LONDON: In the past two weeks the world has become used to seeing photographs of Sudan’s Gen. Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan, whose forces have been locked in combat with the rival paramilitary Rapid Support Forces since April 15, dressed in battle fatigues.
On January 26, however, the country’s de-facto ruler was wearing a dark suit, blue tie, and a broad smile, in full-on red-carpet diplomat mode as he greeted Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed on the runway at Khartoum airport.
It was Abiy’s first visit to Ethiopia’s northern neighbor since the 2021 coup, led by Al-Burhan, that saw the derailing of the transition to civilian rule promised in the wake of the overthrow of the 30-year regime of dictator President Omar Al-Bashir in 2019.
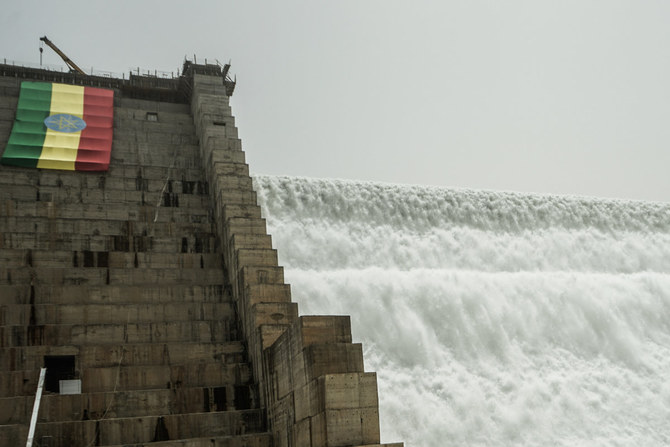
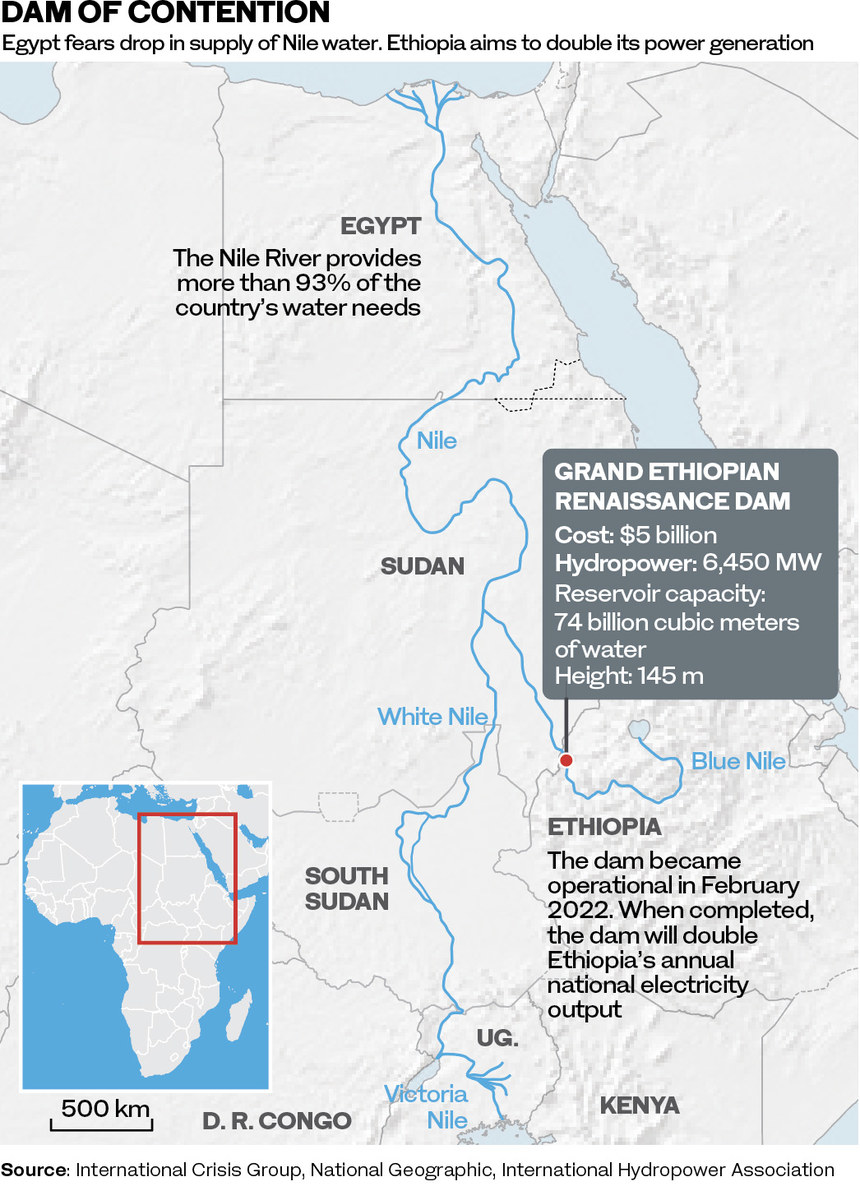
The two men had much to talk about, but top of the agenda for Abiy was winning Sudan’s support for the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, the vast $4 billion hydroelectric project on the Blue Nile, just kilometres from Sudan’s border, that has proved controversial in the region ever since work began on it more than a decade ago.
