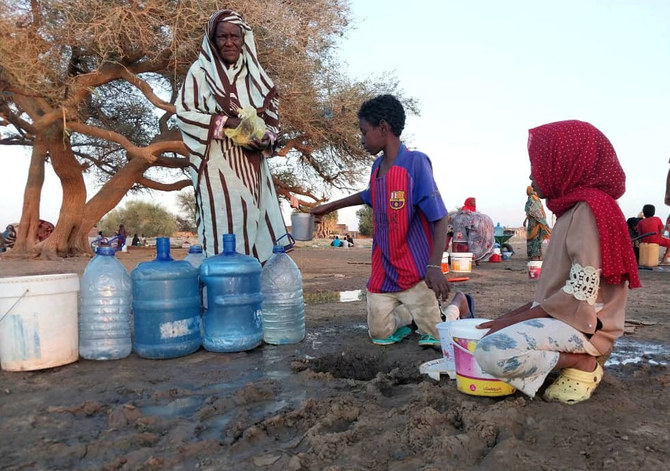
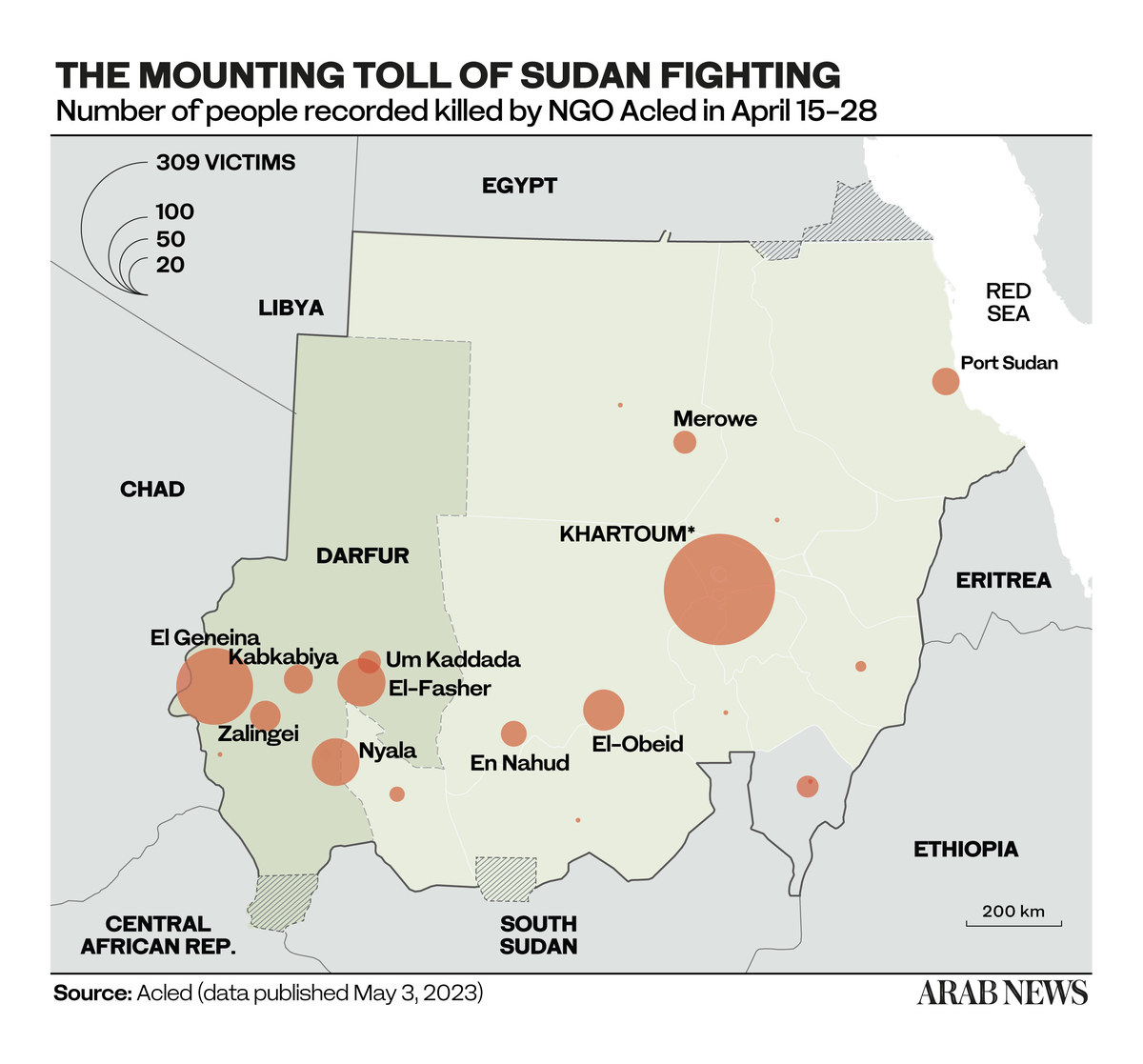
JUBA, South Sudan: The crisis in Sudan, which began when clashes broke out between Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan’s Sudanese Armed Forces and Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo’s Rapid Support Forces on April 15, has claimed more than 500 lives and displaced nearly 300,000 people over a span of just three weeks.
As Sudan’s neighbors, Arab and Middle Eastern countries, and Western powers make fervent pleas for an end to the fighting, many analysts say the Sudanese are actually looking to the East for a resolution.
China has acted as a mediator in several Middle Eastern rapprochement efforts, notably brokering the restoration of diplomatic ties between Saudi Arabia and Iran in early April and encouraging the push for reconciliation between the Syrian regime and Arab countries.
Its recent diplomatic track record, experts say, suggests China is ideally positioned to play the role of a peace broker in the Sudanese conflict as well.
INNUMBERS
$2.03bn China’s exports to Sudan during 2022
$780m Sudan’s exports to China in 2021
$17m Value of China-Sudan economic and technology agreements signed in 2022
“China has more influence on Sudan than the West and regional bodies, and could work with countries of the Arab League to solve the conflict before it escalates,” Manasseh Zindo, a South Sudanese peacemaker and a former delegate to the Intergovernmental Authority on Development-led peace process, told Arab News.
According to Zindo, while Western countries have tended to impose sanctions on Sudan, China has done business with the country’s leaders, giving it a unique opportunity to help end the conflict between the military and the RSF.
“Sudanese leaders do not have much faith in the West and would be more comfortable with mediation championed by China,” he said.
Indeed, the general consensus is that China’s longstanding economic ties with Sudan, which date back to the late 1950s, give it a vested interest in brokering a deal to end the current fighting and pushing for a lasting solution to the crisis.
Over the years, China has emerged as one of Sudan’s largest trading partners, the result of investing heavily in the country’s oil industry and buying up part of the output too.
In recent years, China has expanded its investments to sectors beyond oil, such as infrastructure, mining and agriculture. It has also helped Sudan tap its hydroelectric power potential, notably by financing the construction of the Merowe Dam on the Nile River.
In the area of infrastructure, China has helped to build several major projects in Sudan, including the Khartoum International Airport, the Friendship Hall in Khartoum, and the Roseires Dam on the Blue Nile River.
