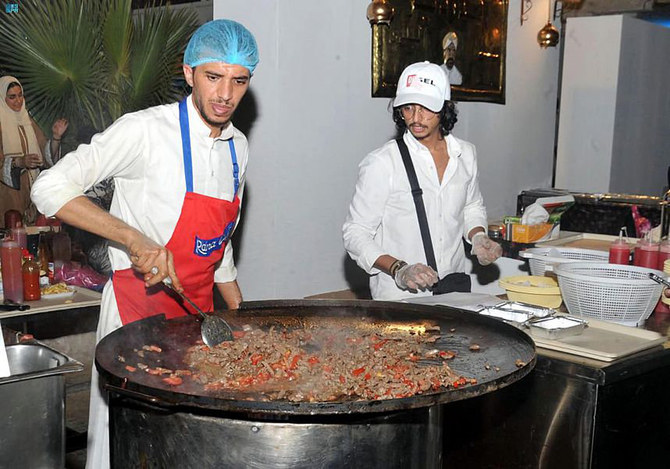
JEDDAH: For centuries, Muslims across the world have shared common traditions during the holy month of Ramadan stemming from Islamic practices, such as breaking their daylight fast with dates, water or laban, as was the Prophet Muhammad’s custom.
However, some local traditions, which are distinct to a particular nation or region, have found their way into the routines, feasts and celebrations that mark the holy month. Saudi Arabia, with its many diverse regions, is no different.
Every year, in the ninth month of the Islamic Hijri calendar, the Kingdom’s 13 regions, its hundreds of towns and cities, and more rural reaches will revive their own unique and beloved local habits and practices.
In the big cities, the streets are regularly packed with pedestrians and vehicles as shoppers race to make last-minute purchases, while devout worshippers find space amid the bustle for regular prayer and to read from the holy Qur’an.
Togetherness is an important theme of Ramadan, with families, friends and often whole communities gathering at long tables to share in the iftar feast each day after sunset in homes decorated with twinkling lights and lanterns.
The dishes served at these gatherings, and when important feasts take place, are often distinct to a particular local culinary culture and the availability of particular ingredients.
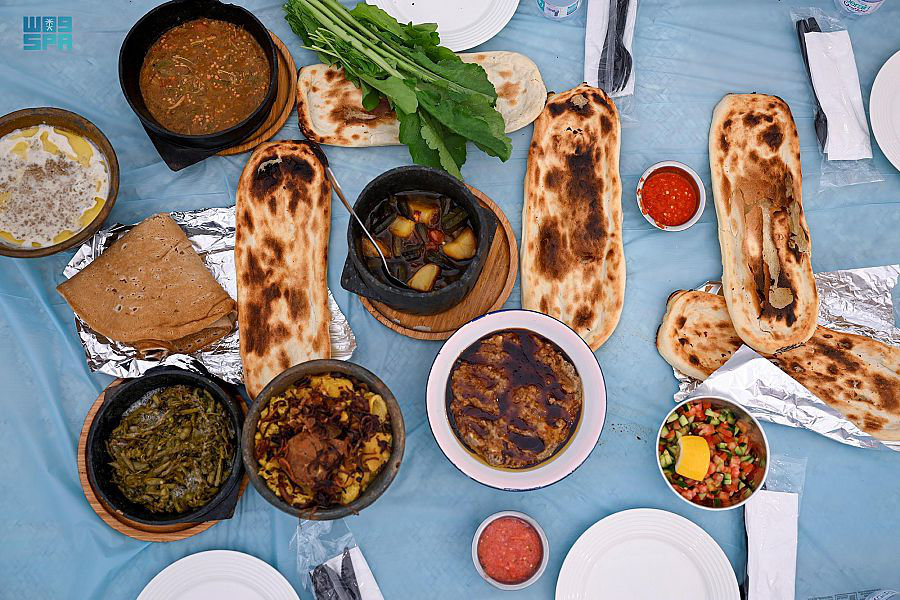

Traditional dishes at a southern table. (Supplied)
In Saudi Arabia’s Eastern Province, many members of the community will meet before Ramadan to share a last meal of familiar dishes that are uncommon during the holy month. The “ghabgah” is usually held on the night preceding Ramadan or a few days before.
