DUBAI: As food-insecure households in the Middle East, Africa and Asia continue to pay a high price for a war raging thousands of miles away, forces beyond the control of any single government or international authority are compounding the problem.
Following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February, and the resultant blockade of the latter’s southern Black Sea ports, skyrocketing food prices raised the specter of increased hunger and malnutrition in many countries.
Despite an easing of that crisis following a four-way agreement in Istanbul on July 22, rising inflation worldwide and global supply-chain disruptions now pose a new threat.
The Federal Reserve raised interest rates in mid-September with the aim of bringing down the rate of inflation in the US. But in the process, the value of the dollar has soared, which is causing prices of food and fuel imports to rise in less-wealthy countries whose currencies are plunging.
These new pressures come at a time when food prices were supposed to be under control, in part thanks to an agreement brokered by the UN and Turkey to create a safe maritime humanitarian corridor from three Ukrainian ports.
To implement the Black Sea Grain Initiative, a Joint Coordination Center was established in Istanbul that includes senior representatives from Russia and Ukraine, along with mediators from Turkey and the UN.
Implementation of the deal to resume exports of grain, foodstuffs, fertilizer and other commodities from the Black Sea basin — often referred to as Europe’s breadbasket — has been halting since it was signed in July.
Nevertheless, it has helped to lower the prices of staples such as bread and cooking oil in developing countries that had been pushed to the brink of debt default and starvation.
“In the month following the outbreak of the conflict, the price of wheat flour rose by 47 percent in Lebanon, 11 percent in Yemen, 15 percent in Libya, 14 percent in Palestine and 10 percent in Syria,” Abdel Mageed Yahia, the World Food Program’s country director in the UAE and representative for the GCC region, told Arab News.
“Global price fluctuations will not immediately dent domestic inflation in countries facing a toxic mix of tumbling currency values and high inflation. While there is no single solution to the food-security crisis in these countries and around the world, the (Black Sea grain deal) is an exceedingly positive development and a step in the right direction.”
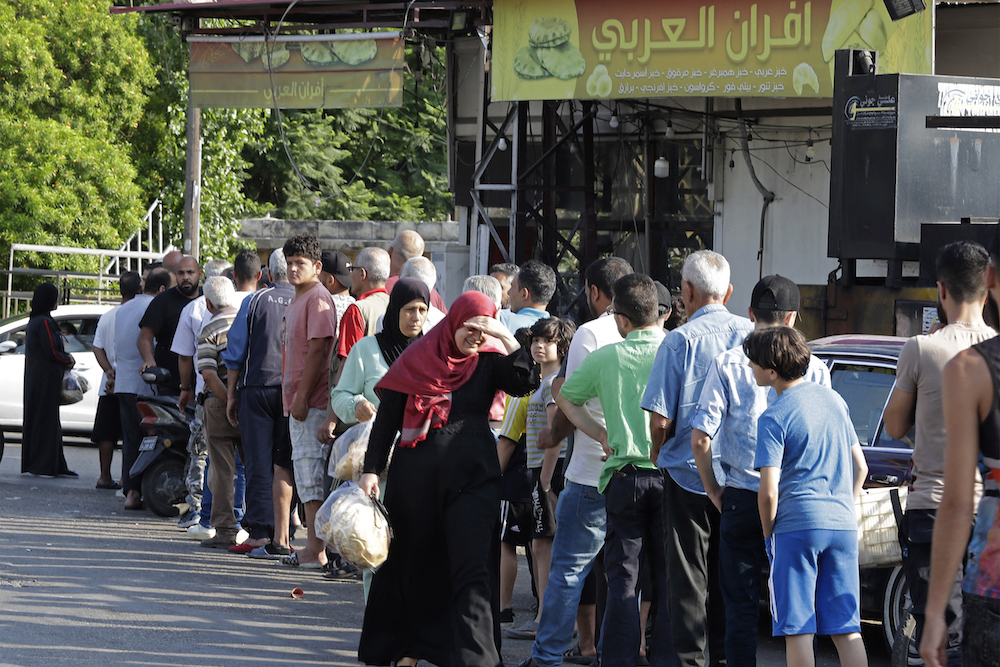

People lining up in front of a bakery to buy bread in Lebanon's southern city of Sidon on June 22, 2022 as fuel and wheat shortage deepened. (AFP/File Photo)
Given that Ukraine was the world’s fifth-largest exporter of wheat prior to the conflict, the blockade of its ports was costing the country billions of dollars in lost revenues and, at the same time, pushing up global food prices to alarming levels.
