JEDDAH: Cancer — one word that can ruin the life of any human being. A word so soul-crushing that it brings disbelief, shock, fear, anger, and can break one’s spirit and the spirits of those around those diagnosed. Medical research has helped scientists develop methods of stopping cancer from metastasizing, but thanks to the momentum of the COVID-19 pandemic, promising new research may help end the battle against cancer.
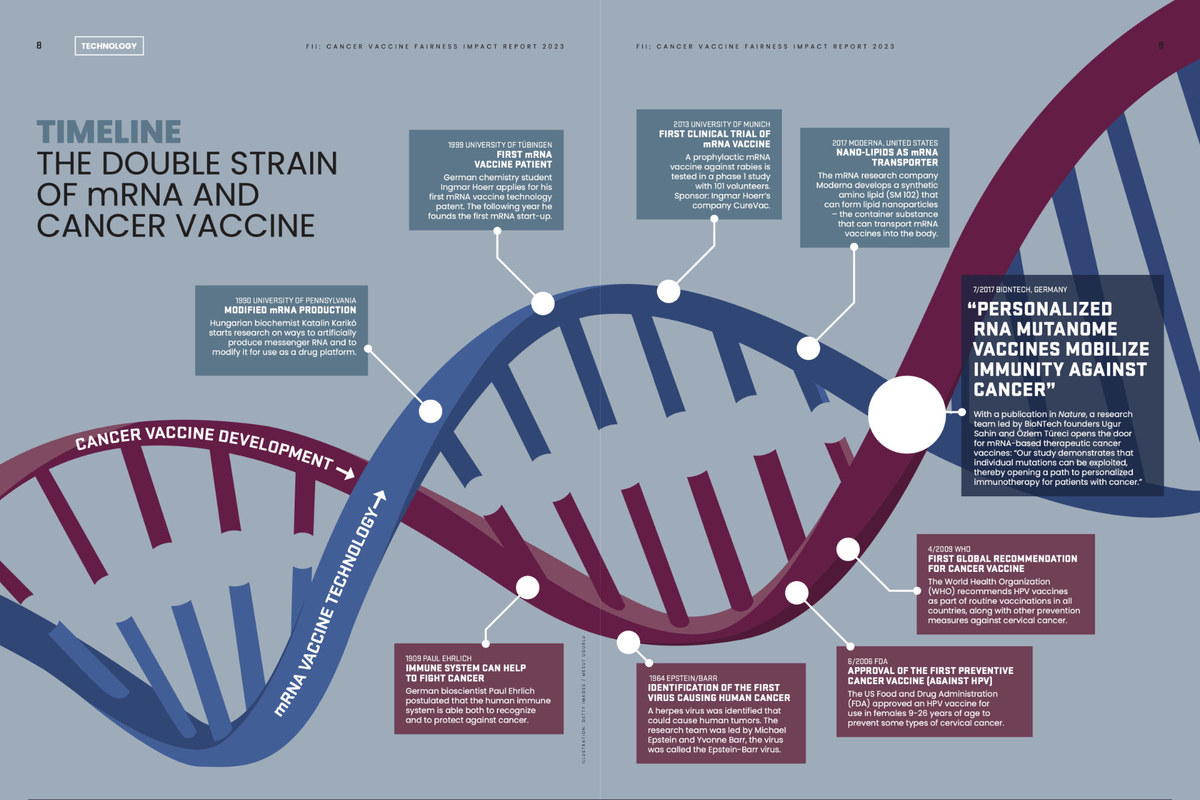
A recent report released by the Future Investment Initiative (FII) Institute, entitled “Tumor No More: How Humanity Can Get Rid of Cancer,” has shed light on how mRNA (messenger RNA) technology is proving to be a promising opponent in the fight against cancer. By producing individualized vaccines for cancer patients, the mRNA technology once deemed absurd by the scientific community is starting to gain attention as scientists begin to tap into its potential thanks to the swift delivery of the world’s first mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine three years ago.

“This is one of the best examples of the positive impact that new technologies can have on humanity. And in this report we tried to find out how the mRNA success story might continue,” Richard Attais, CEO of FII Institute, told Arab News.
The job is simple: mRNA’s role is to carry protein information from the DNA of a cell’s nucleus to the cell’s cytoplasm (gelatinous interior). For vaccines, this works by introducing a segment of mRNA that corresponds to a viral protein, usually a tiny piece of a protein found on a virus’ outer membrane.
The technology is not new. In early experiments, carrying messages to the intended target was deemed unstable and volatile. But not anymore.
The report’s findings look into how the technology may be used, the challenges of cancer therapy and vaccine studies, and, finally, possible proposals by the authors.

