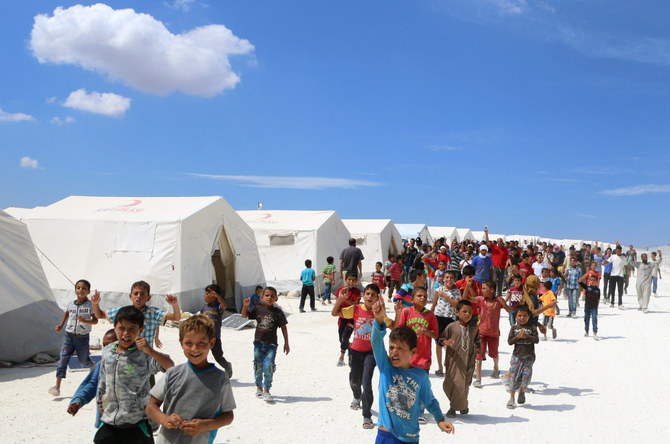
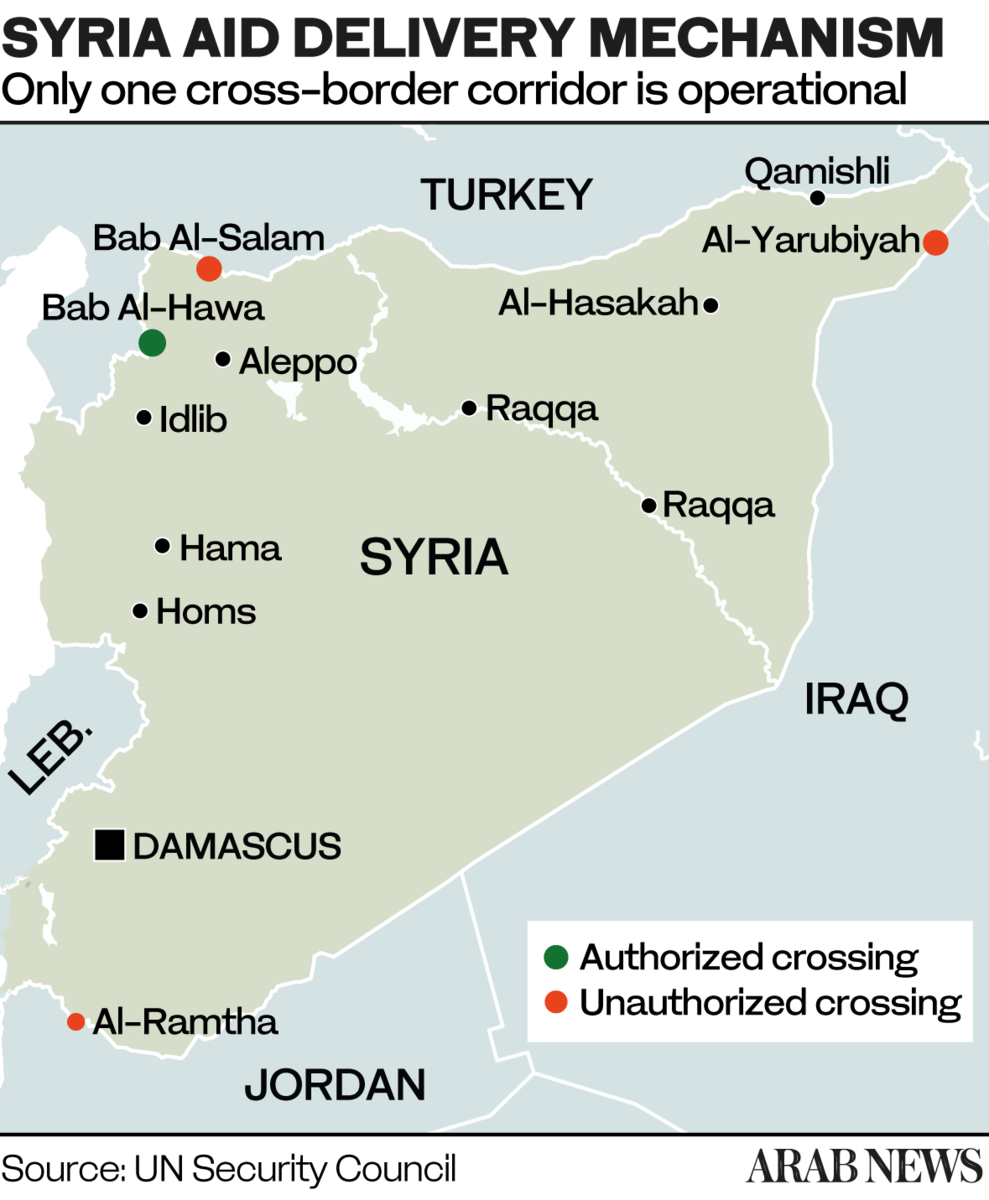
NEW YORK CITY: The four million people in northwest Syria who rely on international aid to survive are unsure whether there will be bread on their tables after July 10. That is when an increasingly fragile UN cross-border mechanism for delivering aid to Syria is set to expire.
Its renewal is up for a vote at the UN Security Council next month amid fears that Russia will use its power of veto to close the last remaining UN-facilitated gateway for aid into Syria, Bab Al-Hawa on the border with Turkey.
Ferit Hoxha, Albania’s permanent representative to the UN and the president of the Security Council for the month of June, told Arab News during a press conference that the closure of the only border crossing would amount to “a condemnation to death, starvation and hunger to millions of people.”
