QAMISHLI, SYRIA: More than a week after twin earthquakes devastated parts of southeastern Turkiye and northwestern Syria, the death toll continues to rise by the hour. As of Tuesday, the total reported dead in the two countries stood at over 41,000, with tens of thousands more people injured.
Although the number of confirmed fatalities is lower in Syria — about 5,814 compared with 35,418 in Turkiye — more than a decade of civil war has left the country wholly unprepared to cope with a disaster of this magnitude.
An already dire situation in the northwest of the country, where a hodgepodge of rival regimes, opposition groups and terrorist factions have long battled for control, has escalated into a full-blown humanitarian catastrophe.
The Washington-based Middle East Institute estimates that up to 60 percent of the region’s infrastructure had already been damaged or destroyed prior to the February 6 earthquake, with medical facilities in particular devastated.
“Before the earthquake, most people were suffering from the humanitarian situation as a result of the destruction of most of the buildings and infrastructure due to the bombing of the Assad regime and its ally Russia, especially in the medical sector, and the lack of logistics and medicine,” Bashar Al-Fares, a journalist in northwestern Syria, told Arab News.
“Today, after the earthquakes that hit the northwestern regions of Syria, the situation has escalated. As a result of the destruction that occurred in the region, which was a shelter for refugees and forcibly displaced families from various Syrian governorates, thousands of people lost their lives in the earthquakes and many more were injured.
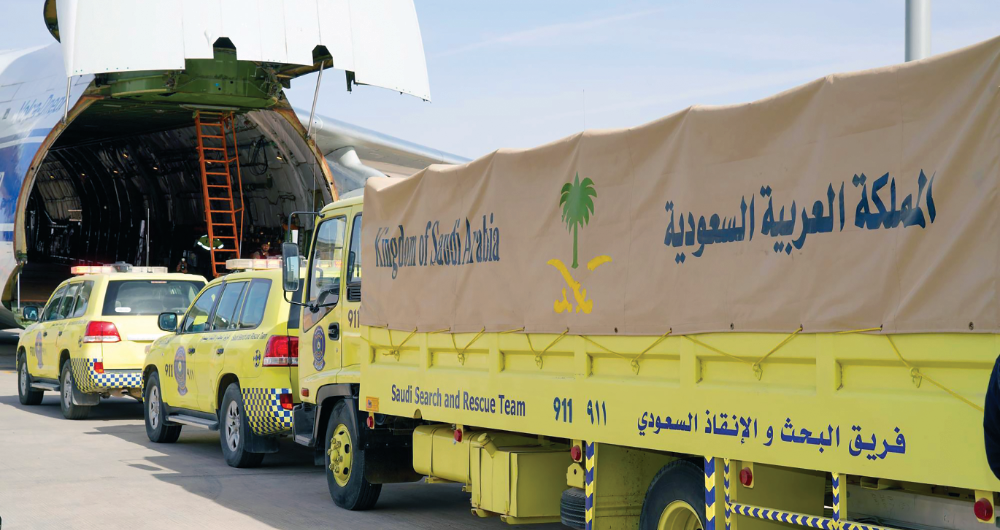

Saudi Arabia sent search and rescue teams to Syria and Turkiye. (SPA)
“This was compounded by the severe shortage of medical staff, medicines, and rescue equipment.”
Having been driven from their homes elsewhere in the country to escape bombardment, conscription, fighting and persecution, about 3 million people in the region of Syria bordering Turkiye are categorized as internally displaced.
Freezing winter temperatures, including heavy snowfall prior to the earthquakes, combined with an unprecedented cholera outbreak and the ongoing conflict in the country have left Syrians facing a litany of overlapping misfortunes with little outside assistance.
The cholera outbreak, which began in August, has so far affected more than 77,000 people across the country, almost 38,000 of them in Idlib and Aleppo governorates — the regions hardest hit by the earthquakes.
Adding to people’s misery, Syria’s currency collapsed late last year. The black-market exchange rate against the US dollar had already risen from 500 Syrian pounds in 2018 to 3,300 in 2021. By the end of last year, it had soared to more than 6,600.
The value of the pound has continued to plummet since the earthquakes, with the exchange rate reaching more than 7,400 pounds this week, further reducing the average family’s purchasing power.