The GERD is now 90 percent complete, and the coming rainy season will see an estimated 17 billion cubic meters of water retained in the fourth filling of the massive reservoir created by the dam.
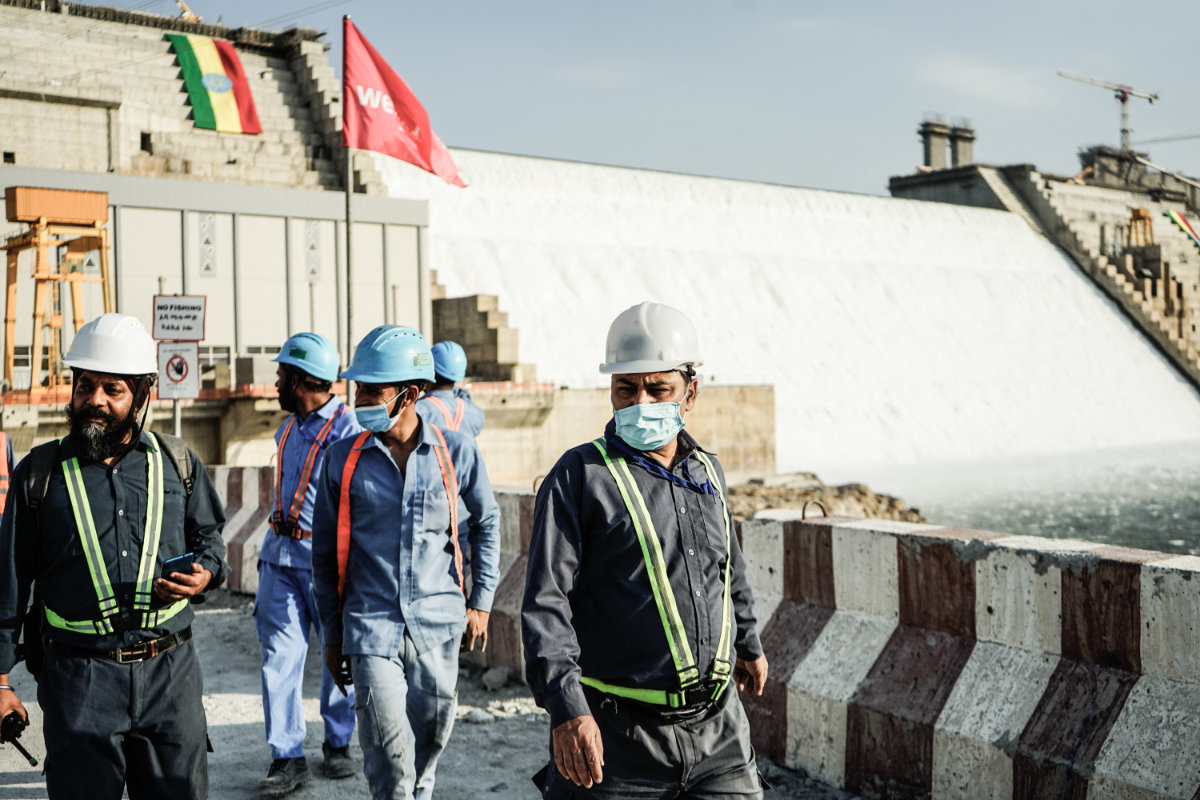

Workers are seen walking at the site of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam in Guba, Ethiopia, on February 19, 2022. (AFP file)
For millions of Ethiopians, half of whom have no electricity and still rely on burning wood for heat, cooking, and light, the dam is a symbol of hope, pride, and a brighter future. At a ceremony on the imposing dam in February last year, Abiy ceremoniously activated the first of its turbines, which began generating power.
When it reaches full capacity and all 13 turbines are feeding into the national power grid, the dam will boost Ethiopia’s industrialization, revolutionize the living standards of millions of its citizens, and earn the country badly needed income as an exporter of power to the region.