Shutterstock illustration image
Fast forward to 2020: Scientists discovered a substance to tame the unstable messenger using fat chemically. Known as “lipid nanoparticles,” these provide a stable and protective layer around the mRNA and unleash the message once a foreign body enters the human body, such was the case for COVID-19 infections. Then, the mRNA kills the virus’ proteins by building a protein specific to a virus, teaching the immune system how to behave when exposed to a potential threat.
“Capitalizing on the knowledge we gained about the use of mRNA technology during the COVID-19 vaccine’s development, we have an opportunity to address the challenges of equality and fairness now as we look toward the future distribution of a potential cancer vaccine. This is a challenge for humanity,” Safiye Kucukkaraca, head of THINK, FII Institute, told Arab News.
Infographic credit: FII: Cancer Vaccine Fairness Impact Report 2023
So how would this work to battle cancer?
Every cell contains protein, including cancer cells. A 2017 paper published in Nature magazine by BioNTech co-founder Ugur Sahin, entitled “Personalized RNA Mutanome Vaccines Mobilize Poly-Specific Therapeutic Immunity Against Cancer,” indicated that scientists were able to design and manufacture a vaccine unique to each cancer patient that had been diagnosed with melanoma. The results were auspicious, as the rate of cancer metastasizing was significantly reduced after the start of vaccination.

BioNtech's CEO Ugur Sahin (R) speaks during a joint press conference with his wife co-founder and Chief Medical Officer of BioNTech Ozlem Tureci (C) and German Chancellor Olaf Scholz at a BioNTech plant making mRNA-based vaccines and therapies in Marburg, Germany, on February 2, 2023. (AFP)
The only difference is that in COVID-19, mRNA can protect billions of people with one vaccine.
Cancer cells differ in each cancer patient, each with a unique genetic fingerprint. The difficulty lies in manufacturing the vaccine, as personalized mRNA vaccines must be developed for each patient. The process requires looking for a common protein in those cancer cells, constructing an mRNA strand that produces the same protein, creating the unique vaccine, and then vaccinating the patient with the mRNA. The immune system would then develop antibodies against the protein and combat tumor cells in cancer.
Developing a separate vaccine for each tumor can only be made possible by the development of a reliable and fast technology for decoding genetic material, a method that is currently being tested in several medical labs across the world.

Infographic credit: FII: Cancer Vaccine Fairness Impact Report 2023
Speed was essential for fighting COVID-19, such was the case with Moderna and BioNTech, two of the first companies to develop the vaccine. Speed will be as crucial for fighting individual cancer cases. Once the targeted structure is identified, the effort required to produce a specific mRNA for that target is relatively minor.
Several cancer vaccine technologies are already used in cancer patients, designed to stimulate the immune system in various ways to attack the tumor cells. The primary forms are protein/peptide-based vaccines, DNA or RNA-based vaccines, dendritic cell therapy, T-cell therapy, and CAR-T-cell therapy, all highly innovative therapeutic options.
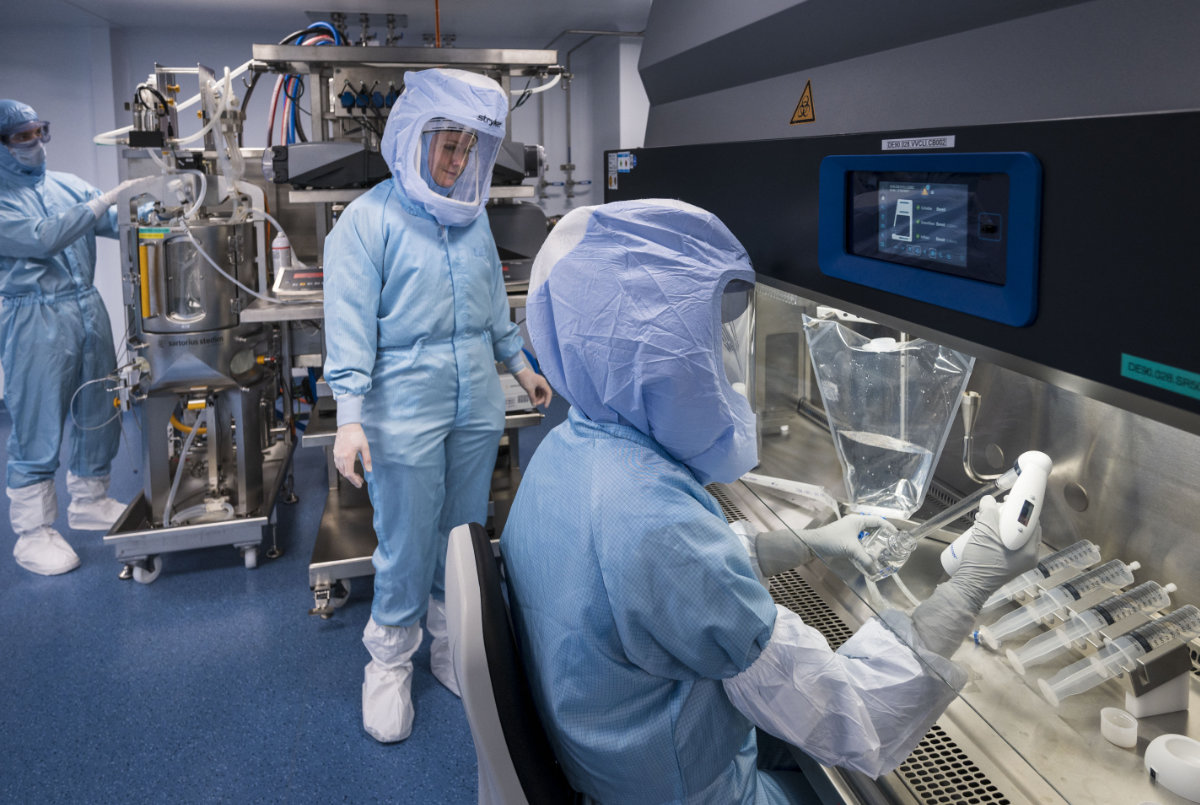

