DUBAI: Two years ago, on Aug. 4, 2020, Ghassan Hasrouty walked into his office at the port of Beirut where he had worked a steady job for the past 38 years. He would not return home that day.
At 6:07 p.m. local time, hundreds of tons of hazardously stored ammonium nitrate ignited in Warehouse 12 where Hasrouty was working. He and several of his colleagues were killed instantly.
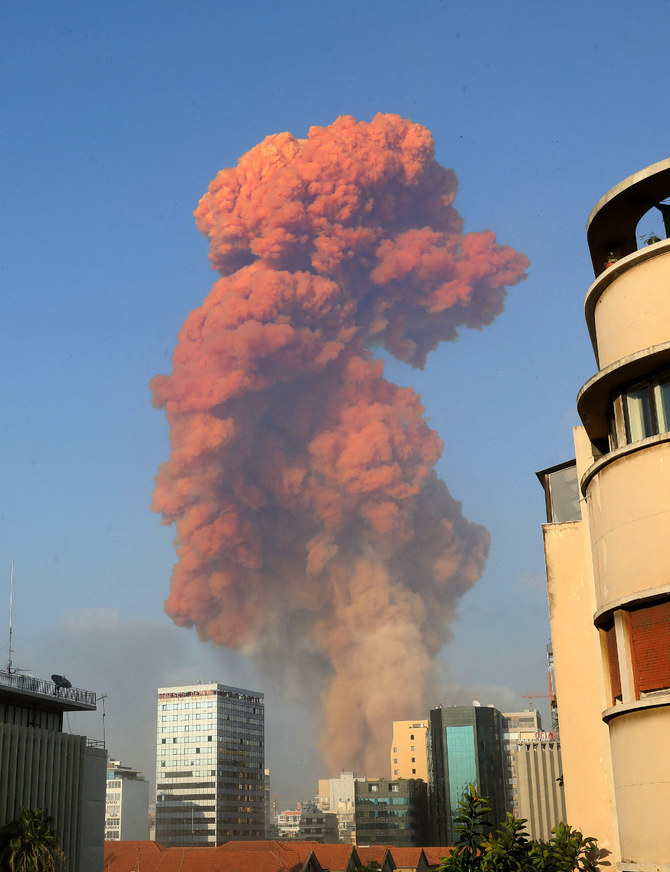
The third biggest non-nuclear explosion ever recorded in history devastated the port and a whole district of the Lebanese capital.
At least 220 people were killed, more than 7,000 wounded, and a city already in the throes of economic and political crisis was left paralyzed under a mushroom cloud of pink smoke.