He added: “I hope no one, not Russia nor any other country, would come to that decision: To condemn civilians in need to death and hunger.”
While the world’s media might have stopped counting the numbers of dead and injured in the Syrian conflict, the widespread destruction of civilian infrastructure and the largest number of internally displaced people in the world lay bare the fact that the war is far from over.

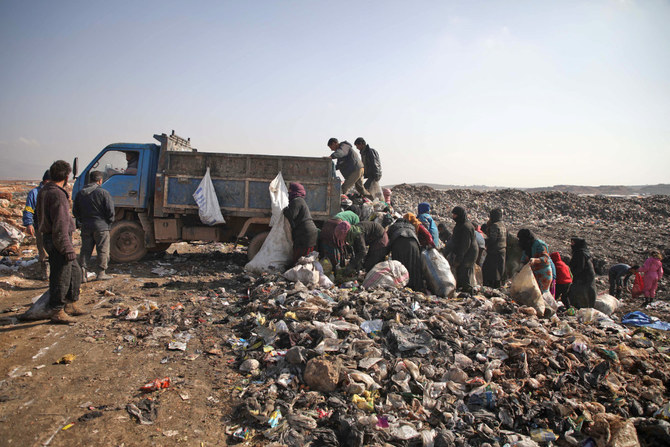
Ninety percent of Syria's population live below the poverty line, with many families left to scavenge to survive. (AFP file photo)
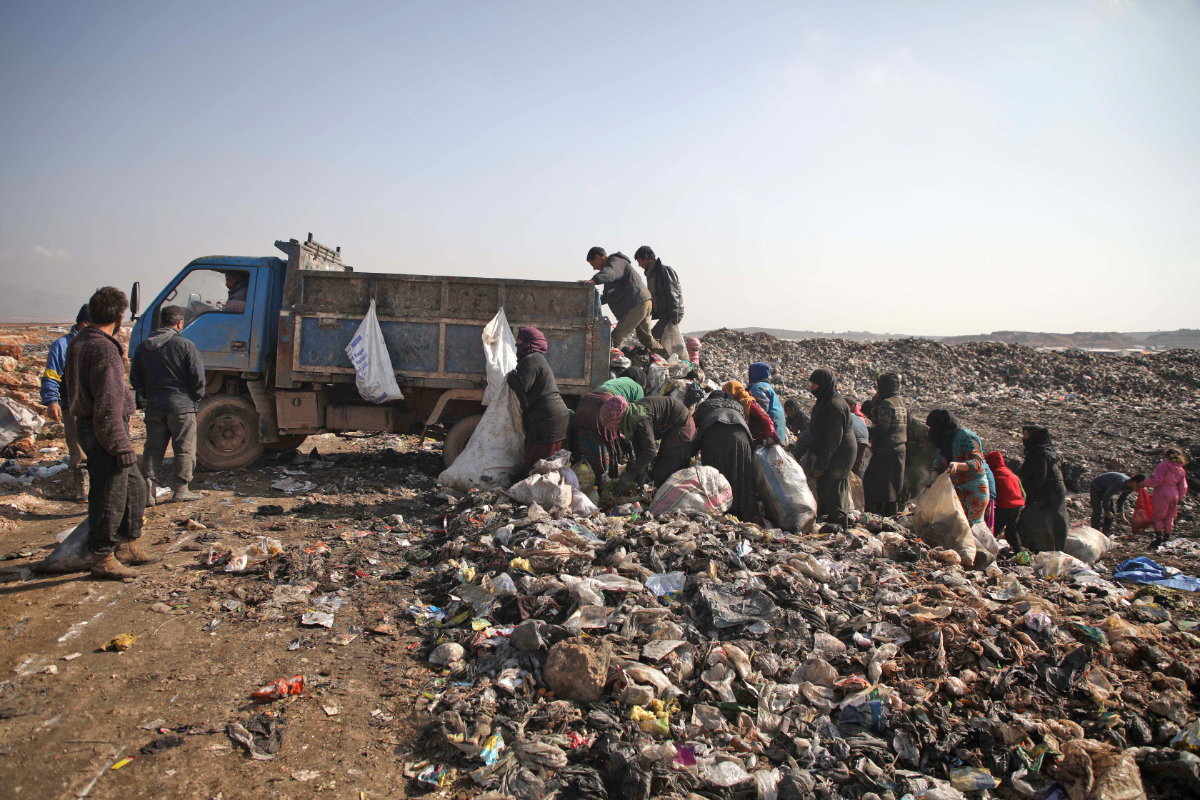
Syria continues to experience one of the worst humanitarian crises in the world, with 90 percent of the population living below poverty line. According to the World Food Program, 14.6 million people now need humanitarian assistance to survive, an increase of 1.2 million compared with last year.
The collapsing economy, coupled with a looming global food shortage as a consequence of the war in Ukraine, have added a new layer of complexity to the situation. Now, the WFP warns, the threat of famine is knocking on Syria’s door.

Ninety percent of Syria's population live below the poverty line, with many families left to scavenge to survive. (AFP file photo)
The cross-border mechanism was created in 2014 to allow the delivery of UN humanitarian aid directly to opposition-held areas of Syria. International humanitarian law requires that all aid deliveries should go through the host government.
However, Syrian President Bashar Assad’s tactic of treating humanitarian supplies as a weapon of war prompted the Security Council to resort to approving the use of four aid crossings along the Syrian border: one from Jordan, one from Iraq and two from Turkey.
