DUBAI: Sigrid Kaag, the UN’s newly appointed senior humanitarian and reconstruction coordinator for Gaza, faces a monumental task as she takes the reins of the world body’s relief operations in the embattled Palestinian enclave.
Twelve weeks of relentless Israeli bombardment and restrictions on the delivery of humanitarian relief to displaced civilians have left the Gaza Strip “uninhabitable” and on the brink of famine, according to aid chiefs.
With the UN thus far unable to provide sufficient assistance to civilians, many in the aid community hope that a change in leadership could help move the dial on the stunted humanitarian response.
“Peace, security and justice have always been my motivations,” Kaag said in a statement on taking up the new UN role. “I have accepted this special assignment in the hope to contribute to a better future.”
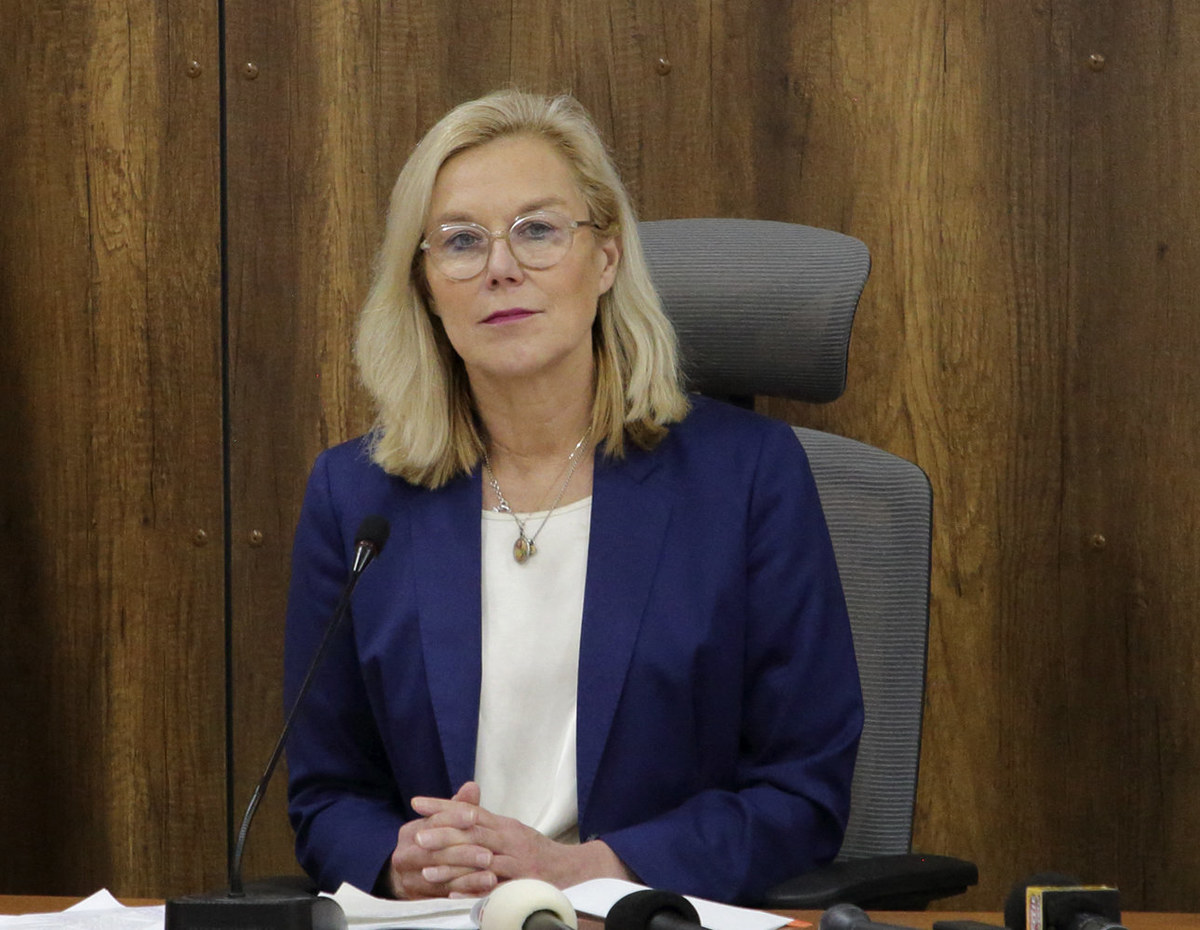

Sigrid Kaag takes on the UN’s aid brief for Gaza as Israeli forces continue to bombard the Palestinian enclave, causing displacement and a mounting health crisis. (AFP/File)
However, given the scale of the humanitarian challenges and the obstacles thrown up by Israel and its allies in Washington, some observers and analysts have been left wondering whether Kaag’s appointment will make any difference.