During the month, the region’s popular dishes include balaleet (sweet vermicelli and eggs), asida (lump of dough made by stirring wheat flour into boiling water, sometimes with added butter or honey), samosas, and sago pudding.
Around the middle of the holy month in the Eastern Province and other parts of the Gulf region, children will dress in traditional clothing and go door-to-door in their neighborhood, singing songs in exchange for nuts and candy, in a tradition known as “gergean” or “knocking.”
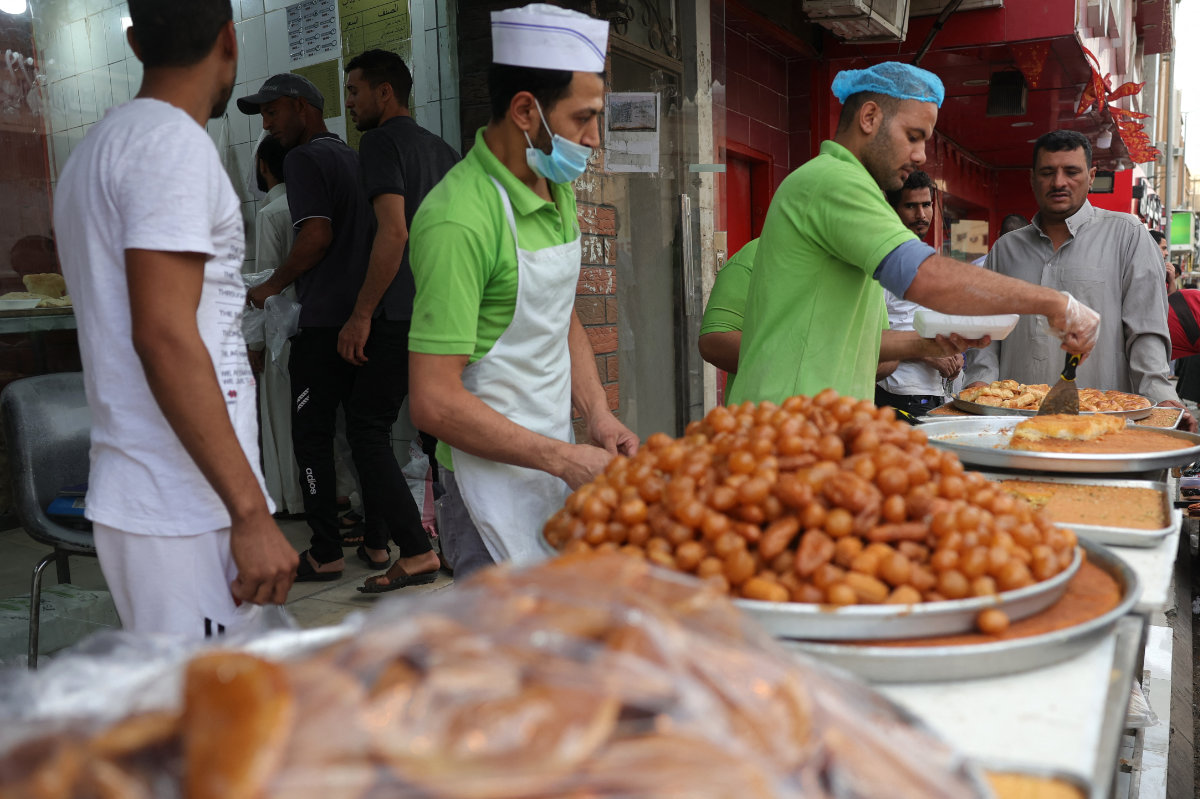

A shopkeeper prepares an order for traditional sweets for a customer in the capital Riyadh on March 27, 2023, during the Muslim fasting month of Ramadan. (AFP)
On the far side of the peninsula, in the western region of Hijaz, the dish exchange tradition is still alive today. “Al-to’ma” is a year-round custom where a plate is never returned empty. Everything from soups and samosas to traditional dessert delicacies such as qatayef, basboosa, or sago pudding is exchanged.
Many families also share subya, a drink made especially in Ramadan to quench one’s thirst, made from barley or bread soaked overnight with spices such as cinnamon, cardamom, sugar and raisins, to give it its distinctive red color.
“It’s a family’s best kept secret,” Umm Khalid Mashady, a resident of Madinah, told Arab News.
