LONDON: Ten years after the US began its mediation efforts, Lebanon and Israel have finally reached an agreement delineating their maritime border in what pundits are describing as a “historic” moment. However, some observers are taking a more cautious view.
“It’s at least 10 years overdue,” said Ambassador Frederic Hof, a former director of the Atlantic Council’s Rafik Hariri Center for the Middle East, who served as US mediator in 2012 under President Barack Obama.
“We need to be cautious at this point. There is still an elongated ratification process in Israel. There is a question of whether, after the Nov. 1 elections, the deal would be sustained if there’s a change in government,” he told Arab News.
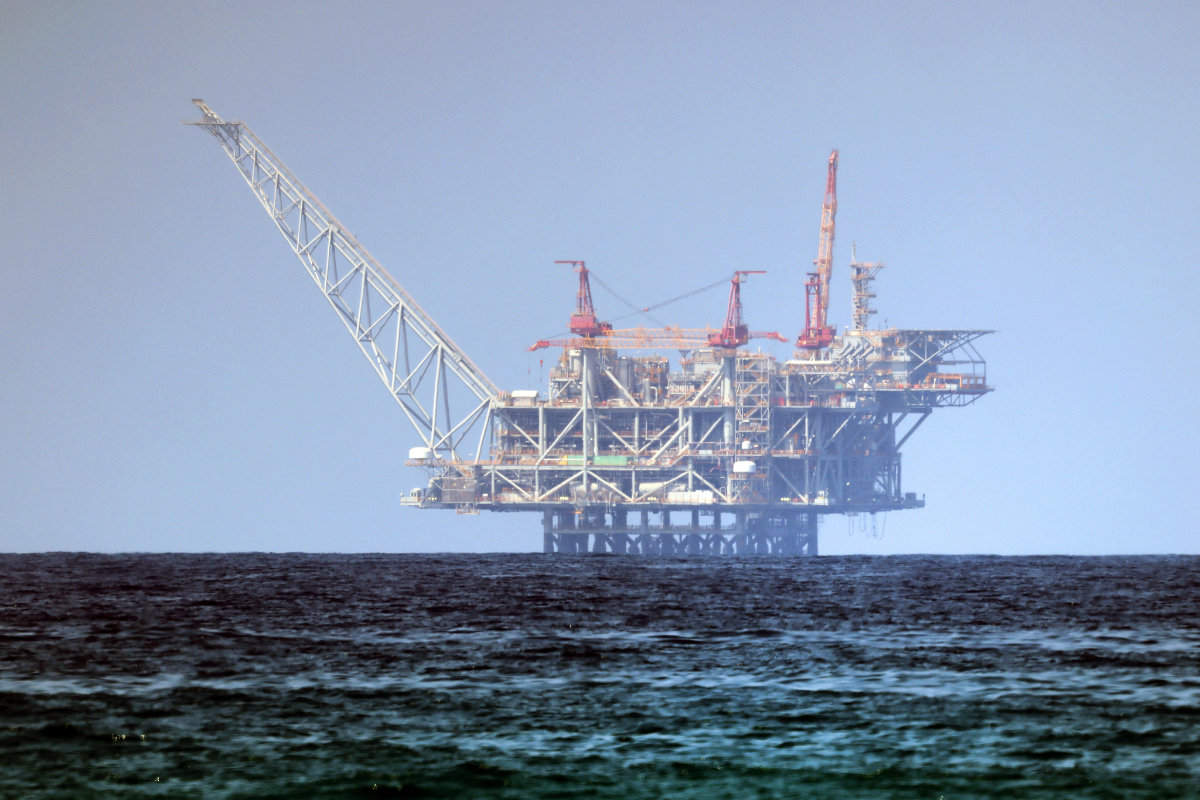

