DUBAI: Eighteen years ago this month, Rafik Hariri, a prominent politician and former prime minister of Lebanon, was assassinated by a suicide truck bomb in Beirut. Originally a philanthropist before his engagement in politics, Hariri, who had made his fortune in construction, donated millions of dollars to victims of war and conflict in Lebanon, and later played a major role in ending the civil war and rebuilding the capital city.
Hariri’s assassination marked the beginning of dramatic political change and movements calling for democracy in Lebanon. For years after his assassination, politicians and important figures opposed to the influence of both Syria and Hezbollah in the country were targeted.
Despite an international tribunal finding members of Hezbollah guilty of Hariri’s assassination after passionate calls for an investigation into his death, the Iran-backed militia group has only tightened its grip on Lebanon, keeping the country in a dire state.
“Hariri was killed 18 years ago and it took about 15 years to destroy the whole country after everything he tried to build,” Lebanese economist Nadim Shehadi said on “Frankly Speaking,” the Arab News current affairs talk show which engages with leading policymakers and business leaders.
“The Special Tribunal for Lebanon and the independent international investigation commission came to Lebanon, and it took them about 15 years to produce their result. And for the first time in the history of Lebanon, where we have had several assassinations, for the first time, we had a conviction,” Shehadi said.
But according to him, despite a conviction in Hariri’s case, Hezbollah’s influence over Lebanon means that the real perpetrators of the assassination will go unpunished, and the group will continue to hold the country hostage.