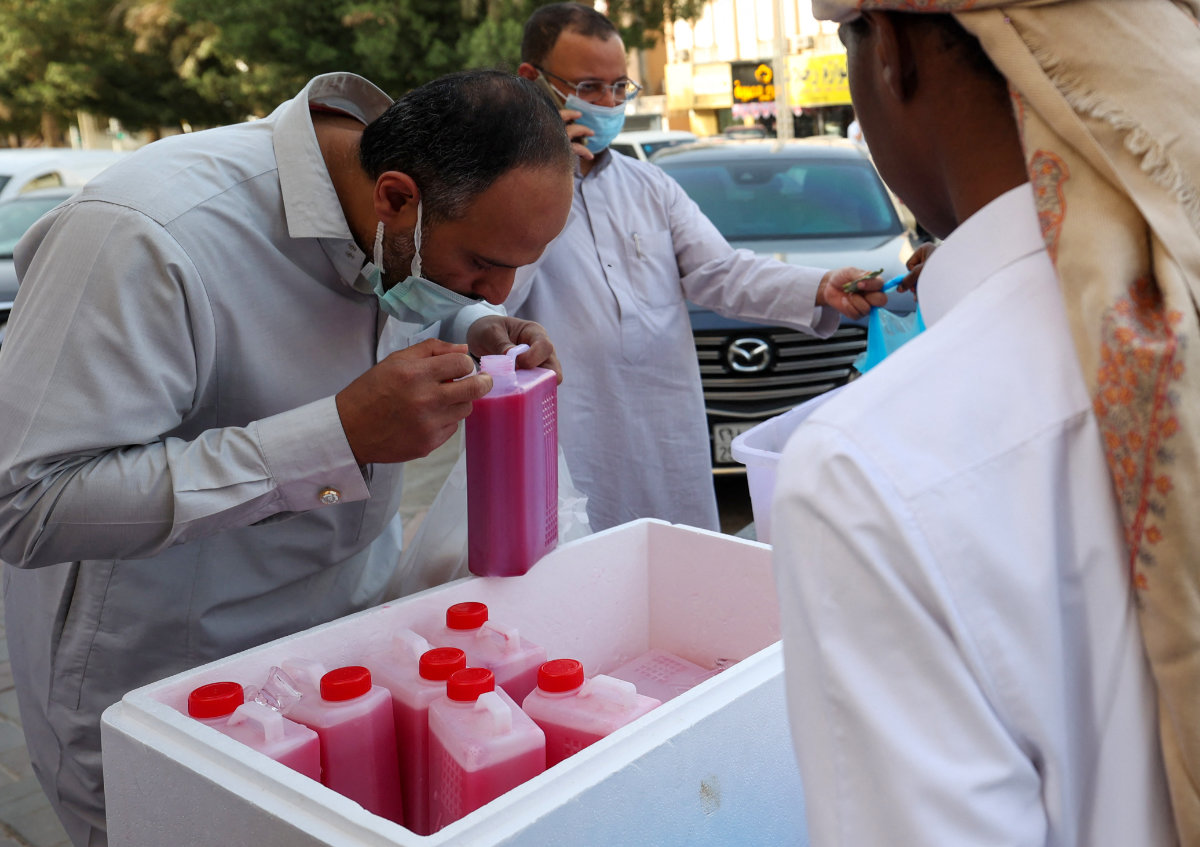

Saudi men shop for traditional beverages during the holy Muslim month of Ramadan in Riyadh. (AFP file)
“My husband takes pride in making the drink every year, and we share it with our neighbors, even those who moved away because that was the way back then. Many people prefer to buy it from stores today, but you’ll still find them following their family recipes.”
Mashady highlights the importance of family during Ramadan gatherings. “A Hijazi table is never without extra family involved,” she said.
“The calm before breaking our fast is common as every household is busy conducting their prayers or reading the holy book in the last hour before sunset, the golden hour. By doing so, even children pick up the habit and grow accustomed to it and will thus pass it down to their children after that.”
Foul (fava beans cooked to a mash) accompanied by tamees (a traditional bread baked in a tandoor) are also two popular staples on a Hijazi table that go hand in hand.
