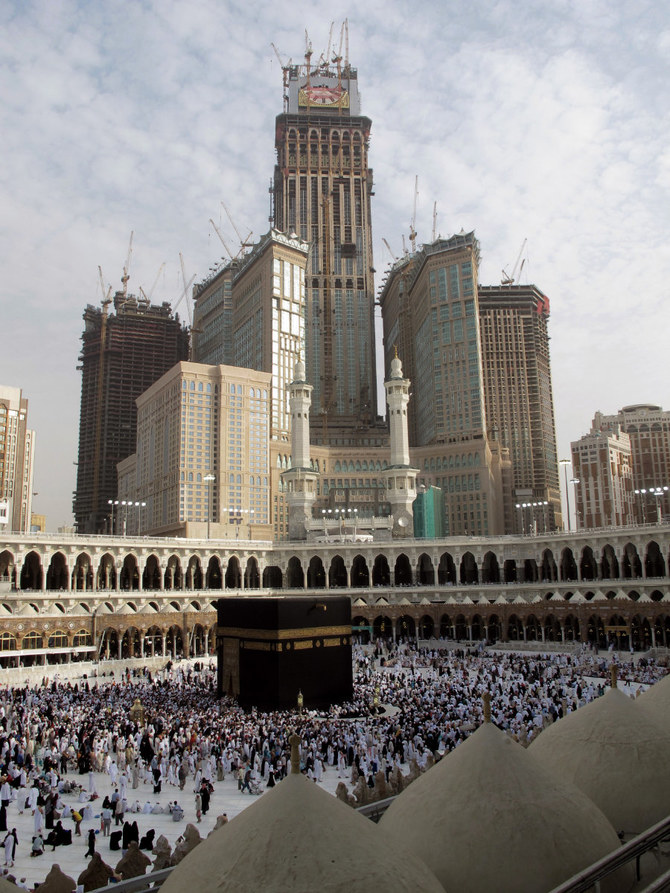
MAKKAH: For centuries, the Two Holy Mosques at Makkah and Madinah have welcomed pilgrims from across the world. To the pleasant surprise of visitors, the glistening white marble floor that surrounds the Kaaba in Makkah remains cool beneath their feet, even during the hottest days.
While some have claimed that hidden cold-water pipes under the floor are responsible for its coolness, the real reason lies in the mosque’s unique choice of building material.
Marble from Thassos, an eastern Greek island near Kavala in the Aegean Sea, has one of the rarest characteristics ever found in the stone. Due to its pure white appearance and high reflection of light, Thassos marble — sometimes called “snow white” marble — has one of the lowest heat absorbances of any marble.
