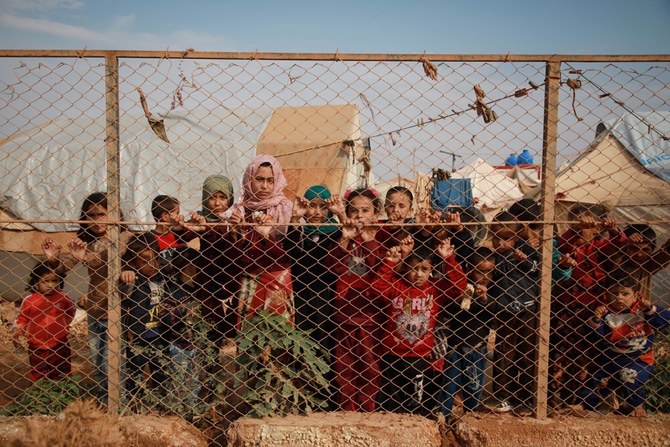
DUBAI: When Amir left his war-ravaged hometown of Homs, western Syria, in 2013, he believed he was heading somewhere that would offer him and his family lasting security and sanctuary from his nation’s grinding civil war.
Packing what few belongings were left unscathed by the regime’s incessant barrel bombing, Amir boarded a bus bound for Lebanon with his sister, Alia, and her toddler, Omar, where the trio settled in a camp in Arsal, Baalbek.
“My brother is a proud man,” Alia told Arab News from her adopted home in Lebanon. “After our parents died under rubble, he took it upon himself to fend for us and to raise my son, Omar.”
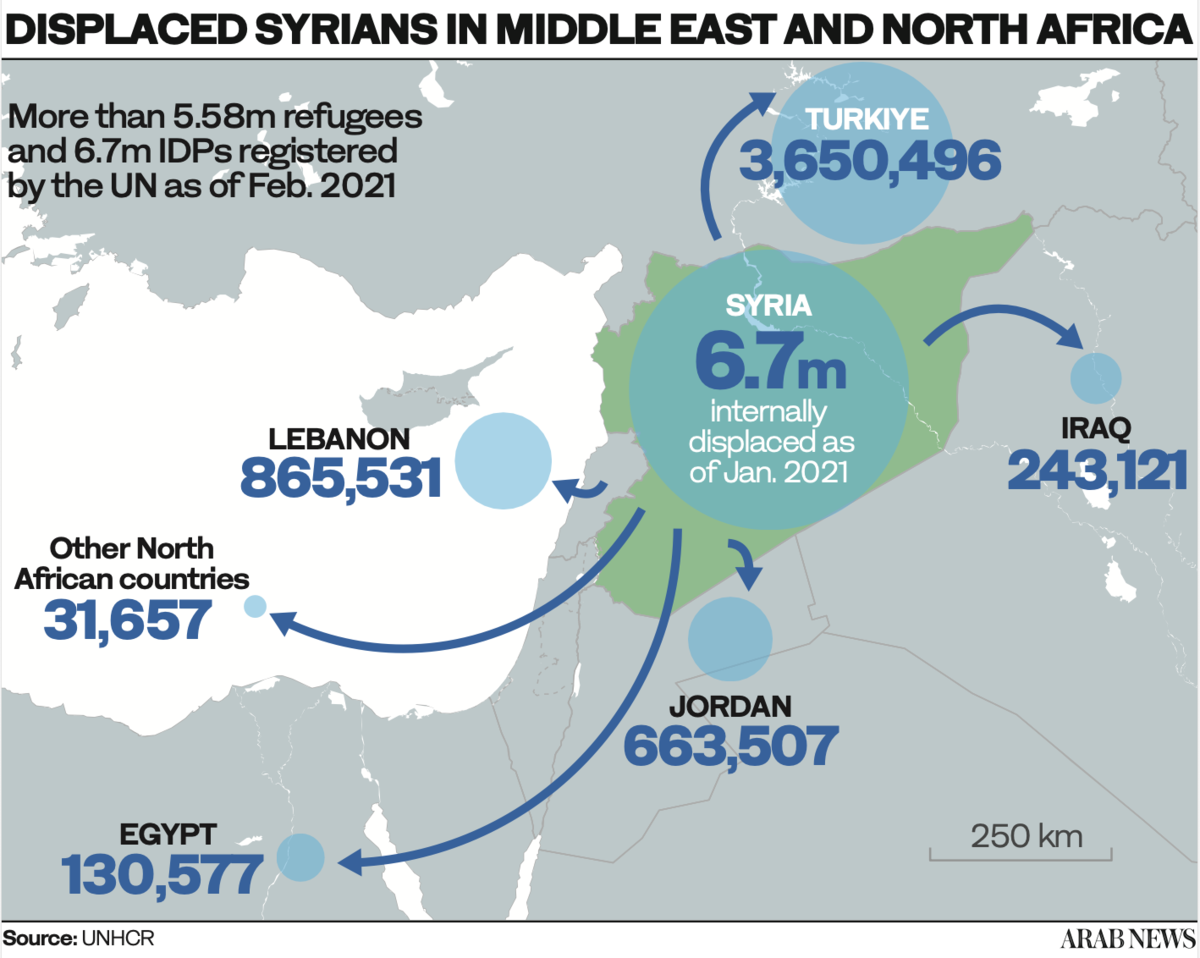
In doing so, Amir and his family joined the ranks of millions of Syrians displaced by the civil war — the majority of whom have settled in neighboring Turkiye, Lebanon, Jordan, and Iraq, while others have struck out for Europe and beyond.