Lebanon’s various political and economic crises have only intensified in recent years, with inflation in the country rising to the highest in the world in 2021 and the value of the Lebanese lira plummeting drastically.
Last year witnessed a series of bank holdups by armed customers seeking to withdraw their frozen deposits. In a country whose capital was formerly referred to as the “Paris of the East,” two-thirds of the population now suffers from poverty, with regular electricity blackouts and shortages of basic necessities such as medicine and water increasingly commonplace.
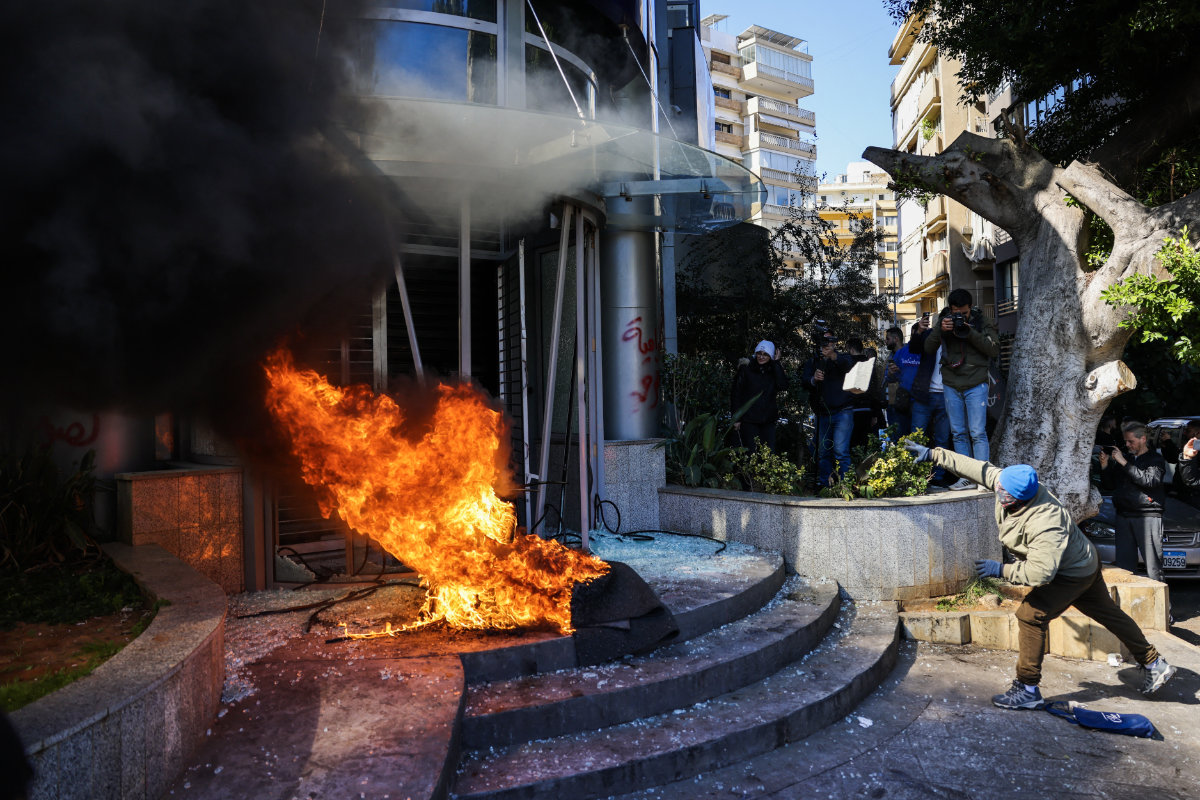
A protester throws a brick at a bank after setting fire to tires during a demonstration in Beirut on February 16, 2023. (AFP)
The country’s chronic instability has deepened in recent years in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as the 2020 Beirut port explosion which killed hundreds, left hundreds of thousands homeless, and damaged over half of the city while inflicting massive economic losses.
Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International, the two international organizations which campaign against injustice and inequality, have called the investigation into the blast a “farce.”
Shehadi asserts that despite Lebanon’s historically “very healthy and functioning judiciary,” Hezbollah has interfered with the investigation.
This series of disasters have pushed many Lebanese to call for the removal of the entire political class, something that Shehadi views as a “ridiculous demand.”
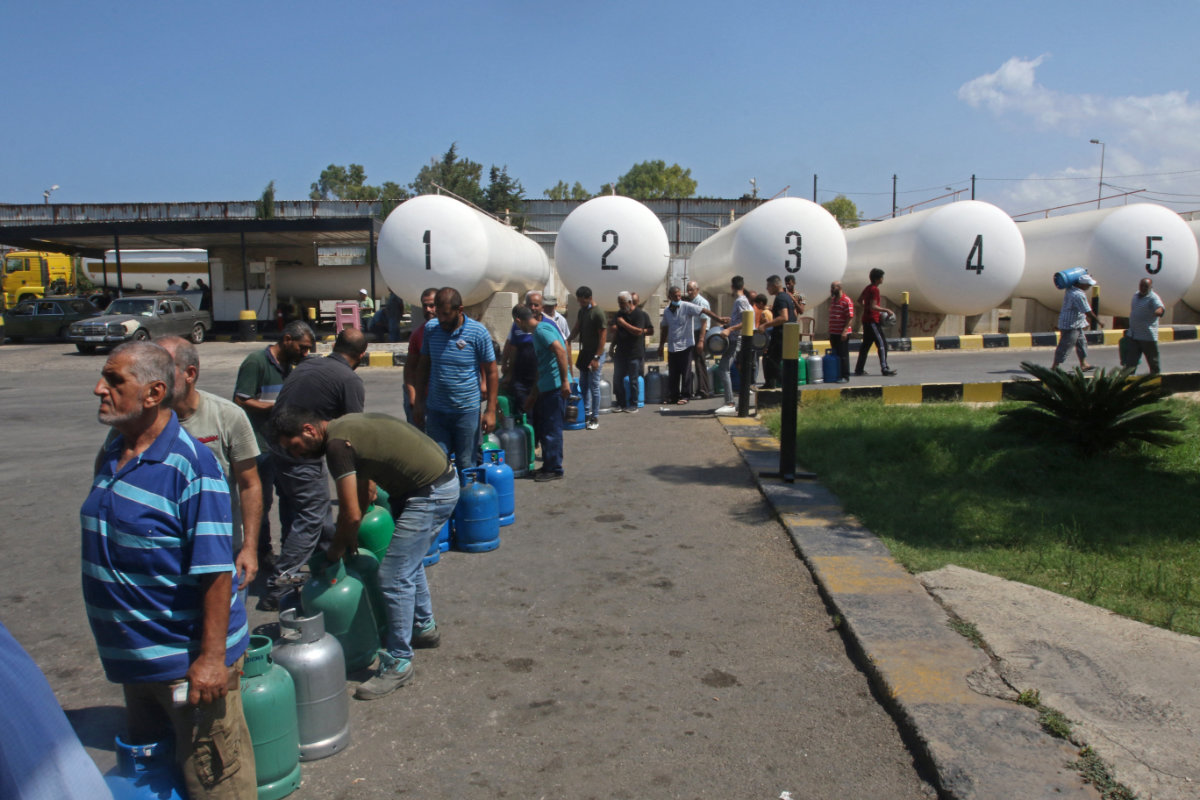

Lebanese wait to fill their gas cylinders in the southern city of Sidon amidst a deepening economic crisis, on August 10, 2021. (AFP)
In his opinion, Lebanon’s political system is not “sectarianism,” as some observers term it, but rather “a political system based on a social contract between communities and which has maintained the country … even before the state was created.”