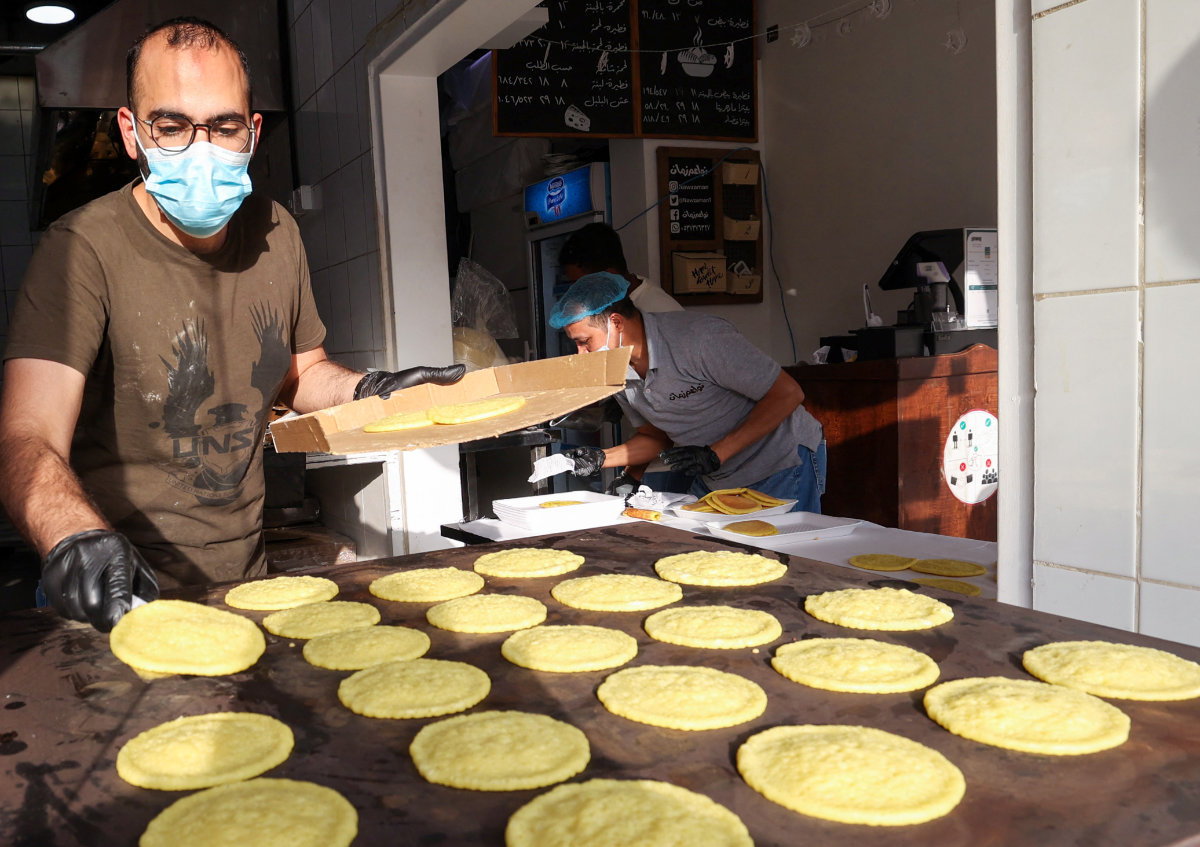

Workers preparing the traditional "Qatayef" sweets, a folded pancake filled with cream or nuts, at a shop in Riyadh. (AFP file photo)
Also common on Saudi dinner tables during Ramadan are dates of all shapes and colors, oats soup, meat and cheese samosas, luqaimat (fried dough), Vimto drink, and kunafa.
These gatherings are about more than just food, however. Games and other family activities are also important traditions. A carrom board, a tradition brought to the Kingdom decades ago from India, is often brought out after the meal and Taraweeh prayers, while others prefer to kick around a soccer ball.
Today, many young men and women like to gather after evening prayers to play baloot, a popular card game in the region, similar to the French Belote.
FASTFACTS
This Ramadan the Grand Mosque in Makkah has launched a welcome initiative for pilgrims and Umrah visitors arriving in Saudi Arabia.
The Grand Mosque has 120 areas for prayer and 12,000 containers of Zamzam water to help ensure a comfortable visit for pilgrims.
Souqs in Saudi Arabia are the best place to buy Ramadan essentials and to experience the hustle and bustle of the holy month.