Until December 2019, the members of the Security Council renewed the mandate for these crossings without much fuss. In January 2020, however, permanent member Russia used its power of veto to force the closure of all but one: Bab Al-Hawa.
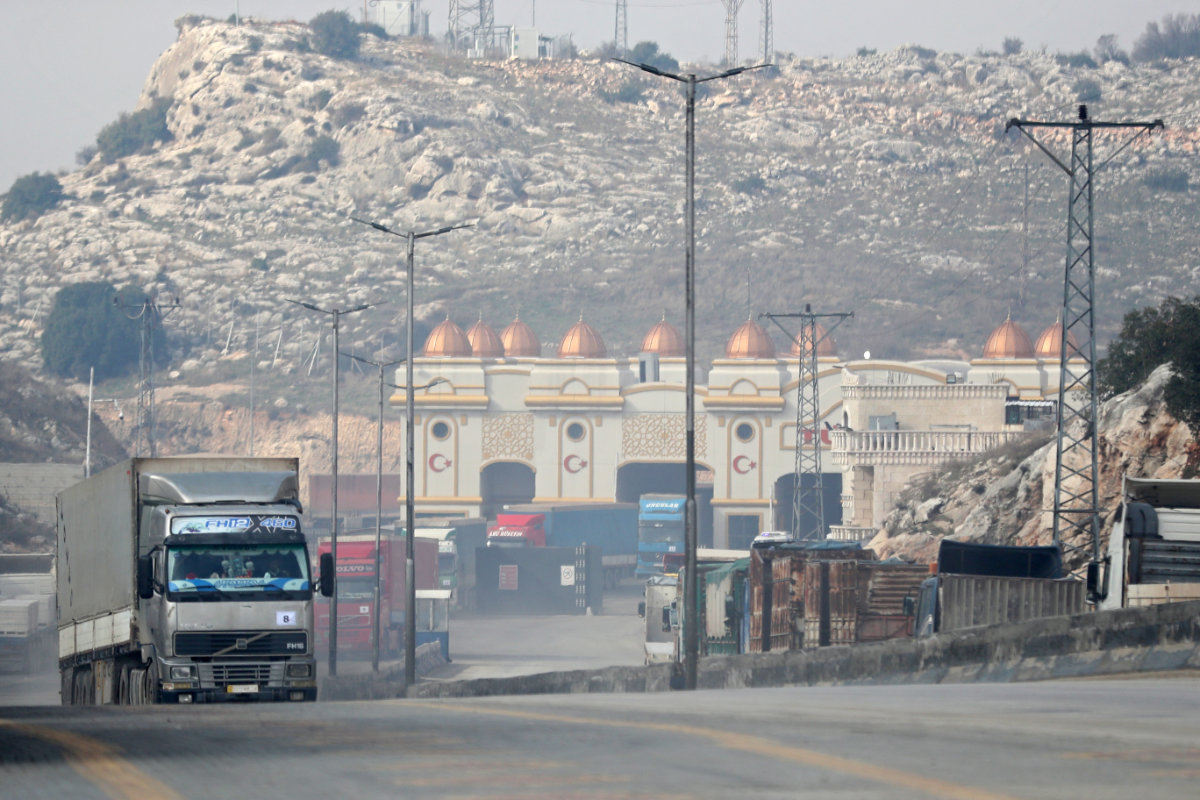

A convoy transporting humanitarian aid crosses into Syria from Turkey through the Bab al-Hawa border crossing on Jan. 18, 2022. (AFP)
If this last remaining crossing is closed — and the fear that this could happen is real — humanitarian agencies say they will be unable to feed more than about 10 percent of those in need. Moreover, finding any alternative to the UN aid operations is nearly impossible.
“The problem is that you have organizations and institutions that have been in emergency mode for 12 years,” said Jomana Qaddour, co-founder of Syria Relief & Development, a humanitarian organization active in northwestern Syria.
“The Syrian crisis has been so consuming and so overwhelming that planning for a massive humanitarian response now — under a totally different umbrella with all the buy-ins from the various different actors, from the local level to international donors — would be really quite a feat.”