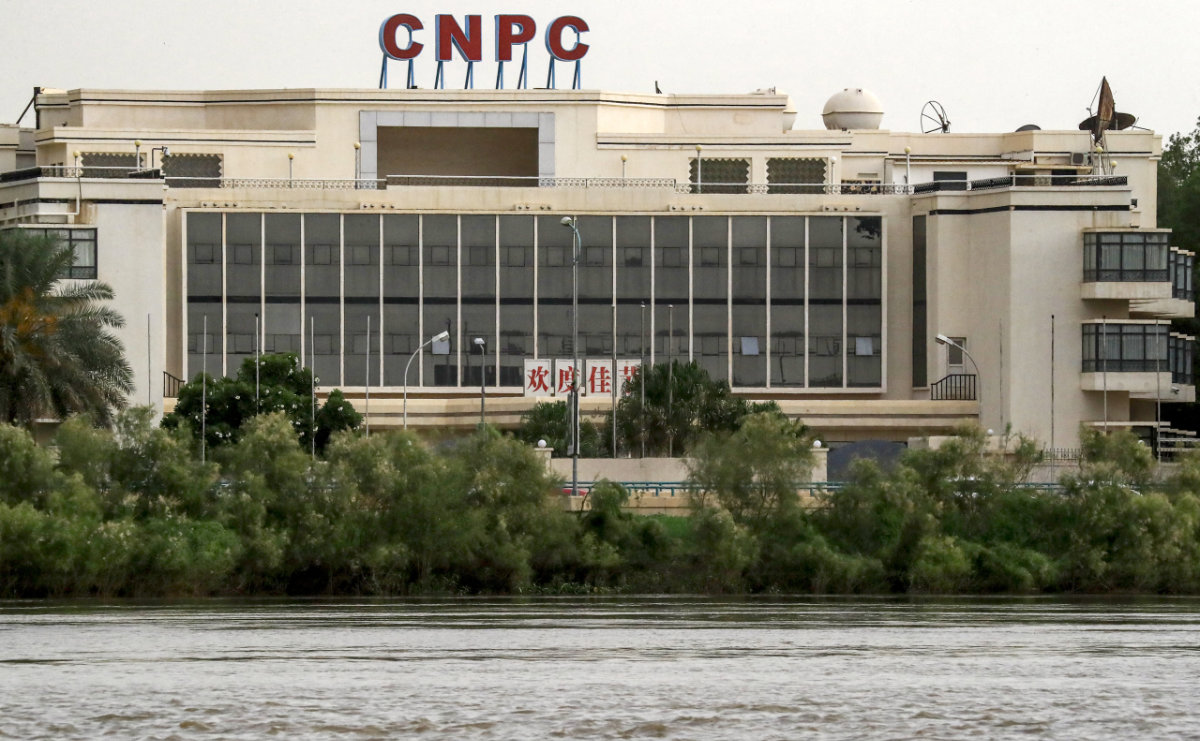

This picture taken on September 15, 2022 shows a view of a building of China's National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) near the Nile river waterfront in Sudan's capital Khartoum. (AFP)
Taken together, these projects have given a boost to Sudan’s transportation and energy infrastructure, contributing to the country’s economic development.
By the same token, China’s web of investments in Sudan would be at great risk were the current fighting to turn into a protracted conflict and exact a heavy economic toll.
“Disruption of production in the country could have serious consequences not just for Sudan and South Sudan, but also to some extent for China,” Augustino Ting Mayai, research director at the Sudd Institute in South Sudan’s Juba, told Arab News.
Since the eruption of violence in Sudan last month, the UN, the African Union and several regional blocs have repeatedly appealed for calm, proposing ceasefires and dialogue. So far, however, the outcomes have not been encouraging, with mere minutes passing between the implementation of a truce and the resumption of airstrikes and small-arms fire.
The two feuding Sudanese factions, who each blame one another for the multiple broken ceasefires, are actually former allies. After the removal of dictator Omar Al-Bashir in 2019, a joint transitional military-civilian government was established, led by Prime Minister Abdalla Hamdok.