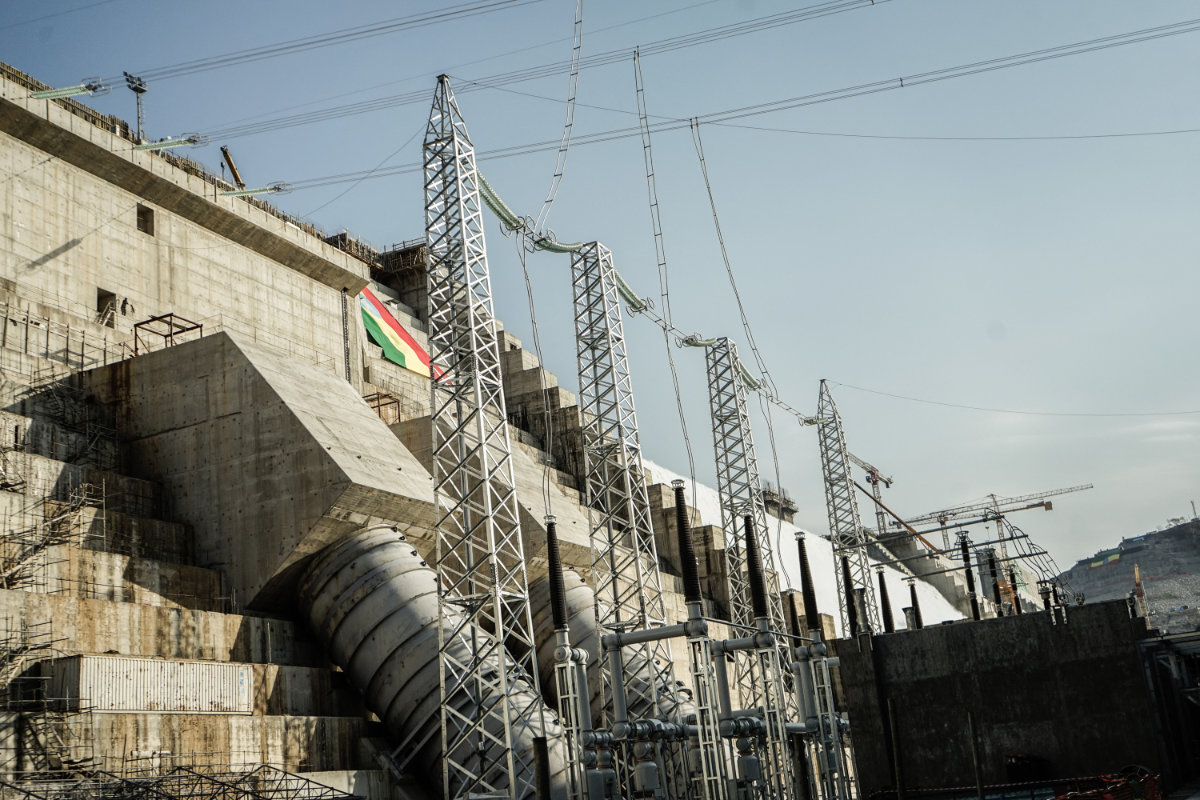

Ethiopia's massive hydro-electric dam project began producing electricity last year after more than a decade since construction work first started. (AFP)
Speaking at the 2022 ceremony, Abiy said: “From now on, there will be nothing that will stop Ethiopia. (The dam) will not disrupt the River Nile’s natural flow.” He noted that the start of electricity generation demonstrated “Ethiopia’s friendly attitude toward the river.”
The project was, he added, “excellent news for our continent and the downstream countries with whom we hope to collaborate.”
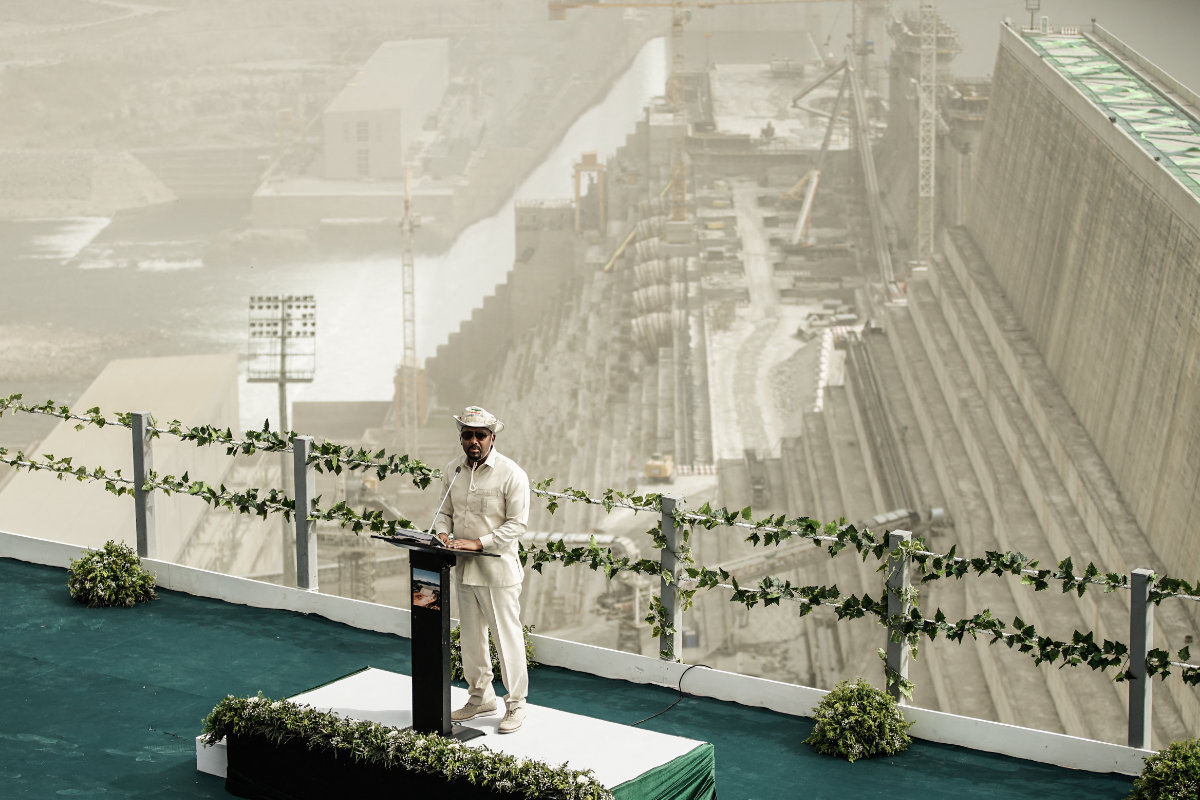

Ethiopia’s Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed speaks during the first power generation ceremony at the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam in early 2022. (AFP)
Ethiopia has always insisted that, as the dam was designed only to generate electricity, neither Egypt nor Sudan, although both downstream, will lose any of the precious water supplied by the Nile.
