LONDON: It is easy to miss the gated entrance to the Gush Katif Museum, squeezed between two low-rise apartment blocks on an unremarkable side street in Jerusalem.
Since it opened in 2008, the museum has been a quiet, reflective backwater, a place of pilgrimage for a group of people who call themselves “the uprooted” — the survivors of a curious and, for them, traumatic chapter in the story of Israel and the Palestinians.
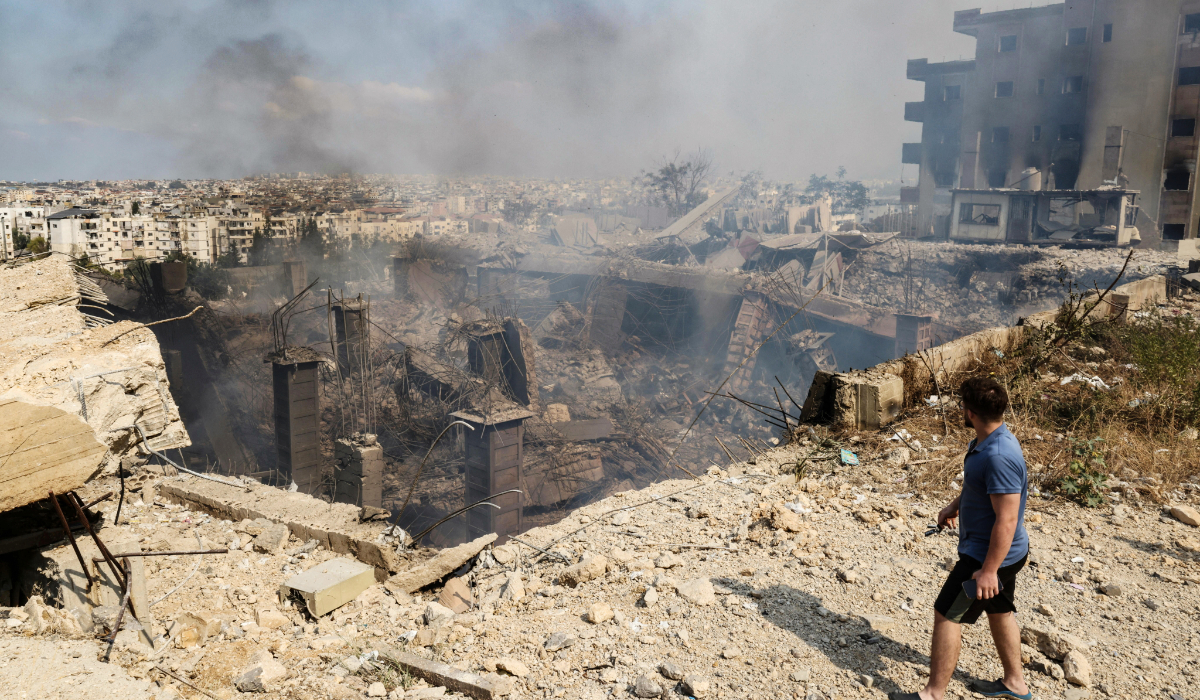
But since the Oct. 7 attack on Israel by Hamas-led militants, and the subsequent devastating retribution visited upon Gaza by the Israeli army, the museum suddenly finds itself rather more than a mere footnote to history.