Israel mounted its military campaign in Gaza in retaliation for the unprecedented Oct. 7 attack on southern Israel by the Palestinian militant group Hamas, which resulted in the death of 1,200 people, most of them civilians, and the kidnap of 240.
In the months since the outbreak of fighting, more than 22,700 people have died in Gaza under Israeli bombardment, according to the Hamas-run health ministry, while almost two million have been displaced.
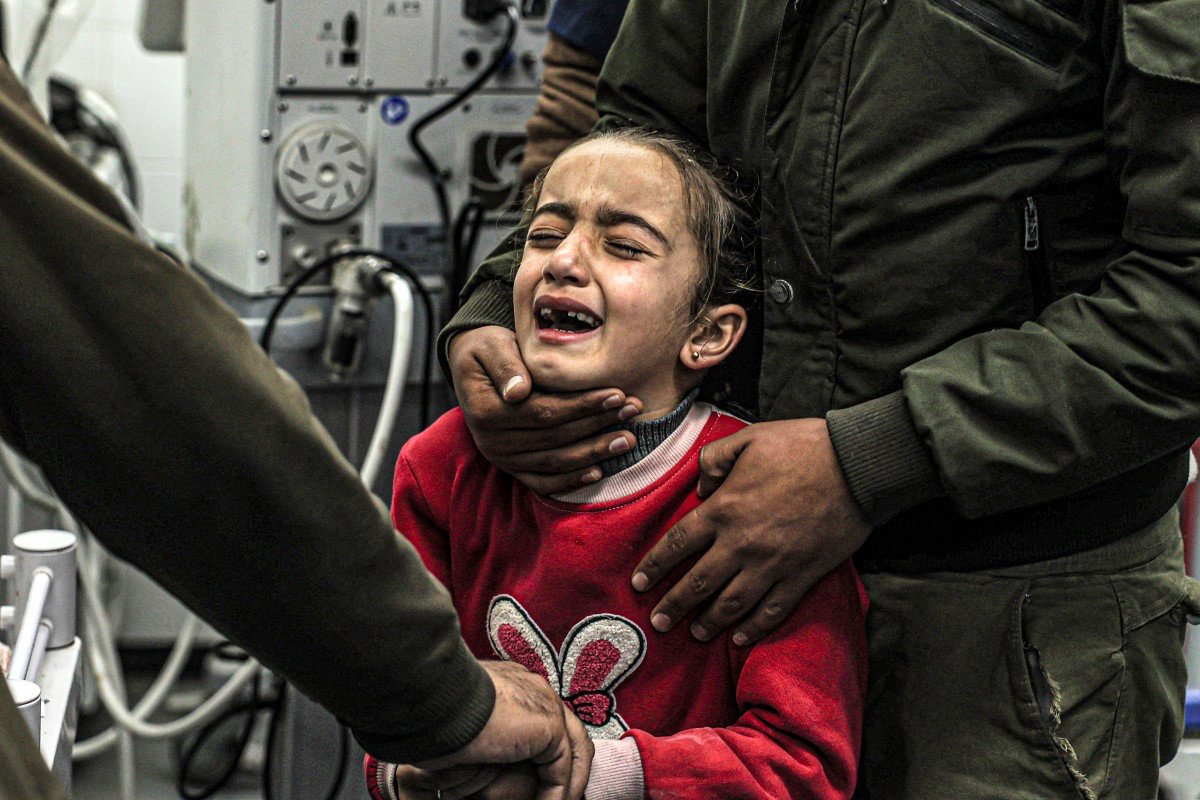

A girl mourns the death of her relatives who were killed by Israeli bombardment at the European Hospital in Khan Yunis in the southern Gaza Strip on December 31, 2023. (AFP)
In southern Gaza — where most of the enclave’s 2.3 million people now live in makeshift shelters with limited access to food, water and health care — the Israeli military has continued bombing raids, despite deeming these areas safe havens for displaced Gazans.