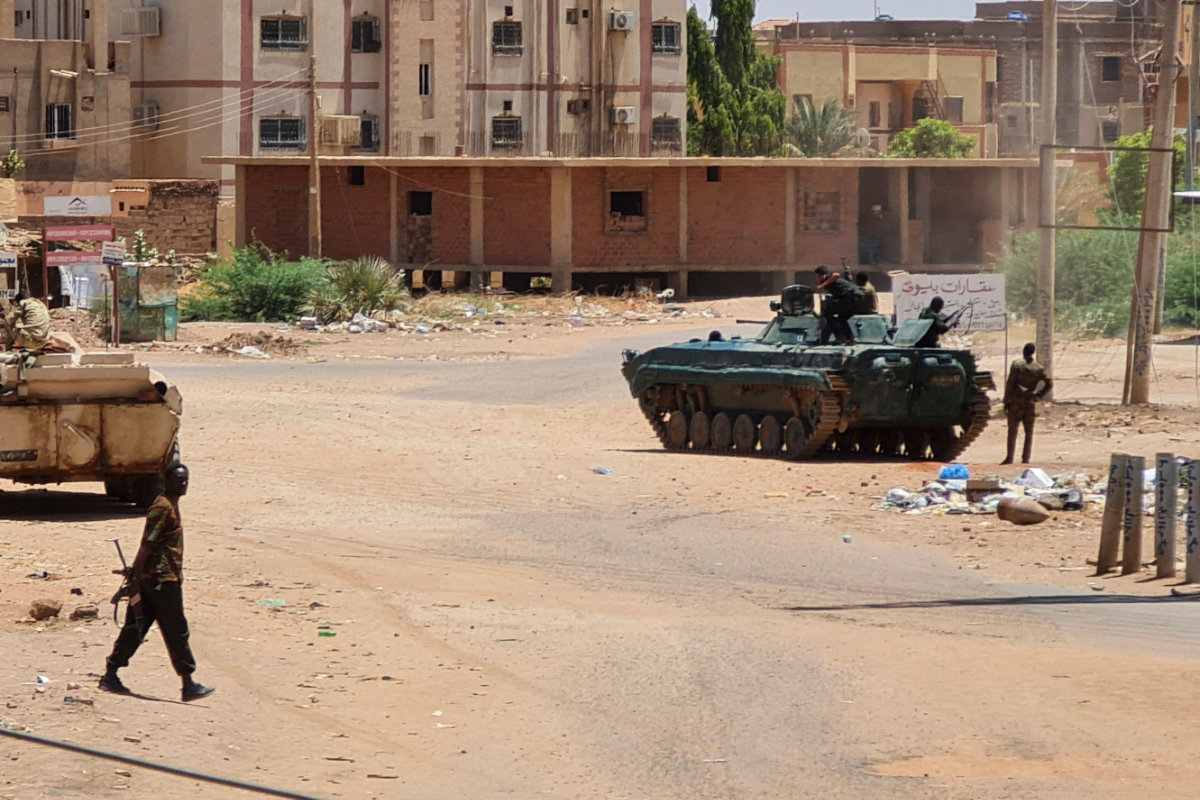

Sudanese Army soldiers walk near tanks stationed on a street in southern Khartoum on May 6, 2023, amid ongoing fighting against the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces. (AFP)
In just two years’ time, Al-Burhan and Dagalo, also known as Hemedti, closed ranks to overthrow Hamdok. Efforts to coax Sudan back toward a civilian-led government began anew, but disputes over the integration of Dagalo’s RSF into the SAF led to tensions, which evidently reached a flashpoint when explosions and gunfire began to rock Khartoum and other cities on April 15.
“The collapse of Sudan could lead to more violence across the region fueled by the spread of weapons, such as in Libya and Somalia,” Kai Xue, a Beijing-based Africa expert, told Arab News.
Libya, which shares its southeastern border with Sudan, and Somalia, on the Horn of Africa, are two examples of how protracted civil conflicts can plunge African nations into vicious cycles of violence with damaging global consequences.
