JEDDAH: For centuries, millions of Muslim pilgrims have undertaken long-distance journeys to the city of Makkah to perform Hajj, one of the five pillars of Islam. Well-established routes crossed the vast Arabian Desert and followed traditional paths from the far east to the north and west of the peninsula, surviving the test of time.
The ancient Hajj land routes from the neighboring regions materialized over time as a result of favored commercial routes and cultural and commercial exchanges. These centuries-old and deeply rooted cultural and religious traditions constitute one of Islamic civilization’s most important material vestiges.
Pilgrims travelled for months in caravans and convoys of camels, horses, and donkeys, stopping at wells, pools, dams, and stations installed by passers-by, following some of the most famous Hajj routes in the footsteps of millions of pilgrims before them to fulfil the spiritual journey of a lifetime.
“And proclaim to the people that Hajj; they will come to you on foot and on every lean camel; they will come from every distant pass.” Qur’an 22:27.
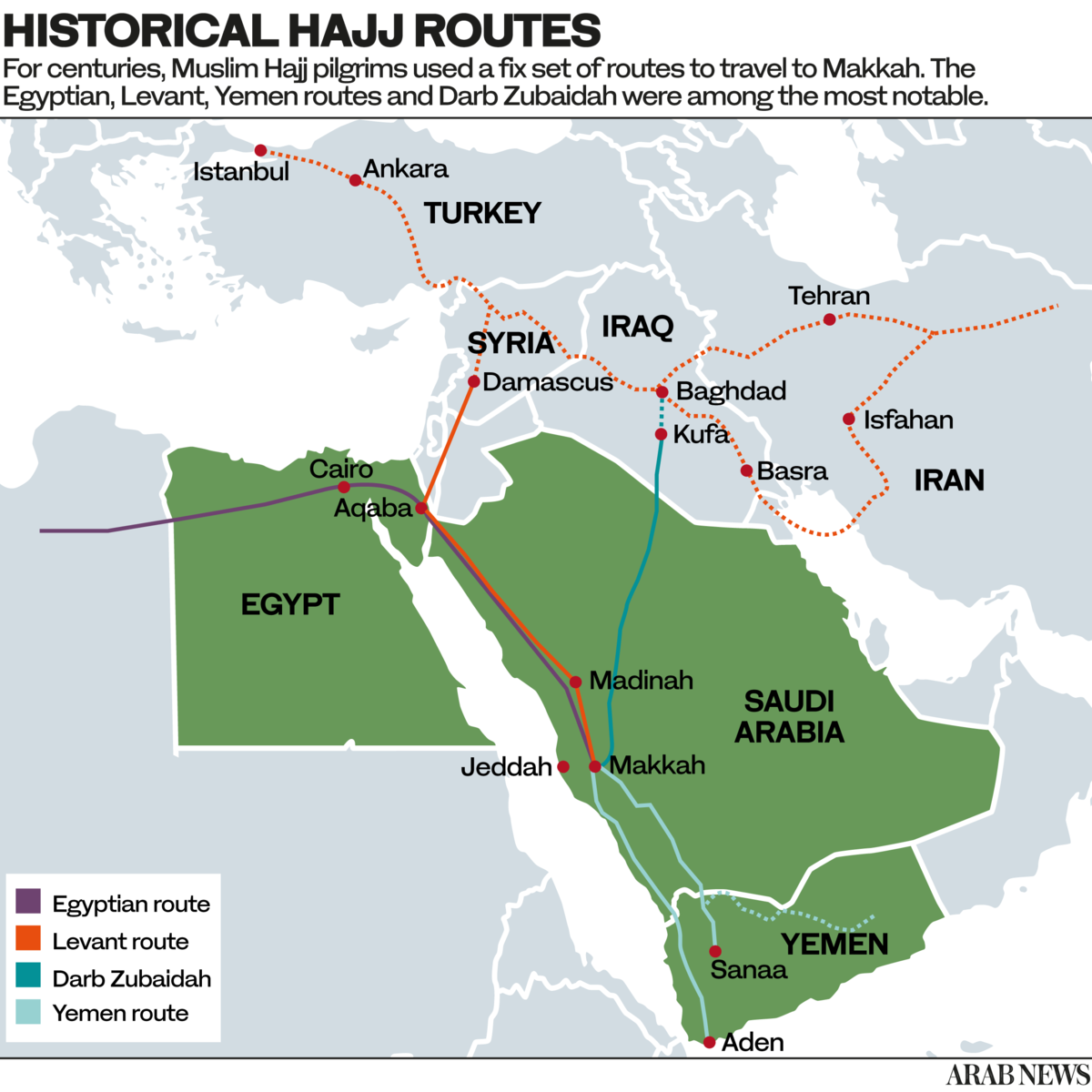
Scholars believe that five main routes reached Makkah; others say there could be up to six or seven, but they are considered secondary routes. The primary four are the northeastern Kufi route, known as Darb Zubaidah, the Ottoman or Shami (Levantine) route, the northwestern African or Egyptian route, and the southern and southeastern Yemeni and Omani land and sea routes, also called the Indian Ocean route.
