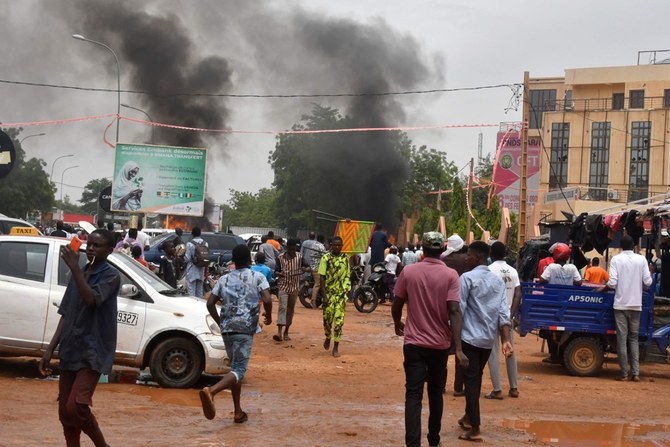
JUBA, South Sudan: Niger has become the third nation in the troubled Sahel region in as many years to suffer a military coup, causing concern among Western leaders and neighboring states over the repercussions for the ongoing fight against Islamist insurgency.
President Mohamed Bazoum, who is currently confined to his official residence in the capital, Niamey, was toppled on July 26 by his own presidential guard. The head of the elite force, Gen. Abdourahamane Tiani, has declared himself the new leader.
Coming in the wake of similar military takeovers in neighboring Burkina Faso and Mali, the US and former colonial power France have demanded Bazoum’s reinstatement, acknowledging his key role in the fight against extremism.
The African Union and the Economic Community of West African States, or ECOWAS, have likewise insisted on the need to restore stability to effectively confront the extremist threat, indicating neighboring states might consider using force to reinstate Bazoum.

General Abdourahmane Tiani, who was declared as the new head of state of Niger by leaders of a coup, arrives to meet with ministers in Niamey, Niger. (Reuters)
Niger’s strategic position in the Sahel region, bordered by countries experiencing violent extremism, makes it an important ally in the international fight against Islamist insurgency. Before the coup, Niger actively participated in regional counterterrorism initiatives.
However, the coup and its potential disruption to governance and security could jeopardize these vital partnerships and impede the progress of regional security efforts.
Aneliese Bernard, director of the Washington D.C.-based risk advisory group Strategic Stabilization Advisors, says similar coups in the region show that extremist groups have the most to gain from these episodes of instability.
“History has shown that groups like the Islamic State Sahel Province and Jama’a Nusrat ul-Islam wa al-Muslimin have successfully capitalized on governance and security vacuums left by states consumed with internal political issues and this has allowed them to expand their influence in Mali and Burkina Faso following recent coups,” Bernard told Arab News.
JNIM and ISSP are two rival radical groups operating in the region. It is not uncommon for individuals to switch sides between these groups, which further complicates the security situation in the region.
JNIM operates in neighboring Mali, with activities extending across West Africa, having pledged allegiance to Al-Qaeda in the Lands of the Islamic Maghreb, or AQIM.

Jama’a Nusrat ul-Islam wa al-Muslimin in Burkina Faso. (Supplied)
ISSP, meanwhile, operates as the Sahelian affiliate of Daesh and has also been involved in attacks across the region.
According to Bernard, the coup has destabilized the governance and security apparatus in Niger’s southwestern Tillaberi region, close to the triple frontier with Burkina Faso and Mali, where the ISSP is active.
“In such situations, JNIM and ISSP might seize the opportunity to exploit the absence of state authority and promote themselves as alternatives to governance and security,” she said.
“By championing the perception that neglected and marginalized communities in the periphery are left without support from the government, these jihadist groups have managed to infiltrate remote communities successfully.”
One targeted group is the Fulani people, an ethnic minority in the region, accused by authorities of harboring terrorist sympathies. Due to their status as a discriminated minority, extremist groups have found some success recruiting among their ranks.
Virginie Baudais, director of the Sahel and West Africa Programme at the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, says the possibility of Western aid being suspended as a result of the coup raises questions about how Niger’s security forces will handle the Islamist threat.
“Armed groups have consistently targeted defense and security forces in the region, making it essential for the international community to realign its priorities and support,” Baudais told Arab News.
FASTFACTS
• President Mohamed Bazoum was toppled by his own presidential guard on July 26.
• The coup follows similar military takeovers in neighboring Burkina Faso and Mali.
• Experts say radical groups like JNIM and ISSP have the most to gain from coups.