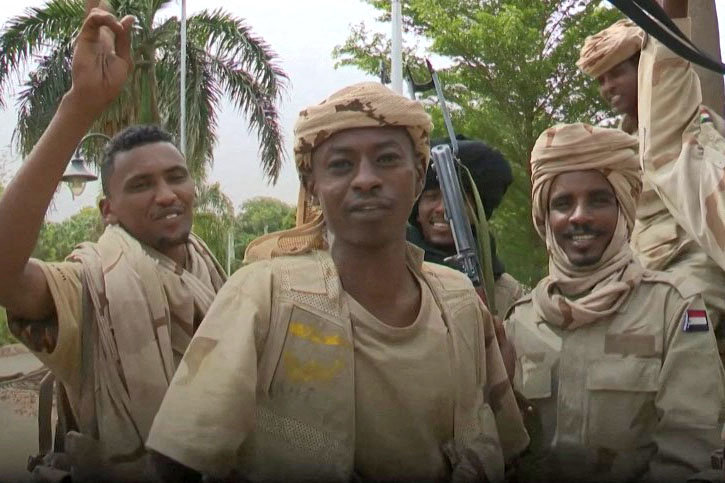

Sudanese paramilitary Rapid Support Forces (RSF) gather near the presidential palace in Khartoum on May 1, 2023. (Screen grab from RSF video/ESN/AFP
In Libya, the fall of former dictator Muammar Qaddafi in 2011 led to the rapid spread of small arms and light weapons throughout the country, which is now home to a large number of warring groups engaged in an unending power struggle.
The unchecked proliferation of arms, ammunition and explosives not only fuels the conflict in Libya but also has a destabilizing effect on the entire region. Neighboring countries, such as Chad, Niger and Sudan, have struggled to stem the misuse, accumulation and illicit transfer of small arms and light weapons across their borders.
The civil war, followed by state collapse and the emergence of armed groups, in Somalia has had a similar effect on nearby countries. The diversion and illicit trade of small arms and light weapons has been a major driver of the Somali conflict, which continues to this day.
The smuggling and transfer of weapons and explosives from Somalia have also had a significant impact on neighboring countries, such as Kenya and Ethiopia. The terrorist group Al-Shabaab, which has links with Al-Qaeda, has launched deadly attacks in both countries using weapons smuggled in from Somalia.
Africa analysts say if Somalia and Libya hold any lesson, it is that the conflict in Sudan potentially has serious implications not just for the future of the country but for that of the wider region too.
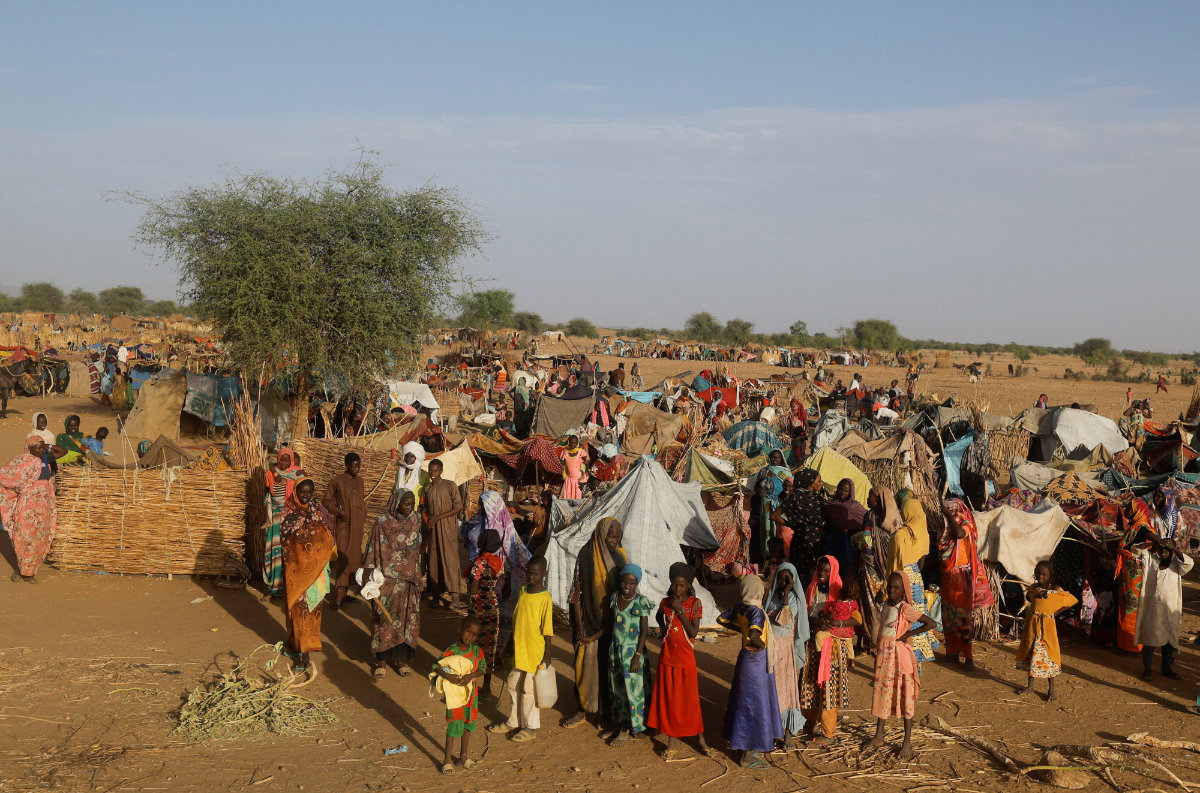

Sudanese refugees, who fled the violence in their country stand beside makeshift shelters near the border between Sudan and Chad in Koufroun, Chad, on May 6, 2023. (REUTERS)
The UN has warned of an impending humanitarian catastrophe as a result of the fighting, saying that 800,000 people are expected to flee the country. Compounding the crisis is the fact that Sudan itself is already home to more than 1 million refugees and 3 million internally displaced persons.
Sudan’s impoverished neighbors also already host large refugee populations and have been plagued for years by political and economic instability as well as natural disasters such as flash floods and drought.
