JEDDAH: Obesity rates worldwide have been steadily rising over the past half-century, reaching a point at which experts say many nations are way off schedule to meet the World Health Organization’s 2025 global nutrition targets.
Mindful of the pressures that high obesity rates place on local healthcare systems, to the detriment of quality of life, countries such as Saudi Arabia are working hard to promote fitness and challenge people to change their sedentary lifestyles.
According to a recent study by Ohio State University College of Medicine, obesity and the associated health implications cost the Saudi healthcare system $3.8 billion in 2019 alone, equivalent to about 4.3 percent of the Kingdom’s total annual health expenditure.
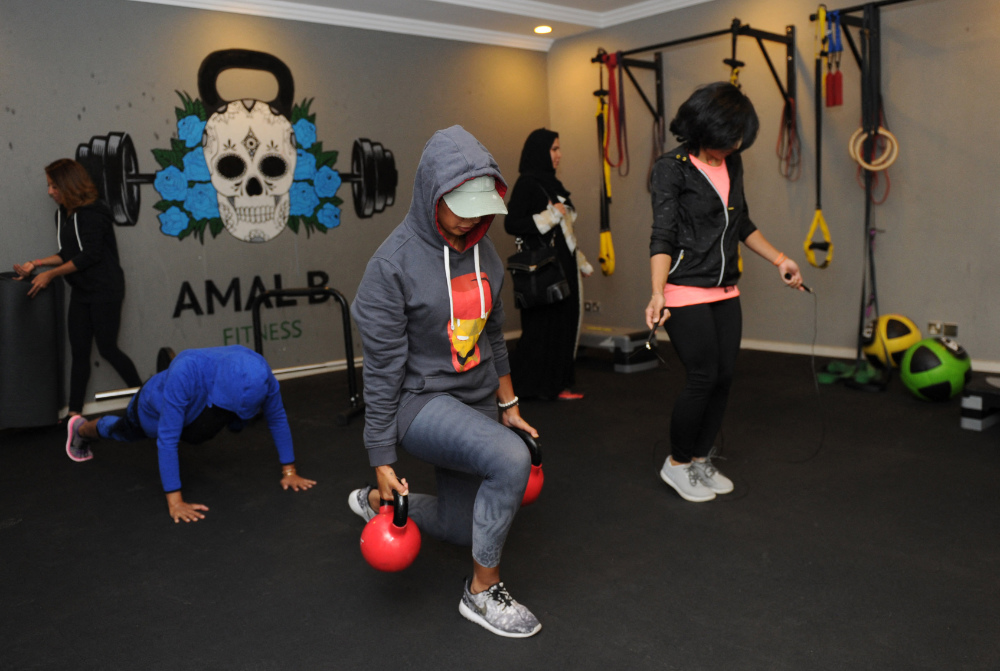

Keeping weight under control is nevertheless easier said than done in the age of globalization. (AFP)
Excess weight and obesity — defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that can impair health — is not only a concern in the Arab world. More than a billion people worldwide are classified as obese, which means that they have a body mass index (a measure of body fat based on height and weight) of 30 or higher, and the number is rising.
