DUBAI: Two of the world’s biggest shipping firms, Maersk and Hapag-Lloyd, recently suspended the passage of container ships through the Red Sea’s Bab Al-Mandab Strait following a spate of attacks on commercial shipping by Yemen’s Houthi militia.
Disruption to the shipping route, which connects the Indian Ocean to the Red Sea, has interrupted the flow of trade and raised geopolitical tensions in the Middle East. One economy in the region that is particularly exposed is Israel.
“Shipping coming from Asia will now have to divert and go through the Cape of Good Hope, all around Africa to reach (Israel),” Riad Kahwaji, a Dubai-based Middle East analyst and founder and director of the Institute for Near East and Gulf Military Analysis, told Arab News.
“Definitely, economically, it will be impacted. It is not good for the economies of all countries that are on the Red Sea.”
And it is not just shipping routes close to home that are feeling the squeeze.

On Wednesday, Malaysia’s government announced it was imposing a ban on all Israeli owned and flagged ships, as well as any vessels headed to Israel, from docking at its ports, in response to Israel’s conduct in its conflict with Hamas.
Attacks on commercial shipping vessels in the Red Sea have increased significantly since mid-November in response to Israel’s bombardment of Gaza, prompting some vessels to halt operations in the region or to reroute via the southern tip of Africa.
Besides Maersk and Hapag-Lloyd, oil firm BP and oil tanker group Frontline have also said they will be avoiding the Red Sea route and rerouting via Africa’s Cape of Good Hope — a detour that can take 10 days longer, adding some 3,500 nautical miles to the journey.
Oil and gas prices have surged and shipping premiums have almost doubled for some carriers in response to the disruption.
The Houthi militia, which is part of the same Axis of Resistance as the Palestinian militant group Hamas, has said that the attacks on commercial shipping are an act of retaliation for the “oppression of the Palestinian people.”
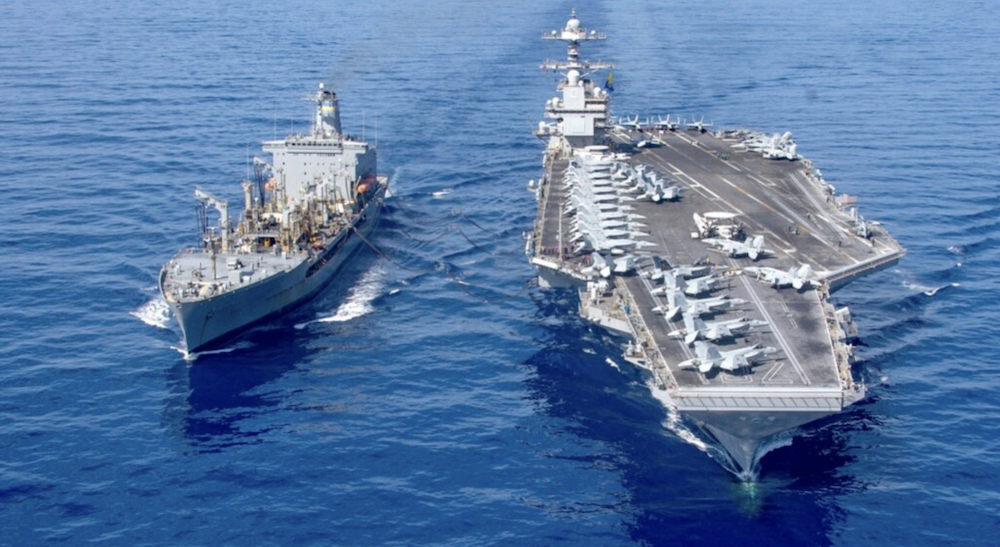

The USS Gerald R. Ford aircraft carrier refuels from the underway replenishment oiler USNS Laramie in the eastern Mediterranean Sea, Oct. 11, 2023. (US Navy via AP)
In one high-profile incident on Nov. 19, Houthi gunmen filmed themselves rappelling from a helicopter onto the deck of the cargo vessel Galaxy Leader, seizing control of the ship and its 25 international crew.
The Bahamas-flagged, British-owned vessel, operated by a Japanese firm but having links to an Israeli businessman, was headed from Turkiye to India when it was seized and re-routed to Yemen’s port of Hodeidah, where it has become a tourist attraction.
Experts warn that such attacks have raised the possibility of Israel’s war with Hamas in Gaza, launched in response to the Palestinian militant group’s attack on southern Israel on Oct. 7, spilling over into the wider region.
On Dec. 15, Danish shipping company Maersk instructed all its vessels in the Red Sea to pause voyages through the Bab Al-Mandab Strait after a “near-miss incident” involving a Maersk Gibraltar vessel and “yet another attack on a container vessel.”
Friday’s attacks on the Maersk Gibraltar and Hapag-Lloyd’s Al-Jasrah occurred near the Bab Al-Mandab, through which around 20,000 ships pass annually, serving ports throughout the littoral states, including Israel’s Port of Eilat.
The Maersk Gibraltar vessel was targeted by a missile while traveling from Salalah, Oman, to Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Both the crew and the vessel were reported safe.