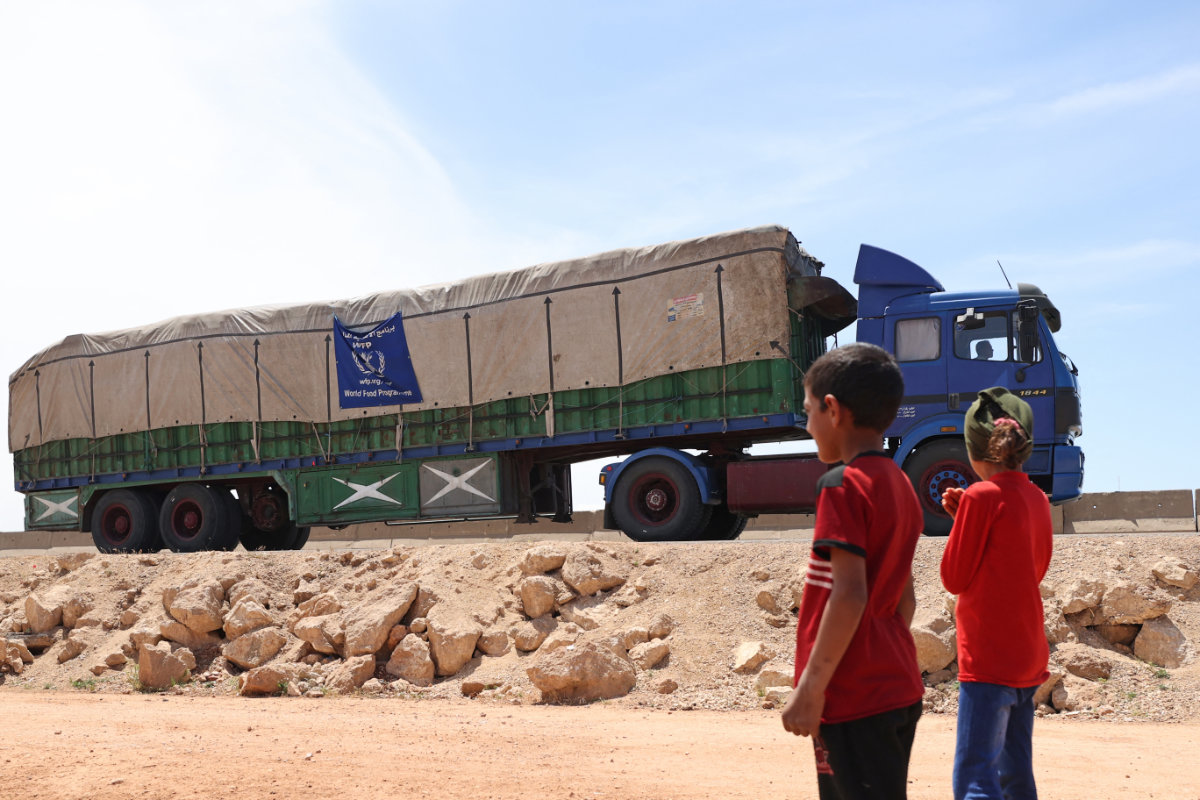

A truck carrying aid packages from the World Food Program drives through the town of Hazano in the rebel-held northern countryside of Syria's Idlib province, on May 16, 2022. (Omar Haj Kadour / AFP)
The effects of the war on Ukraine on food security are “systematic, severe and speeding up,” according to UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres. He has said that the war, combined with other crises, threatens to unleash an unprecedented wave of hunger and destitution, leaving social and economic chaos in its wake.
Lamenting the skyrocketing prices of food and a near doubling of the cost of fertilizers, and the resultant shortages of corn, wheat, rice and other staple crops, Guterres warned that while this year’s food crisis is about lack of access, “next year’s could be about lack of food.”
INNUMBERS
90% of Syrian population lives below the poverty line.
14.6m Syrians are dependent on humanitarian assistance.
While the UN warns that no country will be untouched by looming food shortages, especially those that are already vulnerable, one can only imagine the devastating severity of its effects on a place such as Syria, which has been reeling under similar conditions for the past 12 years of conflict.
In the run-up to the Security Council vote in July, intensive negotiations for a new resolution to extend the cross-border mechanism are continuing behind closed doors, led by Ireland and Norway, according to sources at the Irish mission to the UN.
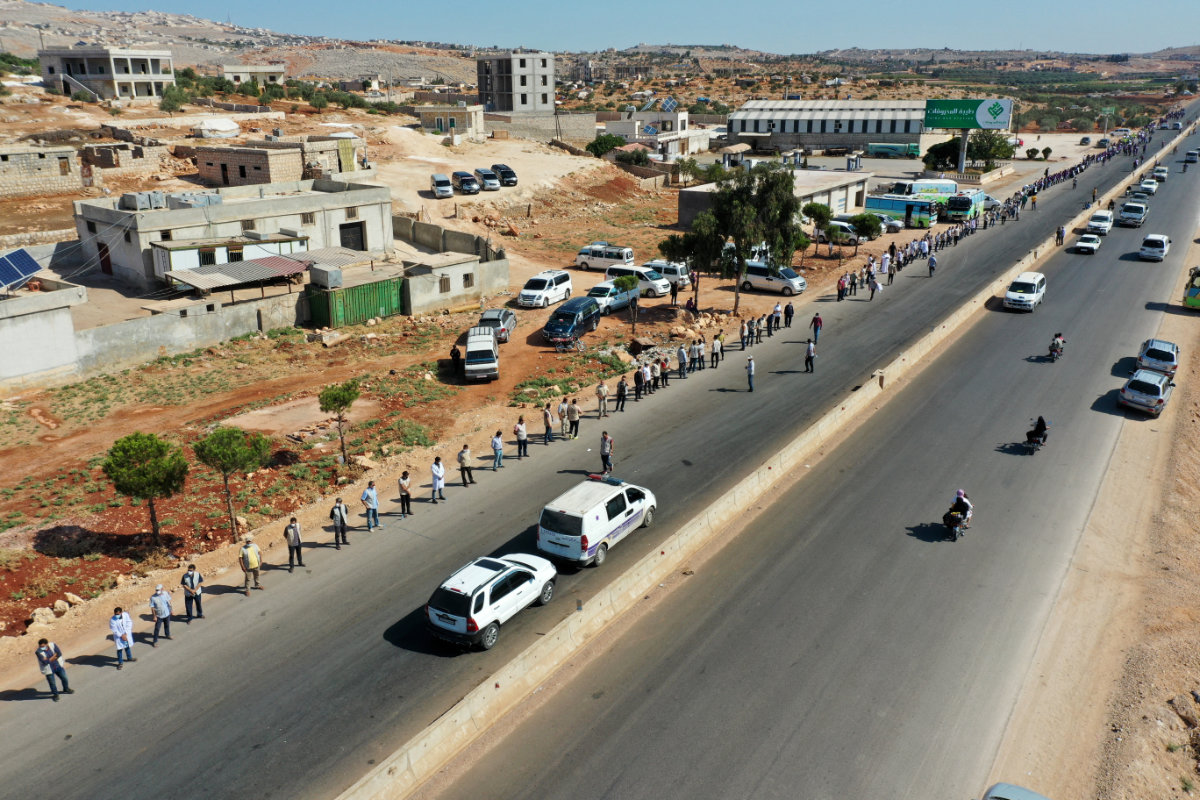

Civil society activists, aid, and medical and rescue services form a human chain rally on July 2, 2021 calling for the continued passage of humanitarian aid into Syria's rebel-held Idlib. (AFP file)
The two countries are the chief advocates at the UN for humanitarian issues in Syria. Last year at around this time, their ambassadors to the UN, Geraldine Byrne Nason and Mona Juul, were seen rushing back and forth from one UN chamber to another, trying to rally council members around a resolution they had drafted to reauthorize Bab Al-Hawa.