Al-Balad is Jeddah’s oldest neighborhood, founded in the 7th century A.D., and is home to a plethora of some of the oldest traditional markets.
In the Kingdom’s central region, many male members of Najd families typically break their fast at their local mosque, where they arrive bearing dishes from home.
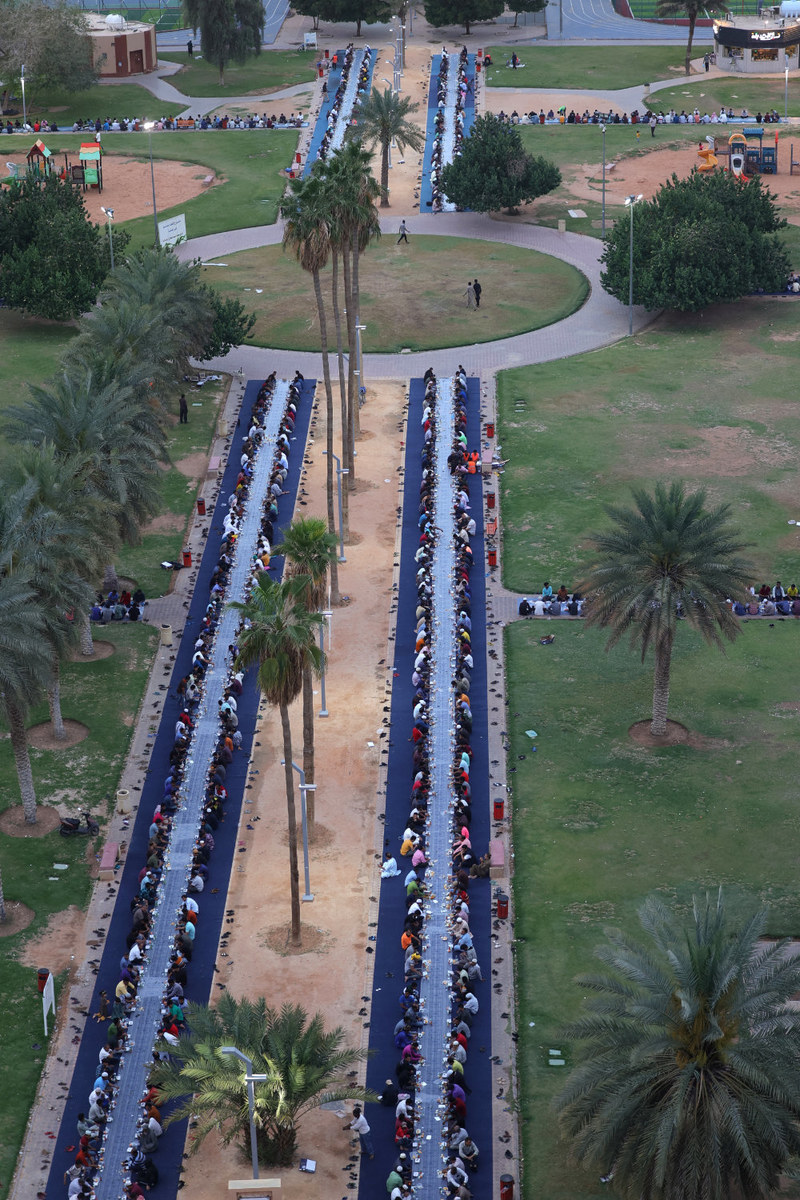

Foreign workers their fast during the Muslim fasting month of Ramadan at a park in Riyadh on March 27, 2023. (AFP)
The tradition is believed to have stemmed from the area’s remoteness and harsh environment, where lower-income families found it difficult to provide for their families.
More privileged families shared their meals and distributed them to the needy as part of the holy month’s custom of helping the underprivileged.
Though it might seem slightly different today, many believe that once people sit at the table together, it does not matter what social class they belong to because they are all equal.