But when the plan was first unveiled, it was condemned by both Cairo and Khartoum as an existential threat — both nations are utterly dependent upon the life-giving waters of the Nile, which have flowed down from the Ethiopian Highlands since time immemorial.

A man rides a boat on the waters of the White Nile river in Sudan's Jabal al-Awliyaa area on March 11, 2023. (AFP)
More than once over the past decade Egyptian concern over the scheme has threatened to escalate into violence.
In June 2013, several Egyptian politicians were overheard live on television discussing military options to halt the dam, with proposals ranging from backing Ethiopian rebels to sending in special forces to destroy it.
In March 2021, during a visit to Khartoum four days after signing a military cooperation agreement with Sudan, Egypt’s President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi said: “We reject the policy of imposing a fait accompli and extending control over the Blue Nile through unilateral measures without taking the interests of Sudan and Egypt into account.”
A few days later he upped the stakes, declaring that “the waters of Egypt are untouchable, and touching them is a red line.”
No one, he added, “can take a single drop of water from Egypt, and whoever wants to try it, let him try.”

Egypt relies on the Nile for its very survival. (AFP)
As recently as March this year, Egypt’s foreign minister, Sameh Shoukry, warned that on the issue of the dam “all options are open, all alternatives remain available.”
Since then, however, Sudan’s attitude toward the dam has appeared to ease, leaving Egypt increasingly isolated in its outspoken opposition to the project.
In Sudan in January, in addition to meeting Al-Burhan, Abiy also sat down for talks with Gen. Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, known as Hemedti, the leader of the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces, with whom the head of Sudan’s Sovereign Council is now locked in a bloody power struggle.
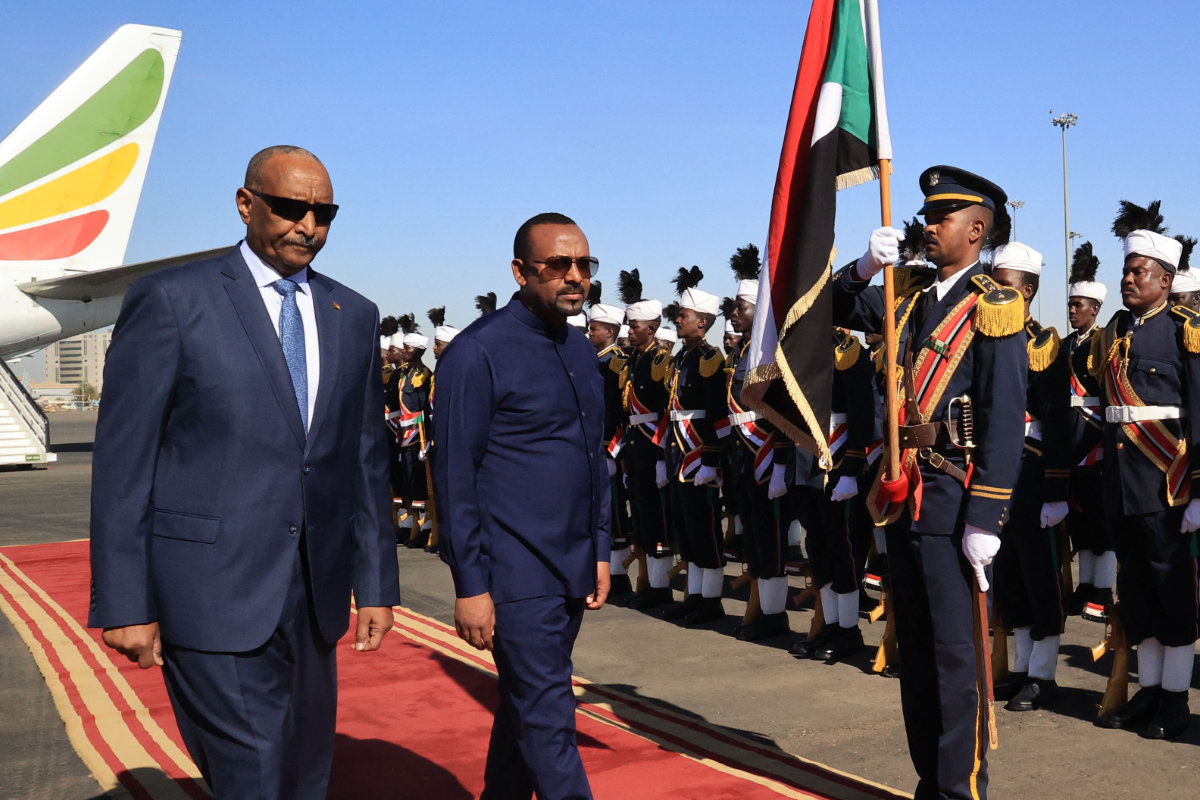

Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed (R) walks alongside Sudanese Army Chief Abdel Fattah al-Burhan at Khartoum Airport during a welcome ceremony on January 26, 2023. (AFP)
A statement issued by the council after the meeting welcomed the fact that Abiy had “confirmed that the Renaissance Dam will not cause any harm to Sudan but will have benefits for it in terms of electricity.” The two countries, it added, were “aligned and in agreement on all issues regarding the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam.”