What started in 2011 as a peaceful protest movement demanding greater civic freedoms quickly escalated into one of the world’s bloodiest conflicts, with a death toll now numbering in the hundreds of thousands.
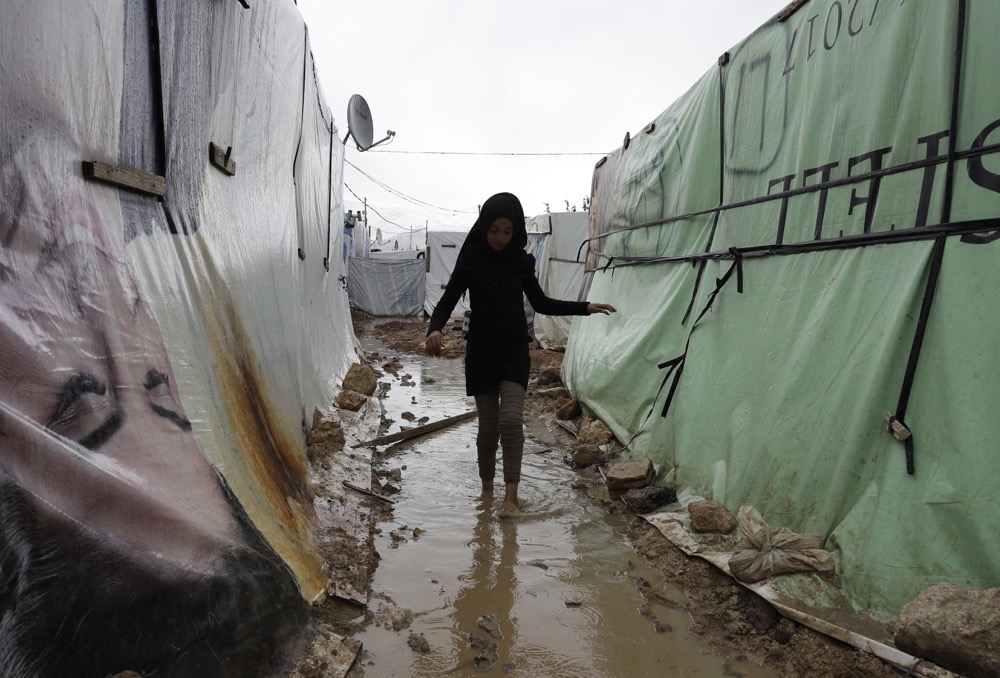

Around 13 million people have been displaced by the war. (AFP)
Another 100,000 people have disappeared, likely abducted by security service agents to be tortured and killed in Bashar Assad’s prisons. To date, around 13 million people have been displaced by the war — 5.6 million of them fleeing abroad.