“It is good that everybody is calling for peace, but there is almost a traffic jam of peacemaking when everyone wants to get involved,” Tibor Nagy, a former US ambassador to Ethiopia, told Arab News.
He expressed regret that the US did not provide more support for Sudan’s transition to civilian rule.
“I think if the US had been quicker, then maybe Prime Minister (Hamdok) would not have been overthrown,” Nagy said. “Yet, at the end of the day, the fault lies with General Al-Burhan and Hemedti, as it is now clear that neither one of them wanted a real civilian-led government.”
As for China, Nagy said the country “tends to issue good statements when there is a flare-up like the current conflict in Sudan, but it tends to stay back and wait for others to make peace, as we saw in the case of Ethiopia’s recent civil war,” Nagy said.
Under the circumstances, China’s involvement in the Sudan feud is likely to be passive, according to Benjamin Barton, of the University of Nottingham, Malaysia. Citing the scale of the crisis and the size of Sudan, he said China will wait for the violence to ebb before getting involved.
“It’s all really dependent on the warring parties,” he told Arab News. “Sometimes these conflict situations go way beyond China’s ability to intervene.”
The once laudable Western goal of seeing a civilian-led government formed to steer Sudan’s transition to a democratic dispensation seems far-fetched now. So, some in Africa hope that given its political clout and economic influence, China can at least have a mitigating effect on the current tensions.
“China could use its diplomatic channels to bring both sides of the conflict to the table,” Onyando Kakoba, secretary-general of the Forum of Parliaments of the International Conference on the Great Lakes Region, told Arab News, adding: “It should avoid taking sides, which could escalate the crisis.”
His view is seconded by Deng Dau Deng Malek, the acting minister of foreign affairs and international cooperation of South Sudan, who told Arab News: “Pressure must be exerted by all international partners (to end the fighting in Sudan), including China.”

