Before the invasion, Ukraine exported about 6 million tons of food every month. That figure had fallen to an average of just 1 million tons a month before the Black Sea Grain Initiative took effect.
As a result many countries, such as those in the Middle East and North Africa that import more than 40 percent of their wheat and almost 25 percent of their vegetable oil from Russia and Ukraine, faced a double blow in the form of acute food shortages and soaring prices.
The grain deal, described at the time by UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres as “a victory for diplomacy,” is designed to maintain Ukrainian food exports of 5 million tons a month.
“There is no solution to the global food crisis without ensuring full global access to Ukraine’s food products and Russian food and fertilizers,” Guterres said during a visit to Ukraine in August.
The agreement has undoubtedly helped millions of people who were struggling with the rising cost of living, as well as Ukraine’s embattled farmers. But according to experts, it alone cannot solve the wider problems of famine and food insecurity, the causes of which are much more complex and range from drought and climate change to bad governance and state collapse.
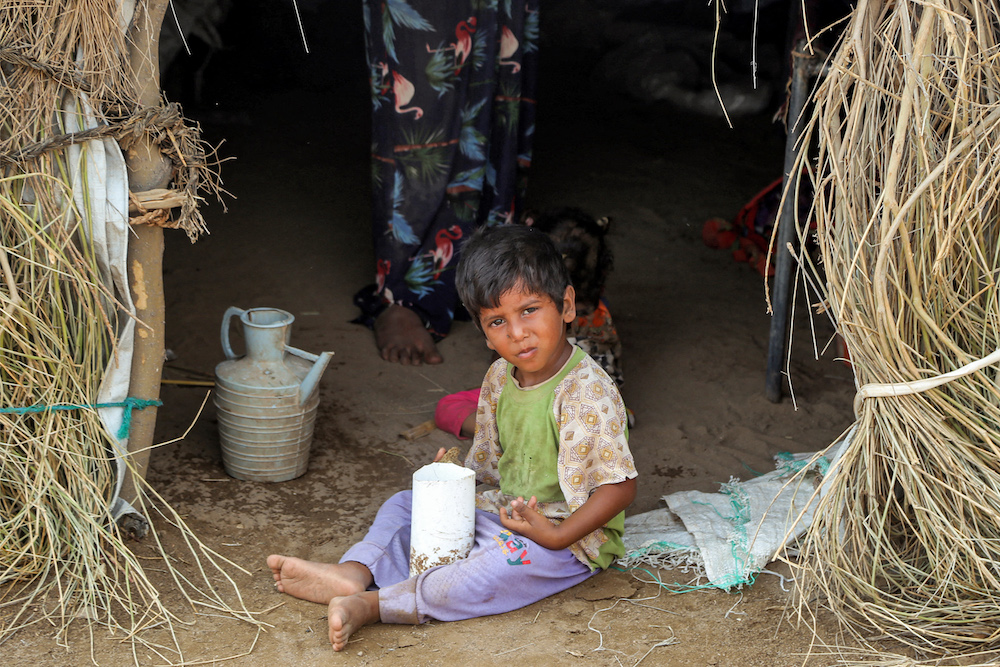

A child sits at the entrance of a shelter at a camp for displaced people damaged by torrential rains in the Jarrahi district of Yemen's western province of Hodeidah. (AFP)
More than two months after the grain deal was signed, famine continues to stalk the most food-insecure regions of the world, particularly Yemen and parts of East Africa, where commodity prices remain stubbornly high, hunger-relief operations face disruption and drought are destroying crops and livestock.
The prices of imported goods and commodities have been rising in the Middle East and North Africa region since early 2021, linked to growing demand as economies began to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Domestic food prices have risen by more than 15 percent in more than 50 countries, while inflation is running in triple digits in Lebanon, Venezuela, Sudan and Zimbabwe.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization’s Food Price Index, which measures monthly changes in the cost of a basket of key food items, prices hit an all-time high in March this year. By the end of April, the international price of some varieties of wheat had reached $477 a ton — an increase of 53 percent on 2021 figures.