When Russia and the US agreed a compromise on the issue last year, American President Joe Biden hailed it as a diplomatic victory. The vote took place just days after he had held a summit with Russian counterpart Vladimir Putin, during which the cross-border issue was discussed.
After the successful adoption of Resolution 2585 by the council last year, both leaders commended “the joint work of their respective teams following the US-Russia summit that led to the unanimous renewal of cross-border humanitarian assistance to Syria today in the Security Council.”
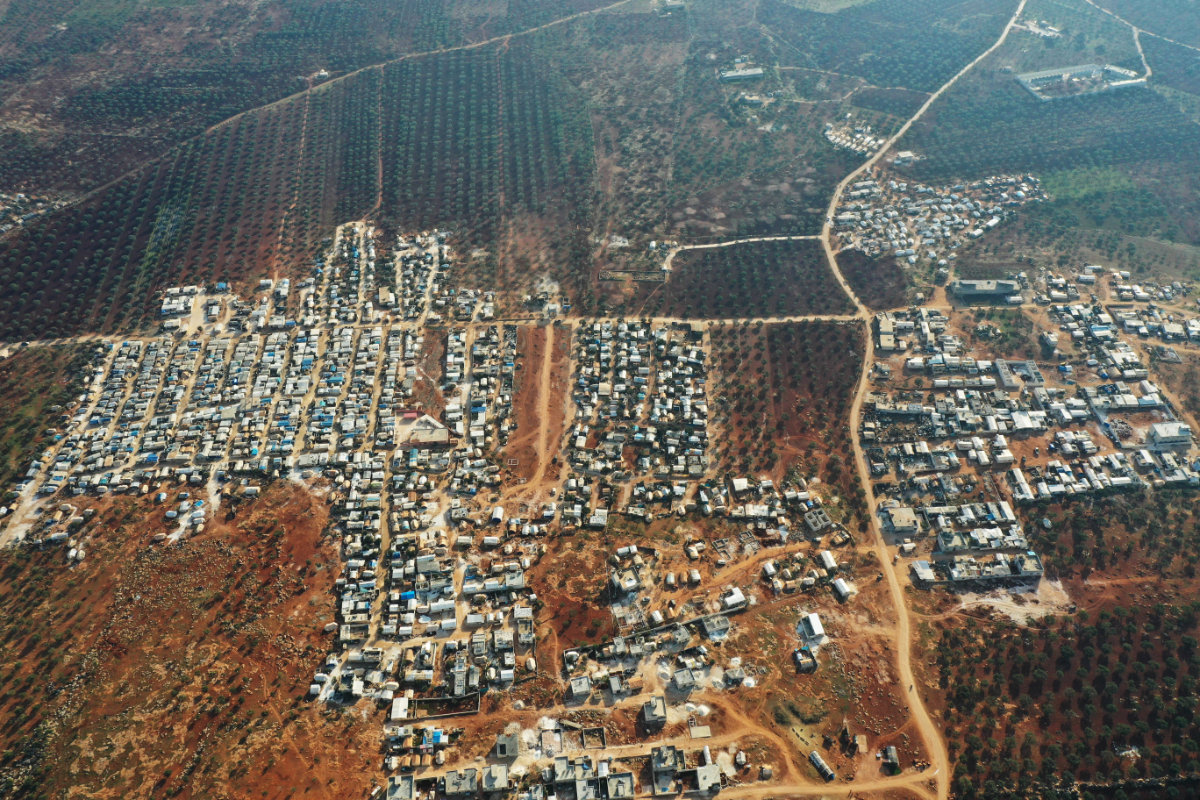

An aerial picture shows camps for displaced Syrians in the village of Killi, near Bab al-Hawa by the border with Turkey, in Idlib province, on Jan.9, 2021. (AFP photo)
The US had long asserted that progress on the aid process would open the door to more meaningful engagement with Russia on some of the thornier diplomatic questions relating to Syria, such as the issue of detainees and the forcibly disappeared, the return of refugees, and the work of the constitutional committee.
This time around, however, diplomatic talks between the two major powers have all but ground to a halt following the outbreak of the war in Ukraine in February.
Linda Thomas-Greenfield, the US ambassador to the UN, has been investing her personal legacy in seeking an extension to the mandate for Bab Al-Hawa. She touched on the issue during several of the meetings she convened when her country held the presidency of the Security Council in May.
