NAIROBI, Kenya: In the vast semi-arid expanse of West Africa’s Sahel, a series of military coups have dealt a heavy blow to the region’s political stability and democratic transformation, and created a new era of uncertainty and insecurity.
The July 26 coup in Niger, the latest in the region, where presidential guards ousted democratically elected President Mohamed Bazoum, was met with swift condemnation by the international community, including the African Union and the Economic Community of West African States.

Niger's President Mohamed Bazoum, shown in this picture addressing the 77th Session of the UN General Assembly on Sept. 22, 2022, has been under detention since Niger presidential guards toppled him late last month. (REUTERS/File Photo)
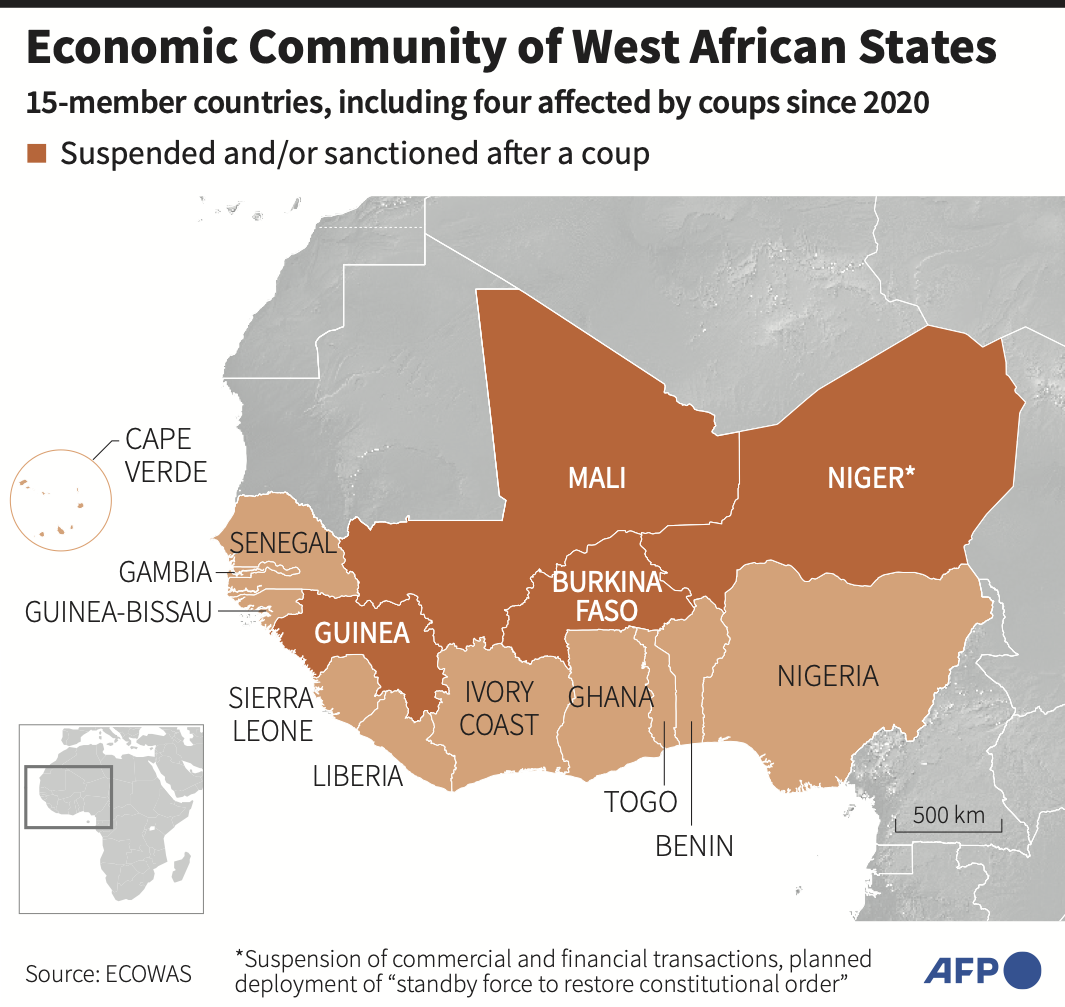
Sanctions have been imposed against the new ruling junta, led by Gen. Abdourahmane Tchiani, but hopes for the restoration of Bazoum’s rule are dwindling with each passing day.
The coup has raised questions about the viability of democratic transitions in Africa and the trajectory of political movements in the region.
The unsettling reality is that these military takeovers have derailed the democratic progress that many African nations had painstakingly made over several decades.
Before the recent wave of coups, the continent seemed to be moving toward civilian rule complete with democratic institutions and a more accountable and participatory system. These hard-won gains now appear to be under threat.
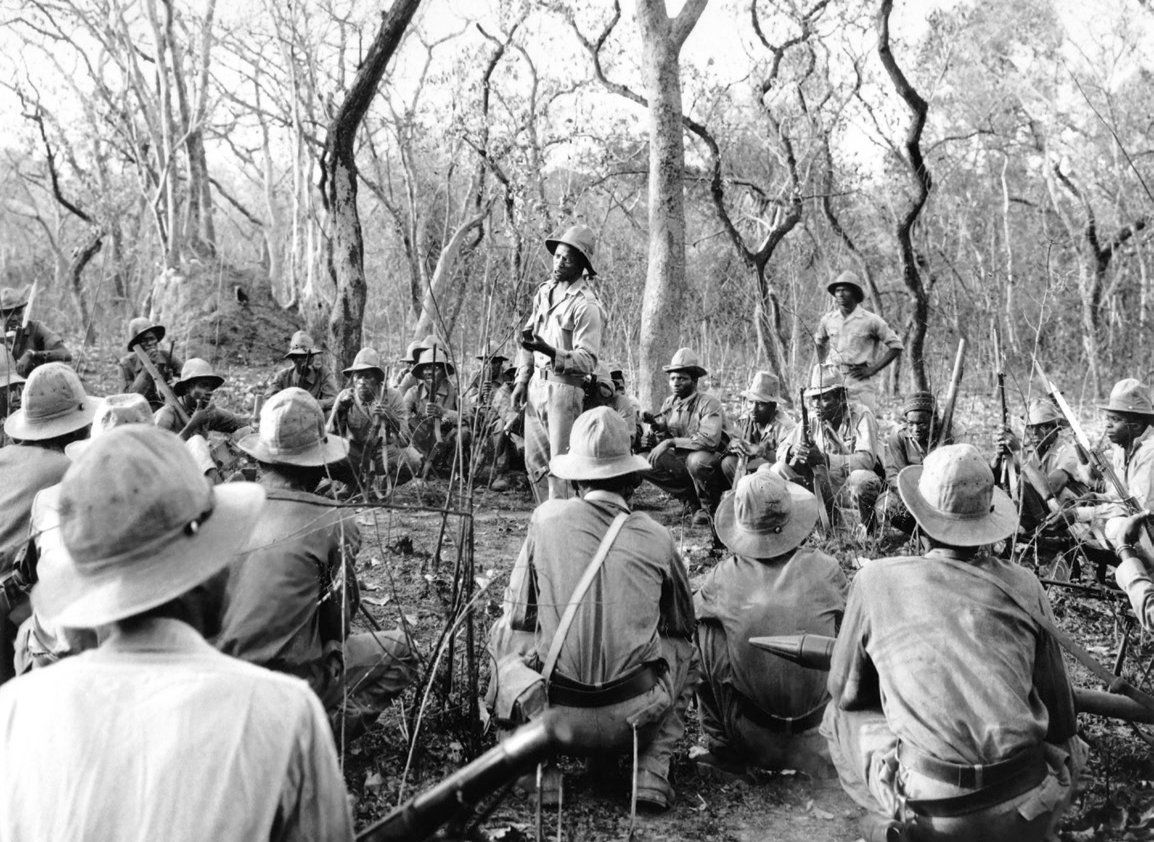