Although the annual death toll in the country last year was the lowest since the start of the conflict more than a decade ago, the fighting continued between various factions in the regions destined to be devastated by the earthquakes.
As recently as Feb. 3, regime forces bombarded the outskirts of Al-Bara in rural Idlib with heavy artillery. Just two days before the earthquakes, clashes between Hayat Tahrir Al-Sham, a network of hardline Islamist groups, and regime forces in Latakia left dozens dead.
Afrin, one of the areas hit hardest by the disaster, has been in a state of chaos since Turkish forces and the Turkish-backed Syrian National Army invaded the region in 2018, capturing it from the Kurdish-led Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES).
Up until then, Afrin had been considered a relatively peaceful region throughout most of the conflict, and so hundreds of thousands of internally displaced people from other regions had settled there.
The violent upheaval in 2018 displaced the predominantly Kurdish population, with 300,000 fleeing to other parts of Syria and abroad, according to a 2018 report by the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights.
With their homes now destroyed by the earthquakes, the remaining Kurdish population might be forced to follow those who left and risk the perilous journey to find sanctuary elsewhere.
INNUMBERS
• 9m+ people affected by earthquakes in Hama, Latakia, Idlib, Aleppo and Tartus.
• 5,814 confirmed fatalities in Syria as of Tuesday.
• 90% of Syrians living below the poverty line.
According to the International Organization for Migration, almost 250 migrants were killed while trying to cross the Mediterranean Sea to Europe last year. From 2021 to 2022, the number of Syrians attempting the risky sea crossing from Africa to Europe increased six-fold, according to EU border agency Frontex.
For those with no choice but to remain in Syria, the effects of the earthquakes and their aftermath simply add to their misery.
“The situation in Syria is terrible in every way,” Sardar Mullah Darwish, a Syrian Kurdish journalist and analyst, told Arab News. “These earthquakes are just the latest disaster of many. Many civilians will die and no one can help them.
“It’s very difficult to help them. Everyone should have come together and put their conflicts aside but, unfortunately, this hasn’t happened.”
Darwish said more than a decade of civil war essentially has divided Syria into three different countries: The areas controlled by the regime, the opposition and the AANES.
The destruction caused by the earthquakes encompasses areas within and beyond regime control, including Jinderis in Afrin, which is controlled by the opposition, and Aleppo and coastal cities controlled by Damascus.
“Now a major issue is that because Syria is divided politically, the regime only wants to bring aid for itself and the opposition only wants to bring aid for itself,” said Darwish.
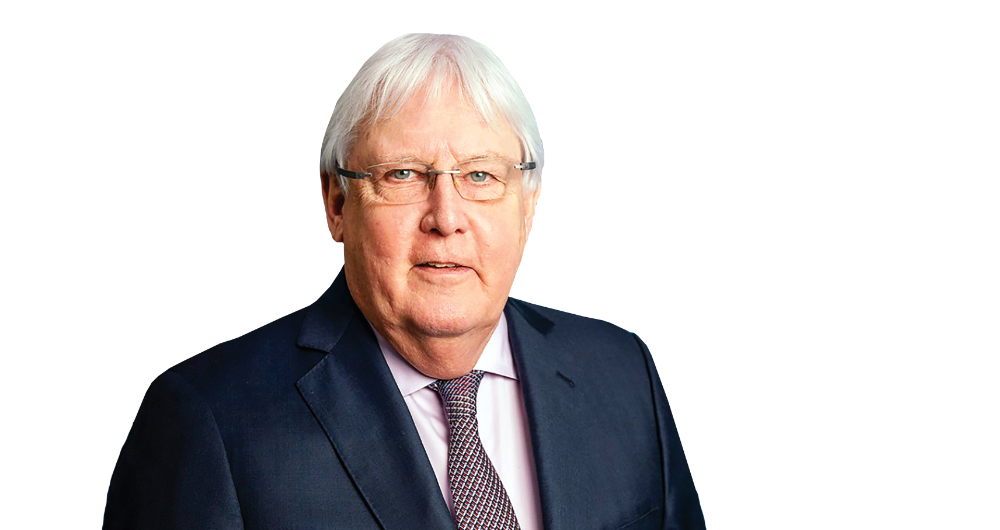

“We have so far failed the people in northwest Syria. They rightly feel abandoned,” said Martin Griffiths, UN under-secretary-general for humanitarian affairs, emergency relief coordinator. (Supplied)
Political agendas surrounding the provision of aid to the Syrian people have further complicated the humanitarian response in an already vulnerable area.