“However, while the situation has continued to deteriorate, people do not feel protected by international troops. That is why they support their armed forces in the fight against terrorism, but support for the coup perpetrators is not unanimous.”
Alex Nkosi, a Malawian policy specialist based in the West African country of Togo, likewise highlights the potential for divisions within Niger’s military ranks.
“The coup could invoke divisions within the military because not all soldiers support the military indulgence in politics,” Nkosi told Arab News. He is also doubtful Niger’s armed forces will have the means to go it alone against the extremist groups.
“If military aid and assistance from the US and France are suspended due to the coup, Niger’s security forces may face challenges in maintaining operational capabilities,” said Nkosi.
“The loss of resources, intelligence-sharing platforms, and training programs could therefore weaken their ability to confront well-armed and organized Islamist groups effectively. Niger may have to seek alternative sources of support or re-evaluate its strategies to address the security challenges independently.”
Those alternatives may include Russia’s Wagner Group — the private military contractor now based in Belarus since its abortive uprising against Russia’s military leadership in June this year.
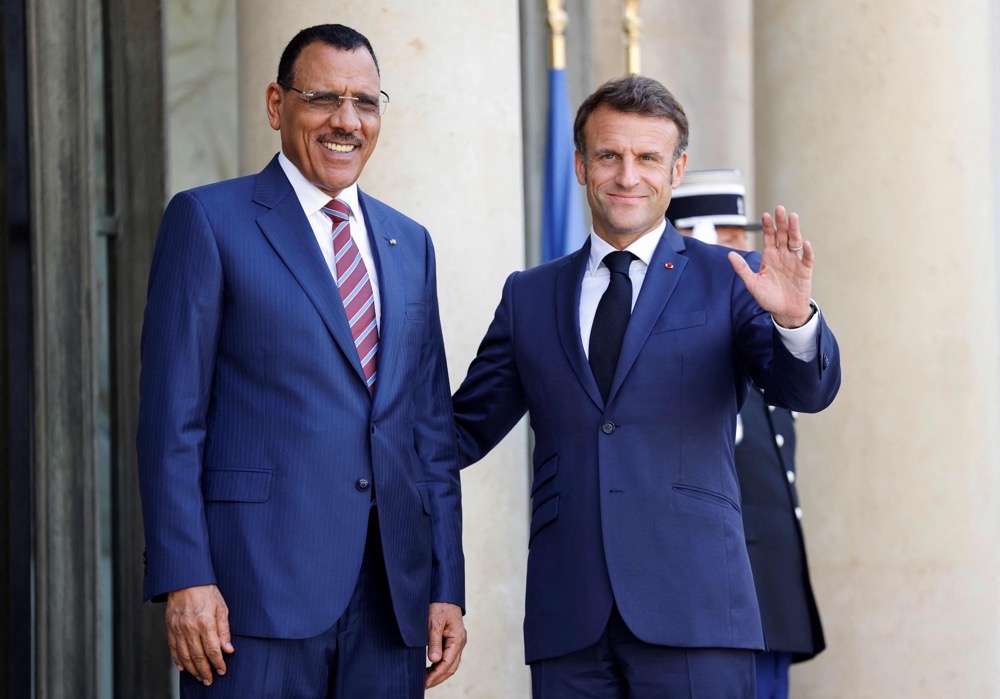

French President Emmanuel Macron with Niger's President Mohamed Bazoum at the Elysee Palace in June. (AFP)
Wagner has been making significant inroads into Burkina Faso and Mali since their respective militaries took power, providing manpower and expertise in the fight against extremists. Given the pro-Russian sentiments among Niger’s coup leaders, it is perhaps only a matter of time before Wagner soldiers emerge from the shadows.
Against this backdrop, according to Wim Zwijneburg, humanitarian disarmament project leader for the Dutch peace organisation PAX, a pullout by French forces from Niger will likely also prompt a removal of MQ-9 Reapers by the Americans, who have drone bases in Agadez, 740 kilometers northeast of Niamey.
“Combat drones operated by the two countries have been instrumental in the monitoring of militant cross-border movement in the Sahel,” Zwijneburg told Arab News.
“A lack of these air assets for intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) missions will mean less information available to track militant groups, including Daesh affiliates, in the region and to respond in a timely fashion.
“This may translate into a new wave of attacks if the national armies do not have alternatives to fill the vacuum. Though Niger recently stocked its own armed drone fleet with Turkish TB-2s, it is not clear if security forces have succeeded in integrating them fully into existing counterterrorism operations.”