“These rising global prices got transferred to local economies, particularly in import- and aid-dependent countries, compromising the access of already vulnerable populations to an affordable diet,” said Yahia.
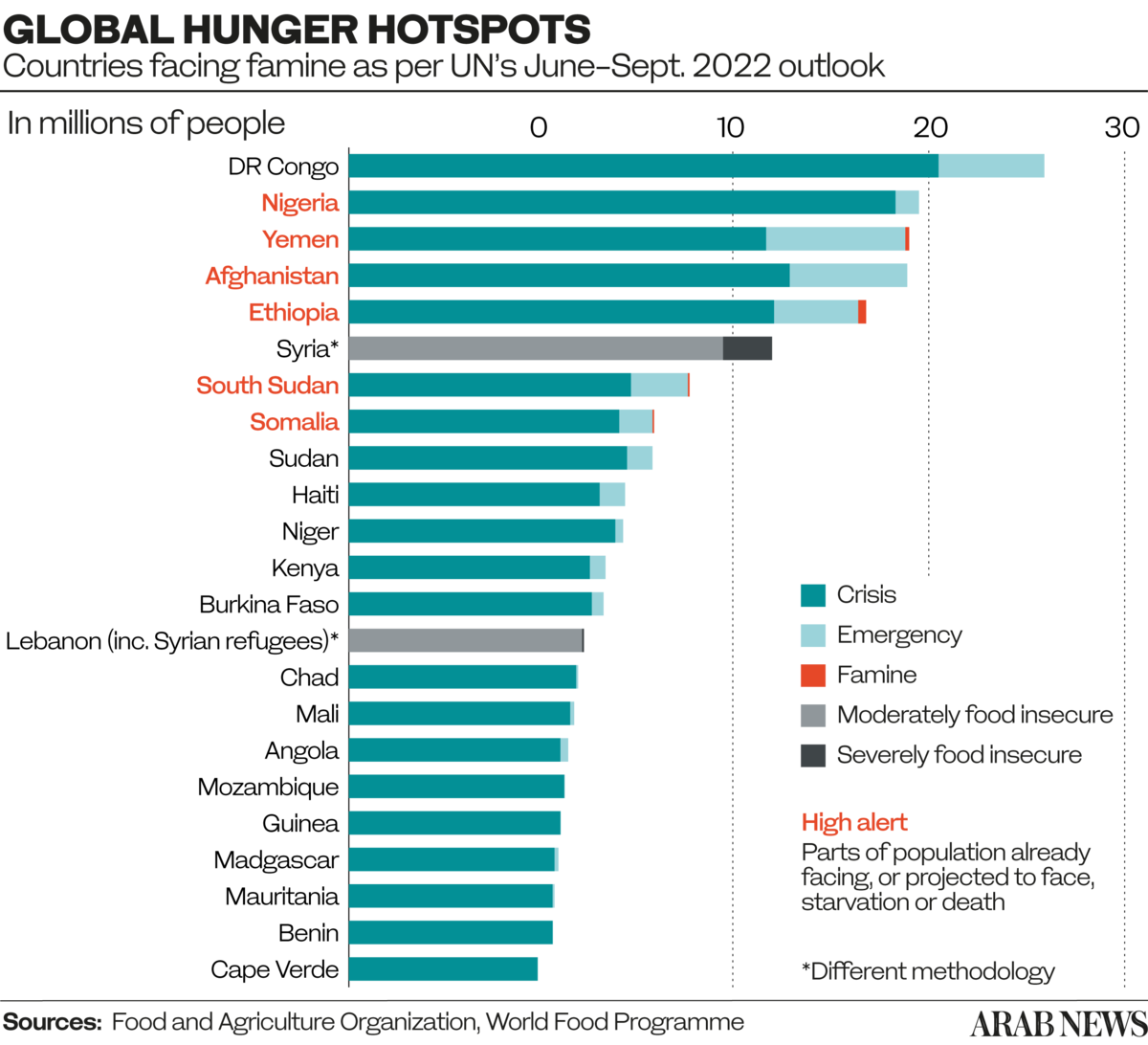
A recent report from Deep Knowledge Analytics, titled Global Food Security Q2 2022, found that 868 million people in 25 countries are at “high risk and deteriorating,” based on an evaluation of their food systems and economic resilience.