“We have a banking system which was the banking center of the region. We have political parties. These are pillars that distinguish Lebanon … and the revolution is asking almost for the dismantlement of all these pillars,” he told Katie Jensen, the host of “Frankly Speaking.”
While Shehadi acknowledges there are definitely issues with Lebanon’s political class, which he says was compromised by 15 years of occupation and political infiltration by the Syrian regime, “this doesn’t justify calling for the abolition of the whole system.”
Eight months after the country’s general elections, Lebanon still has not reached a consensus regarding its president or a functioning parliament.
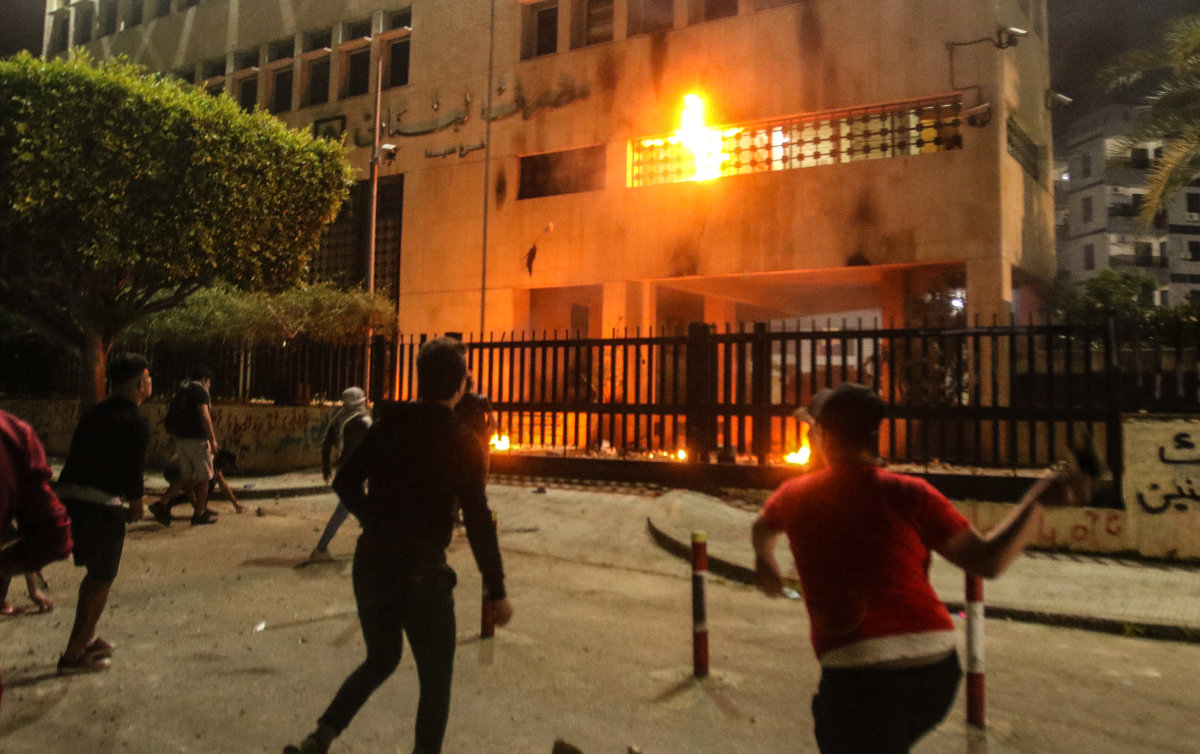

Lebanese protesters gather to protest against tax increases and official corruption outside the Sidon branch of Lebanese Central Bank in southern city on November 30, 2019. (AFP)
Urgent political reforms are needed to unlock the $3 billion in emergency funds from the International Monetary Fund, but with Lebanon’s political system in tatters and its parliamentarians regularly staging walkouts, accessing these funds seems unlikely.