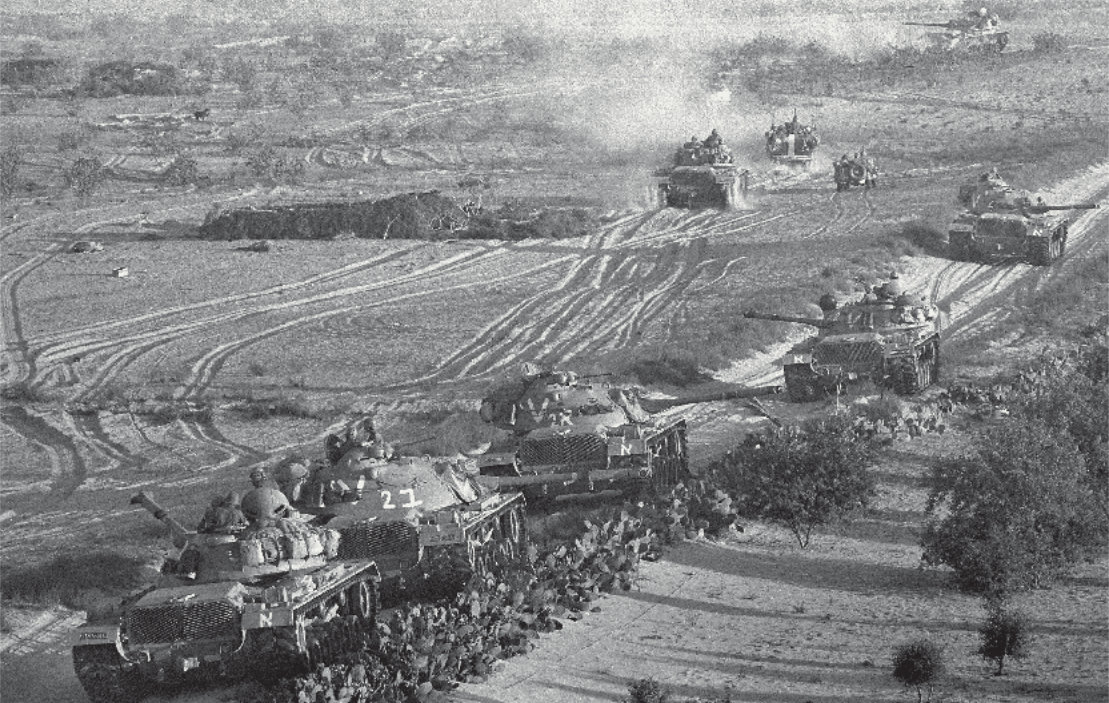

Israeli armor advances against Egyptian troops at the start of the Six-Day War June 5, 1967 near Rafah, Gaza Strip. Thirty-eight years later, the Israeli army pulled out of Gaza under Prime Minister Ariel Sharon's disengagement plan. (AFP/Getty Images/File)
Instead, it has become the spiritual home of an increasingly vocal rightwing movement in Israel calling not only for the reoccupation of Gaza by Israel, but also for the ethnic cleansing of all Arabs from the territory.
Situated barely 1.5 km west of Jerusalem’s Old City, the museum was established in August 2008 to commemorate the 17 Israeli settlements that sprang up in Gaza in the wake of the 1967 Six-Day War.
From 1970 onward the agricultural settlements, inhabited mainly by orthodox Jews and known collectively as Gush Katif, occupied a narrow coastal strip running north from the Egyptian border for about 12 km.
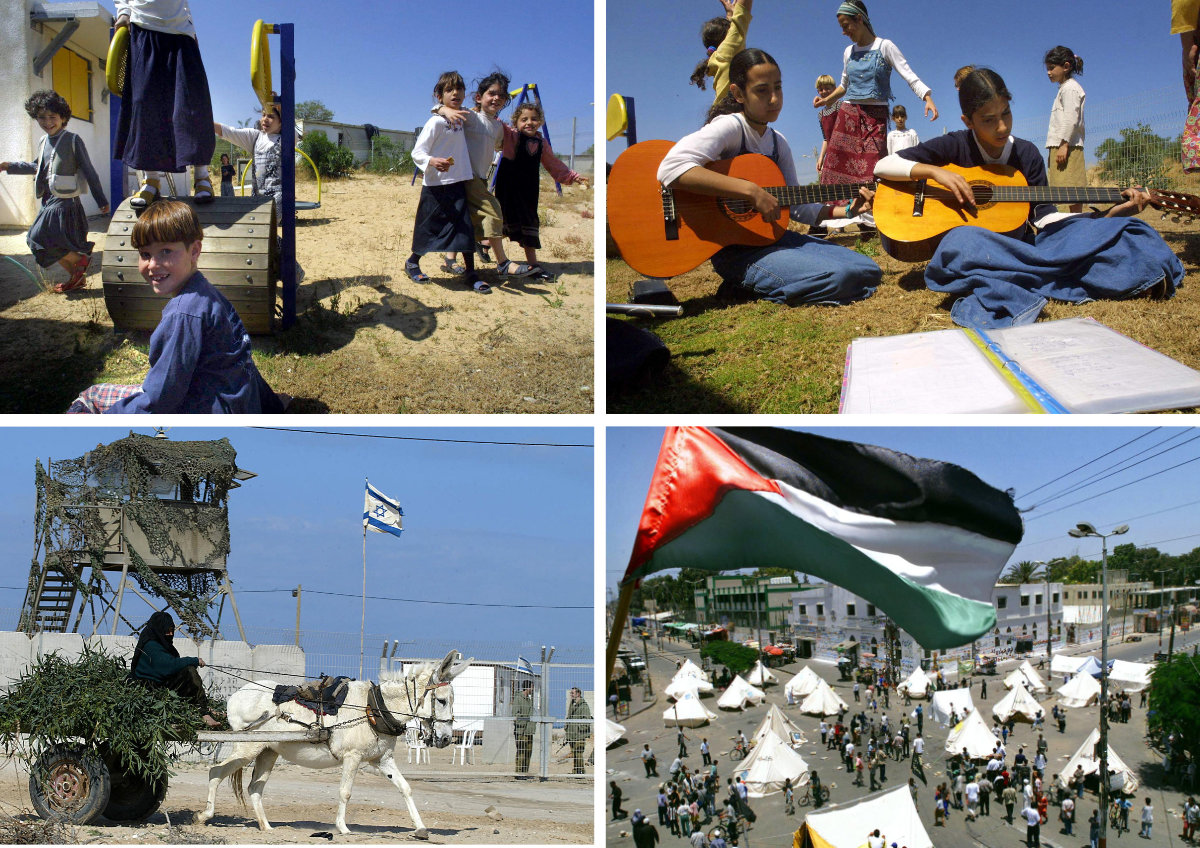

In this combination of images taken from 2001 to 2004, Israeli children (top photos) are seen at play in the Netzarim settlement in Gush Katif near the Gaza Strip. At the bottom are Palestinians living as refugees in their own homeland. As Palestinians escalated their resistance, the Israeli government decided to pull out from Gaza, forcibly uprooting Jewish settlers that it had previously encouraged to build homes on Palestinian lands. (AFP/File)
