KARACHI: Foreign investment in Pakistan’s equities has declined by 83 percent to an estimated $1.4 billion since 2016, a recent study by a leading Pakistani brokerage house suggested on Monday, with financial experts attributing it to persistent economic and political instability and a US interest rate hike.
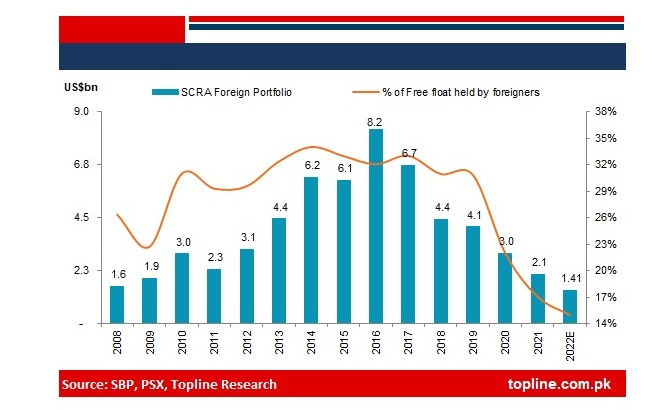
Foreign investment in equities through the Pakistan Stock Exchange (PSX) peaked to $8.2 billion in 2016 as the South Asian country displayed robust economic growth and currency stability.
However, political instability, triggered by the Panama Papers leak in 2016 that led to the ouster of former prime minister Nawaz Sharif, forced foreign investors to offload their positions in Pakistan.
The investment fell to $6.7 billion in 2017, $4.4 billion in 2018, $4.1 billion in 2019, $3 billion in 2020, $2.1 billion 2021, and $1.4 billion in 2022, according to a research report shared by the Karachi-based the Topline Securities brokerage house on Monday.
“Pakistan’s currency and market were stable and economy was growing back in 2016 which are one of the key considerations of the foreign investors to take investment decisions,” Umair Naseer, a Topline Securities research director, told Arab News on Tuesday.
“The reasons of foreign investment fall among others include inconsistent economic policies and instabilities and political uncertainties which are negative for foreign investors and play bigger role in keeping them away.”
Khurram Schehzad, chief executive officer at the Alpha Beta Core financial advisory firm, agreed with Naseer and said the country’s issues were largely related to macroeconomics.
“Political uncertainty and policy inconsistency have been two key reasons for low foreign interest. We have been downgraded back to Frontier Markets too,” Schehzad told Arab News.
“Low liquidity, IPOs (Initial Public Offerings), issues with investors getting their dividends out (and general inflow/outflow of foreign direct investors) have been additional issues associated with our investment climate. Higher taxes and most of all, extreme volatility in currency have kept foreign investors away. So our issues have largely been macro.”
MSCI, a New York-based global index provider, downgraded Pakistan to a frontier market in 2021, four years after its status was elevated to an emerging market.
Another key reason, analysts say, for the outflow of foreign investment from Pakistan was an interest rate hike by the Federal Reserve (FED) of the United States.
“In recent years we have witnessed a global trend that the investment from emerging markets has flown out to other investment avenues due to the USA FED rate hike,” Naseer said. “International investors do not see any attraction in risky emerging markets.”
In July, the US Federal Reserve increased the interest rate by 75 basis points that, coupled with earlier hikes in March, May and June, jacked up the central bank’s interest rate from near zero to 2.25-2.50 percent overnight. FED is expected to raise the rate by another 50 basis points next month.
But while the South Asian country witnesses dwindling foreign equity investment, anticipated $1 billion inflows from the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are likely to rejuvenate the bourse, experts said.
“The investment is at lower ebb but we don’t see it going further down keeping in view the expected upcoming investment from the UAE, which would improve the equity investment numbers in the coming days,” Naseer said.
Pakistan has successfully secured $4 billion from friendly countries, including $2 billion from Qatar, $1 billion from Saudi Arabia for deferred oil payments, and $1 billion from the UAE through investment in equities.
The South Asian country is also expected to receive $1.2 billion from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) after its board meeting on August 29 l, which could open the door to financing from other multilateral and bilateral lenders.
PSX officials say they are in the process of coming up with new measures and products to improve the investment climate at the bourse and attract foreign investment.
“We are constantly working on improving the investment climate by offering new products, digitization of services, and IPOs with enhance focus on the listing of IT companies to attract foreign investment,” Raeda Latif, PSX head of marketing and business development, told Arab News.
“We have made an alliance with the Pakistan Software Export Board for listing of 40 IT companies that would be funded because the foreign investment also comes through IT companies and it also boosts countries exports.”


