Shehadi said that while he is not opposed to a “fragmented” parliament with diverse political opinions, “what we have is not a fragmented parliament. What we have is a paralysis of all institutions that’s been building up for 15 years, 17 years almost.”
He added that Lebanon and its institutions are “a hostage to the veto power” of Hezbollah, which has gained footholds in Lebanon by means of assassinations and building of political alliances.
Shehadi compares Hezbollah’s gradual infiltration of state institutions in Lebanon to the behavior of drug cartels in power in narco-states in Latin America.

Hezbollah supporters attend a televised speech by the group's leader Hassan Nasrallah in Beirut's southern suburbs on January 3, 2023. (AFP)
“They bribe politicians, the judiciary, the police, the army. Those who cannot be co-opted, if you like, are probably dead, and those who can be framed or blackmailed — that’s how criminal organizations gain power in a country,” he said.
The Lebanese parliament has held eleven electoral sessions to elect the president since Sept. 29 last year, with every session failing to elect a candidate.
In recent days, Joseph Aoun, commander of the Lebanese Armed Forces, has emerged as a potential contender. However, this would require a constitutional amendment, and consensus from the parliament, which is currently headed by Speaker Nabih Berri.
Though he calls Berri “a brilliant operator” who is familiar with the ins and outs of Lebanon’s tangled political web, Shehadi says Berri is “also a hostage himself.”
Berri is the leader of the Amal Movement, which engaged in a years-long war with Hezbollah in the 1980s which saw thousands killed.
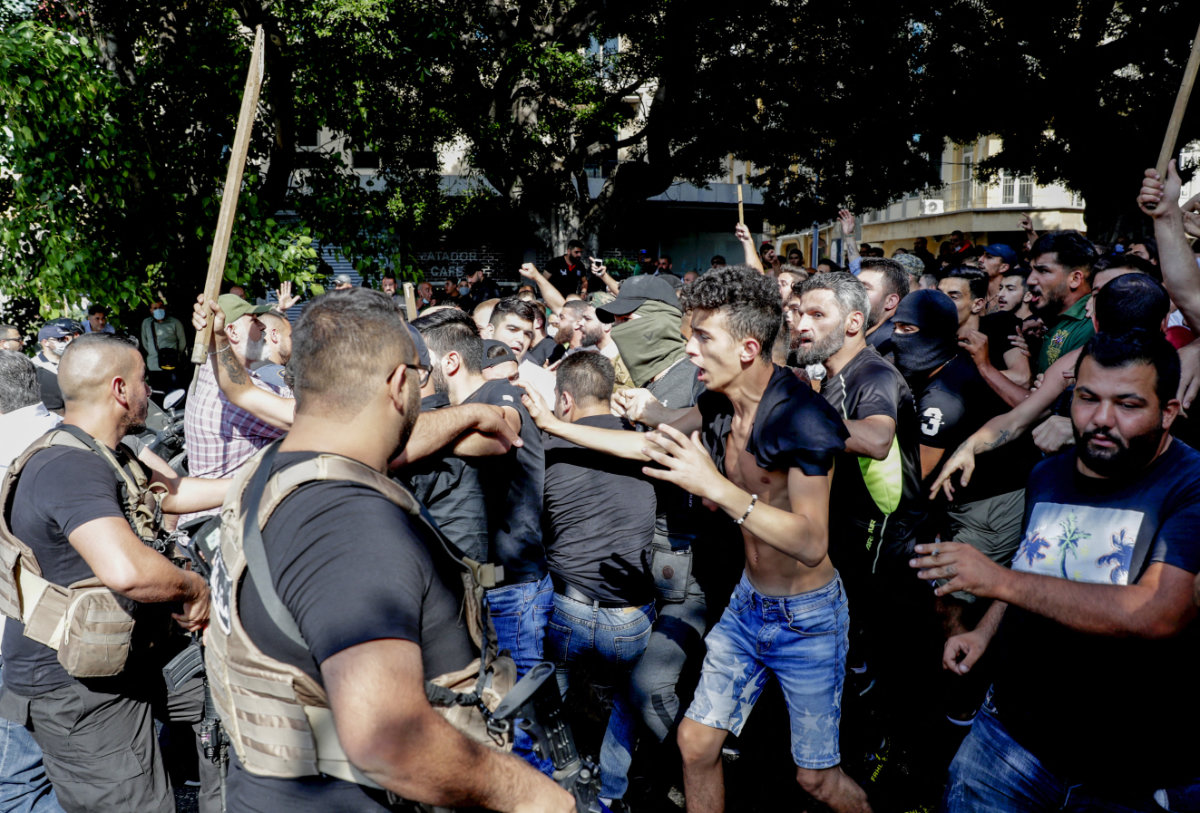

In this photo taken on June 6, 2020, Lebanese troops block supporters of the Lebanese Shiite movements Hezbollah and Amal trying to crash through a rally in Beirut decrying the collapse of the economy. (AFP)
