LONDON: The World Health Organization downgraded its assessment of the coronavirus pandemic on Friday, saying it no longer qualifies as a global emergency. The action reverses a declaration that was first made on January 30, 2020, when the disease had not even been named COVID-19 and when there were no major outbreaks beyond China.
A look at what WHO’s decision means:
Why end the global health emergency?
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said the pandemic has been “on a downward trend for more than a year, with population immunity increasing from vaccination and infection.” That, he said, has allowed most countries “to return to life as we knew it before COVID-19,” meaning that the worst part of the pandemic is over.
Tedros said that for the past year, WHO and its emergency committee experts have been analyzing COVID-19 data to decide when the time would be right to lower its level of alarm. On Thursday, the experts recommended to Tedros that COVID-19 no longer qualifies as a global emergency and the WHO chief said he accepted that advice.
What are the practical effects?
For the average person, nothing. The classification of a health threat as a global emergency is meant to warn political authorities that there is an “extraordinary” event that could constitute a health threat to other countries and requires a coordinated response to contain it. WHO’s emergency declarations are typically used as an international SOS for countries who need help. They can also spur countries to introduce special measures to combat disease or release extra funds.
Many countries, including Britain, France, Germany and the US, have long dropped many of their pandemic-era restrictions. The US is ending its public health emergency next Thursday, which Dr. Rochelle Walensky cited Friday in announcing her decision to leave as head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention next month.
Is COVID-19 still a pandemic?
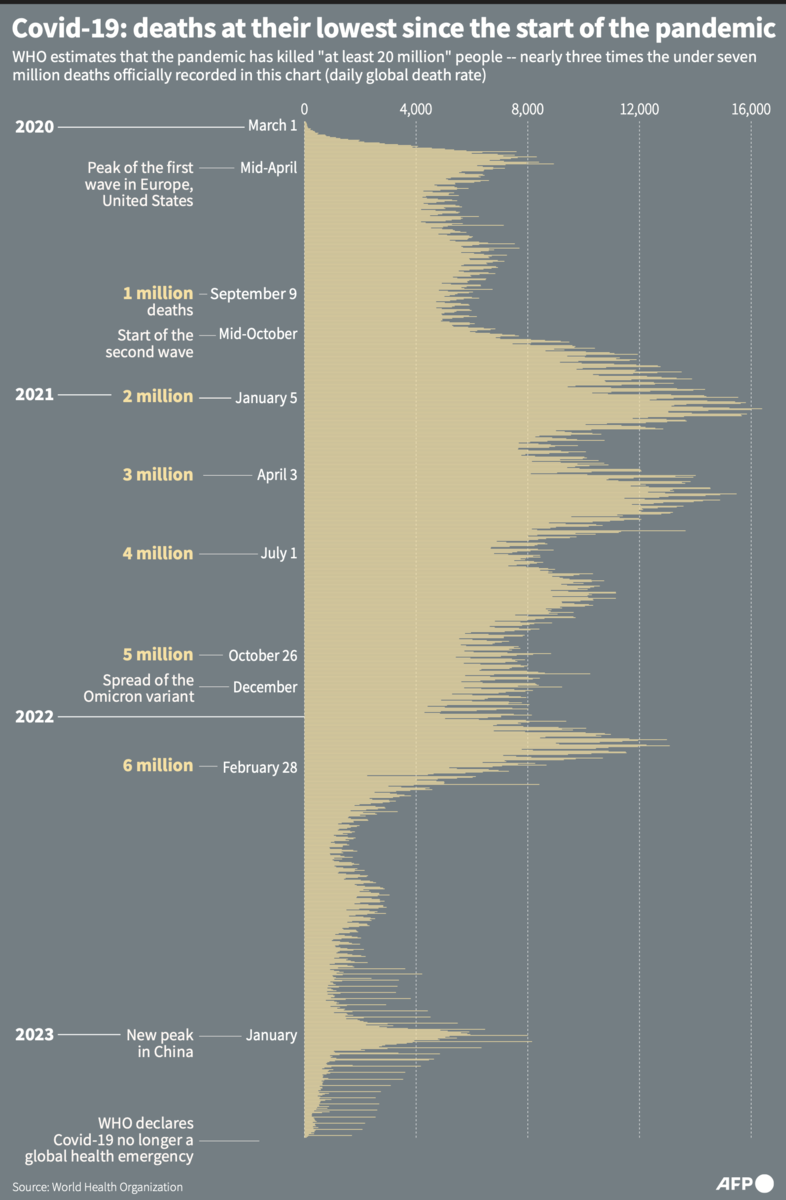
Yes. Although WHO chief Tedros said the coronavirus emergency was over, he warned that the virus is here to stay and that thousands of people continue to die every week. “The risk remains of new variants emerging that cause new surges in cases and deaths,” Tedros said. “What this news means is that it’s time for countries to transition from emergency mode to managing COVID-19 alongside other infectious diseases.”