INNUMBERS
* 345m people in 82 countries face acute food insecurity.
* 50m people in 45 countries are on the brink of famine.
Source: WFP
Among the lowest-ranking countries are Syria (148th) and Yemen (160th), both of which are in the grip of multiple, overlapping crises fueled by war.
The report also found that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has led to a 25 percent increase in the number of countries that have restrictions on food exports in place.
By the end of March this year, about 53 new policies directly affecting the food trade had been adopted globally, of which 31 restricted exports in general and nine limited wheat exports specifically, contributing to a further spike in prices.
Simultaneously, the price of fertilizers has risen by 30 percent since the beginning of this year, contributing to reductions in crop yields worldwide.
Despite all these supply-side challenges, there are at least signs the supply of Black Sea grain is stabilizing.
“Since Aug. 1, more than 4.3 million metric tonnes of food have been moved, bound for 29 countries across three continents,” Amir Abdulla, the UN coordinator for the Black Sea Grain Initiative, told Arab News.
Currently, the Black Sea Grain Initiative facilitates exports from three Ukrainian ports, feeding into the global food market while at the same time freeing up the country’s silos to accommodate the next harvest.
“Although the war had an impact on agricultural production, there is still a lot of grain, other foodstuffs and ammonia to be exported in the coming months,” said Abdulla.
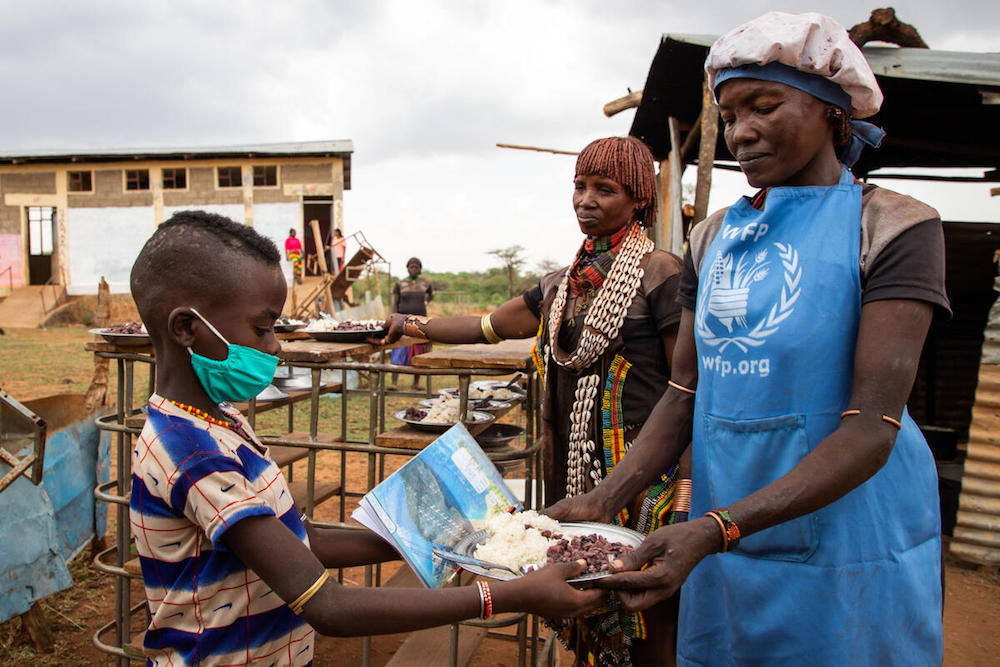

In Ethiopia, the value of school meals is equivalent to approximately 10 percent of household income. When several children are enrolled in school, the provision of school meals can translate into substantial savings. (AFP)
Ukrainian grain silos held an estimated 20 million tons of grain in August this year. An additional 19.5 million tons of harvested wheat was expected over the remainder of the summer and 38.2 million metric tons of feed grain is expected in the fall.