Kaag, who took over the UN’s Gaza relief operation on Jan. 8, was appointed to the new role following a breakthrough UN Security Council resolution passed on Dec. 22, which called on all parties to “facilitate and enable the immediate, safe and unhindered delivery of humanitarian assistance at scale.”
One of the Netherlands’ leading lawmakers, Kaag formerly served as the deputy head of government and finance and foreign minister under the country’s longtime prime minister, Mark Rutte.
FASTFACTS
Sigrid Kaag is the UN’s newly appointed senior humanitarian and reconstruction coordinator for Gaza.
Her role was created as part of a breakthrough UN Security Council resolution passed on Dec. 22.
The veteran politician has worked for UNRWA, UNICEF and as UN special coordinator for Lebanon.
When the Dutch coalition government collapsed and new elections were called at the end of November 2023, Kaag declared she would be retiring from politics. However, the Arab studies graduate has since returned to her old place of work at the UN to take on one of the most challenging tasks of her career.
From 1994 to 1997, Kaag was the head of the Donor Relations Department at UNRWA, and subsequently headed UNICEF’s Middle East and North Africa Regional Directorate in Amman, Jordan.
In 2013 and 2014, she led the joint mission by the UN and Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons to destroy Syrian chemical weapons. Afterwards, she held the position of UN special coordinator for Lebanon.

In this photo taken on July 28, 2009, Sigrid Kaag, then UNICEF's regional director for the Middle East and North Africa, gives a press conference in front of the debris of the American School in Beit Lahia, northern Gaza Strip, which was demolished during an Israeli military operation. (AFP/File)
Antonio Guterres, the UN secretary general, said Kaag “brings a wealth of experience in political, humanitarian, and development affairs as well as in diplomacy,” and is also fluent in Arabic as well as five other languages.