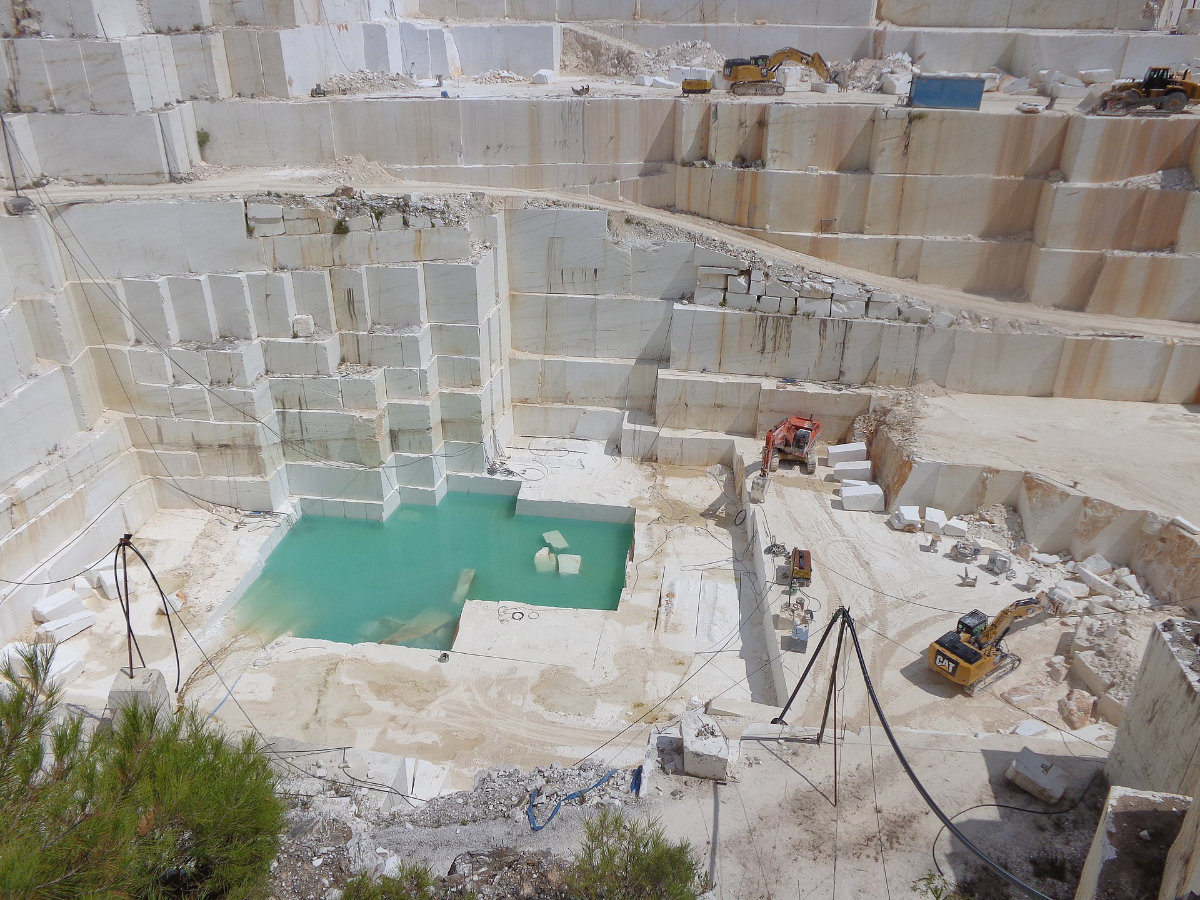

Marble quarry on Thasos island, northern Greece. (Dr Peter Tzeferis via Wikimedia Commons)
The stone has been quarried from the island since ancient times, and is still used all over Greece today. It has formed the walls, floors, and statues of some of history’s greatest sites, including the ancient Macedonian tomb at Amphipolis (the largest ever discovered in Greece) and Hagia Sophia in Istanbul.
The stone’s unique properties see its frequent use in luxury villas and interior decoration, though it does not come cheap. Individual tiles can range between $250 and $400 per square meter, according to Indian marble supplier RMS Marble.