“The investigation of the port explosion will be transparent. Take five days, and any officials involved will be held accountable,” Mohammed Fahmi, Lebanon’s interior minister at the time, said after the blast.
And yet, two years on, as families still reel from the loss of their homes, businesses and loved ones, the official Lebanese state’s investigation remains stagnant.
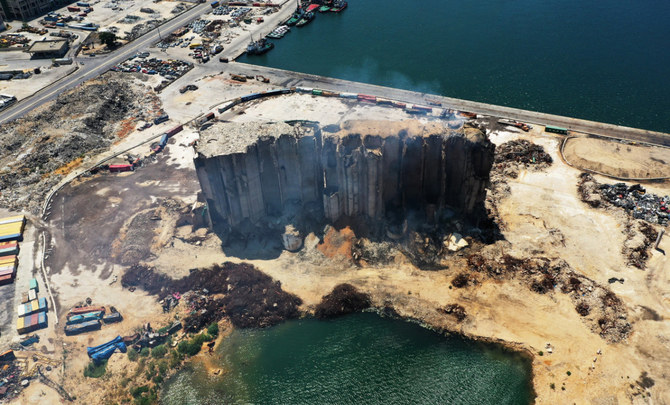
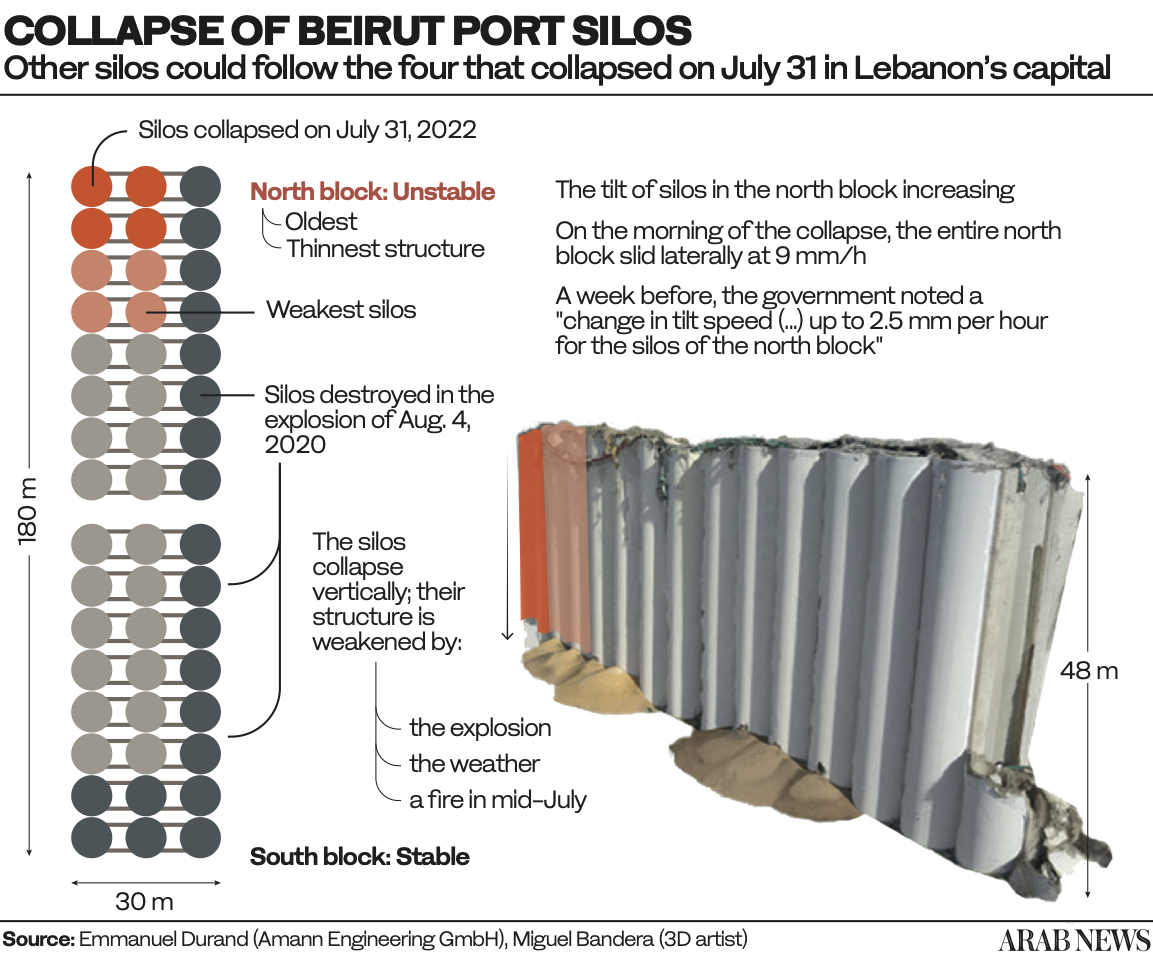
On July 31, part of the port’s now grimly iconic grain silos collapsed, sending a cloud of dust over the capital, reviving traumatic memories of the blast.
The Lebanese Cabinet recently approved plans for the controlled demolition of the silos, which were badly damaged but miraculously survived the 2020 blast, having sustained much of its force.