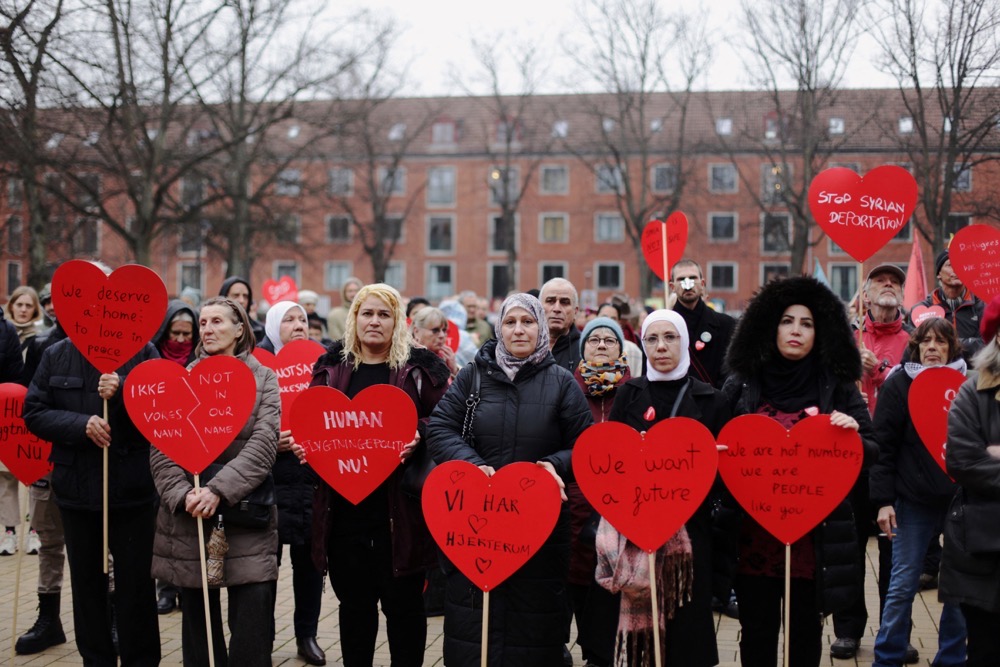
Now, many of those countries that had offered sanctuary have devised plans to return their Syrian guests, either voluntarily or by force, despite warnings from aid agencies and refugees themselves that Syria remains unsafe and blighted by poverty.
Syrian refugees are viewed by the Assad regime and its loyalists as traitors and dissidents. Human rights monitors have identified cases of returnees being harassed, detained without charge, tortured, and even disappeared.
Nevertheless, countries like Lebanon, Turkiye and Denmark, grappling with their own economic pressures and rising anti-immigrant sentiments, have been upping the ante on Syrians to return home, claiming the civil war is now over.
In 2021, Denmark adopted a “zero asylum-seekers” policy, resulting in many Syrians who had been based there since 2015 having their residency status revoked, while others were removed to deportation facilities.
Struggling to take care of its own native population, the caretaker government of crisis-wracked Lebanon announced its own repatriation plan in October this year, with the aim of sending back 15,000 refugees per month.
The situation in Turkiye is no different, according to reports. Stories have emerged on social media of refugees being forced to sign voluntary return forms.
According to reports from the France-based advocacy group Syrians for Truth and Justice, Syrians dropped off at the Bab Al-Salama border crossing by Turkish authorities are classified as “voluntary returnees,” despite this being a regime-controlled crossing.
Returnees — voluntarily or otherwise — often face harassment, extortion, forced recruitment, torture and arbitrary arrest upon arrival on the regime side, irrespective of their age or gender.
Mazen Hamada, a high-profile activist and torture survivor who has testified about the horrors of Syrian regime prisons, mystified the world when he decided to return to Damascus in 2020.
Hamada, who long spoke of his mental torment following his release and his loneliness in exile, returned to Syria from the Netherlands under an amnesty agreement supposedly guaranteeing his freedom.
However, upon arrival in Damascus in February 2020, Hamada was arrested and has not been seen or heard from since.
Last year, human rights monitor Amnesty International released a report, titled “You’re returning to your death,” which documented serious violations committed by regime intelligence officers against 66 returnees, 13 of whom were children.

Around 100,000 people have disappeared, likely abducted by security service agents to be tortured and killed in Bashar Assad’s prisons. (AFP)
Five returnees had died while in custody, while the fate of 17 remains unknown. Fourteen cases of sexual assault were also recorded — seven of which included rape — perpetrated against five women, a teenage boy, and a five-year-old girl.
Voices for Displaced Syrians, another advocacy group based in Istanbul, published a study in February this year, titled “Is Syria safe for return? Returnees’ perspective,” based on interviews with 300 returnees and internally displaced persons across four governorates.
Their accounts outlined extreme human rights violations, physical and psychological abuses, and a lack of legal protections. Some 41 percent of respondents had returned to Syria voluntarily, while 42 percent said they had returned out of necessity, as a result of poor living conditions in their host country and a longing to reunify with family.
With regard to their treatment upon arrival, 17 percent reported they or a loved one had been arbitrarily arrested, 11 percent spoke of harassment and physical violence inflicted upon them or a family member, and 7 percent chose not to answer.
