DUBAI: As anti-government protests in Iran enter their third week, the death toll has continued to rise, with more than 90 people reportedly having lost their lives in the wave of unrest sparked by the death of Mahsa Amini.
The 22-year-old’s death at the hands of Iran’s morality police, the Gasht-e Ershad, unleashed an outpouring of anger in almost every province over the strict policing of personal freedoms and the deteriorating standard of living.
Iran’s large diaspora, spread across Europe and North America, has joined the protests in solidarity, with large demonstrations taking place outside Iranian embassies in Western capitals.
Regime authorities have so far acknowledged the death of 41 people since the unrest began yet have refused to give in to demands to relax the strict dress code imposed on women, including the mandatory headscarf.
Ebrahim Raisi, Iran’s ultra-conservative president, has dismissed the anti-regime protests as a “conspiracy” orchestrated by outside enemies and has vowed to “deal decisively with those who oppose the country’s security and tranquility.”

Tehran has attempted to limit the spread of information about nationwide protests with blocks on mobile internet. (ZUMA Wire/Alamy Live News)
In a statement on Sunday, he said: “At a time when the Islamic Republic was overcoming economic problems to become more active in the region and in the world, the enemies came into play with the intention of isolating the country, but they failed in this conspiracy.”
Videos and photographs emerging from Iran on social media tell a different story. Shocking images of police brutality meted out on young protesters have gone viral on social platforms, eliciting international condemnation.
To counter the spread of images and information, the regime has limited internet access and clamped down on applications like WhatsApp, Twitter and Instagram — claiming the move was necessary in the interests of “national security.”
Tehran is no stranger to this kind of information warfare. The regime has adopted this strategy multiple times since the proliferation of smartphones and social media in order to control the narrative.
“Shutting down mobile internet services has become a go-to for the Iranian government when dealing with civil unrest,” Doug Madory, director of internet analysis at monitoring firm Kentik said.
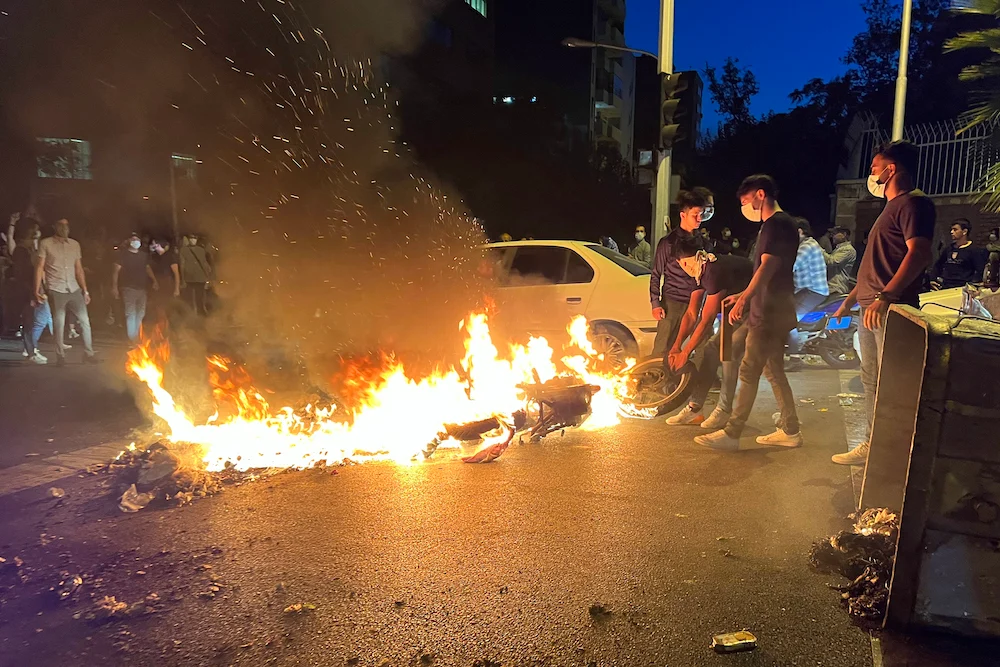

Regime authorities have so far acknowledged the death of 41 people since the unrest began. (AFP)
Protesters have been getting around the regime’s internet controls using secure private connections. They have also been sharing footage and details about forthcoming protests with outlets like the London-based broadcaster Iran International.
Iran’s misinformation strategy is as old as the regime itself. In the 1970s, the revolutionaries fighting to topple the US-backed monarch, Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, sought to portray their leader, Ruhollah Khomeini, as a freedom fighter.
Khomeini’s close entourage, which included Western-educated advisers, helped him weave a message that appealed to Iranians inside and outside the country, cleverly modifying his words to appeal to Western audiences.
Their methods proved extremely effective. Western journalists, who at the time relied on the translations given to them by Khomeini’s advisers, willingly broadcast these messages to the world.
Today, the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps utilizes a stable of media outlets, including Fars News, Tasnim and others, to set the political agenda and undermine domestic dissent.