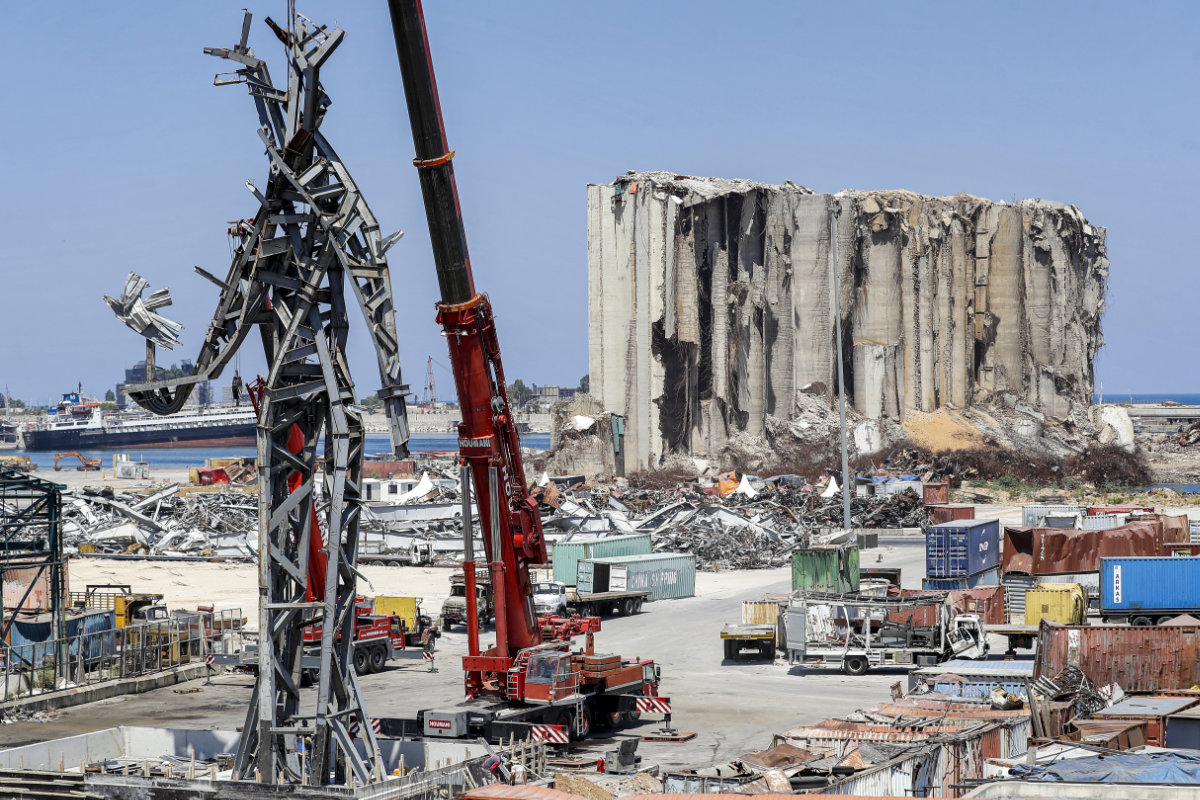

Plans to demolish what remained of Beirut's grains silos has sparked outrage among victims’ support groups, who want the structures preserved until a full probe into the blast is concluded. (AFP)
The decision has sparked outrage among Beirut residents and victims’ support groups who have called for the silos to be preserved until a full and proper investigation into the blast is concluded.
Many place the blame for the blast and its aftermath on corruption and mismanagement within the Lebanese government.
With a status quo originating from the days of the 1975 to 1990 civil war, which has rendered those in power effectively untouchable, the inquiry has descended into little more than a finger-pointing match as it moves from one presiding judge to the next.
With that, politicians have effectively ensured the complete impunity of officials who have long been wanted for questioning, arrest and prosecution.