A platform of the Leviathan natural gas field in the Mediterranean Sea as seen from the Israeli northern coastal beach of Nasholim. (AFP)
“On the Lebanese side, there are a couple of questions. The obvious question is: Are there indeed marketable natural gas deposits under Lebanese waters? And, given the fact that there will not likely be any revenues for five years, will the Lebanese political system undergo some changes that would enable the Lebanese people to benefit from all of this?”
The dispute goes back to 2012, when the two countries failed to reach an agreement over the location of their shared maritime border. Israel initially pushed for Line 1 (see map), while Lebanon favored Line 29.
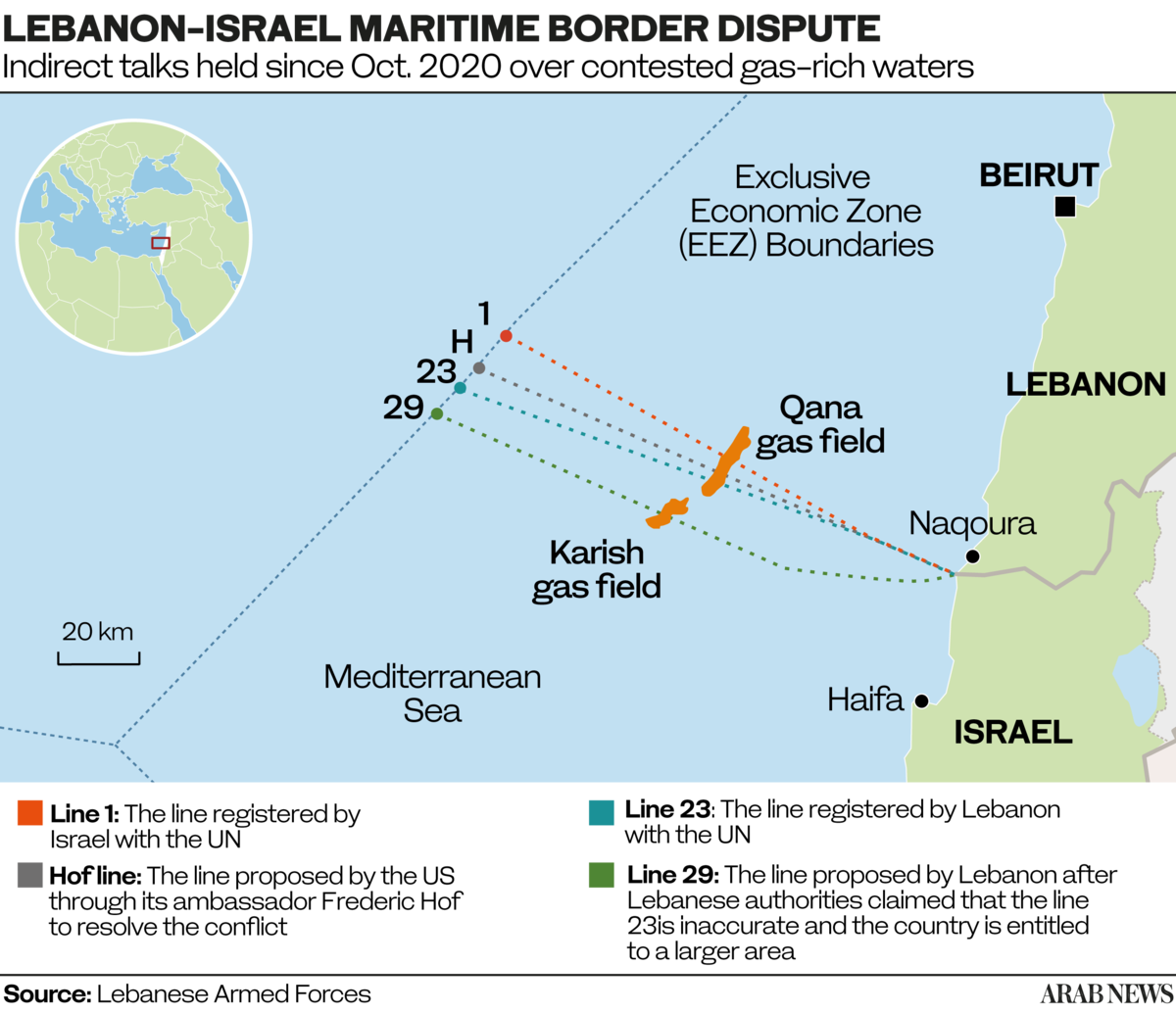
Hof, who was the first US mediator appointed to the process, proposed a line that lay closer to the Israelis’ preferred option. In the end, however, the border that was agreed is Line 23, which is closer to Lebanon’s preferred boundary.
At the heart of the dispute are two offshore natural gas fields: the untapped Qana field in Lebanon’s territorial waters and the Karish field in Israeli territory. The contested claims to the resources escalated in July when Hezbollah, the Lebanese Iran-backed militia, launched a drone attack on the Karish field. Israeli air defenses managed to shoot down all three drones before they reached their target. It is hoped this week’s border agreement will stave off similar incidents.
According to leaked details of the deal, revenues from gas extracted from the Qana field will be split between Lebanon and French energy company Total, and 17 percent of Total’s revenues will go to Israel. Israel will continue to have exclusive rights to the Karish field.