“This means that storage and silos must be urgently emptied of last year’s harvest,” said Abdulla.
The grain initiative gives Ukrainian farmers restored access to export markets at competitive prices, as well as incentives to plan for the 2023 harvest, which will be critical in efforts to avoid another global grain shortage.
As of mid-September, about 140 vessels had sailed from Ukraine’s ports carrying more than 3 million tons of food, including critical grain supplies such as wheat, corn and barley, sunflower and other oilseed products, and soya beans.
Among them were four vessels chartered by the WFP to transport about 128,000 tons of grain destined for Afghanistan, Yemen and the Horn of Africa.
As an aid agency that sourced 40 percent of its emergency wheat supplies from Ukraine, the WFP’s humanitarian response was severely disrupted by the Russian invasion.
Understandably, therefore, the “WFP has supported the Black Sea Grain Initiative, providing expert advice on shipping and logistics during negotiations,” Yahia said.
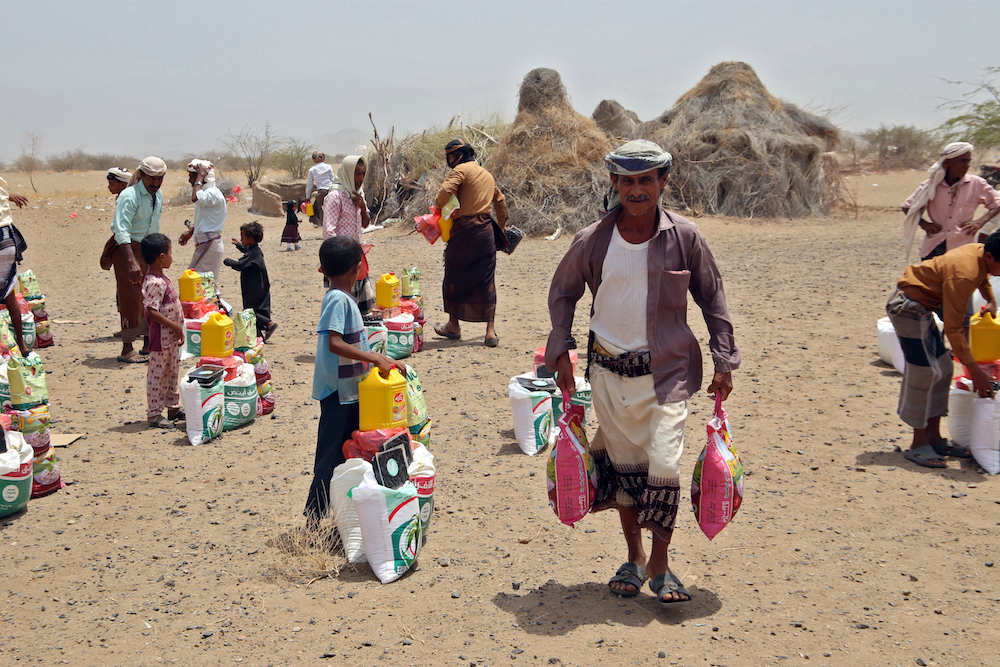

Hungry Yemenis displaced by conflict collect food aid. (AFP)
The MV Brave Commander was the first ship chartered by the WFP under the initiative. It transported about 30,000 tons of wheat — enough to feed 1.5 million people for a month — to Ethiopia, where prolonged drought and civil conflict have pushed millions into acute food insecurity.
“In total, WFP has already procured some 300,000 metric tons of wheat grain from Ukrainian suppliers since the signing of the Black Sea Grain Initiative,” said Yahia.
While the initiative has provided a much-needed respite, most indicators suggest the UN Sustainable Development Goal of achieving “zero hunger” will not be achieved by the end of the decade.
In fact, experts say much of the progress that had been made in this area in recent decades is being undone by unforeseen setbacks and crises.
Underlining this point, Yahia told Arab News: “The world is moving further away from its goal of ending hunger, food insecurity and malnutrition in all its forms by 2030.
“And the crisis may not yet have reached its peak; 2023 could be worse if we do not get ahead of the situation.”



