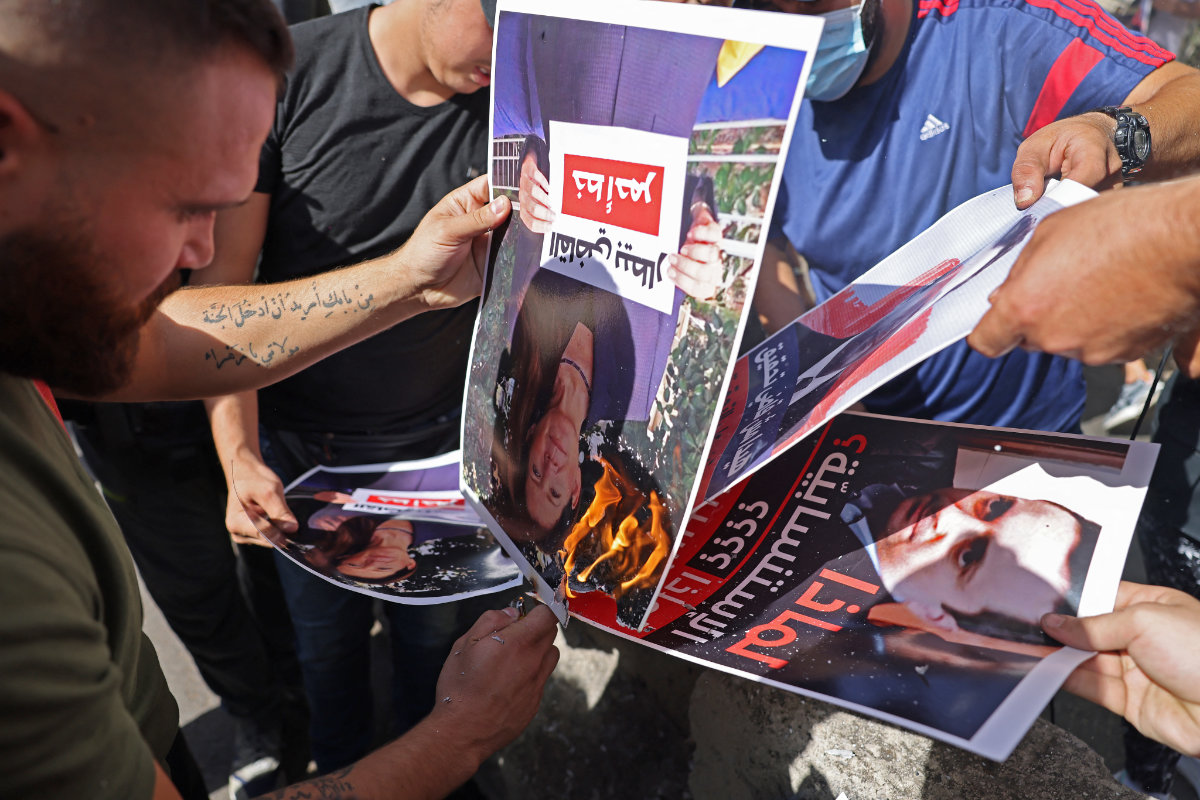

Supporters of Hezbollah and the Amal movement burn a portrait of Judge Tarek Bitar, the Beirut blast lead investigator, during a gathering in October 2021 to demand the Judge's dismissal. (AFP)
Officials potentially implicated in the blast have filed more than 25 requests demanding the dismissal of Judge Tarek Bitar and others involved in overseeing the inquiry.
Judge Bitar had charged four former senior officials with intentional negligence resulting in the deaths of hundreds of people in the explosion.
In response, some of the suspects have filed legal complaints against the judge, which led to the near-total suspension of the investigation in December 2021.
Two of these officials, Ali Hassan Khalil and Ghazi Zaaiter, were just reelected as members of parliament.
“After seeing how the officials reacted after the blast, I know the path for justice is going to be long. Two years in, all the corrupt state is doing is just blocking investigations and escaping justice,” Tatiana Hasrouty, Ghassan’s daughter, told Arab News.