United Nations peacekeeping force vehicles patrol in Naqura, south of the Lebanese city of Tyre, on the border with Israel on June 6, 2022. (AFP)
Although the deal settles the maritime border issue, it does not affect the yet-to-be recognized land border between the two countries, the so-called Blue Line that was demarcated in 2000 and is supervised by the UN Interim Force in Lebanon.
Reflecting on why a maritime border agreement could not be reached 10 years ago when the process began, Hof said the then government of Najib Mikati — who now serves as Lebanon’s caretaker prime minister — had already started to “steadily fall apart.”
He added: “Now, the decision-making process seems to be in the hands of the three presidents in Lebanon (the president, prime minister and speaker of parliament) and unless things change, which I don’t think they will, all three seem to agree that Lebanon did well in this mediation.”

Lebanese President Michel Aoun (R) meeting with US envoy Amos Hochstein and US Ambassador Dorothy Shea (L) at the Presidential Palace in Baabda on June 14, 2022 . (Dalati & Nohra photo via AFP)
Others, such as Tony Badran, a research fellow at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies and Levant analyst for Tablet Magazine told Arab News that “what changed now is that the Biden administration abandoned the earlier framework of dividing the disputed area along a 55:45 ratio, and managed to press a pliant lame duck government to concede to 100 per cent of Hezbollah's demands.”
US officials also view the maritime deal, mediated by Amos Hochstein, the Biden administration’s senior advisor for energy security, as a diplomatic win that will ultimately improve overall security and stability in the region.
“At the end of the day, the US was able to mediate a deal between Lebanon and Israel — two enemy countries — to get into a maritime border deal that they think would stabilize the situation between both countries and make it harder for them to go to war,” Laury Haytayan, the Middle East and North Africa director at the Natural Resource Governance Institute, told Arab News.

Indeed, she believes that Israel, which already enjoys sufficient energy supplies, correctly identified the security benefits offered by a deal that favored Lebanon’s territorial claims over Israeli economic self-interest.
“If Lebanon is stable, and Lebanon focuses on its economy, they think that they will be less interested in war” and, in turn, less dependent on Hezbollah and Iran, Haytayan added.
Officials in Beirut likely had other concerns in mind, however. As Lebanon faces economic catastrophe, the caretaker government is eager to show it is playing ball with the international community’s demands for reforms in exchange for assistance.
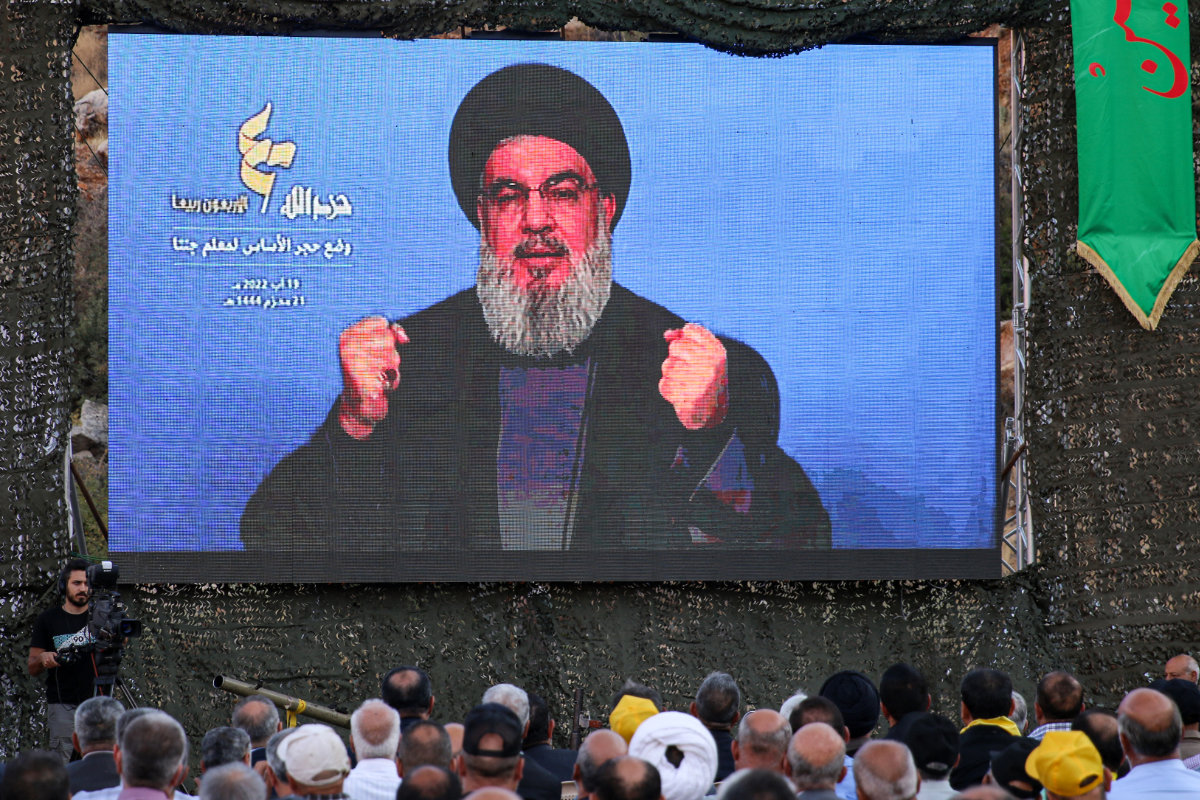