“It ended with an agreement between them, sponsored by Iran and Syria, whereby they basically formed one block in parliament and one list, which means they have the monopoly of Shiite representation. They do not have a monopoly of Shiite support, but they have the monopoly of Shiite representation because of the way they manipulate lists in their areas,” Shehadi said.
During multiple electoral sessions stretching from September 2022 to January this year, many MPs left their ballot papers blank, with some in early sessions even casting their votes for “For Lebanon,” “Righteous dictator,” and “Nobody.”
Shehadi explained that major decisions and appointments within the Lebanese administration must be made by consensus, and with the signature of the president, speaker of the parliament, and prime minister. In the midst of the current political power vacuum, this means that the government in Lebanon has all but ceased to function.
“We had that for 29 months, without a president, without a parliament, and without a functioning government … we had a caretaker government, until our politicians, if you like, compromised and accepted to elect the favorite candidate of Hezbollah. So, we are in the same position, and it’s a difficult position because the longer we resist, the more damage there is, and I think our economic collapse is mainly caused by paralysis,” Shehadi said.
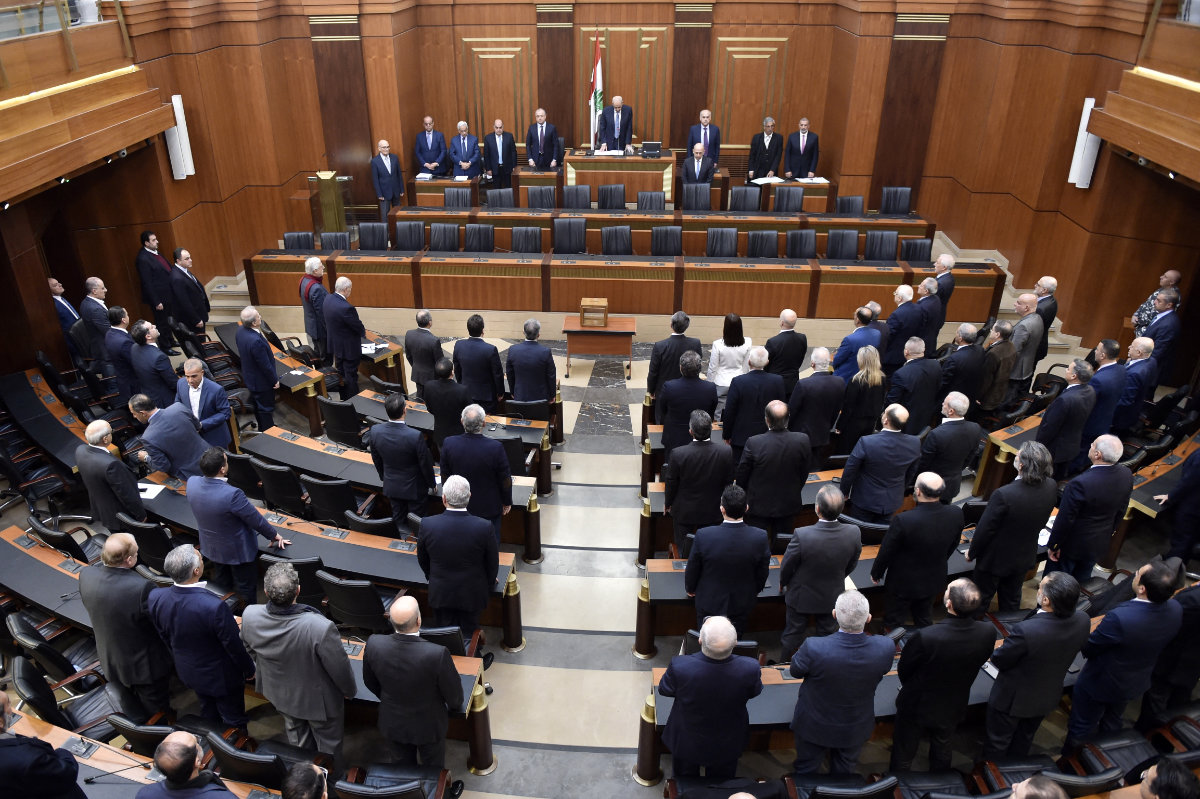

A January 19, 2023, photo shows Lebanon's Parliament convening to elect a new president. Because of sectarian divisions, the election failed. (AFP file)
“The priority now is to have a president and a functioning parliament and a functioning government so that state institutions do not collapse further.”
Shehadi added that though there is no shortage of credible candidates, the parliament is “held hostage, and the whole system is held hostage because you need a certain majority to start the process of elections. You need a two-thirds plus one majority, which means that one-third of parliament can spoil the process.”