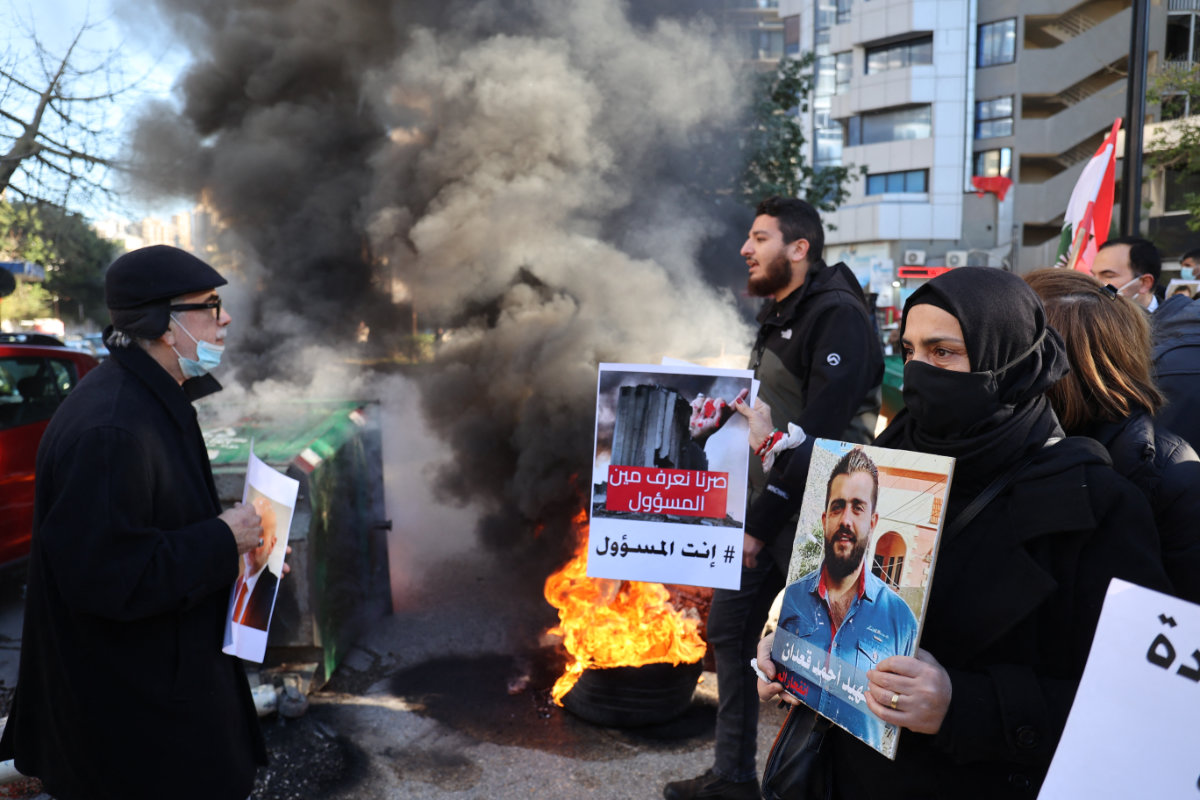

Relatives of victims of the Beirut port blast voice their anger. (AFP)
“This corruption is well rooted and was on full display when the director general of the Internal Security Forces, Maj. Gen. Imad Othman, was observed in the presence of Ghazi Zaaiter and Ali Hassan Khalil — two men he was supposed to be issuing arrest warrants against but did nothing instead,” she said.
“My father deserves better than this, and we, as his family, as Lebanese citizens, and as those affected by the blast, deserve to know who did this to us and why. I would not want it to happen to anyone. Nobody deserves to live through this kind of pain.”
Despairing and demoralized, survivors and the families of victims have turned to courts outside Lebanon in pursuit of justice.
Alongside local and international organizations, they have called on the UN Human Rights Council to put forward a resolution at its upcoming session in September to create an independent and impartial “fact-finding mission” to get to the bottom of the matter.
It is hoped that such an investigation will record the facts, assess the aftermath, determine the root causes of the explosion and establish individual responsibility.
“We’ve been working with the victims and survivors since September 2020 on this request,” Antonia Mulvey, executive director of Legal Action Worldwide and power of attorney for a number of blast survivors, told Arab News.
“While a domestic investigation is preferable, we understand that the system in Lebanon is very flawed and is incapable of delivering truth when it entails standing up to senior members of government.
“If the resolution is passed, UN members can be deployed on a time-bound mission of one year to support and assist the criminal investigation. The only thing blocking the resolution from passing is France and we cannot work out why.
Mulvey believes that French President Emmanuel Macron’s statements and visit to Lebanon following the blast have, paradoxically, become an impediment to the delivery of justice.