But even as he worked to allay Sudanese fears over the dam, Abiy was walking a diplomatic tightrope between Al-Burhan and Dagalo.
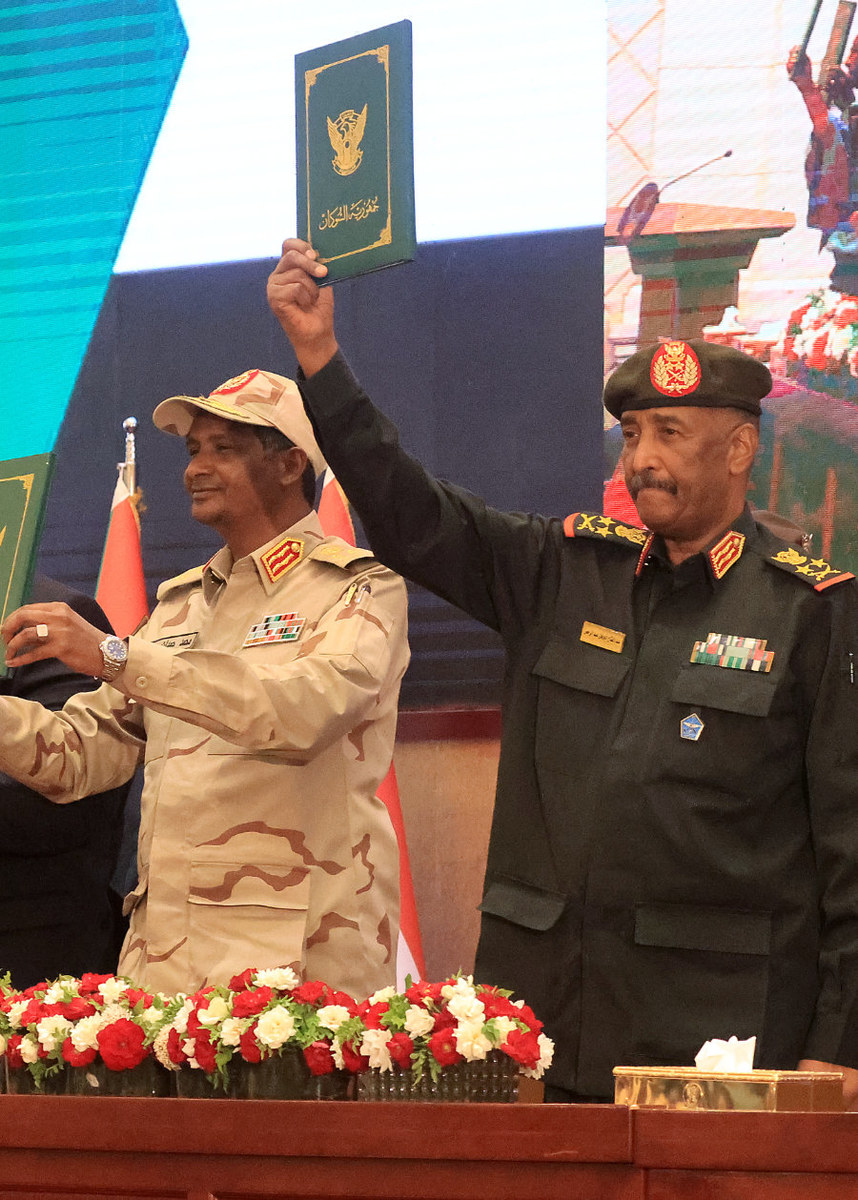

Sudan’s army chief Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan, right, and paramilitary leader Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo after the signing of a 2022 truce. (AFP)
In December, a framework agreement outlining a two-year transition to democracy was signed between the two generals and some Sudanese pro-democracy groups. On his visit to Khartoum in January, Abiy had supported the agreement, tweeting that he was “pleased to come back again and be amidst the wise and vibrant people of Sudan,” and adding that “Ethiopia continues to stand in solidarity with Sudan in their current self-led political process.”
But a prescient commentary in February by the head of a Khartoum think tank highlighted the tensions between the two generals.