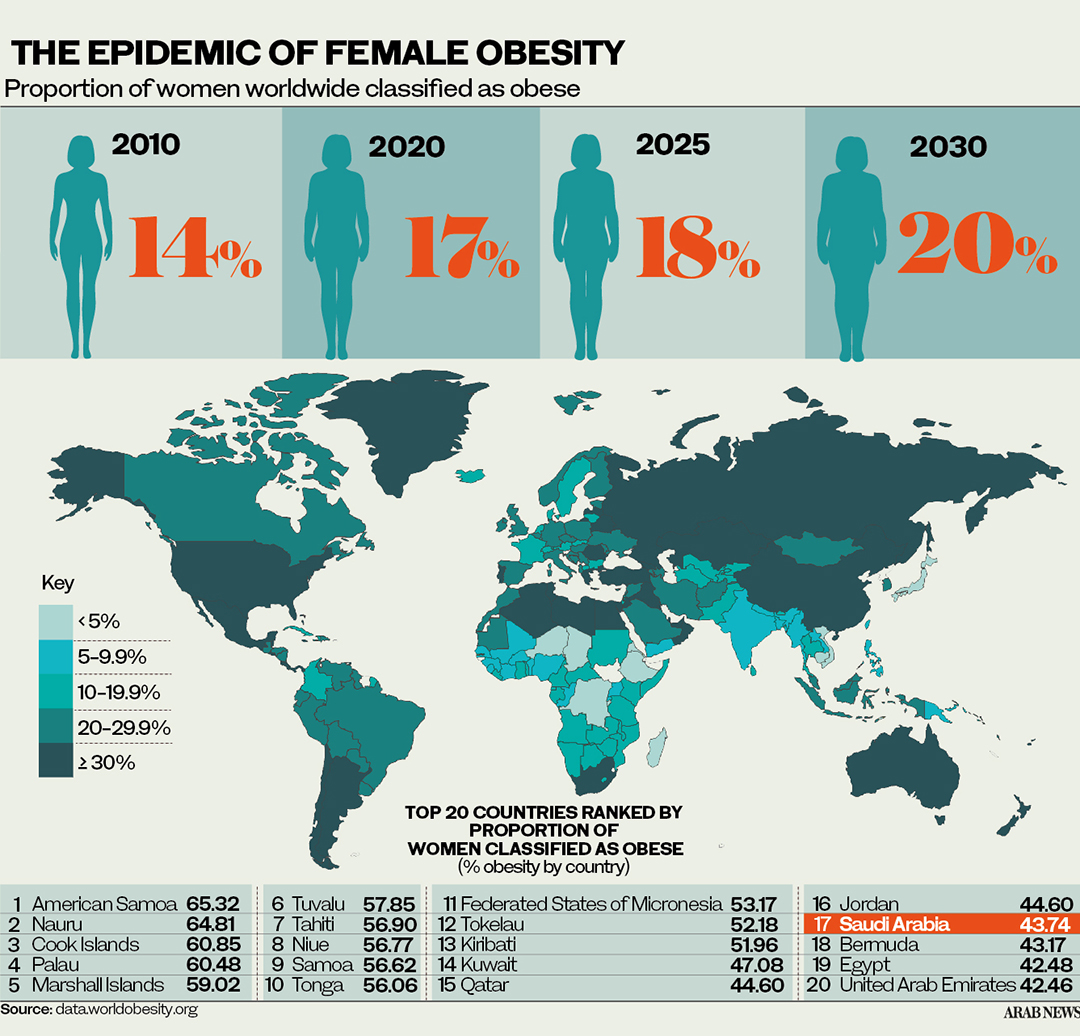
According to the WHO, obesity is more prevalent among women than men, with factors such as sociocultural issues, economics, genetics and biology all contributing factors. Worldwide, obesity affects 15 percent of women and 11 percent of men. In the Middle East and North Africa, this gender gap is even wider, with 26 percent of women classified as obese compared with 16 percent of men.
A recent article published by The Economist attributes the problem in the region to two key factors: Socioeconomics, on the grounds that the cheapest local foods are usually the most unhealthy, such as bread and rice; and culture, on the grounds that pervasive social conservatism in the Arab region can prevent women from participating in outdoor exercise or shedding calories passively in the workplace.
The reality is, of course, more complex than that. The perception of Arab women as mere sedentary housewives appears grossly outdated as women in the region increasingly enter the labor force, take charge of their diets, and seize new opportunities in the worlds of sports and fitness.

Obesity and the associated health implications cost the Saudi healthcare system $3.8 billion in 2019 alone. (AFP)
Keeping body weight under control, in any case, is easier said than done in the age of globalization. Arab countries, too, have experienced significant lifestyle changes and rapid urbanization that have introduced many additional high-fat foods to the market alongside the pre-existing unhealthy eating habits, including the traditionally carbohydrate-rich Arab diet.
Populations of the Gulf states, including Saudi Arabia, have found themselves at the sharp end of these developments. Notably, obesity levels have soared in recent decades owing to a mix of unhealthy eating, inactivity and keeping “fat in fashion” — a stereotype associated with Gulf nationals on account of their perceived affluence.
Globally, the perception of obesity varies widely. In many high-income and, increasingly, middle-income countries, weight gain carries a social stigma that fuels a perception of individual weakness that undermines the support for comprehensive prevention, treatment and management measures.
Different ideals associated with weight and body shape can found in various cultures. Specific cultural pressures to be tall and thin are postulated to cause people to misreport their height and body weight in an attempt to appear what is deemed more socially popular and desirable.