As for internally displaced persons, 46 percent reported they or a relative had been arrested, 30 percent recounted bodily harm, and 27 percent said they had faced persecution owing to their origins and hometowns. Many also reported difficulties reclaiming private property.

With regard to their treatment upon arrival, 17 percent reported they or a loved one had been arbitrarily arrested, 11 percent spoke of harassment and physical violence inflicted upon them or a family member. (AFP)
Despite the mounting body of evidence suggesting the regime is continuing to target civilians it considers dissidents, several countries are choosing to pursue normalization with Assad, lobbying for his rehabilitation into the Arab fold and reopening their embassies in Damascus.
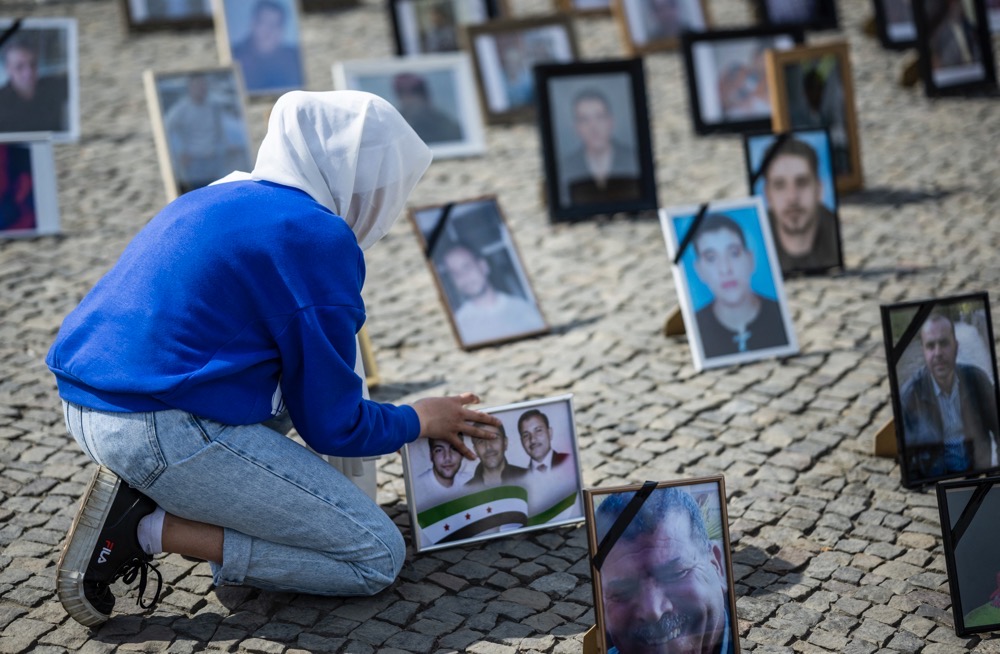
For the relatives of returnees who have since gone missing, these developments smack of betrayal.
Amir, who eventually returned to Syria voluntarily, appears to have suffered the same fate as the activist Hamada. Tired of living in poverty in Lebanon, far from his extended family, he went back in Oct. 2021. He has not been heard from since.
“Life in Lebanon has become rather unbearable. Amir would return humiliated every time he left the house,” his sister Alia told Arab News.
Having initially lived in a UNHCR-provided tent in Arsal, Amir and his family finally managed to acquire a small one bedroom house near the camps. Alia said it was a constant struggle to scrimp together enough money to pay the rent.
Most refugees are unable to secure consistent employment due to their lack of official papers, which, under normal circumstances, would grant them residency and facilitate a stable income. Amir, like many working age men around him, resorted to hard manual labor.
Those who try to find work in the big cities risk being arrested at Lebanese checkpoints, imprisoned, and deported for staying in the country illegally.
Since Amir’s disappearance, Alia has been forced to make do on a single income cleaning houses.

What started in 2011 as a peaceful protest movement demanding greater civic freedoms quickly turned into a brutal crackdown by the Bashar Assad regime, and one of the world’s bloodiest conflicts. (AFP)
“He couldn’t take it anymore, being spoken to like a little boy by some of his employers and the degrading comments he’d hear at times,” said Alia.
“It happens to me too, but I hold back my tongue. I cannot afford to stand up for myself. He thought he would take his chances and return to Syria in the hope of finding us a place, back to familiarity.”
She says she begged her brother not to leave, aware of the many refugees they knew personally who had been mistreated upon their return to Syria. Some had been held in prison until they made bail, while others had gone missing.
“But he didn’t listen,” said Alia. “It’s been over a year since he left and I haven’t heard from him.”





