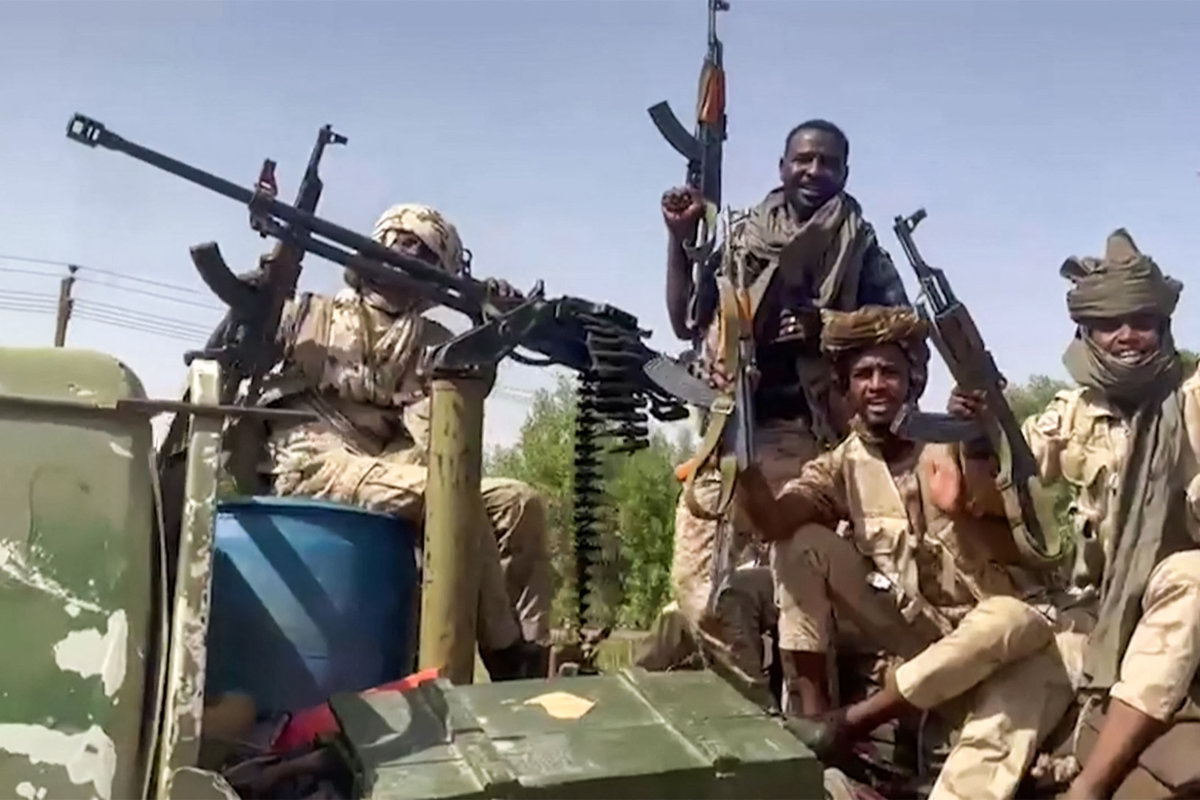

A prolonged conflict in Sudan has the potential of posing a risk on the country's ties with Ethiopia. (AFP)
Kholood Khair, the founder and director of Confluence Advisory, told Africa Report: “When Abiy Ahmed visited Khartoum, he lent his support to the framework agreement, which favors Hemedti.
“By doing so, he is trying to get both generals on board ... they have diverging foreign policies, they have diverging income streams, they have diverging political constituencies domestically that they play to.
“Because you have that inherent divergence between the two generals, you get different and unpredictable sorts of power plays.”
Those power plays have now exploded into a conflict which Jordan-based Jemima Oakey, associate in Middle East and North Africa water and food security at London-based consultancy Azure Strategy, said has serious implications for the future management of the dam.

Jemima Oakey. (Supplied)
“Informal discussions were looking pretty positive,” she told Arab News. “From recent reports, Sudan certainly seemed to be coming to an arrangement with Ethiopia, while Egypt had begun to accept its new water reality and had begun developing adaptation measures through increasing the number of desalination plants and rehabilitating its irrigation networks.”
Now, she said, all-important regional cooperation on the management of the dam, for the benefit of Sudan and Egypt, as well as Ethiopia, may hinge on who emerges victorious from the current struggle.
In addition to generating electricity that could be supplied not only to the 60 percent of Ethiopians who currently have no access to mains power, but also to Sudan and Egypt, the dam promises to maximize agricultural yields, in Sudan especially, by ending the destructive cycle of floods and droughts caused by the seasonal variations in the flow of the Nile.

Proponents of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam argue that it could stop the destructive cycle of floods and droughts caused by the seasonal variations in the flow of the Nile in both Egypt and Sudan. (AFP)
But the only way this is going to work, Oakey noted, was “through a data-sharing agreement where water availability and water releases from the dam are clearly laid out and fairly divided between the Nile’s riparians, both through droughts and periods of high rainfall.