A similar situation exists in some places in terms of attitudes to excess weight. Many African and Polynesian, and some Arab, cultures associate overweight women with affluence, health, strength and fertility. In the Gulf region at least, however, being fat is certainly no longer in fashion.
Sulafa Kurdi, a photographer and cafe owner, has been overweight almost all of her life. In August 2020, she took the first steps on a nearly two-year journey to get fit and healthy by signing up with a gym. She chose Sweat Army in Jeddah and began her transformation.
“I was waiting for the right time to make the move and turn my life around,” she told Arab News. “Breaking down that wall was tough but, with the support I received from my coach, the journey was what I needed. I wanted to lose weight the healthy way, the right way and the difficult way.
“Within three months of signing up, I found the discipline to maintain a healthy lifestyle that I still stick to as best as I can. Yes, we all fall off the wagon and feel sluggish at times. With the right support, I’ve managed to get back again and move, breaking my own records.”
FASTFACTS
• Obesity is closely linked to chronic health problems, including cardiovascular disease and cancer.
• Excess weight and the associated health implications cost the Saudi health system $3.8bn in 2019.
Indeed, contrary to the assertions in The Economist’s article, anecdotal evidence suggests more and more women in the Arab world are taking control of their physical lives and setting off on a journey to improved their fitness. This has in turn motivated many to pursue their dreams of becoming professional athletes.
Studies have found that engagement in sports and physical activity has been lower among women than men. Now various government-led and private programs are providing women and girls with access to sports facilities, encouraging them to become athletes and even role models for younger generations.
This has challenged outdated stereotypes about women in Saudi Arabia and the wider Arab region and the incorrect notions about social conservatism preventing them from going outdoors both to exercise and to take part in organized sports.