The Bab Al-Hawa border crossing near Idlib on the border between Syria and Turkiye is the only approved crossing for the delivery of UN aid via Turkiye direct to people in Syria. The crossing was closed for three days as a result of damage it sustained during the earthquakes.
As a result, it was not until Thursday, Feb. 9, that six trucks from the UN Office for the Coordination of Human Affairs, carrying shelter and non-food items, arrived in northwestern Syria.
On Monday, a week after the earthquakes struck, Syrian President Bashar Assad told the UN he would reopen two other crossing points, Bab Al-Salam and Al-Raee, for an initial period of three months to allow timely delivery of aid to the affected areas.
Largely isolated from the wider country, northwestern Syria was forced to fend almost entirely for itself in the days immediately following the disaster.
“All cities in Idlib governorate and the northern countryside of Aleppo have Civil Defense centers (the staff of which are better known internationally as the White Helmets) and they are always prepared for anything to happen,” said Darwish.
“However, the lack of heavy rescue equipment for all rescue teams was one of the biggest problems because what happened in northwestern Syria was a catastrophe that no country could handle.
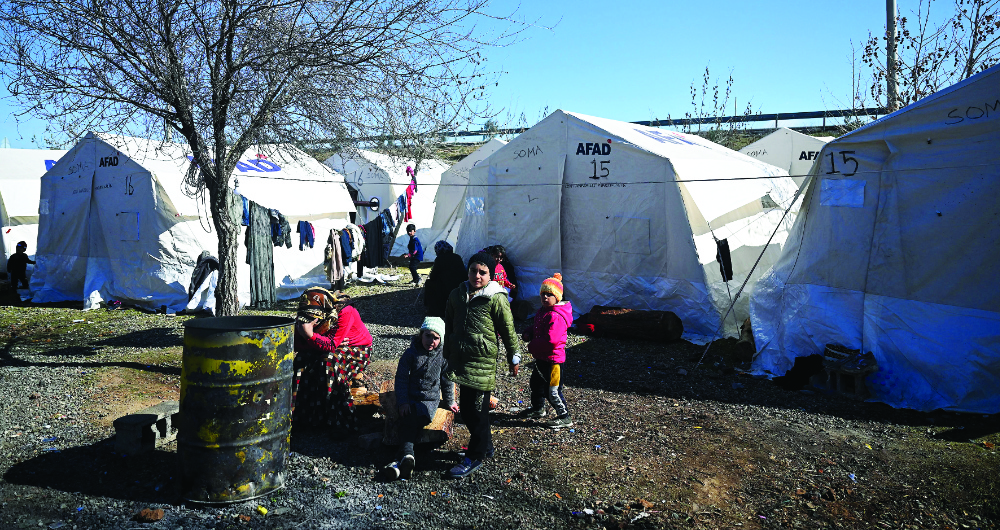

The civil war, cholera outbreak and collapsing economy have forced thousands of Syrian refugees into neighboring Turkiye. (AFP)
“Until now, the Civil Defense and rescue teams are still continuing their work in searching for the victims and pulling them out from under the rubble.”
The broader aid response has been chaotic. Although the Assad government pledged to provide aid for all areas affected by the earthquake, including those it does not control, Al-Fares said that, to his knowledge, no regime-supplied deliveries had arrived in Idlib so far.
Hundreds of trucks carrying food, fuel, water and other essential supplies from the AANES were stuck in Manbij for several days. For political reasons, neither the opposition nor the regime was giving permission for the trucks to enter the city’s earthquake-stricken areas.
Asked whether the devastation could result in many more Syrians seeking refuge in neighboring countries, or beyond, Al-Fares said: “There are no clear and safe crossings for them if they intend to migrate to other, more stable countries.”
In other words, there is simply nowhere left for Syrians left destitute by one crisis after another to go.





