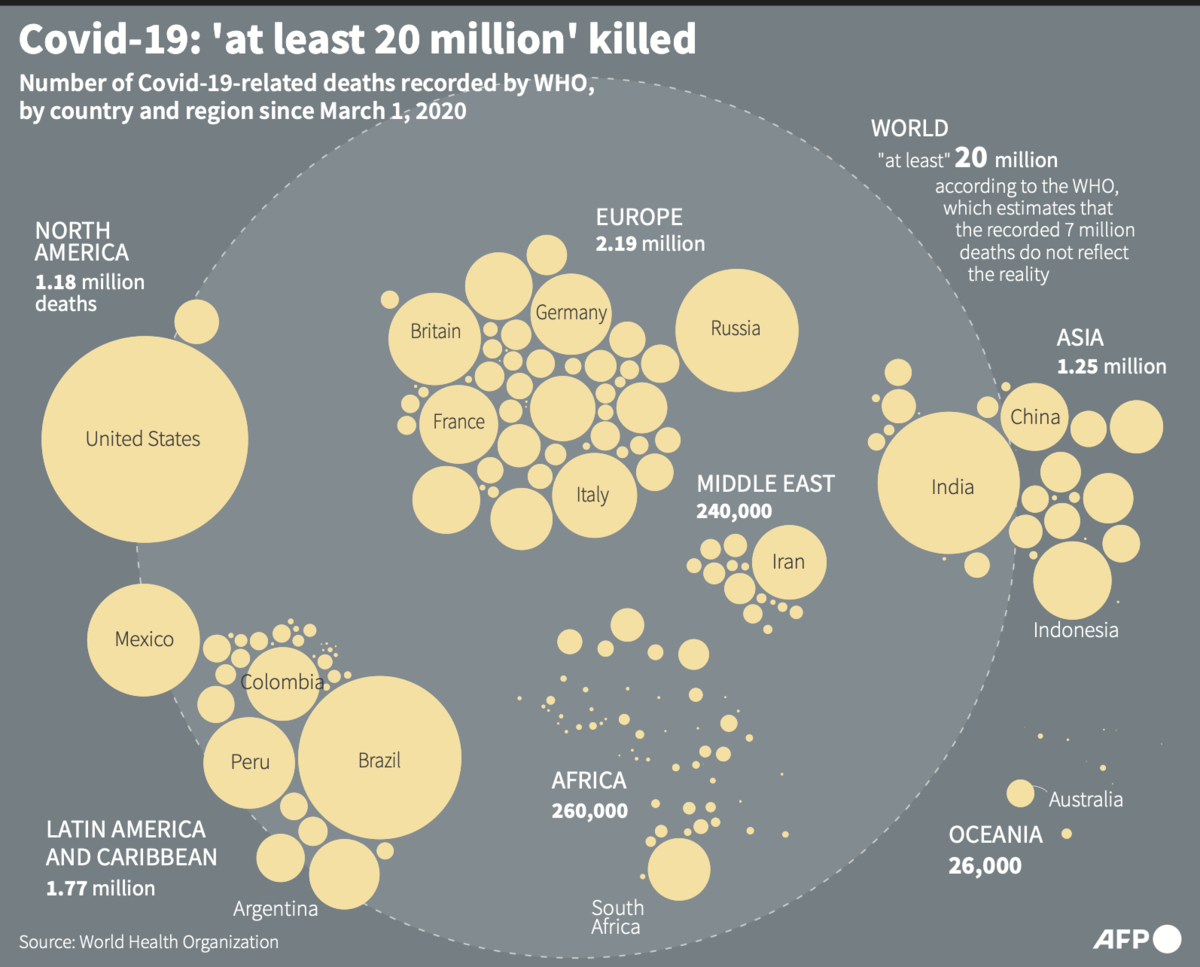
In April, there were nearly 3 million cases and more than 17,000 deaths reported, including spikes in Southeast Asia and the Middle East, the United Nations agency noted.
So when will the COVID-19 pandemic end?
It’s unclear. WHO emergencies chief Dr. Michael Ryan said the coronavirus is still a public health threat and that its continued evolution could yet cause future problems. “It took decades...for the pandemic virus of 1918 to disappear,” he said, referring to the Spanish flu that is thought to have killed at least 40 million people.
“Pandemics only truly end when the next pandemic begins,” he said. Ryan said that while COVID-19 will continue to spread among people for a very long time, it is doing so at a much lower level of threat that does not require the extraordinary measures taken to try to curb the virus’ spread.
What else has been declared an emergency?
WHO has previously declared global emergencies for outbreaks of swine flu, Zika, Ebola, polio and mpox, formerly called monkeypox. Polio was declared nearly nine years ago. Its emergency status has persisted even as officials work to wipe out the disease from a shrinking number of countries.
Last July, WHO chief Tedros declared the explosive spread of mpox to dozens of countries to be a global emergency, overruling the emergency committee he had convened to assess the situation. The disease peaked in Europe and North America shortly after, but technically remains a global emergency.
Do we still need to take COVID-19 precautions?
Yes. Health officials say the virus isn’t going anywhere and advise people to get vaccinated, including getting booster doses if they qualify. Although many of the measures seen at the height of the pandemic — including masks and social distancing — aren’t required except in certain settings, like hospitals or nursing homes, officials say people with other health conditions or compromised immune systems may still want to continue with some of those precautions.
Unlike in the early years of COVID-19, high immunization levels, both from vaccination and previous infection, have helped dramatically reduce disease spread.
Simon Clarke, an associate professor of microbiology at Britain’s University of Reading, warned against people dropping all COVID-19 protections.
“The message to the public should still be to take care and think of others. If you’re ill with a respiratory infection, like a bad cough, don’t put others at risk, especially not those who are vulnerable,” he said. “If you pass on a COVID infection, no one will thank you. If you’re fit and young, COVID can still be nasty and if you’re old and frail, it can kill you.”