Researchers test procedures for the manufacturing of the messenger RNA (mRNA) for the COVID-19 vaccine at a new manufacturing site of German company BioNTech on March 27, 2021 in Marburg, Germany. (Thomas Lohnes / AFP)
The report indicated that several clinical studies, often combined with other cancer therapies, are currently in the works, focusing on patients with advanced-stage melanoma, advanced lung cancer, and brain glioma (tumors that spread in the brain), to name a few. Several published findings showed promising results, whereas others are still forthcoming.
The report stressed the scalability of the technology, adding that it will probably take at least another five years before the first mRNA vaccine against cancer is approved. Though it may seem that it is still a long way off, there is hope for developing “a new and effective weapon.”
Infographic credit: FII: Cancer Vaccine Fairness Impact Report 2023
However, the road ahead is long and challenging.
According to Dr. Niels Halama, a professor of translational immunotherapy at the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, “tumor cells have developed a number of very diverse mechanisms to protect themselves.”
He noted in the report that some tumors grow without the immune system being able to detect them or stop them, raising the question if vaccines alone are enough to reverse the process of detecting them, adding that there are several clinical studies currently that could shed more light on the matter.
Halama also noted that there are cancers, such as melanoma or lung cancer, that can respond well to immunotherapy.
“A significant proportion of patients respond and we know that the tumor allows the cells of the immune system to enter the tumor microenvironment. So, if you use a therapy that activates the immune system in the right way, you can kill the tumor,” he said, adding that it seems possible that vaccines could alter the response system for other cancers like pancreatic cancer or breast cancer that cannot be treated with immunotherapy.
Though many questions are still unanswered, Halama indicated that due to the COVID-19 vaccines, the structures of how mRNA is processed, packaged, and transferred to the individual have improved, unlike how it was before as molecules are known to having a short lifespan and quick to degrade.
One other challenge highlighted in the report was risk.
“Tumor vaccination is a therapy that is very well tolerated, with few to almost no side effects. But it is possible this will change in combination with other therapies, as some of them weaken or even overactivate the immune system,” said Halama.
Numerous studies are underway worldwide to test vaccines against a wide range of cancers, from lung cancer to melanoma, listed in an international database, ClinicalTrials.gov, which covers a variety of cancers.

This photo taken on November 17, 2021, shows a laboratory employee at work at the Transgene biotech firm, which is developing a neo-antigen cancer vaccine, in Illkirch-Graffenstaden, France. (AFP File)
For scientists and researchers, the challenge of selecting which type of cancer to use the vaccine therapy on, the stage of cancer, the mechanisms that tumors use to “hide from the immune system,” suitable candidates, a patient’s overall state of health, and what properties must a target structure have in order to be considered is massive due to the unpredictable nature of some cancers and further responses to various forms of therapies.
A significant portion of cancers in industrial nations are attributable to preventable environmental and occupational risks, posing another challenge.
The report clearly indicates that vaccines are not a miracle cure; in fact, it is merely “a tool in a big toolbox” as it has to be integrated into a comprehensive therapy plan with considerations for how it can be utilized alongside other methods such as surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other immunotherapies.
Though the success of cancer therapies is increasing, there is still a need for additional, innovative research, as although researchers agree that mRNA vaccine technology has enormous potential, it is still in its infancy “in terms of concrete implementation.”