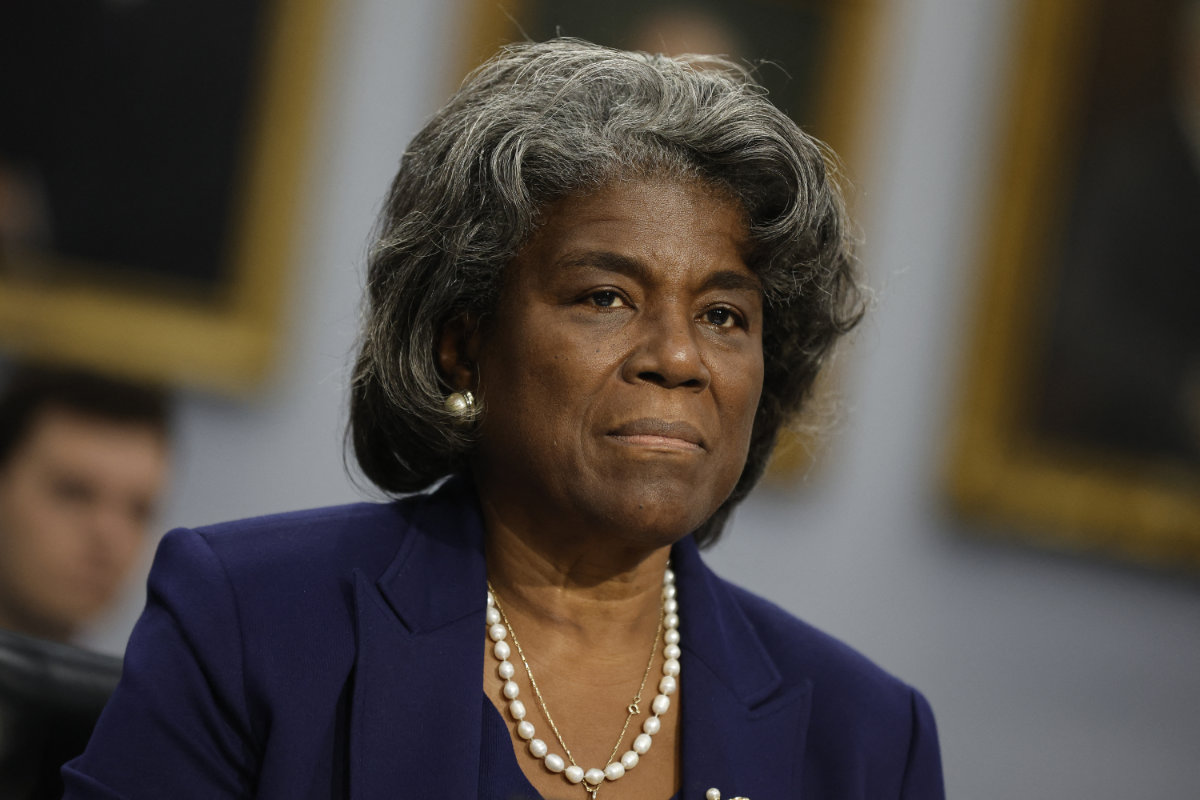

Linda Thomas-Greenfield, the US ambassador to the UN, h
She also recently returned from an official trip to Turkey, her second this year, during which she visited the Syrian border to assess the potential consequences should the UN be forced in July to end its humanitarian deliveries to Idlib. She warned that without aid, “babies will die.”
“We have not forgotten Syria,” Thomas-Greenfield said as she vowed to do “everything possible” to ensure the UN mandate to deliver cross-border aid continues and is expanded to meet the growing needs on the ground. She said she would try to reopen discussions with Russian diplomats at the UN in an effort to keep the aid flowing.
The Russian mission at the UN did not immediately respond to requests for comment, but Dmitry Polyanskiy, Moscow’s deputy permanent representative to the UN, recently offered a pessimistic view of the prospects for a revival of diplomacy with Washington, citing the “current geopolitical circumstances.”
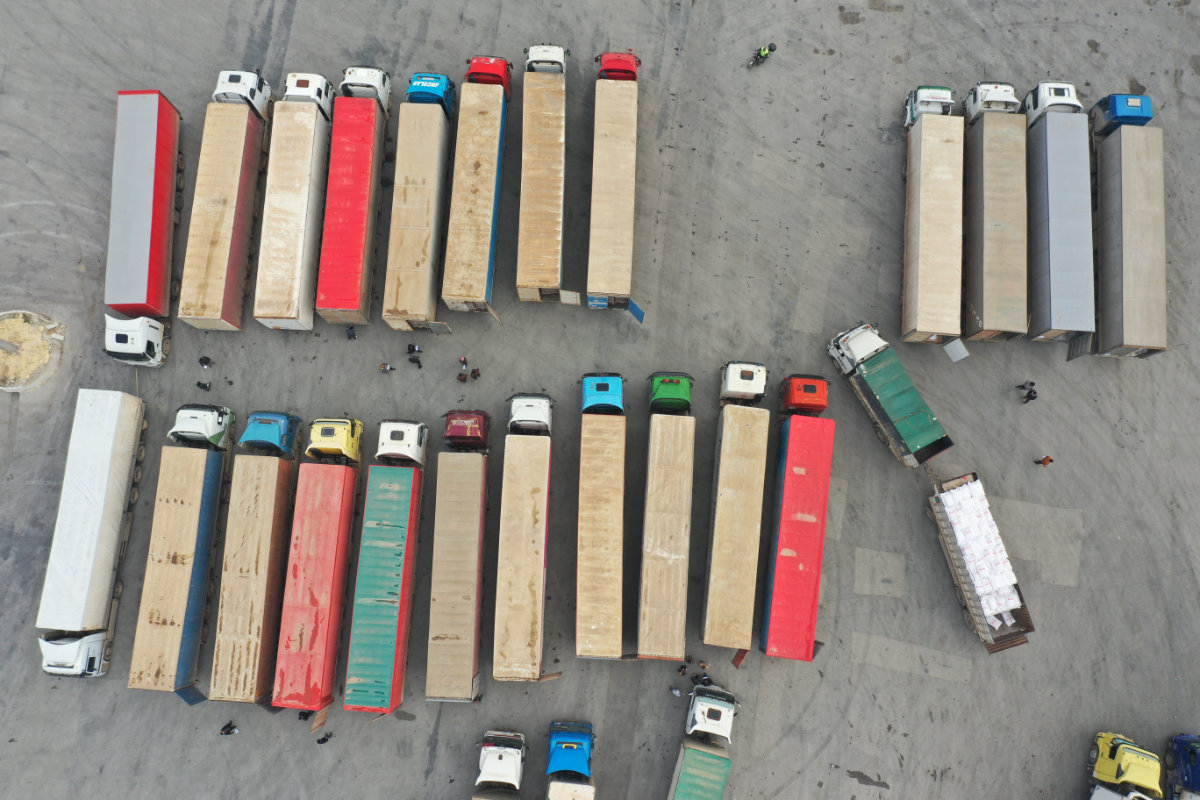

An aerial view shows a convoy transporting humanitarian aid parked at customs in Syria after crossing from Turkey through the Bab al-Hawa border crossing on Jan. 18, 2022. ( AFP)
Russia argues that the cross-border mechanism violates the sovereignty of Syria. With China’s backing, Moscow has lobbied for all aid to be channeled through Assad’s government and blames the humanitarian crisis in the war-torn country on American and European sanctions against the Syrian regime.