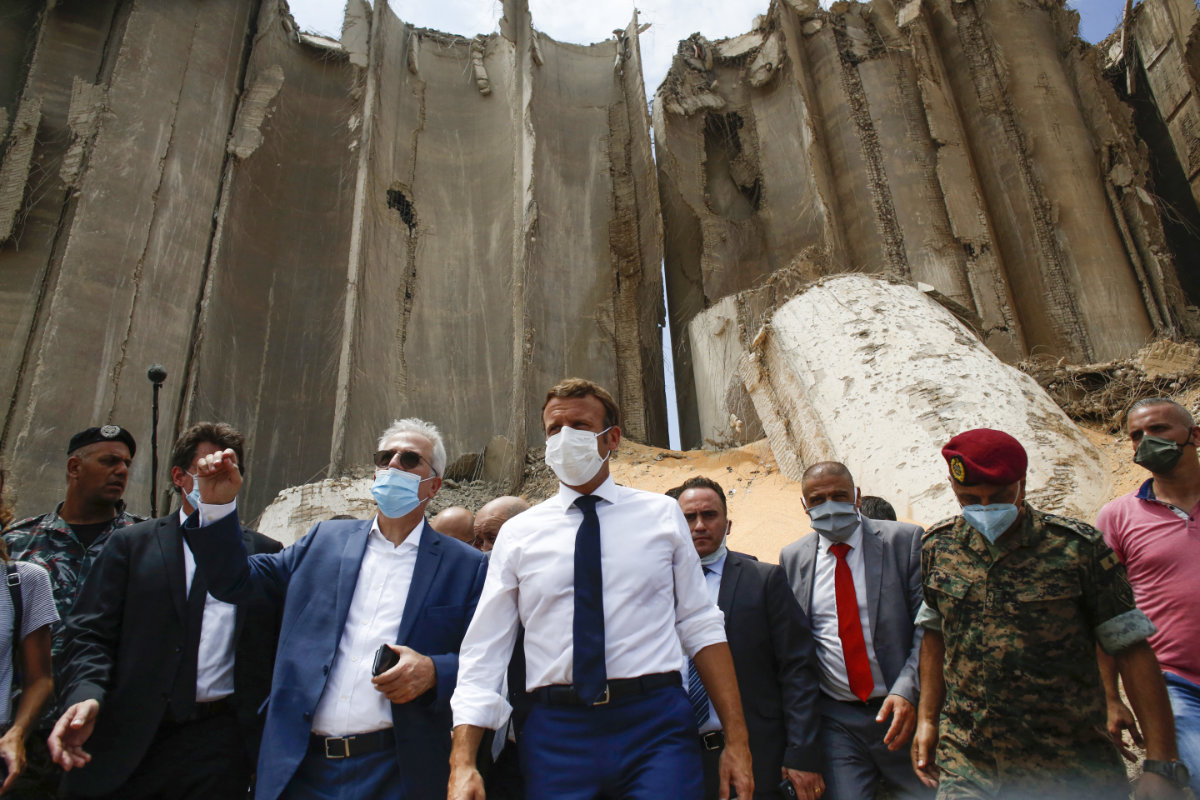

French President Emmanuel Macron (C), surrounded by Lebanese servicemen, visits the devastated site of the explosion at the port of Beirut on August 6, 2020, two days after a massive explosion. (AFP)
After arriving in Lebanon just two days after the explosion, Macron said that “an international, open and transparent probe is needed to prevent things from remaining hidden and doubt from creeping in.”
Many hoped that this call signaled a shift from the traditional French policy of propping up Lebanon’s political class. But now they fear the politicians have been thrown a lifeline by Macron’s “road map” toward reform.
Critics of French actions at the UN Human Rights Council say they stand in stark contrast to the commitments Macron made to the port blast victims.
Mulvey says the situation is intolerable because the slow pace of justice is compounding the grief of the survivors and the families of the victims.