Dubbed “Cleopatra Squash,” Egyptian Nuran Johar has won padel tournaments such as the England Open Junior Championship five times. Meanwhile, Ulfah Alkaabi, one of the UAE’s top padel players, has been making her mark on the court.
Halfway around the world, Saudi Arabia’s female national football team won a silver medal at the Special Olympics Unified Cup in Detroit, Michigan this month.
Although Saudi sprinter and first-time Olympian Yasmeen Al-Dabbagh fell short in her first race in Tokyo 2020, she has set her sights on bringing home a medal from the next Games in Paris in 2024.
By all accounts, women’s participation in sports and fitness boils down to a supportive community. In the Kingdom, the Sports For All Federation has been building community-driven programs to improve overall health through community sports programs, a powerful tool to create a healthy society in line with the Vision 2030 Quality of Life objectives.
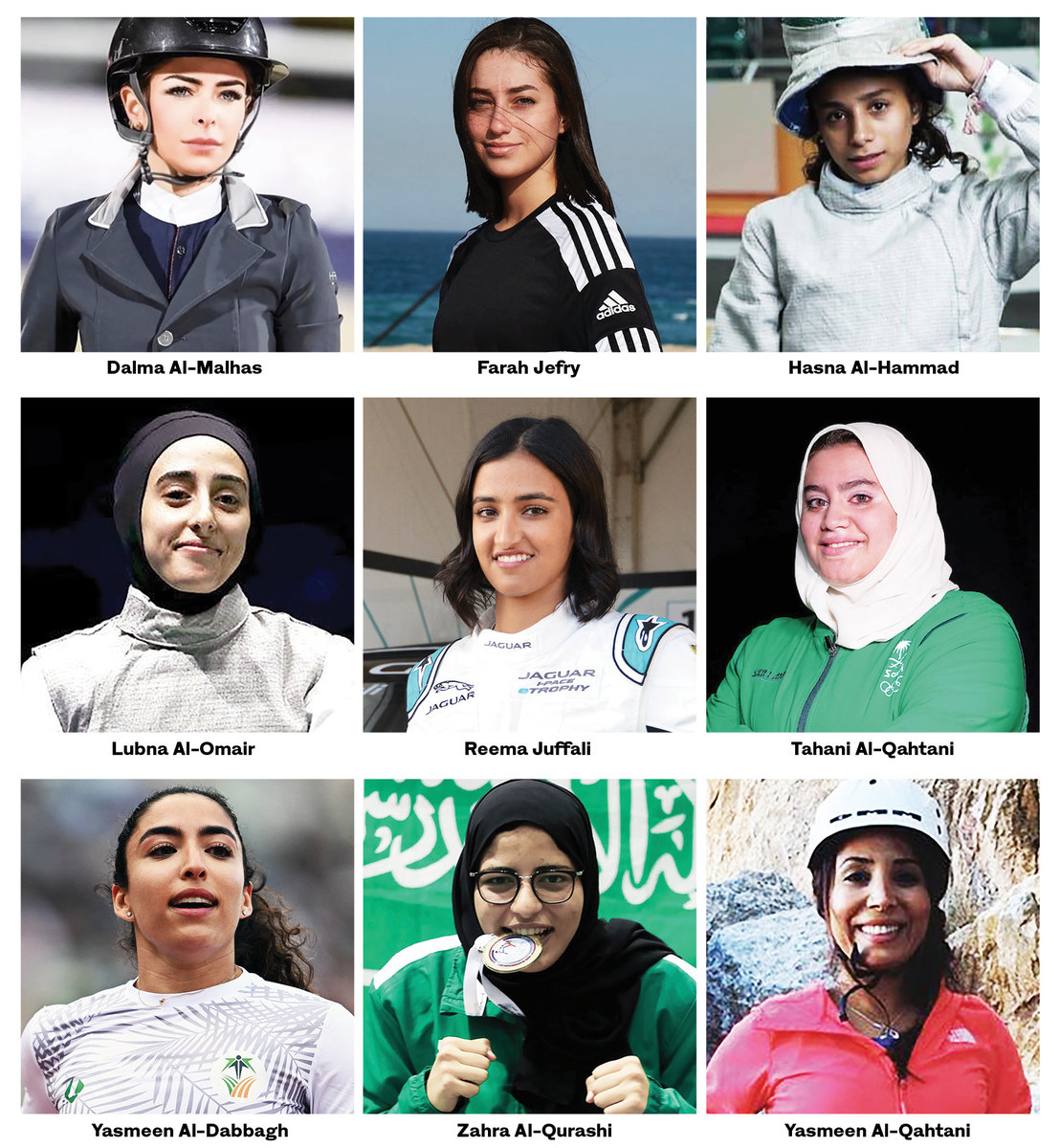

The Saudi female athletes leading the way.
SFA says its programs and initiatives are created based on a community’s specific needs and what motivates them, and can be incorporated easily into their daily routines such as walking, running, cycling and other activities. It says the number of female participants in community sports has increased dramatically.
“Since 2018, we’ve seen the numbers reflected across our programs,” an SFA spokesperson told Arab News. “SFA wants to provide women with the right programs and female-driven initiatives to encourage them to go further.
“We provided a special course for ladies in our Spartan race, there was an area for women at SandClash to compete, and the same goes for our Neighborhood Clubs across the Kingdom for women who prefer to have their own spaces.
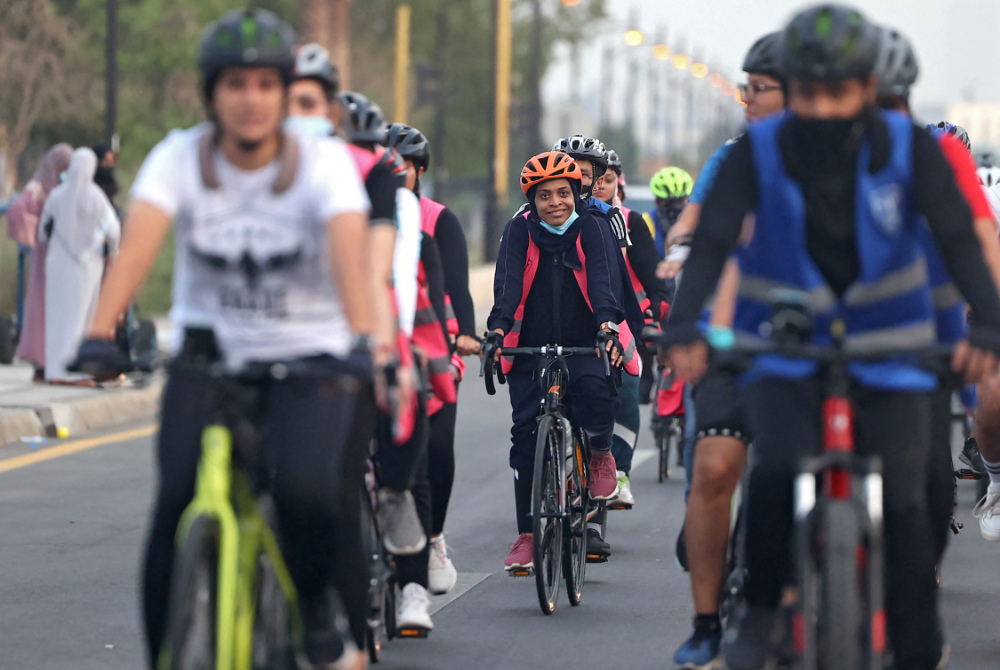

Women’s participation in sports and fitness boils down to a supportive community. (AFP)
“SFA has also hosted the Global Goals World Cup, a five-a-side women’s football tournament, and is the first country to add basketball to the games. One of the main objectives of SFA is to enable them, provide them with access to facilities, motivate them and feel that they are part of the community.”