For 35 years the communities of Gush Katif, insulated from their Palestinian neighbors by a system of roads closed to Arab drivers and patrolled by a dedicated unit of the Israeli army, put down deep roots and thrived. They built homes, schools, synagogues and greenhouses on land they believed would belong to Israel forever.
But then it all came crashing down.
In what some in Israel still describe as a betrayal, and even a crime, in 2003 Ariel Sharon, the Israeli prime minister, announced his “disengagement” plan — a unilateral decision, taken in the face of stalled peace talks between Israel and the Palestinian Authority, to withdraw all Israeli settlements from Gaza.
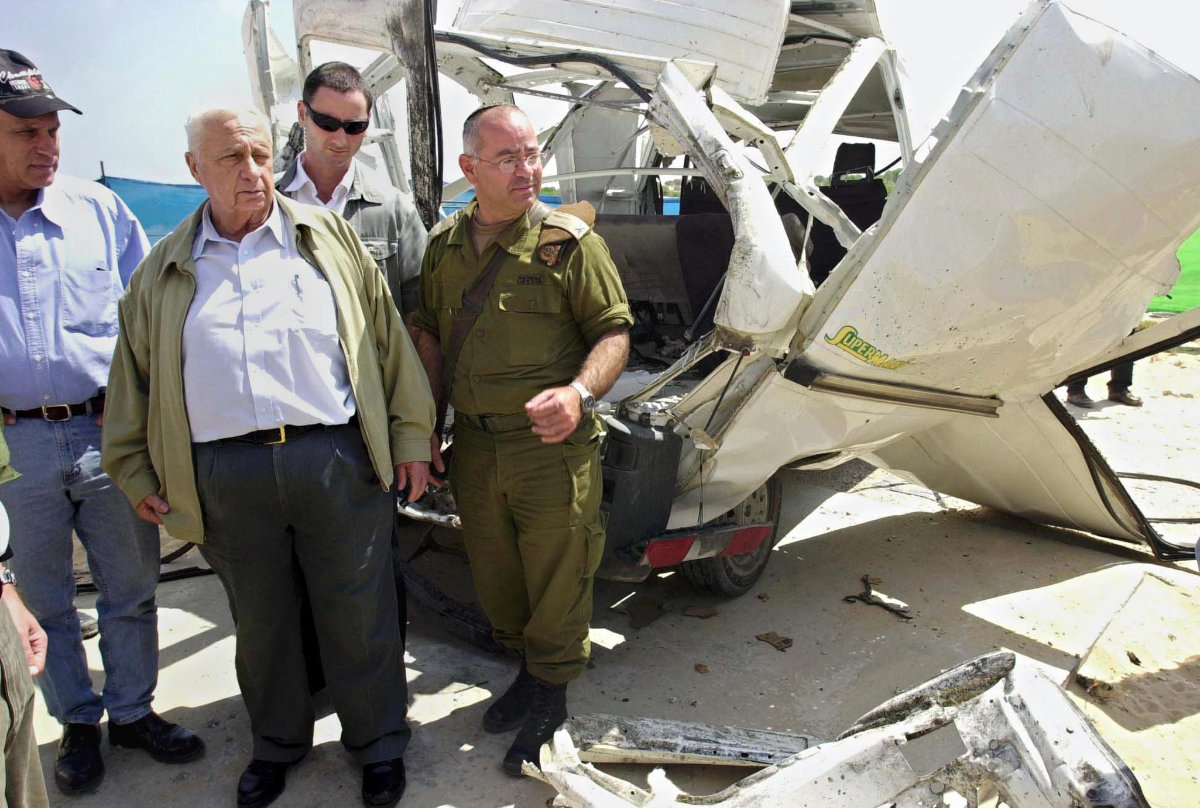

In this picture taken on May 4, 2001, Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon views the wreckage of a car that exploded at Rafah Yam in the Gush Katif group of Jewish settlements, amid Palestinian resistance. Sharon subsequently ordered an Israeli disengagement from Gaza, to the dismay of settlers who came to the captured Palestinian territory on government invitation. (AFP)
In a televised speech on Aug. 15, 2005, Sharon described the withdrawal as “the most difficult and painful step of all … very difficult for me personally.”