“She will facilitate, coordinate, monitor and verify humanitarian relief consignments to Gaza,” said Guterres, emphasizing how she will also establish a UN mechanism to accelerate aid deliveries “through states which are not party to the conflict.”
Antony Blinken, the US secretary of state, held a call with Kaag on Monday in which they underscored the importance of strengthening the coordination mechanism delivering humanitarian assistance to civilians in Gaza, according to a State Department statement.
They emphasized a shared commitment to reach the most vulnerable, including urgently expanding the entry of aid and commercial goods into Gaza, increasing the use of localized aid to meet immediate needs, and enhancing funding for humanitarian assistance.
While Kaag’s resume is impressive, the challenge of getting aid into Gaza is immense, frustrating the best efforts of the UN’s top humanitarian officials.
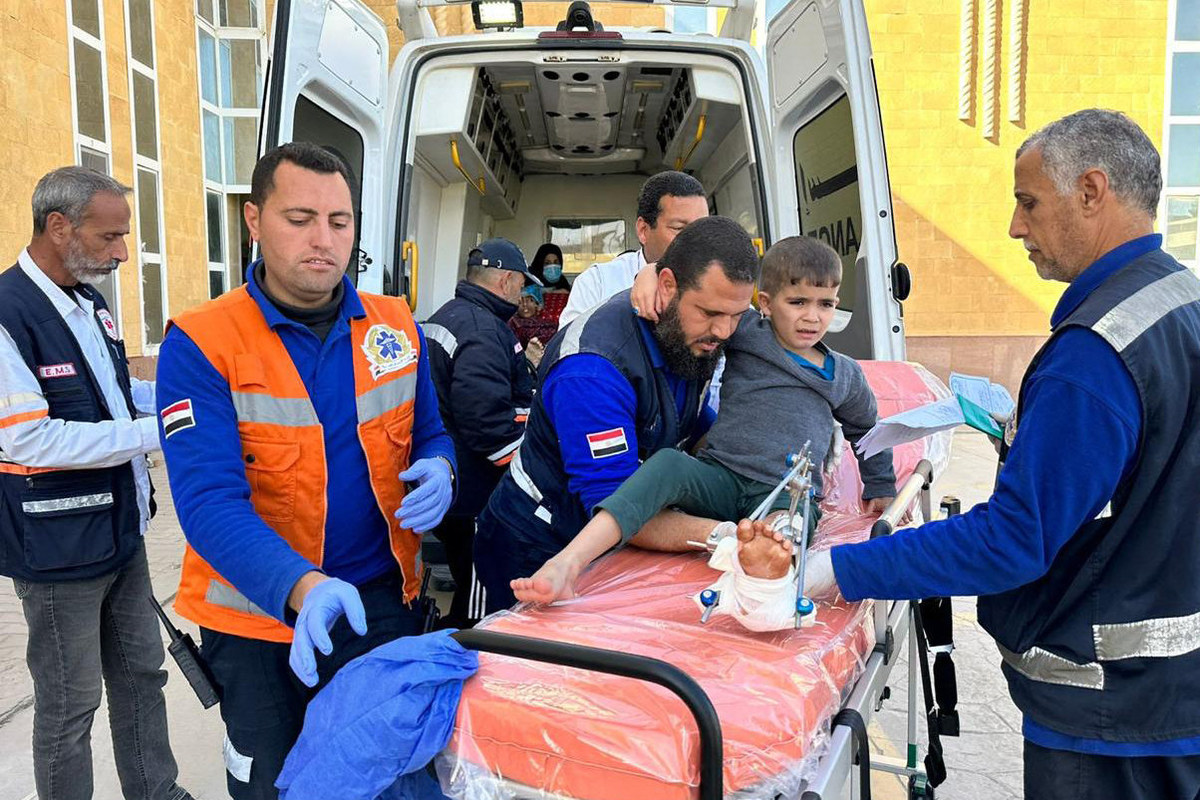

Egyptian paramedics transport an injured Palestinian child to a Red Crescent ambulance upon his arrival from Gaza via the Rafah border crossing on January 10, 2024. (AFP)
According to the UN’s aid chief, Martin Griffiths, Gaza has become a place of “death and despair” for Palestinians. In a special statement on Jan. 7, he said: “Gaza has simply become uninhabitable. Its people are witnessing daily threats to their very existence — while the world watches on.
“A public health disaster is unfolding. Infectious diseases are spreading in overcrowded shelters as sewers spill over. Some 180 Palestinian women are giving birth daily amidst this chaos. People are facing the highest levels of food insecurity ever recorded. Famine is around the corner.
“For children, the past 12 weeks have been traumatic: No food. No water. No school. Nothing but the terrifying sounds of war, day in and day out.”