“(Right now) we have no idea of what the position of Hemedti on territorial disputes in the Al-Fashaga region in northern Ethiopia might be, if he might try to claim that region for Sudan, or whether he would lend support to rebel militias in Ethiopia’s Tigray region.
“Any of that could derail any agreements or understandings over access to the dam’s water flows, and really damage Sudan’s access to both water and electricity,” she added.
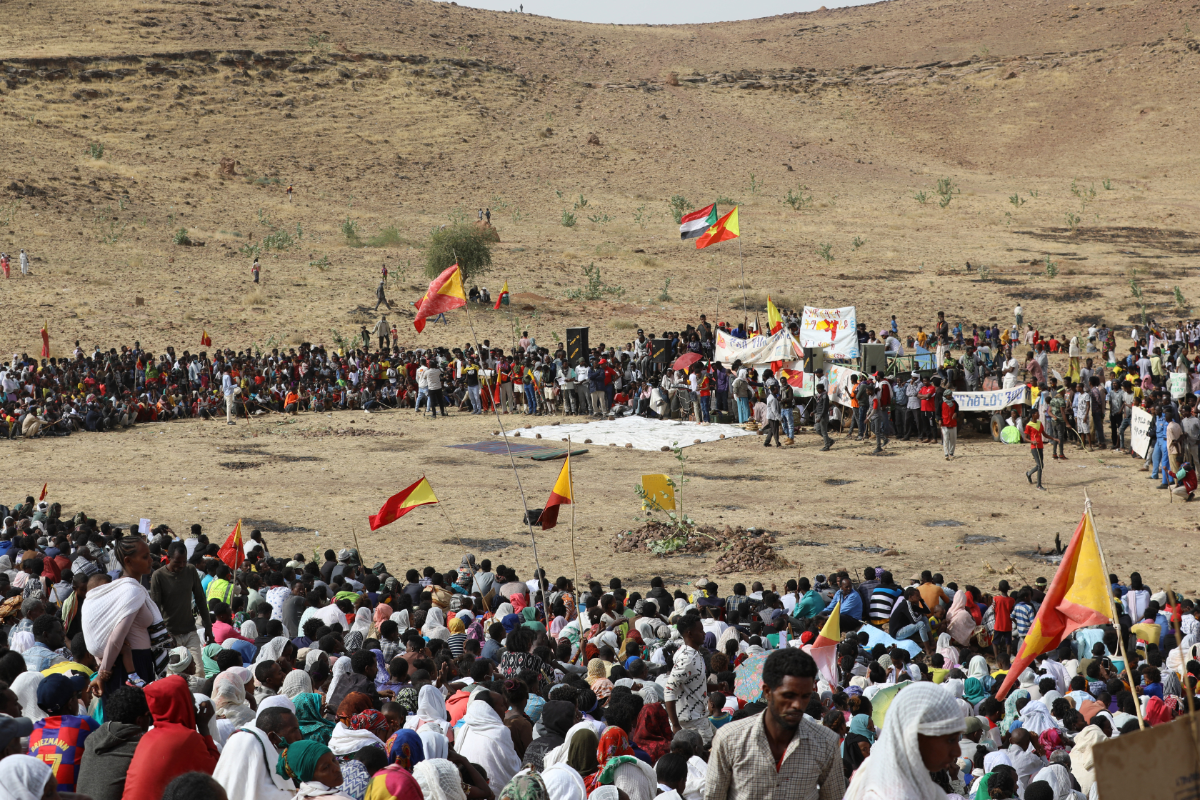

Ethiopian refugees gather to celebrate the 46th anniversary of the Tigray People's Liberation Front at Um Raquba refugee camp in Gedaref, eastern Sudan, on February 19, 2021. (AFP)
And she pointed out that such a development could also have serious consequences for Egypt.
“Following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Egypt has been trying to expand its agriculture sector in order to become more self-sufficient in wheat production and make up for lost Ukrainian wheat imports, so they really need that water, and they need a reliable supply of it,” Oakey said.
“That’s why an agreement for water access and monitoring availability is so crucial.
“But if there’s a prolonged conflict in Sudan, that could really throw both Sudan’s and Egypt’s water and food security into massive uncertainty.”

One scenario, according to Oakey, was as unlikely as it was unthinkable, whatever happens in Sudan’s internal conflict: military action being taken by either side against the dam.
“Over the past few years there has been alarmist speculation in the media that GERD could be attacked in order to prevent its completion, but I seriously doubt that either side in the Sudan conflict would ever consider using this to secure a military advantage,” she said.
“There are now almost 73 billion cubic meters of water behind the dam. To destroy it and unleash that volume of water would inundate most of southern Sudan with catastrophic flooding, so no, no one is going to try that.”