Critics of Russia’s stance say Moscow’s priority is not cross-border assistance, and that it seeks to use its power of veto as leverage to gain support for its position on Syria. According to the critics, Russian diplomats at the UN have been linking the vote on the cross-border mechanism to unrelated issues such as sanctions relief, reconstruction efforts and counterterrorism.
While UN chief Guterres has repeatedly asserted that cross-border operations are among the most transparent and scrutinized mechanisms in the world, Russia claims that the aid that flows through them has been benefiting designated terrorist groups in and around Idlib, such as Hayat Tahrir Al-Sham.
Washington declared a victory when the cross-border mechanism was renewed last year, but Qaddour, who in addition to her work with Syria Relief & Development is also a senior fellow with the Rafik Hariri Center and Middle East Programs at the Atlantic Council, believes it is Russia that has gained the most from this situation.
She believes it is unlikely that the extension of the Bab Al-Hawa gateway will be vetoed, the reason being that this is a useful political card that has been played repeatedly, and will be played again in the future.
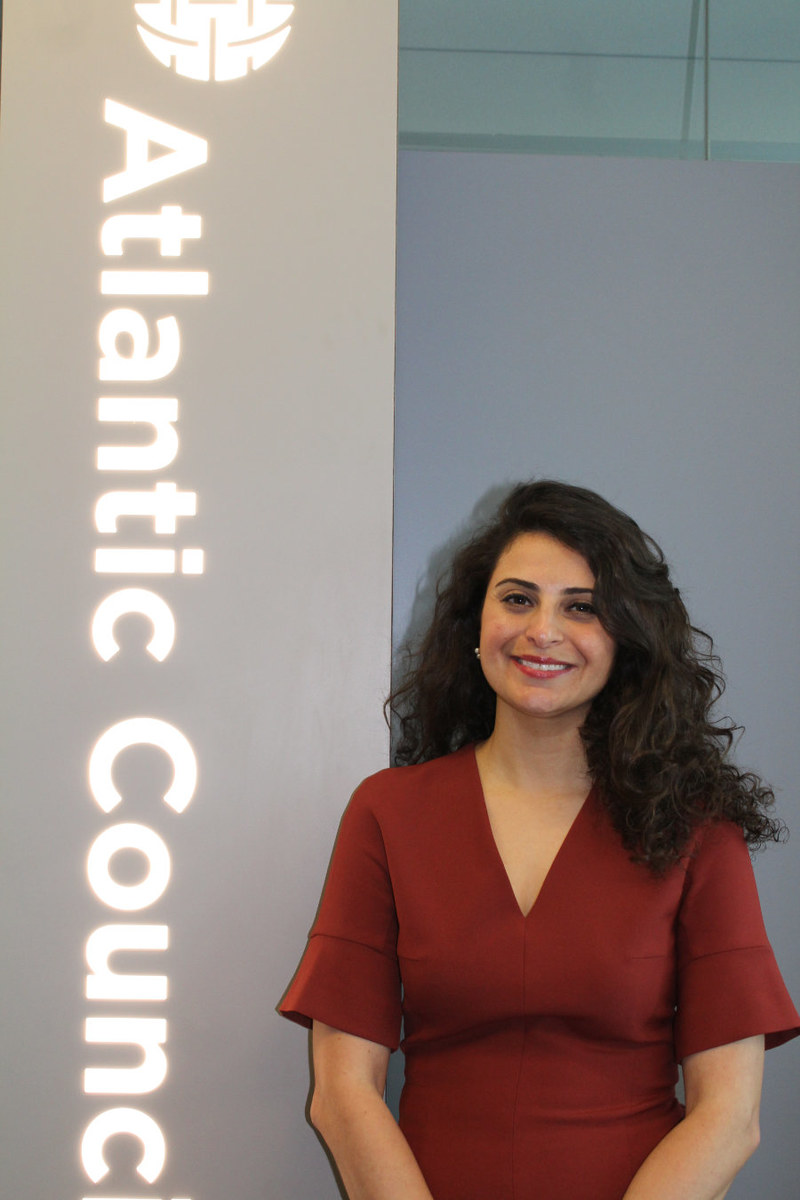

Jomana Qaddour. (Supplied)
In each round of renewals, according to Qaddour, Moscow has been able to extract a variety of concessions from Washington and its allies, such as a UN resolution endorsing certain early recovery projects that were previously contingent on a broader political settlement, as well as a qualified easing of sanctions on the Assad regime.
