RIYADH: Although the conflict in Sudan is viewed by many in the international development sphere as a major setback, the EU’s special representative for the Sahel believes donors and aid agencies must not lose hope but continue to remain engaged.
Speaking to Arab News on the sidelines of the Ministerial Meeting of the Global Coalition to Defeat ISIS in Riyadh on Thursday, Emanuela C. Del Re said there were great hopes that Sudan would stabilize and prosper following the toppling of longtime dictator Omar Al-Bashir in 2019.
However, after the military’s removal of Abdalla Hamdok, head of the short-lived transitional government, in October 2021, followed by the sudden outbreak of violence between the Sudanese Armed Forces and paramilitary Rapid Support Forces on April 15 this year, those early glimmers of hope were quickly dashed.
“I was very saddened by the crisis in Sudan. There was a moment in which we were really hoping that the country would have a chance to stabilize and to prosper,” Del Re said.
Recalling the mass protests that prompted the military to move against Al-Bashir, she said the international community had been inspired by the energy and ambition of Sudan’s urban youth who led the revolt and had been eager to help them realize their goals.
“It was a moment in which the students of the universities … were proposing a new society,” she said. “At that time, there was a lot of support by the international community and the leadership was willing to create a new renaissance for the country.”
Amid clashes between the regular army, led by Sudan’s de facto leader Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan, and the RSF, led by Al-Burhan’s deputy-turned-rival Mohamed “Hemedti” Hamdan Dagalo, Del Re said there was a risk the world would give up on Sudan’s transformation.
“It is particularly sad because it is having an impact on the global public opinion, making people think that no matter how much you invest, there will always be something happening that may completely destroy what you have been building,” she said.
“We must not lose optimism, but continue to believe that we need to help the countries, especially if they are in a very difficult condition.”
One particularly vulnerable demographic among the displaced in Sudan are women and girls. Stories of harassment, violence and rape are already pouring out of the country, where armed men are able to act with impunity amid the state of lawlessness.
Asked what the EU was doing to bring some sort of pressure to bear upon the feuding factions to make sure their forces do not target women and girls, Del Re pointed to the union’s record on protection and on helping to secure a ban on the practice of female genital mutilation.
“Of course, we are doing a lot,” she said. “We always engage in and fund projects that are aimed at protecting women and girls, and all our projects have obtained good results in Sudan.
“For instance, at one point, it was a very great success that with the pressure of the international community, female genital mutilation was introduced in the criminal code as a crime.”
Since the violence in Sudan began almost two months ago, security analysts have raised concerns about the conflict’s potential spillover across the Sahel, an area of the African continent encompassing parts of Senegal, Mauritania, Mali, Burkina Faso, Algeria, Niger, Nigeria, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Sudan, South Sudan, Eritrea and Ethiopia.

Saudi Arabia Minister of State for Foreign Affairs, Member of the Council of Ministers, and Envoy for Climate of Saudi Arabia Adel Al-Jubeir receives the special representative of the European Union for the Sahel region, Claudia C. Del Rey, where they reviewed aspects of cooperation between KSA & EU, as well as issues of common concern. (Supplied)
Possible knock-on effects include the proliferation of light weapons, involvement of mercenaries and, more immediately, the massive cross-border displacement of civilian populations, which could trigger a new global refugee crisis.
The EU’s contribution to the work of the Global Coalition to Defeat Daesh comes, to a large extent, in the form of funding for counterterrorism and counter-radicalization initiatives.
“The role of the EU is very important because the EU is composed of 27 countries and their contribution to the issues of terrorism is very consistent,” Del Re said. “We spend per year something like 500 million euros in activities dedicated to combating terrorism.
“If you look at the total amount, 60 percent of the money that we spend in the missions and activities and actions is dedicated to Africa and to the Sahel. We are particularly interested in tackling terrorism for the benefit of the continent of Africa and in the world in general.
“We know very well that unless we have a balance in power and also an opportunity for all populations, of course we will not be able to fight against this very serious phenomenon.”
Part of this is the EU Strategy for Security and Development, which introduced a new “integrated vision” for the Sahel in 2021 related to security.
“We have to act on all the sectors to make sure that society develops a strong resilience against all sorts of security threats, terrorism, of course, and you can only do this by working on education, health and access to basic services,” Del Re said.
“If we can help the Sahel countries develop a sound welfare system, this would be the start of a change. At the moment, the real threat that comes from terrorists is not only violence, which is already causing a lot of casualties. Because there is a vacuum of power and institutions, the terrorists are able to create an alternative system of welfare, which is absolutely fake.
“Of course, this is the biggest challenge and danger, because if the territory is controlled by terrorists, this means it will be very difficult to regain it. And the populations lose, in particular, young people, who are recruited by being given a small amount of money, being promised a career.
“They are given a pistol that would give them the sense of power because the young people often feel very much marginalized and humiliated.”