Palestinians salvage their belongings after an Israeli strike in Rafah, Gaza Strip, in December. (AP)
On Dec. 19, the US government announced “Operation Prosperity Guardian” — an international maritime coalition involving Western and Arab countries to protect shipping in the Red Sea.
Lloyd Austin, the US defense secretary, held a virtual meeting with ministers from more than 40 countries on Tuesday, and called on more nations to contribute to efforts to keep shipping safe in the region.
“Right now, we have a multinational force led by the US, so the Israelis have been asked to not regulate (the situation) but to allow an international response force to deal with it so as not to turn it into a confrontation between the Houthis and Iran with the Israelis,” said Kahwaji.
“The pretext (for this new force) is that it is an attack on international shipping, so it is a global response. Today we have a coalition of nine countries that will likely grow larger, and it will conduct operations to protect the sea lanes and will likely retaliate to the attacks on the ships.”
INNUMBERS
* 12% Proportion of annual global trade that passes through the Red Sea.
* $1tn Value of commercial goods passing through the Red Sea per year.
* 20,000 Number of ships that pass through the Bab Al-Mandab Strait annually.
* 3,500 nautical miles Added distance around the Cape of Good Hope.
In some cases, Houthi militiamen have boarded or attempted to board merchant vessels, while in other instances they have targeted cargo ships with missiles and drones. Although damage has been minimal, the situation remains tense.
According to Reuters, several container ships anchored in the Red Sea have turned off their tracking systems while they adjust course.
Many ships are continuing to use the waterway, with several that have armed guards on board, according to Reuters news agency, citing data from the London Stock Exchange Group.
Although the Houthi attacks and resulting disruption to commercial shipping will likely have an impact on Israel’s economy, experts believe the country is unlikely to experience shortages or significant price inflation as a result.

Members of the Houthi militia during the capture of an Israel-linked cargo vessel at an undefined location in the Red Sea. (AP)
“Israel has outlets on both the Red Sea and the Mediterranean,” said Kahwaji, predicting that Israeli authorities will divert all shipping to the Port of Haifa, the largest of Israel’s three major international seaports.
“Yes, the Israeli economy will be affected, but does it mean that Israel will not be able to get anything? No,” he added.
As one of the world’s busiest shipping channels, the Red Sea is positioned south of the Suez Canal and constitutes the most significant waterway connecting Europe to Asia and East Africa.
Any ship passing through the Suez Canal to or from the Indian Ocean has to come via the strait of Bab Al-Mandab and the Red Sea.
The Suez Canal is the quickest sea route between Asia and Europe and is particularly important in the transportation of oil and liquefied natural gas.
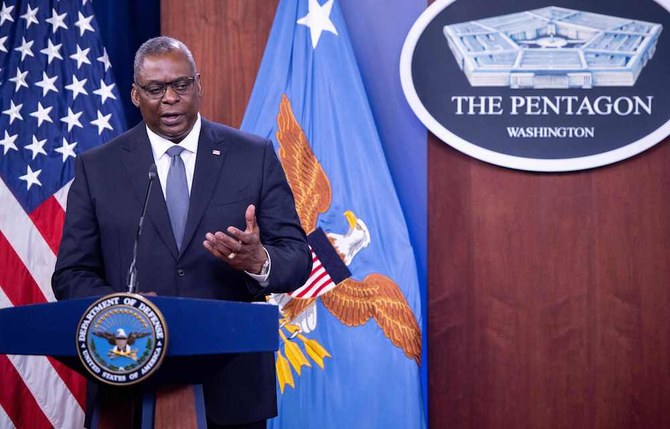

Lloyd Austin, the US defense secretary, held a virtual meeting with ministers from more than 40 countries on Tuesday, and called on more nations to contribute to efforts to keep shipping safe in the region. (AFP/File Photo)
About 12 percent of global trade passes through the Red Sea, including 30 percent of global container traffic and $1 trillion worth of goods each year.
Billions of dollars worth of commercial goods and supplies pass through the Red Sea every year. This means that delays or disruption can impact petrol prices, the availability of electronics and other aspects of global trade.
The Bab Al-Mandab Strait is a particularly vulnerable choke point along the shipping route, making it a target for piracy and terrorism. Located at its southern end of the Red Sea between Djibouti and Yemen, the strait is 18 miles wide at its narrowest point.
If the US-led naval operation in the Red Sea fails to deter further Houthi attacks on commercial shipping, leading to prolonged disruption, Israel may feel compelled to act against the Yemeni militia, marking a potentially dangerous regional escalation.
Indeed, given that the US is eager to avoid direct involvement in a potential conflict or an escalation involving Iran and its many proxy militias throughout the region, few expect the joint naval force to do more beyond patrols.
“It all depends on the rules of engagement to be adopted by this new naval joint force,” said Kahwaji.
“Will they adopt limited rules of engagement that confine them to protecting just the ships and providing defense against drones or missiles? Or will they take proactive measurements, carrying out pre-emptive strikes, retaliating against the attacks by going after the missile launchers, targeting the bases from where they are launching the drones?”
As of now, the attacks on commercial shipping pose a threat to regional economies, many of which are still adjusting their supply chains following the disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
If Houthi attacks in the Red Sea continue or become more severe, resulting in casualties among crew, the sinking of vessels, or attacks on military targets, then the conflict has every possibility of spreading beyond Gaza and engulfing the region.

