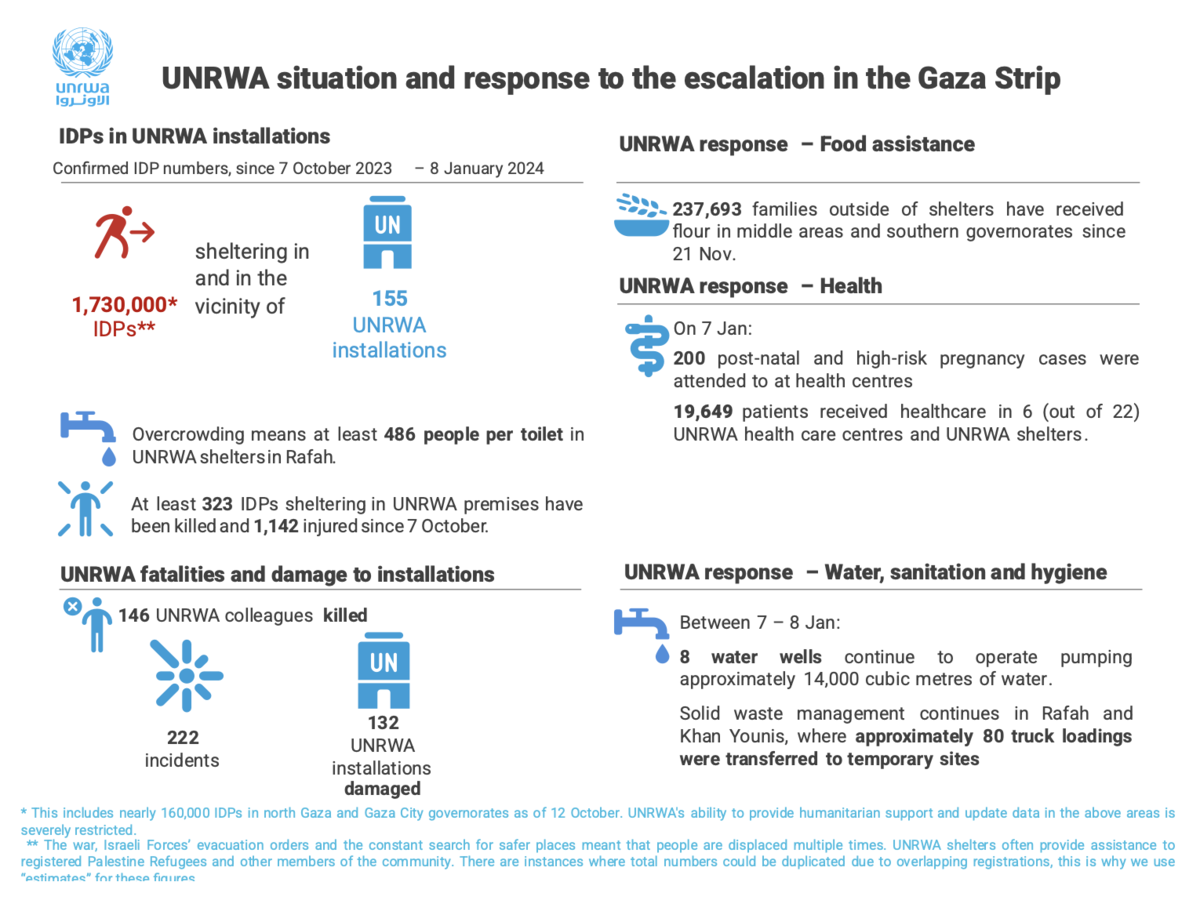
Amid severe shortages of food, water and medicine, disease and hunger are spreading throughout Gaza. According to UNRWA, some 40 percent of Gaza’s population is “at risk of famine.”
A report released at the end of December by 23 UN agencies and NGOs said that out of Gaza’s entire population of 2.3 million, 576,000 people are at catastrophic or starvation levels, with the risk of famine “increasing each day.”
The report blamed the hunger crisis on insufficient aid entering Gaza.
Although it is constrained by the geopolitical wrangling of the UN Security Council, the UN is widely seen as the only body capable of responding to the massive humanitarian challenges posed by the war in Gaza.
“Everything that happens in Gaza will require consensus,” Ziad Asali, the founder and president of the American Task Force on Palestine, a non-profit, non-partisan organization based in Washington, told Arab News.
“That is why the UN is the main venue for getting things done and not just proposed.”
However, there is a widespread view that the UN Security Council’s Dec. 22 resolution on aid for Gaza, adopted with 13 votes in favor and the US and Russia abstaining, has been so watered down that it will fail to meet the challenges posed by the conflict.
Lahib Higel, a senior analyst at the Middle East and North Africa program at International Crisis Group, told Arab News that only an immediate and lasting ceasefire would allow sufficient aid into Gaza.
“What we have argued at ICG from early on, and what was also reflected in the (UN) secretary general’s press conference after the resolution was adopted, is that you’re not going to have a significantly improved situation in Gaza unless you have a ceasefire,” Higel said.
“That’s really the bottom-line condition, but there’s an understanding that it is not on the horizon anytime soon.”