Stretching more than 1,400 km through present-day Iraq and Saudi Arabia, the Kufi route was used as a path to Makkah even in the pre-Islamic age. Also known as the Zubaidah trail, it runs from the Iraqi city of Kufa to Makkah, passing through Najaf and Al-Thalabiyya to the village of Fayd in central Arabia.
The trail then diverts west to Madinah and southwest to Makkah, passing through the vast and treacherous desert sands of the Empty Quarter, Madain Ban Sulaym and Dhat Irk before reaching Makkah.
Historians believe the Zubaidah trail was named after Zubaidah bin Jafar, wife of the Abbasid Caliph Harun Al-Rashid, for both her charitable work and the number of stations she ordered to be established along the trail. The ancient path was also a known trade route, gaining increased importance and flourishing in the days of the Abbasid Caliphate between 750-1258 A.D.
The trail is a candidate site for entry into UNESCO’s World Heritage list, similar to the Egyptian route, which also attracted the attention of Muslim rulers throughout history. These rulers established structures on the path such as pools, canals and wells.
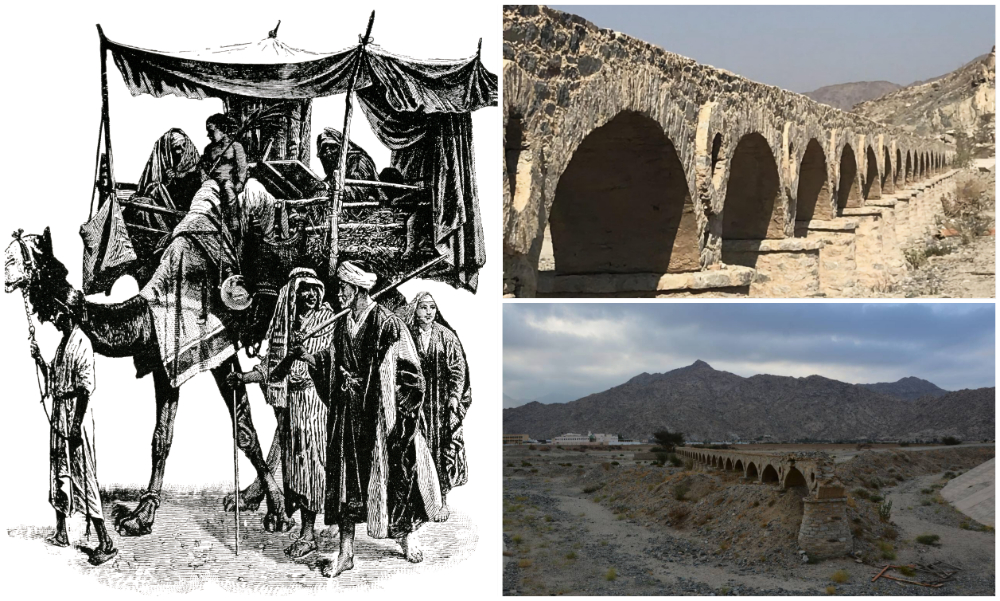

Some of the routes to Makkah stretch back to the pre-Islamic age, while Zubaidah well (right) has refreshed pilgrims and residents of Makkah for more than 1,255 years. (Universal History Archive/AFP)
They also built barricades, bridges, castles, forts and mosques. Researchers have discovered numerous Islamic inscriptions and commemorative writings engraved on rocks by pilgrims as they traveled along the road as a reminder of their Hajj journey.