Rashid Hassan of Arab News interviewed Emanuela C. Del Re, EU special representative for the Sahel, on Thursday in Riyadh. (AN photo by Abdulrahman Binshulhub)
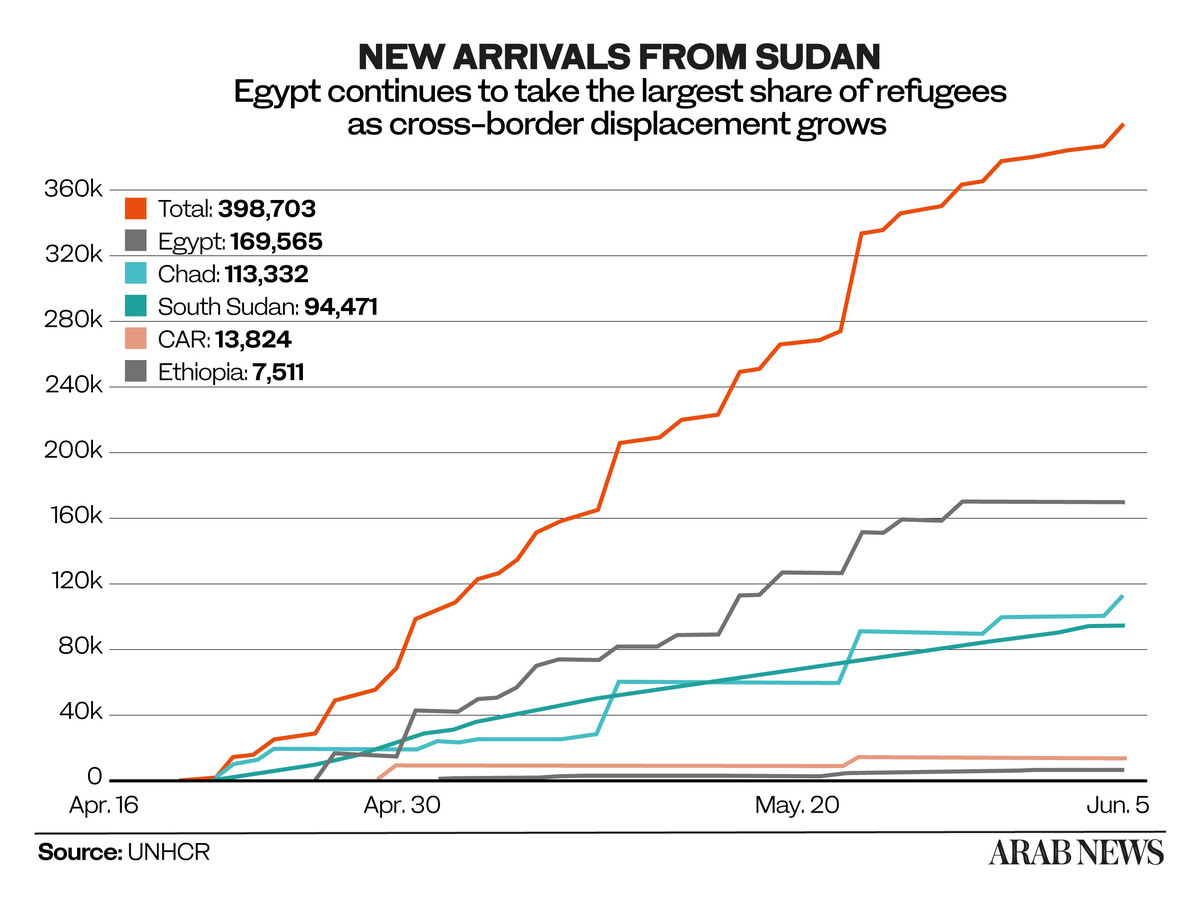
To protect displaced communities and host nations in the Sahel, Del Re said the EU was donating funds to support humanitarian programs, with a particular focus on Chad — a country that as of June 5 had accepted 113,332 people who had entered from Sudan.
As one of the most poorly equipped nations to offer sanctuary, Del Re said Chad was already hosting Sudanese citizens displaced by previous crises.
“The EU is helping in terms of humanitarian aid, especially in Chad,” she said. “This is our duty and our help in terms of humanitarian aid is particularly consistent. We are one of the biggest donors at the global level and in particular in the Sahel.”
Commenting on the GCC-EU Conference on Countering Extremist Ideology and Radicalization, which ended on Wednesday at the GCC General Secretariat in Riyadh, Del Re said the main aim was to identify the causes and possible remedies for radicalization.
“I highlighted the perception we have, for instance, of a specific region like the Sahel in Africa, where terrorism is actually multifaceted, with very different identities, and we need that to redefine our strategy to fight against it,” she said.
“The most important thing that emerged is the need to work on the root causes of terrorism, from poverty to lack of education and lack of access to basic services, work to create a good system of governance that can reinforce the social contract and make sure that people can develop their own skills, that we have employment for young people and prevent them from be recruited by extremists.”

Special representative of the European Union for the Sahel region, Claudia C. Del Rey, participates in the conference between the European Union and the Cooperation Council in Riyadh on combating extremist ideas and ideologies. (Supplied)
Del Re said the ministerial meeting on Daesh in Riyadh served to highlight the terror group’s evolving strategies as well as clarify the ways in which the international community could confront the continuing threat.
An extremist group which began life as an offshoot of Al-Qaeda, ISIS — another name for Daesh — seized vast swathes of territory in Iraq and Syria in 2014 before the coalition was able to dislodge its fighters from their final holdouts in 2019.
The group’s members and sympathizers were also responsible for several mass-casualty attacks in Europe, prompting governments to overhaul their security policies and revamp screening protocols for migrants and refugees.
“The meeting in Riyadh was a very important moment that will really be valuable for a long time,” Del Re said.
“Not only was the participation incredibly rich, but we had the presence of Saudi Foreign Minister Prince Faisal bin Farhan and US Secretary of State Antony Blinken, showing the fact that we are all together, motivated, engaged to defeat the challenges of Daesh.
“It is important to increase the cooperation between like-minded countries because it is the only way by which we can really create a barrier against terrorism that is very urgent to be created in this historical moment.”


