Fighters of the African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde, shown in this picture released in August 1971, started an armed rebellion since 1956 for the independence of the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, a Portuguese colony. (XINHUA / AFP)
After a decline in the number of such coups in Africa since 2000, Mali appeared to be the outlier when its military seized power in 2020.
However, 2021 saw a significant rise in military takeovers, with coups and attempted coups taking place in Chad, Guinea, Sudan and Niger. In 2022, there were five coup attempts, with two proving successful in Burkina Faso.
The implications of these coups extend beyond the borders of the affected countries, sending shockwaves across the entire continent, and causing concern about the fragility of democratic governance in Africa in the face of several existential threats.
The international community now watches with a mix of dismay and apprehension as military interventions become more frequent, raising doubts about the long-term stability of many African nations.
As neighboring countries and regional institutions grapple with the consequences of these coups, it is crucial to understand the unique challenges faced by African nations, particularly those in the Sahel region.
Experts say it is not only critical that the root causes of instability, such as economic stagnation, political discontent and historical legacies, are addressed. They say regional- and international-level cooperation has a strong role to play in supporting the restoration of democratic governance and preventing future military interventions.
“The recent coups witnessed in Africa are orchestrated by opportunistic military personnel who exploit the vulnerabilities of their nations’ feeble institutions and underdeveloped human conditions,” Gbenga Erin, a Nigeria-based analyst with ECOWAS, told Arab News.