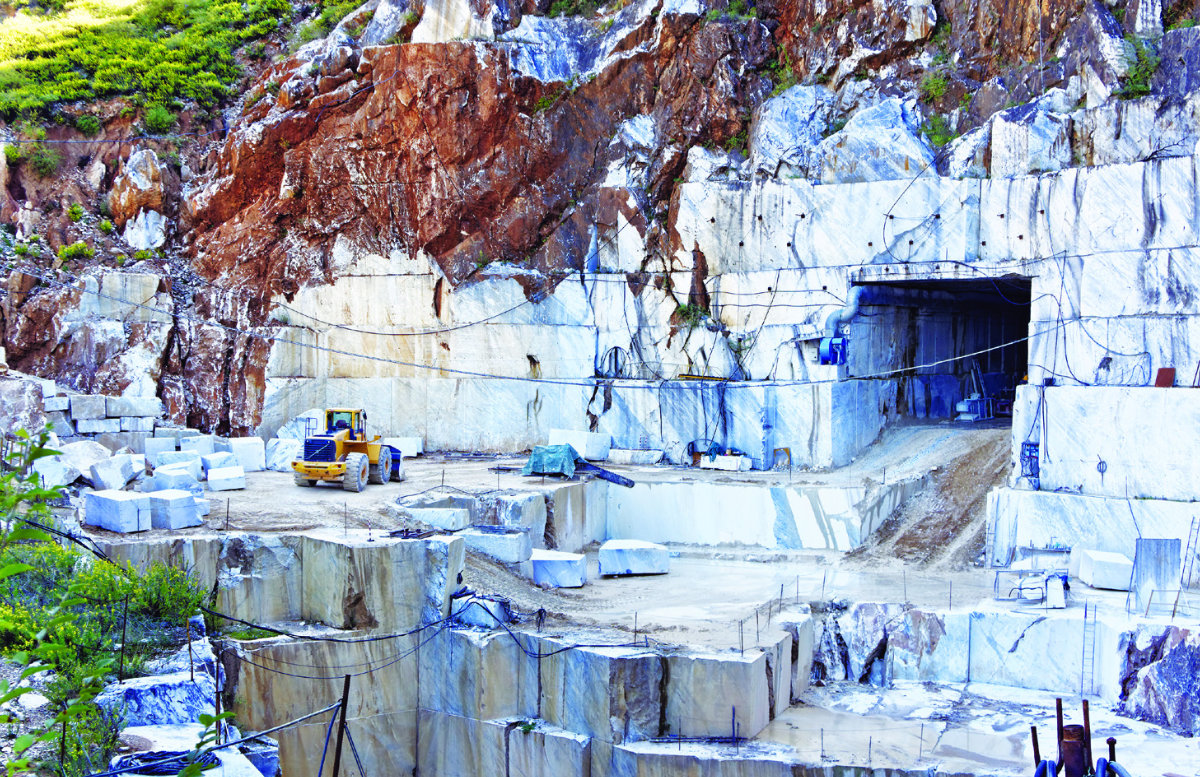

Marble mined at a quarry in Thassos, Greece, is one of its most impressive features of the floor of the Grand Mosque in Makkah. (Shutterstock)
For decades, Saudi Arabia has imported the unique dolomitic marble for exclusive use at the Two Holy Mosques to provide relief and avoid unsafe surface temperatures, as mosque visitors are required to enter barefoot.
Undersecretary-general for technical, operational, and maintenance affairs at the General Presidency for the Affairs of the Two Holy Mosques, Eng. Fares Al-Saedi, told Arab News that Thassos marble is characterized by its extreme coldness, despite intense heat that may reach 50-55 C in the summer months.

Pilgrims use umbrellas to protect themselves from the extreme hear during summer, but on the marble floor they need no protection. (AFP file)
Al-Saedi added that the Kingdom’s leadership decided to import the self-cooling stone for the construction of wide yards and open spaces where millions of pilgrims pass annually.
Al-Saedi explained that the General Presidency supervises marble maintenance work across the area by treating, restoring, and then polishing the marble or replacing old and unusable tiles.
“Maintenance is carried out 24/7 by over 40 engineers and technicians … each marble slab is five centimeters thick, and what makes it stand out is its ability to absorb moisture through its delicate pores during the night and release that moisture during the day, making it cooler under high temperatures,” he said.
According to a study published in the international journal Construction and Building Materials in 2021, the thermophysical features of the stone both reflect and dissipate solar insolation heat.