Protests have spread across Iran over the death of Mahsa Amini after the young woman was arrested by morality police. (AFP)
The IRGC also uses these platforms to broadcast propaganda about operations in Iraq, Syria and elsewhere in the Middle East where the regime holds sway with local proxies.
At the same time, the English-language state broadcaster Press TV is used to appeal to viewers in the West, often featuring American and European commentators who support Tehran’s policies and worldview.
In March this year, Ruhollah Mo’men Nasab, former head of the Iranian Culture Ministry’s Digital Media Center, lifted the lid on how the regime disrupts the flow of information and discredits activists.
Describing his work as “psychological warfare,” Nasab boasted of developing software and “cyber battalions” to manipulate the narrative on Twitter through fake accounts.
Arash Azizi, a history and Middle East specialist at New York University, says the regime has been developing its techniques for internet information manipulation for more than a decade.
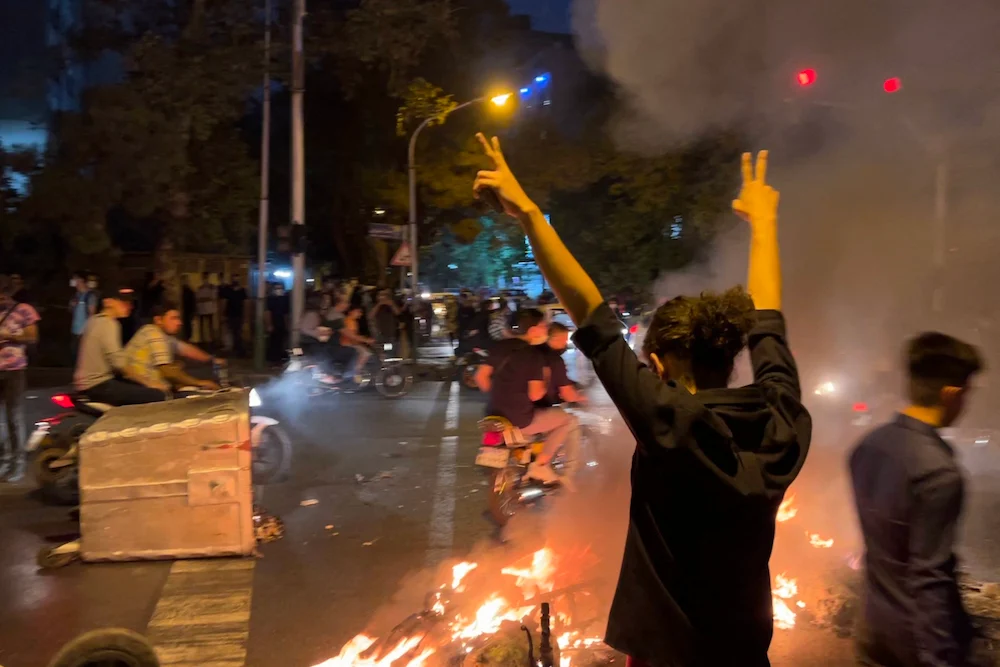
Shocking images of police brutality meted out on young protesters have gone viral on social platforms, eliciting international condemnation. (AFP)
“Perhaps the first Twitter revolution was in 2009 as events were unfolding in Iran,” Azizi told Arab News, referring to that year’s mass protests, known as the Green Movement, which exploded in response to the disputed reelection of then-President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad.
“Nowadays, Iranians use a variety of online tools to get their voice out, which is why the government has tried to shut down the internet entirely,” said Azizi.
“Iranians abroad and many tech experts, however, are playing an active role in dominating social media with messages about what’s taking place.”
A Twitter account called @1500tasvir, which is run by a group of 10 Iranian activists based inside and outside the country, was first set up in 2019 during the wave of protests sweeping Iran at that time.
Since the latest outbreak of unrest, the account has posted thousands of videos captured by protesters. One of @1500tasvir’s contributors warned that the regime’s limiting of mobile internet services could undermine the protests.
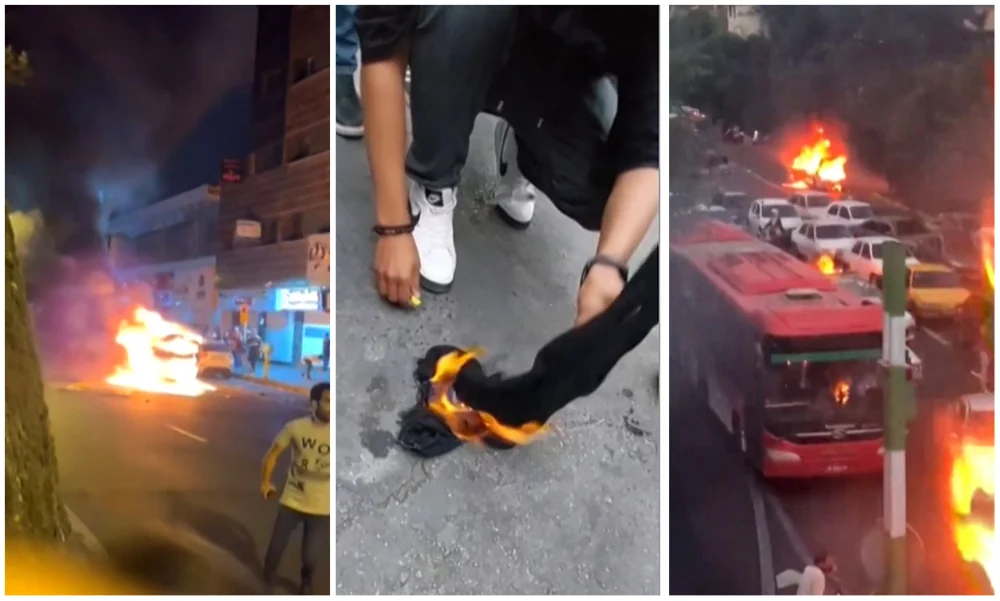