Since West African nations gained independence, economic underdevelopment and grievances blamed by some on colonial rule have contributed to successive military coups. (AFP file)
Across the continent, there is a broad consensus that democracy offers the most favorable governance structure and warrants safeguarding, he said.
Nevertheless, the persistent issues of terrorism, corruption, poor infrastructure and socio-economic backwardness mean that much of the African population has been experiencing nothing but varying states of deprivation.
These challenges have consistently served as a pretext for those plotting coups.
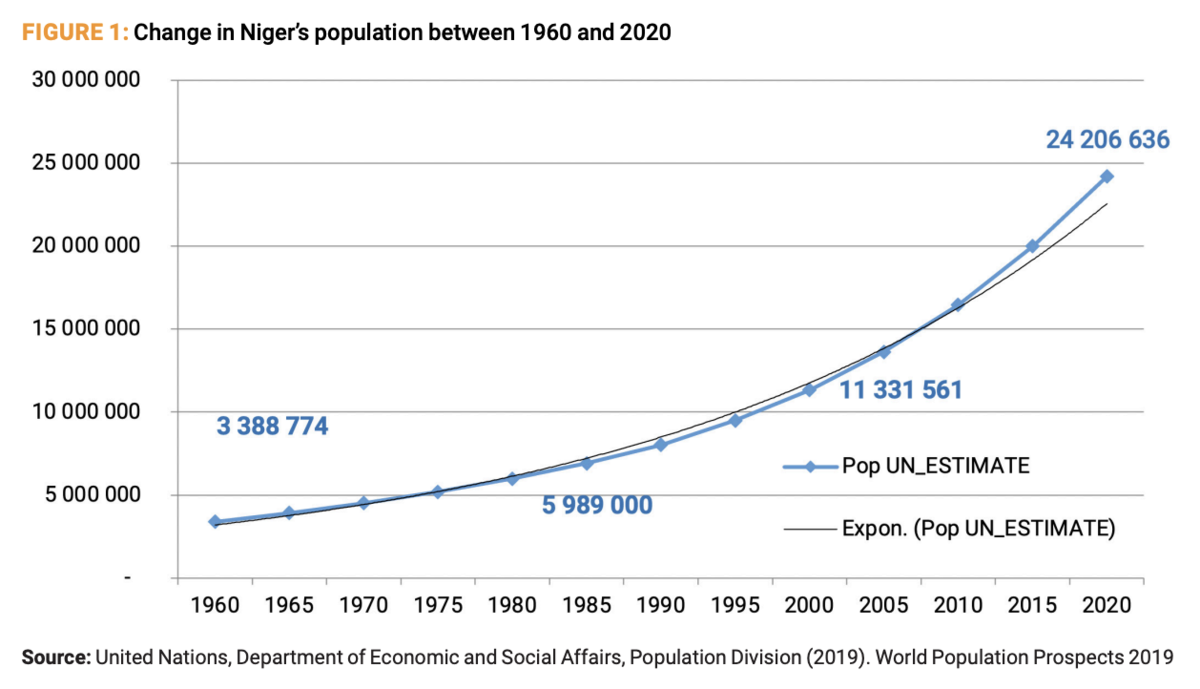
Demographic trends further magnify these challenges. Niger has the world’s fastest-growing population at a rate exceeding 3 percent annually.
UNFPA Infographic
The Sahel region, where these incidents are taking place, is currently home to approximately 354 million people, and the population in some of these countries is projected to more than double by 2050.
By then, Africa will have 40 percent of the global youth population aged 15 to 24, leading to larger class sizes in schools and universities that will outpace teacher training.
Consequently, young people are entering the labor market at a rate far greater than the growth of available jobs.

Infographic from World Bank Group discussion paper, August 2016.
Analysts believe the failure of regional governments to meet the basic expectations of their peoples, such as employment, physical safety, education and healthcare, has contributed to the recent spate of military coups.
“The local populations in these countries often have high expectations for improved governance, economic development and security,” Ovigwe Eguegu, a Nigeria-based policy analyst, told Arab News.
“But when these expectations are not met, there can be frustration with the existing government, leading some to support military interventions that promise change.”
Alex de Waal, a British researcher on African elite politics, argued in a recent piece for the New York Times that the response from developed nations has also been far from adequate.