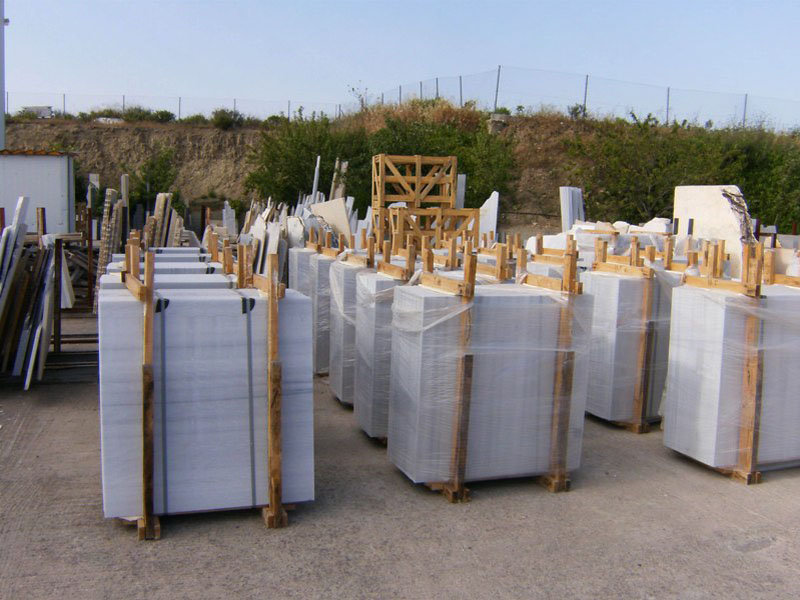

Crates of high quality marbles from Thassos ready for shipping. (Courtesy of Thassosmarbles)
The study found that Thassos marble has an uncommonly high level of high solar reflectance and a high rate of thermal conductivity relative to limestone, another stone commonly used in Islamic architecture.
Collectively, these properties have proven to be capable of sustaining cool surface temperatures even during hot summer periods, and provide an overall reduction in night-time convective shedding of thermal energy into the overlying atmosphere.
At the same time, the marble adds to the mosques’ artistic ambiance, which provides an exceptionally memorable experience.
Another study carried out by a joint Saudi-Egyptian team and published in the Arabian Journal of Geosciences in 2018 referred to the marble as “heat-dissipating smart marble,” attributing its high whiteness purity to the stone’s dolomite-rich crystal formation.
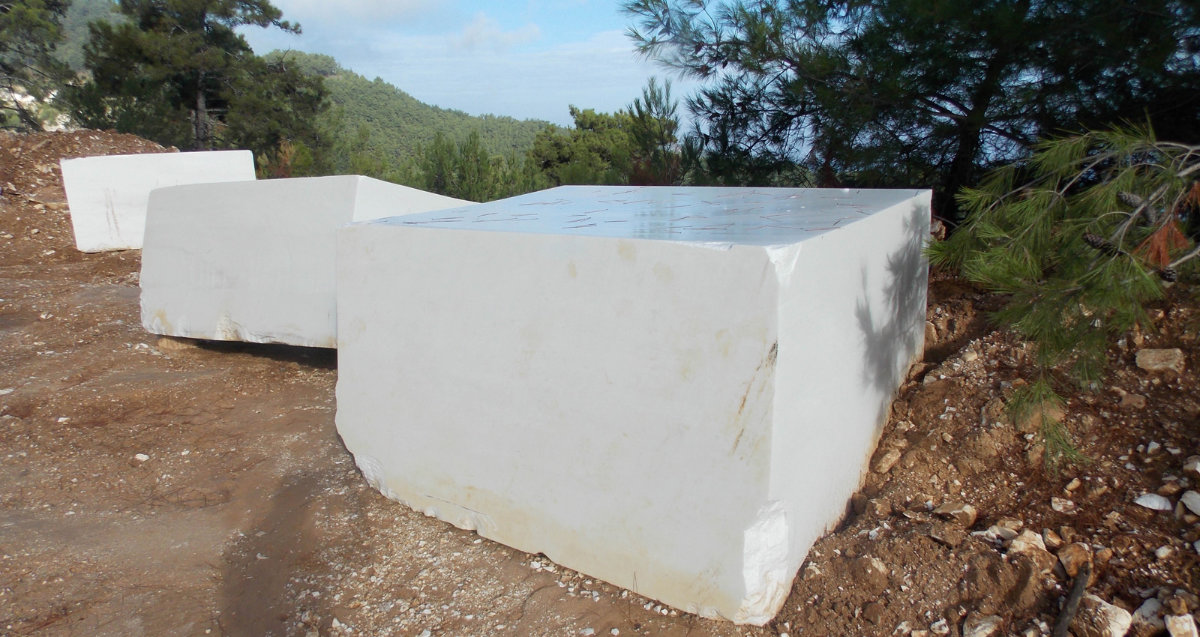

White marble blocks ready for slicing. (Courtesy of Thassosmarbles)
Writer and heritage researcher Abdullah Al-Batati told Arab News that the unroofed and paved stone floor of the mataf (the place where pilgrims circumambulate the Kaaba) was slightly curved and filled with pebbles and stones smaller than the size of a bean before the pavement.