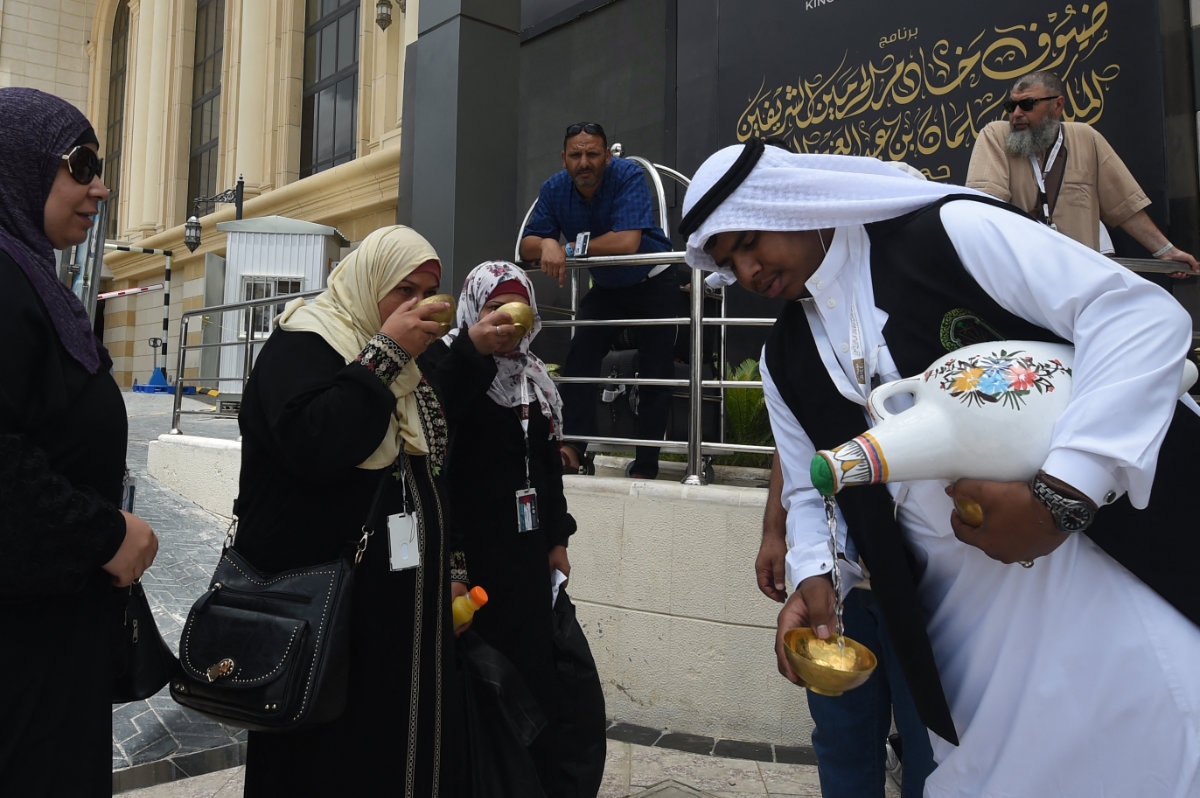

A Saudi man offers Muslim pilgrims Zamzam water upon their arrival in the holy city of Makkah. (AFP file)
“It didn’t matter which family or clan you belonged to. The month brings forth its blessings and we share them with our family and others,” Umm Waleed, 72, a resident of Riyadh and native of Hail, told Arab News.
“Our grandmother taught us that in order to be blessed, we had to share. It does not matter where you are. Our Islamic teachings meshed with our local traditions (have) became an essential part of our community.”
Turning to the northern region, an area close to the border with Iraq and Jordan, many households share traditions with their neighbors, focusing on large gatherings of family and friends with children serving their elders throughout the evening.
Like subya in Hijaz, camel’s milk is a staple ingredient in several of the region’s dishes, such as tarshreeb (pieces of bread soaked in stock and meat), jareesh, al-mlehiya and thareed.
ALSO READ: Makkah’s historic Ramadan cannon remembered 8 years on
Moving toward the southwestern region of the Kingdom, many families have maintained the tradition of breaking their fast at mosques and only have proper meals after evening prayers once they have returned home.
A rifle round is traditionally fired to announce the call of Maghrib prayer in the areas high in the Asir mountains.
Across Saudi Arabia, Ramadan’s Islamic traditions complement local cultures and customs as the close-knit Saudi community prides itself in honoring old ways of celebration and incorporating new ones that fit well into an ever-evolving society.


