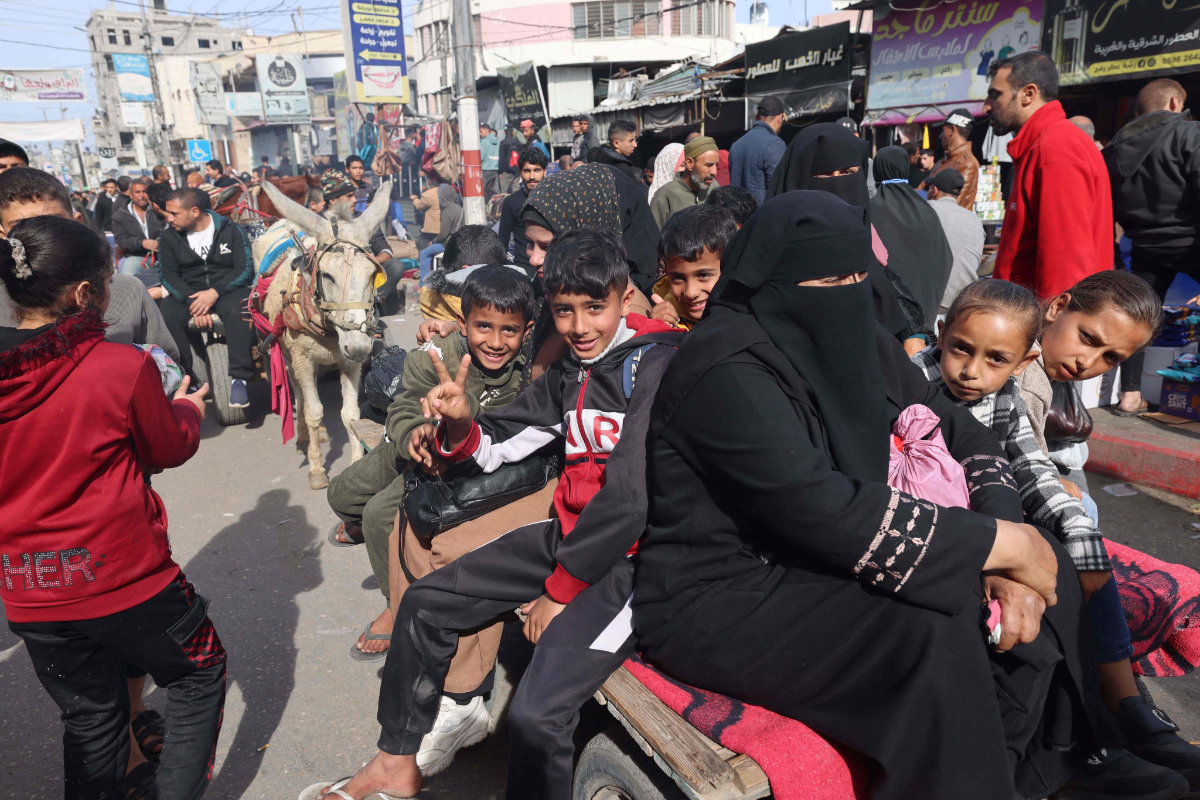

Palestinian children look from the windows of a minibus at a market in Rafah refugee camp in the Gaza Strip on January 8, 2024 amid continuing battles between Israel and Hamas forces. (Photo by AFP)
With a ceasefire off the table for the time being, humanitarians and diplomats must find ways to help Gaza.
“There have been several obstacles throughout this period,” Higel said. “The main one is, of course, that Israel not only shut down its border crossings with Gaza through which most of the commercial and aid traffic was coming … it also shut down all essential services to Gaza — electricity grids, water pipelines.”
Although some of those water pipelines have resumed operations, damage caused by Israeli bombardment is still widespread.
“They don’t operate full-time. You still don’t have electricity. There are constant communication blackouts, which means that distribution becomes extremely chaotic because people have been used to being notified through SMS messages, which they then can no longer receive,” Higel said.
“And then what was left was the border crossing in Rafah, which initially was a pedestrian crossing. It doesn’t have the infrastructure that Kerem Shalom (border crossing) has.”
While about 500 trucks a day used to enter Gaza via Kerem Shalom crossing with Israel before Oct. 7, only about 100 trucks a day can pass through the Rafah crossing with Egypt.