“This confusion over what the West is actually gaining from these negotiations places them, at a minimum, in a weak position,” Qaddour told Arab News. “And, at the maximum, it does hamper the ability of partners, such as aid organizations, to continue to rely on UN aid.”
The Syrian civil war has presented Putin with an opportunity to re-establish Russia as a powerful player in the region by protecting its ally and defeating what it considers a US-led regime-change campaign.
“Syria was the stage for Russian resurgence,” said Qaddour. “I can’t be optimistic to think that this is going to be a place that Russia abandons with ease. This is something they will continue to absolutely fight for and shape.
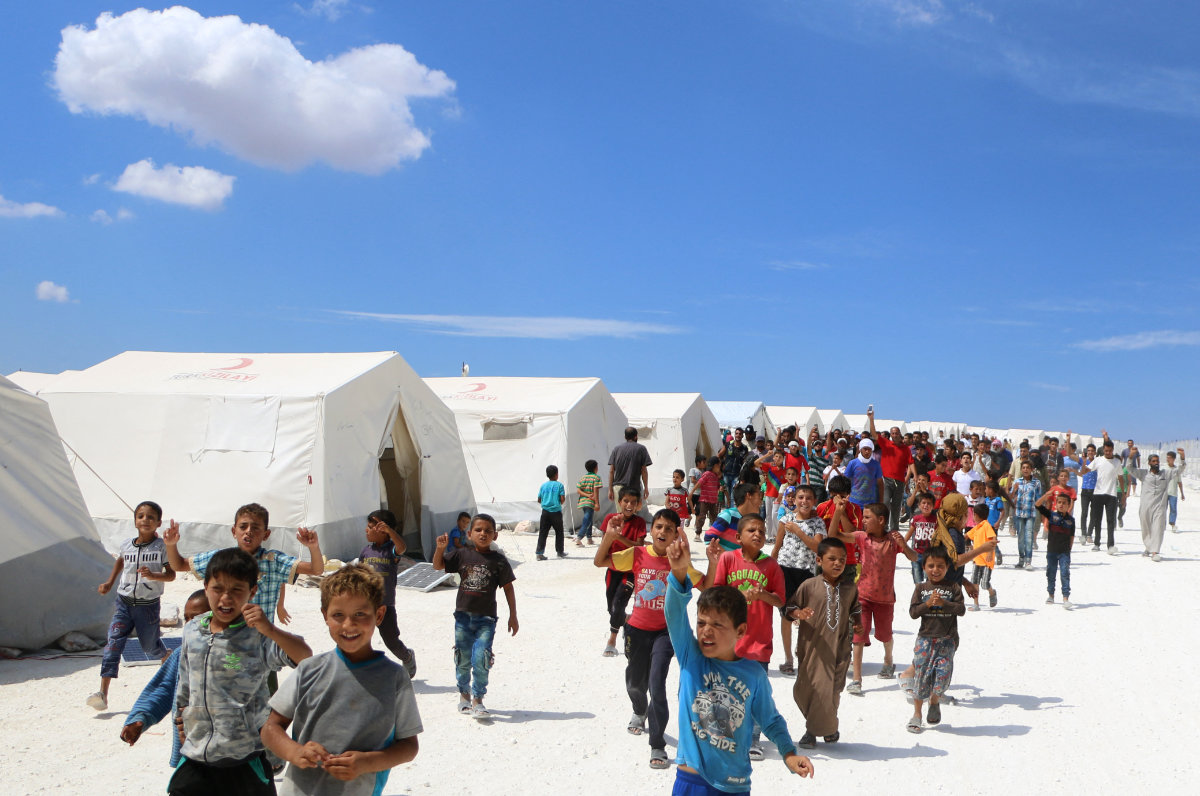

Displaced Syrians protest against the regime and its ally Russia at a camp for displaced people in Kafr Lusin near the Bab al-Hawa border crossing with Turkey on Sept. 7, 2018. (AFP)
Not that Syria is close to being uppermost on the agenda in Washington, said Qaddour.
“Am I under any illusion that the US or the West are recalculating and going back and putting Syria at the top of their priority list? No. I don’t think that anything indicates such a reprioritization in the US foreign policy circle. Ukraine now dominates everything,” she said.
Meanwhile, even if the aid corridor is not blocked, the northwest of Syria remains one of the most vulnerable areas in the country. Many agree that its ultimate fate lies thousands of miles away in New York, where calls for reforms to the Security Council have become louder since the start of the war in Ukraine — reforms that would allow humanitarian assistance to be delivered to the most vulnerable people without worrying whether it might be blocked by a veto from a permanent member of the council.






