Even if this litany of political challenges were overcome and Lebanon managed to receive assistance from the IMF, Shehadi said that IMF funds would not be a solution to all of Lebanon’s financial problems. However, he stressed that “engagement with the IMF is crucial.”
“Following the IMF recommendations is very important, especially on fiscal and monetary policy. There’s a lot of opposition to some of the IMF reforms, which I understand,” he said, adding that many observers say that $3 billion in funds will do very little to alleviate the country’s $90 billion deficit.
“But I think, in my view, it’s more important to remain engaged. The country is being paralyzed and isolated from the West, from the Arab countries, and now will be isolated from international institutions too, like the IMF and the World Bank and the UN and all that. It’s very damaging to ignore the IMF route.”

Nadim Shehadi speaks to Frankly Speaking host Katie Jensen. (Supplied)
Shehadi concurs with the World Bank’s assessment of the meltdown in Lebanon as one of the worst modern crises in recent history. But asked if he thinks there is a way out of the quagmire, he replied: “Yes, but I don’t see it only for Lebanon. The whole region is suffering from the same problem. The Lebanese case is similar to what is happening in Palestine, in Syria, in Iraq, in Yemen, and this could spread to other countries in the region who could be vulnerable.”
He continued: “It should be treated as a regional phenomenon, which is, basically, the role of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. The IRGC, as a paramilitary, non-state actor, has taken over the Iranian state and society in the same way as Hezbollah is acting in Lebanon, in the same way as Iranian-sponsored militias are behaving in Iraq, and definitely in the same way as Hamas has paralyzed the whole of the peace process in Palestine.”