With time, these structures mostly deteriorated or were destroyed by raids, but many of them have left behind remnants which shed light on the history and heritage of Arabia.
From the west, the Egyptian Hajj trail benefited the masses of Muslim pilgrims from Egypt, Sudan, Central Africa, Morocco, Andalusia, and Sicily who journeyed via Cairo. The trail travels through the Sinai to Aqaba, where a fork in the road separates the route into two. The first split is a desert trail that heads toward the holy city of Madinah and vast valleys towards Makkah. The other is a coastal trail that follows the Red Sea through Dhuba, Wajh, and Yanbu, then heads east to Khulais and onwards to the southeast, reaching Makkah.
The course of this trail changed through time, depending on political circumstances and technological development, and at one point in time, it crisscrossed with the Ottoman or Shami trail.
Perhaps one of the most well-documented journeys of Hajj can be found in the manuscripts of Moroccan scholar and explorer Ibn Battuta, which depict the journey through copious illustrations and notes.
Propelled by the quest for adventure and knowledge, Ibn Battuta left his hometown of Tangier in 1325. He took the African route, traveling by land along the Mediterranean coastline toward Egypt and seizing an opportunity to acquire knowledge of religion and law and meet with other Muslim scholars.
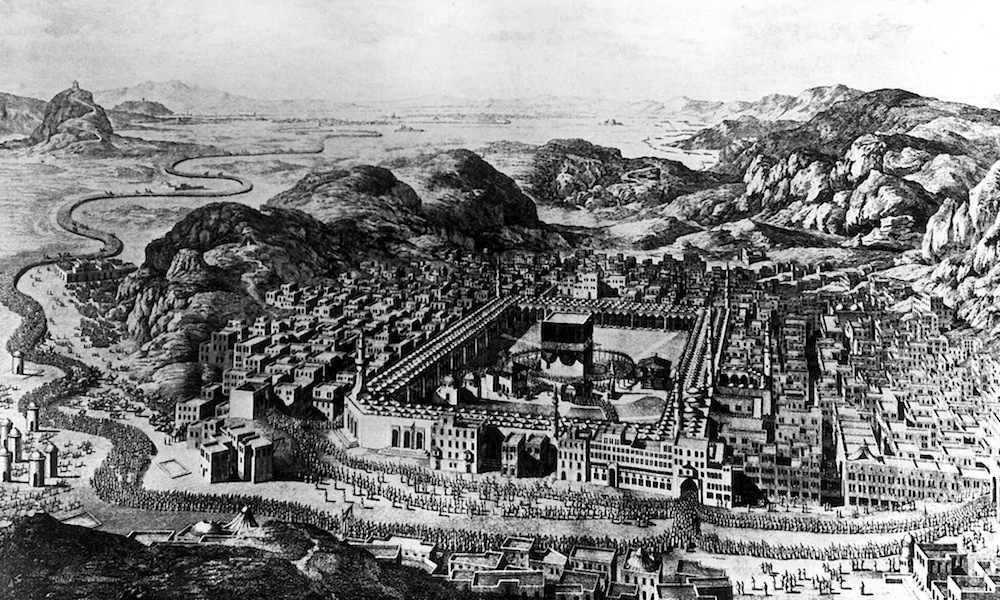

The sacred shrine of Islam in the courtyard of Masjid Al-Haram (Sacred Mosque) at Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Engraving from Mouradgea d'Ohsson, Paris, France, 1790. (Photo: ullstein bild/ullstein bild via Getty Images)
Over a year after the start of his journey, Ibn Battuta took a road less traveled through the Nile Delta in Egypt to the Red Sea port of Aydhad, and from there by ship to Jeddah on the other side of the Red Sea coast. His travels took him to Jerusalem, then Damascus, before finally joining a caravan of pilgrims following the Levant trail in 1326.
Connecting the Levant to Makkah and Madinah, the trail starts in Damascus, cuts through Daraa, then passes through Dhat Hajj north of Tabuk, Al-Hijr, and Madain Saleh, then on to Madinah. Pilgrims from the north often stayed in the holy city, visiting the Prophet’s Mosque before continuing their journey to Makkah. Many pilgrims returning through the route settled in Madinah for generations to come, and would welcome passing caravans from their homelands.