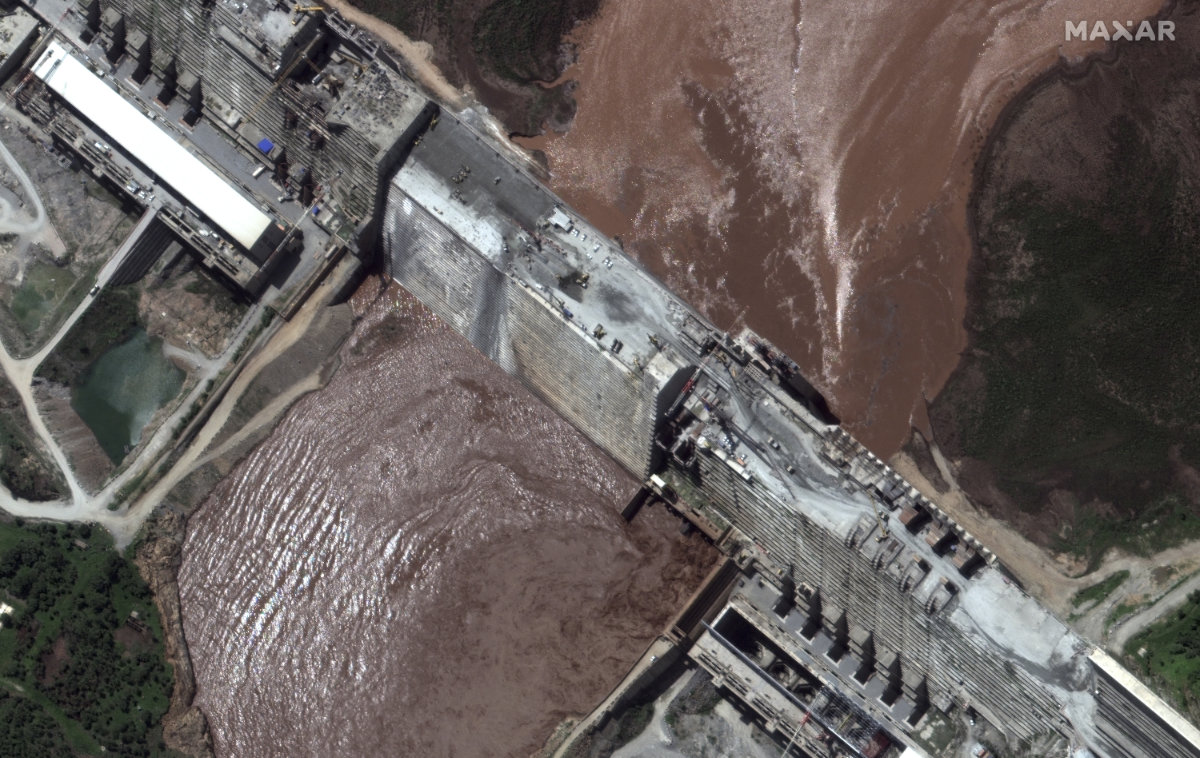

A satellite image obtained courtesy of Maxar Technologies on July 21, 2020 shows the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam and the Blue Nile River. (AFP)
But some experts hope that nature gets the same memo.
The possibility of a catastrophic failure of the dam has been raised in several academic papers over the past few years. These have highlighted “the high risk of soil instability” around the GERD site which, as one recent study by Egyptian civil and water engineers pointed out, was “located on one of the major tectonic plates and faults in the world.”
Around that fault, they added, about 16 earthquakes with a magnitude of 6.5 or higher had occurred in Ethiopia during the 20th century.
The first and largest of the sequence of devastating quakes that struck Turkiye and Syria in February, killing tens of thousands of people and causing widespread damage, had a magnitude of 7.8.
Hesham El-Askary, professor of remote sensing and Earth systems science at Chapman University in California, told Arab News that seismic risks, rather than the current conflict in Sudan, were the real threat to the dam that the world should be focused on.
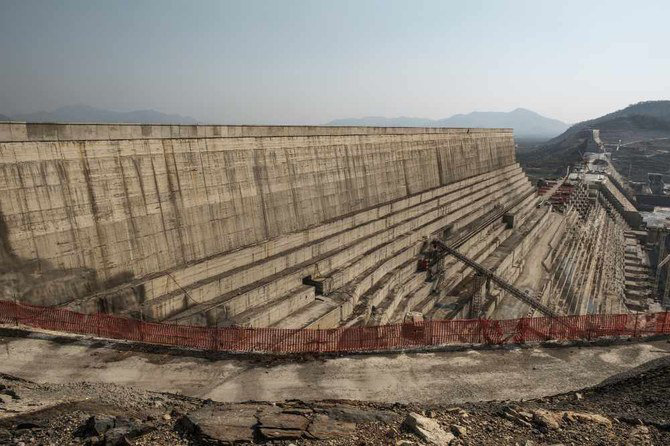

A general view of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam near Guba in Ethiopia. (AFP)
“What really bothers me now is the possibility of tectonic moves in Ethiopia, which is the most tectonically active nation in Africa,” he said.
There was, he added, also evidence that dams could “exacerbate tectonic activities and slippage.
“We saw what happened in Turkiye, when dams were opened to ease water pressure on the crust.
“With the changing climate, what Ethiopia is doing is really serious and, with the situation in Sudan, no one can guess how this will all end up.”
