A street merchant waits for customers in Niamey, Niger, on Aug. 14, 2023. (AP Photo)
He said many European and Middle Eastern countries have tended to focus on deterring migrants from leaving Africa rather than helping to create jobs that would encourage them to remain.
An assessment of democratic progress in Africa does reveal a mixed picture of success and failure. Despite certain advancements, the continent often finds itself taking one step forward and two steps back.
Regular elections coexist with democratic rollbacks, institutionalization of political parties with endemic corruption, and political freedoms with constraints and inequalities.
“Many of these governments are not delivering the so-called dividends of democracy, such as security, economic prosperity, protecting lives and property,” Christopher Ogunmodede, a foreign affairs expert from Nigeria, told Arab News.
“It’s not enough to sit back and lecture people about why democracy is so perfect and things like that. People nominally believe that they should have a civilian government ... but they have this very calling that suggests that if civilian governments are not working, they should be removed very fast.”
African democracies must reform if they are to succeed, says Fidel Amakye Owusu, an international relations and security analyst from Ghana.
“African countries urgently need reforms to enhance trust and legitimacy in elections, while corruption remains a critical issue,” but only democratic governments are equipped to improve things on the ground and fight extremism, he told Arab News.

A man stands outside a shop in a suburb of Niamey in Niger on August 14, 2023. Power grabs in the Sahel have been linked to the failure of many of the region's governments to deivering the so-called dividends of democracy, such as security, economic prosperity, and protecting lives and property. (AF/File)
At the same time, the conditions available to political opposition under which they can hold ruling parties to account, have not always been conducive to sustaining the democratic political order — something armed actors can capitalize on.
For instance, before the coup in Niger, democratic participation was relatively restricted, according to Ogunmodede, who highlighted the case of the M26 movement, composed of several civil society groups.
In 2022, M26 was barred from holding a protest against Operation Barkhane, a French counter-insurgency mission spanning the Sahel region, forcing it to limit itself to social-media campaigning.

Niger's junta supporters take part in a demonstration in front of a French army base in Niamey, Niger, on August 11, 2023. Restrictions against Niger'ss civil society groups are believed to have led them into supporting the military's plot to overthrow the country's democratically elected government. (REUTERS/Mahamadou Hamidou)
Analysts believe social media platforms have allowed for the spread of misinformation and disinformation about the security situation, undermining trust in the region’s democratic institutions.
While social media commentators claim the security situation was not improving, experts say Niger’s counterextremism operations were overall faring better than other nations in the region.
Beatrice Bianchi, a Sahel expert with the Med-Or Foundation, an Italian think tank, identifies social media as a vehicle spreading misinformation in the Sahel countries. “This has raised tensions particularly among the youth, and (has) radicalized people,” Bianchi told Arab News.
Having witnessed the coup unfold in the capital Niamey, Bianchi is of the view that the protests in support of the junta cannot be considered representative of the majority of the population.
“The junta violently crushed the anti-coup protesters, and then called for others to come to support them. These weren’t spontaneous protests in the beginning,” she said.
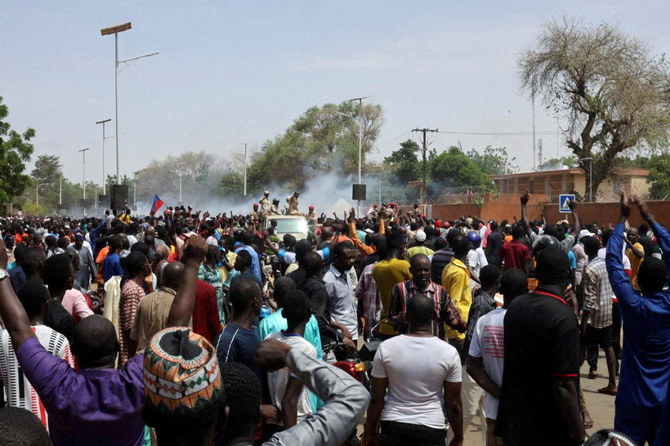

Nigerien security forces launch tear gas to disperse pro-junta demonstrators gathered outside the French embassy in Niamey on July 30, 2023. (Reuters)
Also, playing an anti-colonial card can be a very effective political tool, said analyst Eguegu, because “the legacy of colonialism continues to shape the discourse in all these countries.”
“The struggle for decolonization, coupled with concerns about foreign influence, is a significant factor in the political landscape, while the presence of foreign military installations aimed at fighting extremists, geopolitical interests, and regional security strategies add complexity to the situation,” said Eguegu.
Despite the political turbulence being witnessed in West Africa, Owusu, the Ghanaian expert, insists that “the destiny of Africa is intertwined with the fate of its democracies and the people of the continent deserve leaders who prioritize their welfare, promote accountable governance, and uphold the principles of democracy.”
As a result, the resurgence of military coups serves as a stark reminder that these ideals are not yet fully realized and the path forward requires a united effort to protect and nurture the democratic aspirations of African nations.
Doing so might ensure that the continent’s future is one of progress, prosperity and true democratic representation.