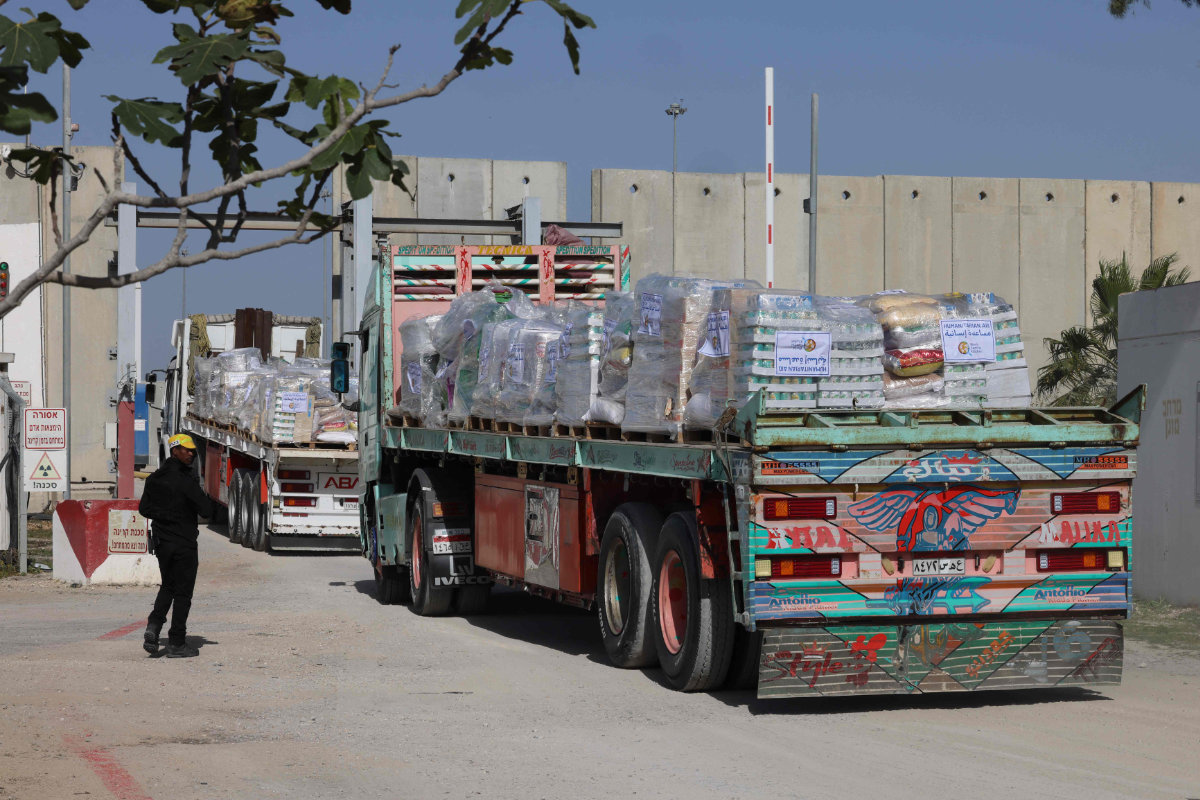

A truck carrying a humanitarian aid cargo arrives from Egypt on the Israeli side of the Kerem Shalom border crossing, before entering the southern Gaza Strip, on January 10, 2024, amid the ongoing conflict between Israel and the Palestinian militant group Hamas. (AFP)
Despite the reopening of Kerem Shalom in mid-December, Higel said that there was still not enough aid entering Gaza.
“Part of the reason is there is only so much that you can facilitate each day, considering the rigid inspections that Israel requires,” she said.
“Secondly, they (Israel) still reject a lot of goods based on their dual-use potential — fuel, construction material — that you would need for shelter.
“What can the UN do under these conditions? Quite little. It also took them quite a long time to set up a logistics hub that is actually working because the UN infrastructure was based in Israel.”
Other barriers to the UN’s work in Gaza include the denial of visas.
In early December, Israel told the UN that it would not renew the visa of its resident humanitarian coordinator in the Palestinian territories, Lynn Hastings, effectively kicking her out of the country.
The precise details surrounding the aid mechanism Kaag will devise have yet to be revealed. One thing is clear, however — she faces a colossal task finding new ways to get aid into Gaza while navigating Israel’s continuing bombardment and strict controls on entry.
Only time will tell whether Kaag’s appointment will prove transformative for Gaza’s stricken population or merely a continuation of the UN’s lackluster response to a deepening humanitarian catastrophe.