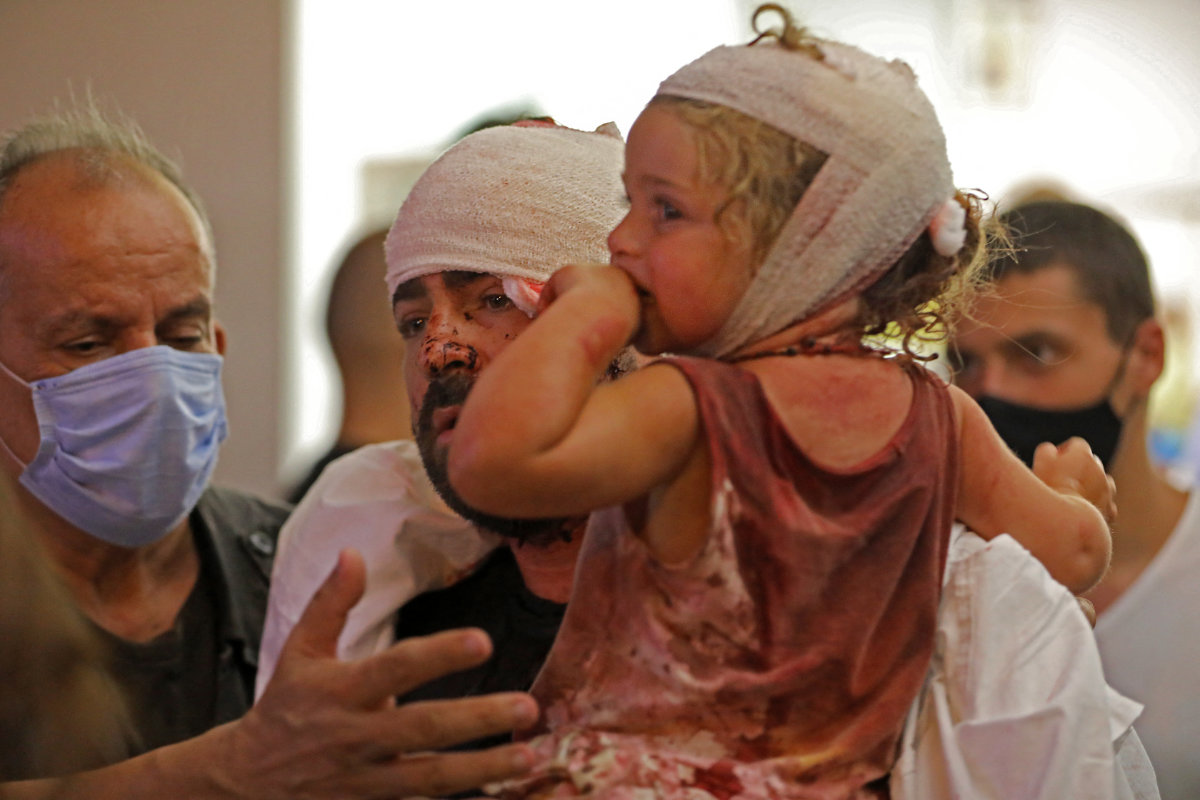

Injured people are treated at a hospital in Beirut following an explosion near the capital city's on August 4, 2020. (AFP)
“One hundred and twenty survivors and victims describe to me how every day is like torture to them. They can’t move on but have no choice but to move forward, particularly those who lost their children,” she said.
“The memorial coming up doesn’t make much of a difference when every day is difficult. We have allegations against senior government and security officials. We must have hope and fight for this. If we don’t, we will still be looking at the same situation 20 and 30 years down the line.”
Another lawsuit has been filed in the US state of Texas by nine Lebanese American plaintiffs and relatives of victims of the blast.
Seeking $250 million in compensation, the lawsuit, launched by the Swiss foundation Accountability Now, was filed against US-Norwegian firms, such as TGS, which are suspected of being involved in bringing the explosive materials to the port.

Support groups for victims of the Beirut Port blast of Aug. 4, 2020 are taking legal actions against everyone responsible, including Lebanese politicians who have been trying muzzle judicial proceedings. (HRW photo)
“This lawsuit will help circumvent the muzzling of the Lebanese judiciary,” Zena Wakim, co-counsel to the plaintiffs and board president of Accountability Now, told Arab News.
“Through the powerful tool of discovery, the victims will unveil the network of corruption that made the blast possible. The politicians have filed removal requests against the judges who could have ruled over their motions to dismiss. They filed a claim against the Lebanese state for gross negligence of Judge Bitar,” effectively freezing the proceedings.
Wakim added: “Although the victims had all recognized the need to give the Lebanese judiciary a chance, they have now come to the conclusion that justice will never happen in Lebanon. Justice needs to be sought elsewhere, in any other possible jurisdiction, through whatever available legal avenues.”