Thousands took to the streets in violent protests in the city of Tehran. (AFP)
“When you see other people feel the same way, you get braver. You are more enthusiastic to do something about it. When the internet is cut off, you feel alone,” the contributor said.
In response to the regime’s internet shutdowns, Antony Blinken, the US secretary of state, pledged Washington would “make sure the Iranian people are not kept isolated and in the dark.”
On Sept. 23, the US Treasury issued Iran General License D-2, adjusting sanctions rules to allow technology companies to offer the Iranian people more options for secure, outside platforms and services to help counter the regime’s narrative.
Unable to completely snuff out the spread of information online, the regime has instead resorted to its time-tested strategy of detaining social media users whose material gains widespread traction.
According to state news agency IRNA, Hossein Mahini, a well-known football player, has been arrested “by the order of the judicial authorities for supporting and encouraging riots on his social media page.”
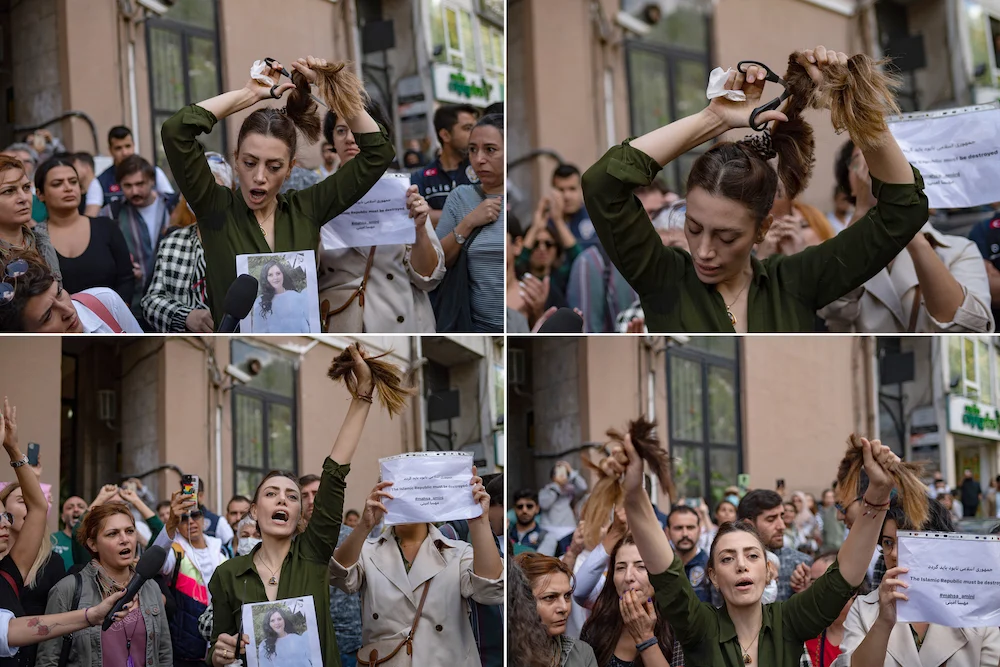

Nasibe Samsaei, an Iranian woman living in Turkey, cutting off her ponytail during a protest outside the Iranian consulate in Istanbul on September 21, 2022. (AFP)
Another high-profile detainee is Shervin Hajipour, a popular singer who composed a piece using people’s tweets on Amini’s death and the protests. He was reportedly taken into custody last week after his song reached 40 million views on Instagram.
Although authorities did not immediately confirm Hajipour’s arrest, Mohsen Mansouri, Tehran’s provincial governor, vowed to “take measures against celebrities who contributed to fueling the protests.”
To get around the internet shutdown, some activists have now resorted to distributing flyers to advertise the time and place of planned protests, indicating the regime has failed to quell the unrest.
“They’re yet to have a way of controlling the narrative,” Azizi told Arab News. “The vast majority of Iranians can now see the brutality of this corrupt regime clearly. There have even been letters of solidarity with the protesters from Shiite seminary students in Qom and Mashhad.
“Internationally, thousands have come out in support of the protesters. Even those who usually defend this regime in the Western media are now silent.”






