Since ancient times, Yemeni routes have linked the cities of Aden, Taiz, Sanaa, and Saada to the Hijaz region of western Saudi Arabia — one trail adjacent to the coast, and another passing through the southern highlands of the Asir mountains. Though it could be considered a main route alongside the Yemeni route, the Oman trail, believed to be secondary, saw pilgrims travel from Oman along the coast of the Arabian Sea to Yemen.
With time, facilities designed to ease the pilgrims’ journeys supplied water and provided protection along these roads to Makkah and Madinah.
Funded by rulers and wealthy patrons, the routes from Egypt, Yemen, Syria, and East Asia remained for centuries. No traveler journeyed empty-handed, as some carried goods with which to pay their way, and others bore local news that they shared among the provinces.
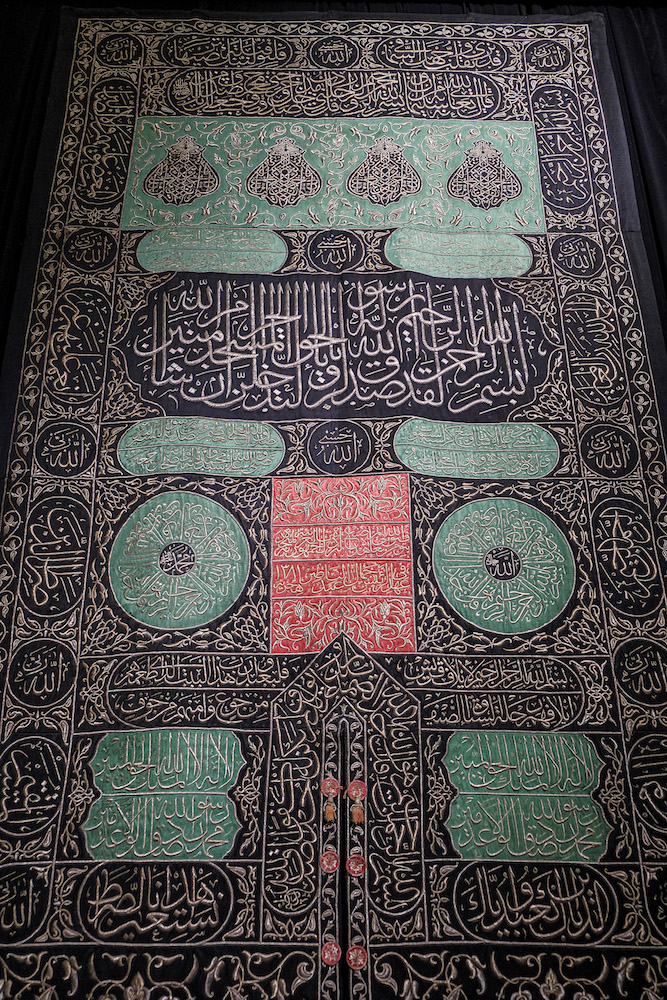

This file picture taken on May 26, 2021 shows a fragment of the Kiswa, the cloth used to cover the Kaaba at the Grand Mosque in the Muslim holy city of Makkah, the final one provided by Egypt (in 1961) during the administration of President Gamal Abdel Nasser, on display at the new National Museum of Egyptian Civilisation (NMEC). (AFP)
For generations, scholars have made their journeys towards the city, bringing along their concepts and ideas, contributing to scientific enterprise, and documenting the trip, noting the historical and cultural significance of the pilgrimage. Many of these scholars stayed in Makkah. Others settled in Madinah or headed north to such important Islamic cities as Kufa, Jerusalem, Damascus and Cairo to continue their studies.
Before the 19th century and the modern age of travel, these journeys would have been long and perilous. Though the actual ritual has remained unchanged in more than 1,300 years, the hardships and means of reaching the city of Makkah have eased and changed beyond recognition, with jets flying people in, buses and cars replacing camels, and Hajj bookings made with the help of the internet.
The routes died out barely half a century ago but they are well documented and preserved in memory as they symbolize the hardships pilgrims went through to perform the Hajj. They will forever preserve the spiritual footsteps of millions of devout Muslims on their climactic journeys.
Pilgrims far and wide have shared a spiritual desire that has brought masses of pilgrims across oceans, deserts and continents, just as it remains to this day and grows with each passing year.





