“Omar Ibn Al-Khattab was the first to stone the Mosque’s floor after the expansion of the mataf in 119 AH (737-738 AD); during the reign of Al-Walid bin Abdul-Malik, the mataf was covered in marble. In 145 AH (762-763 AD), the old floor was covered in marble in the era of Abu Jaafar Al-Mansour, and was tiled with marble in the era of Abbasid Caliphate in 284 AH (896-897 AD),” said Al-Batati.
“In 1003 AH (1594-1595 AD), flint stones were replaced with alabaster stones, while white bright marble covered the mataf’s floor in 1006 AH (1597-1598 AD) during the reign of Sultan Mohammad Khan. In 1344 AH (1925-1926 AD).”
He noted that during the reign of King Saud, the old marble tiles were removed from the old mataf, and the new mataf was leveled and paved. The two were separated by a dividing line of black marble which was brought in from several quarries across Saudi Arabia.

Undated view of the Holy Kaaba at the Makkah Grand Mosque crowded with pilgrims. (AN file)
Dr. Salma Hawsawi, professor of ancient history at King Saud University, told Arab News that King Abdulaziz carried out expansions at the Grand Mosque and the Prophet’s Mosque, which lasted until King Khalid’s reign in the 1970s and 1980s. The latter issued an order to expand the Grand Mosque in its current form and tile its floor with heat-resistant marble imported from Greece in 1978.
King Khalid ordered the tiling of Makkah’s Holy Mosque using heat-resistant white marble to level the site and remove pebble stones so that the mataf could comfortably accommodate the increasing number of worshippers and pilgrims.
“The second expansion of the Grand Mosque occurred between 1985 and 1986 during King Fahd’s reign, who also ordered the tiling of the courtyard around the Kaaba and the squares surrounding the Grand Mosque using cold white marble in a circular and lined manner, making it suitable for prayers,” Hawsawi told Arab News.
In continuation of past expansion projects, King Salman continued developing the services of the two Holy Mosques, as he ordered the completion of the third expansion, in addition to developing many projects, according to Hawsawi.

Cranes are seen in the background at construction sites behind Makkah's Grand Mosque on December 4, 2008 as Muslims from all over the world flocked to Saudi Arabia to perform the annual Hajj pilgrimage. (AFP file)
Hawsawi stated that the marble is imported from Thassos in the form of large blocks of stone, which are then processed and manufactured in the Kingdom’s factories by the Binladen Group, a leading contracting company supervising the construction and development of Makkah’s mosques.
“Engineers and technicians carry out regular inspection visits and maintenance works with high proficiency, and marble tiles that are no longer in good condition and have lost their coolness characteristics are replaced with new ones. The type of marble is natural, and neither the Kingdom nor Greece inserts any additives, nor does it have any impurities.
“This type of marble is rare and expensive; a single marble piece is five centimeters thick, 120 centimeters long and 60 centimeters wide. It absorbs moisture and cold at night through its pores to preserve them during the day. Thus, the surfaces of the Grand Mosque remain moderately cool all year long and for everyone to enjoy,” Hawsawi said.