Underscoring the importance of community-based physical activity programs, Haya Sawan, a fitness trainer and the owner of SheFit Gym in Jeddah, told Arab News that having such programs is helping to build a strong fitness culture among women.
“There’s been a huge jump in the past five years and you can see more people engaged in some sort of physical activity than ever before. It’s not just a matter of gyms opening, it’s more about changing the mindset and changing the lifestyle,” said Sawan.
“The region’s climate and unique environment restrict us from walking for miles, so we need to put in extra effort just to stay active all day. We utilize the space that we have and create programs fitting for the space, and using vast spaces such as malls and outdoor pathways designated for walking or jogging is a great way to engage the public.
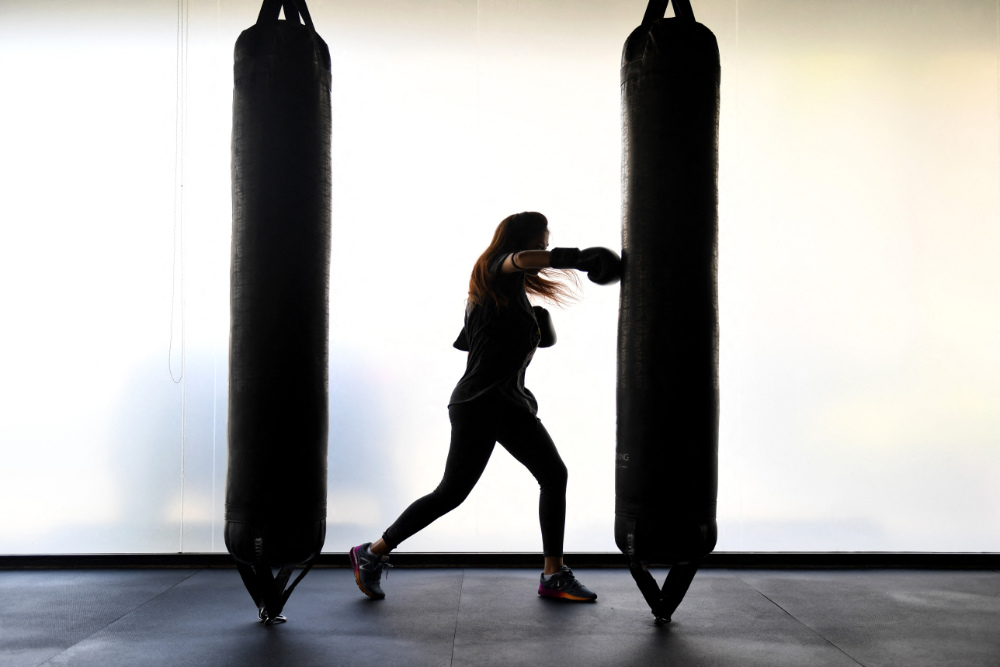

The perception of Arab women as mere sedentary housewives appears grossly outdated. (AFP)
“Initiatives such as the ones launched by SFA where they cooperated with malls makes it so much easier for people to be active. It’s accessible and you can count your steps. It’s a small gesture that makes a difference in the long run.”
That said, personal motivation remains an integral part of any fitness journey, and changing perceptions among Arab women — and wider society — about their role, status and body autonomy no doubt has a part to play.
“I am a strong believer that your thoughts can really control your life,” said Sawan. “A positive mindset will always believe that there’s room for improvement, and look at challenges as a source of motivation to overcome, rather than challenges that would stop you from moving forward. Everything changes.”



