Cameron Hudson, a former CIA analyst and consultant on African peace, security, and governance issues, says if the US and France are serious about combating the radical Islamist threat, Western nations will have to reassess their willingness to engage with military-led governments.
“The seriousness of the Islamist threat and other security challenges in the region might force them to engage with military leaders who now find themselves on the front line of the fight against terrorism,” he told Arab News.
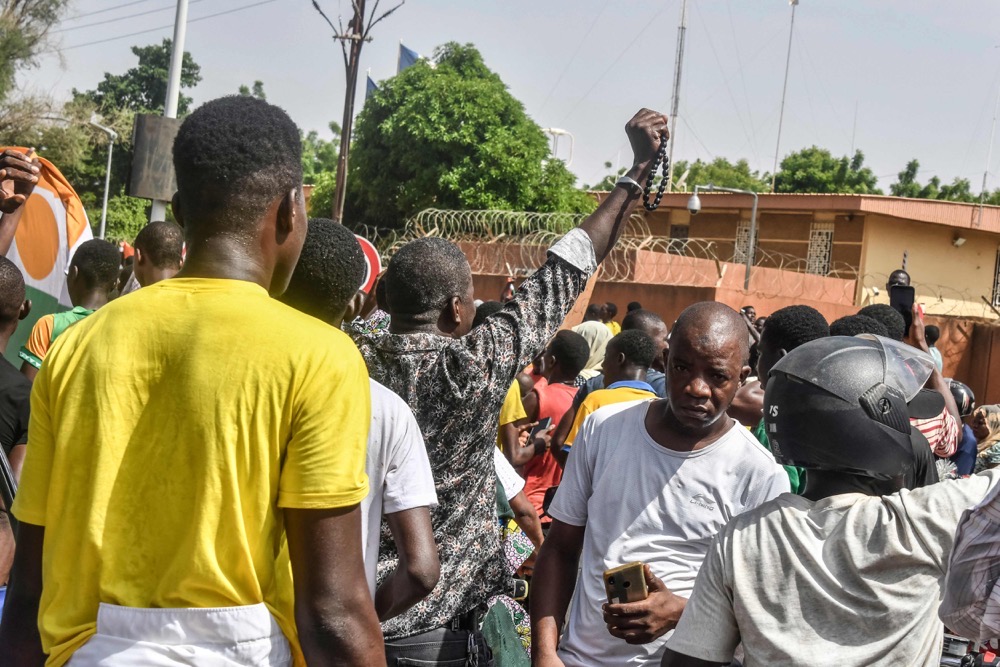
Thousands protested in front of the French Embassy in Niamey. (AFP)
“However, this engagement also raises questions about the promotion of democratic principles and civilian rule, which are core values in Western democracies.”
Ultimately, bridging the difference of opinion between Western governments and African military leaders on approaches to governance will be essential for long-term stability and security of the region, said Hudson.
The cooperation of all parties concerned, including the international community, regional bodies and the local population, will also be critical to finding effective solutions to the complex challenges faced by countries in West Africa.
The military coup has implications for the future of regional cooperation, according to Fidel Amakye Owusu, an international relations and security analyst based in Ghana.
“Nigeria, which borders Niger to the north, has historically relied on close cooperation to address security concerns, particularly in the fight against extremism,” he told Arab News.
However, “the lack of democratic civilian rule might lead to uncertainties and challenges in coordinating intelligence sharing and joint operations against violent extremism,” said Owusu.
“As seen in Mali and Burkina Faso, where military takeovers have occurred, the transition to military rule does not necessarily translate into peace, stability or gains in the fight against extremism.”

Militants in Mali. (Social media)
This can be compounded by the inability of a weak and unstable government to deal with the root causes of socioeconomic challenges effectively.
In such circumstances, there might be limited resources and capacity to implement policies and programs that address unemployment, poverty and social inequality.
As a result, “this situation provides an opportunity for extremist groups to fill the void by offering financial incentives and ideological narratives that resonate with vulnerable populations,” said policy specialist Nkosi.
“There is indeed a risk of Niger becoming a breeding ground for terrorist recruitment if the situation is not effectively addressed.”
Seconding Nkosi’s opinion on the governance crisis, PAX’s Zwijneburg said: “If there is no meaningful attempt to address the grievances of minority groups, there will be enough fertile ground that militants groups will be able to exploit, where even the presence of combat drones won’t make a significant difference.”




