Supporters of Lebanon's Hezbollah react as the group's leader Hassan Nasrallah addresses them through a giant screen on August 9, 2022. (AFP)
Haytayan said Lebanon’s primary aim was to place “a card in the hands of the political class to use to talk to the international community and to talk to the Americans for the first time, so that the Americans will not continue with the sanctions.”
Since Lebanon’s economic collapse in 2019, which was compounded by the COVID-19 pandemic and the devastating explosion at Beirut’s port in August, 2020, the US has put sustained pressure on the Lebanese government to address a culture of rampant corruption.
Among those placed under sanctions by the US is President Michel Aoun’s son-in-law, Gebran Bassil, who is a former foreign minister and the current head of the Free Patriotic Movement.

Gebran Bassil, the current head of Lebanon's Free Patriotic Movement. (AFP)
Because of the reputation of the Lebanese elite for lining their own pockets at the expense of the public purse, citizens cannot help but feel pessimistic about the prospect of any oil revenues that result from the border deal being put to good use.
“I think the threat to revenues not being used for the benefit of the Lebanese people, and for the rebuilding of Lebanon, comes from the existence of a totally corrupt and totally incompetent political class in Lebanon, which enjoys the support and protection of Hezbollah,” said Hof.
Although it will be at least five years before Lebanon sees any financial return on gas explorations, there are several indirect, short-term gains on offer, said Haytayan.
A public commitment given by Total that it will begin drilling operations in the Qana field could help to convince more businesses to invest in Lebanon, which would give the Lebanese government additional “cards to play with negotiators, with the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank, the international community, the US and Europeans,” said Haytayan. “This would ease the pressure for reform that has been put on them for three-and-a-half years.”

Total Energies has committed to begin drilling operations in the Qana field once Israel and Lebanon settle their maritime border dispute. (AFP file)
US President Joe Biden called his Lebanese counterpart, Aoun, to congratulate Lebanon on the maritime deal.
“Everybody is happy that Lebanon has done this deal with Israel, so there is political energy injected into the survival (of Lebanon’s political class),” Haytayan said.
The maritime border deal is no doubt a major step forward. However, Hof doubts it will lead to any normalization of relations between Israel and Lebanon in the near future. Instead, he views the coming years as a test of the willingness of Lebanese politics for reform and of the elite’s readiness to put the needs of the public ahead of their own.
“Five years is the estimate one most often sees (for gas exploration),” said Hof. “This gives the Lebanese people five years to do their best to create a system reflecting rule of law, accountability, transparency, and to build a Lebanese state that is capable of using these God-given resources for the benefit of the Lebanese people.”
As for Badra, he explained that the deal lead Hezbollah to “emerge clearly as the Biden administration’s, and France’s, primary interlocutor in Lebanon -- a recognition that it is the only party that matters in, and that dominates, Lebanon."
“The Biden administration not only assisted Hezbollah’s optics of coercing Israel to concede under fire, but also, the deal itself cements France's partnership with Hezbollah, along with other potential foreign investments.”


