The disregard shown by Lebanese authorities toward survivors and the families of victims manifests not only in the efforts to impede the investigation. Hasrouty recalls the struggle of trying to locate her father’s body, which took almost two weeks after the blast.
After several days, the Lebanese Army called off the search for Ghassan Hasrouty’s remains and those of other people lost in the rubble.
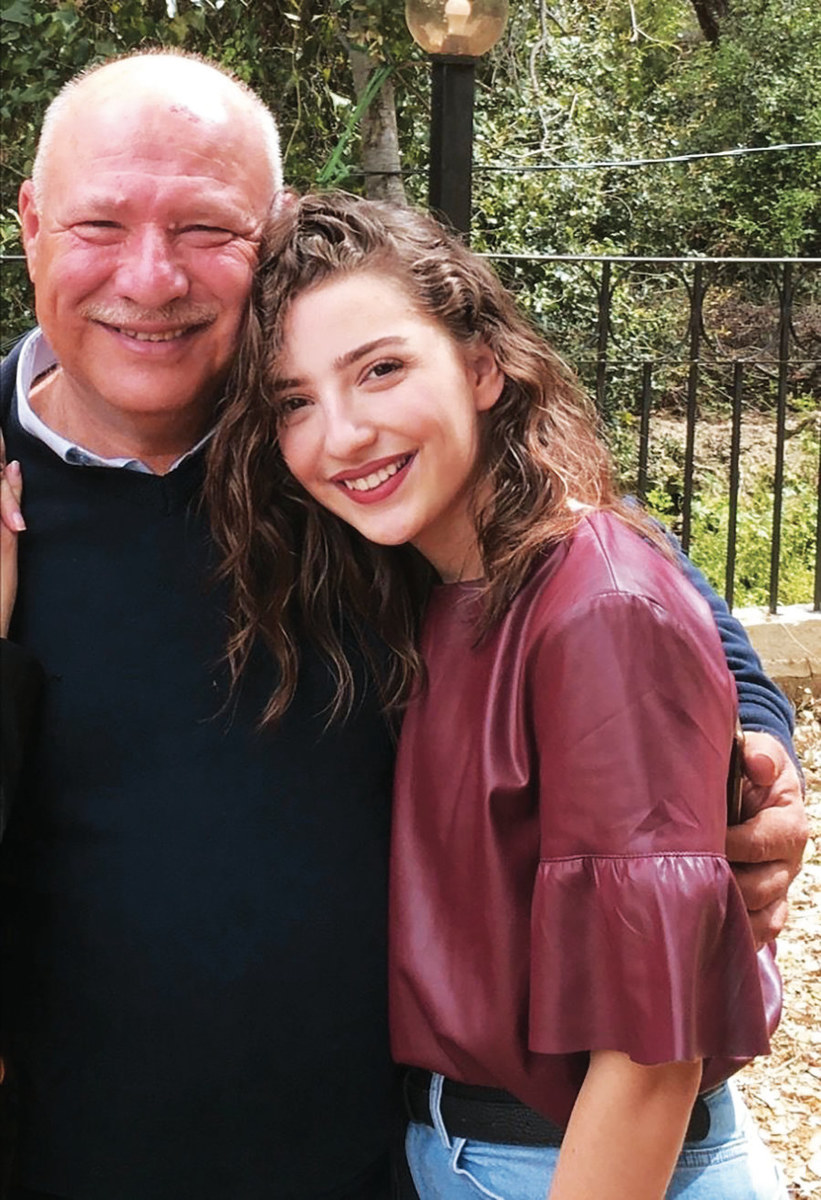

Tatiana Hasrouty and her father Ghassan who died in the blast. (Supplied)
“Nobody talked about them, the people who worked at the silos. The authorities did not want to search for them until we pressured them to,” Tatiana Hasrouty told Arab News.
“My brother was provided maps by my father’s colleagues who survived, and they worked day in, day out, trying to locate the bodies.
“We used to go to the port every day waiting for some news and to visit every hospital. On Aug. 18, my brother got the only official call saying that his DNA matched a body that was found. My father and six of his colleagues were under the rubble of the silos.”






