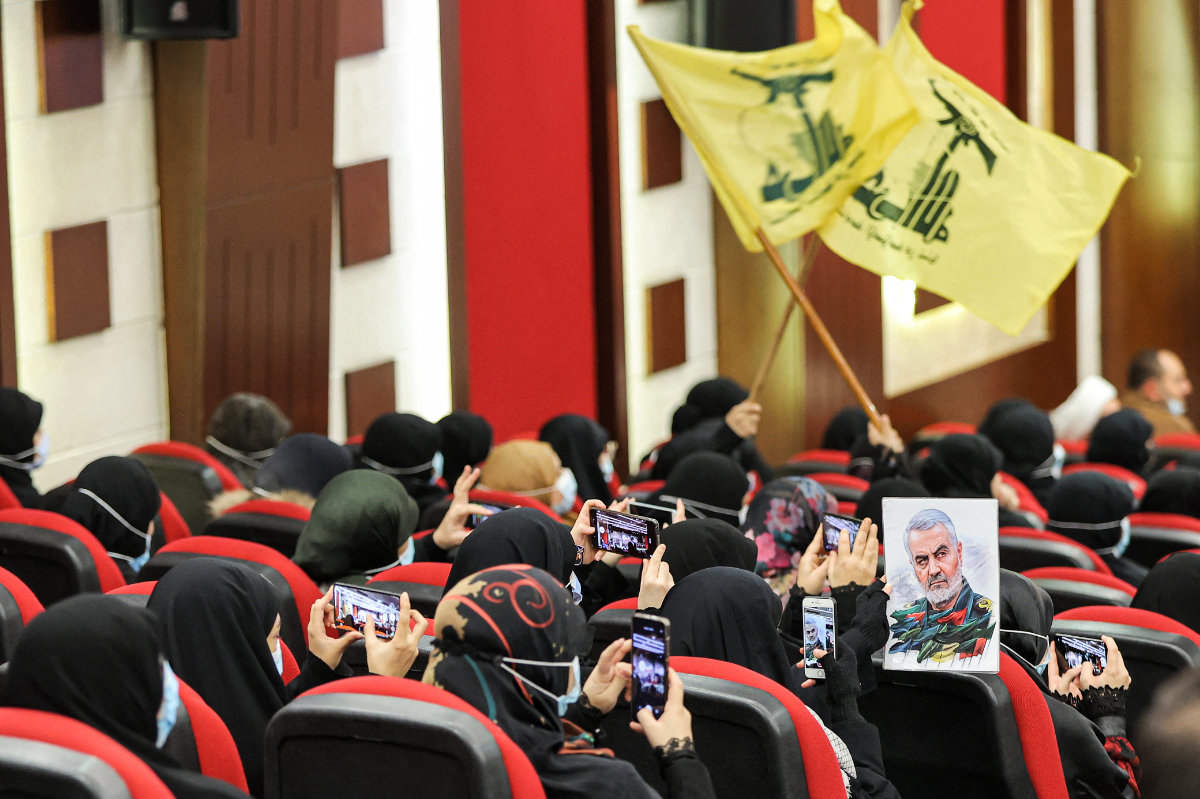

Hezbollah supporters attend a memorial service in Beirut for Qasem Soleimani, the slain top commander of the Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps. (AFP file)
Under the circumstances, Shehadi said the multidimensional crisis in Lebanon is part of a “broader regional problem, which needs to be treated as such. Lebanon is the fault line or the weakest point. A lot of the region’s ills, or problems, surface in Lebanon first.”
Because of this, Shehadi added, international and regional engagement and cooperation are crucial components to solving Lebanon’s crisis, and that the international community must refrain from seeing Lebanon as a hopeless case.
“We are definitely hostages, but we still have a say in the country and we need international support to get out of the grip of (Hezbollah). And again, the grip is regional. So, our fate is similar to Iraq, similar to Palestine, similar to Syria, and similar to Yemen,” he said.
“I don’t think one can see it in a fragmented way. And it’s wrong to abandon a place just because it’s considered to be lost. Lebanon is not a lost case.”


