The decision had not been taken lightly, he said, “but the changing reality in the country, in the region, and the world, required of me a reassessment and change of positions.”
Israel, he added, “cannot hold on to Gaza forever.”
Without doubt, the “disengagement” was traumatic for the Jews of Gush Katif, more than 8,000 of whom lost their homes. For some, it was a second displacement, having been resettled there at the invitation of the Israeli government after Israel handed over the Sinai Peninsula to Egypt in 1982.
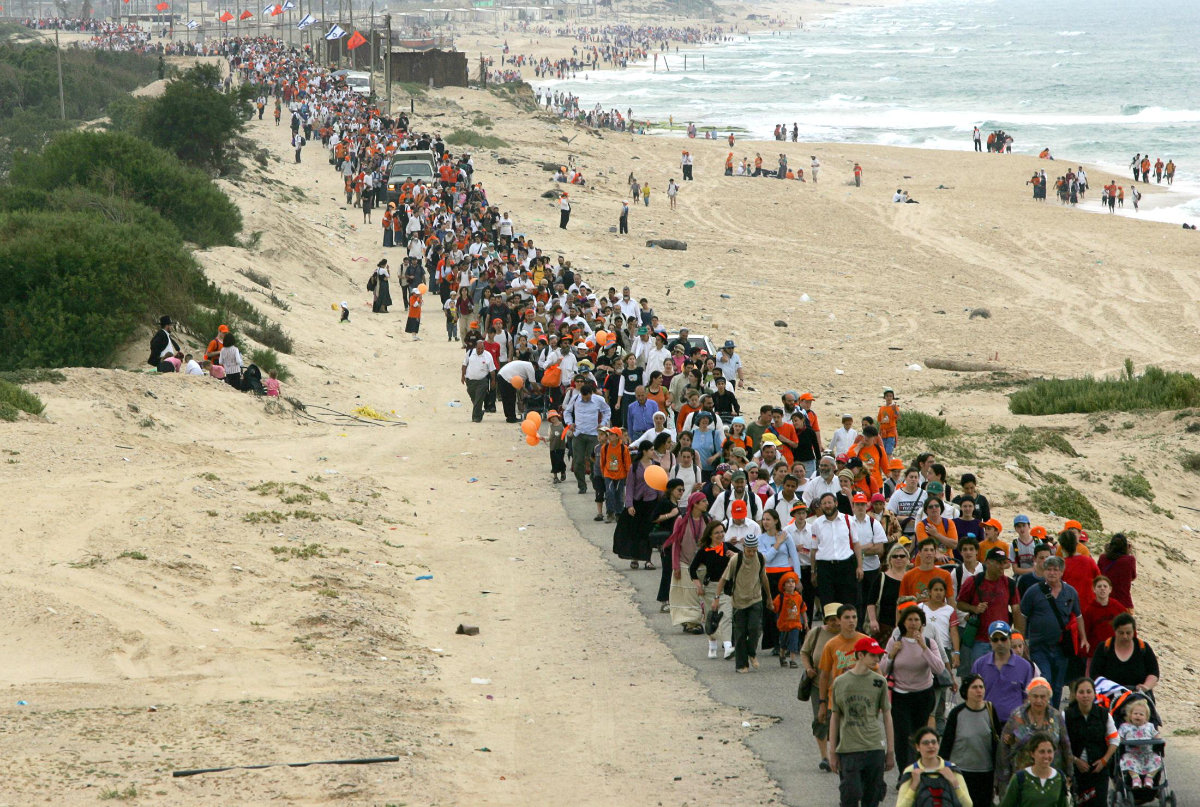

Tens of thousands of Israeli settlers and right-wing supporters march at a Gaza beach on April 27, 2005, in protest against Prime Minister Ariel Sharon disengagement plan. (AFP/File)
Contemporary newsreels playing at the Gush Katif Museum capture the traumatic forced evacuations that took place between Aug. 15 and 22 in 2005. Film of the final day of the evacuation shows women and children, crying and screaming, being dragged away from their homes by Israeli soldiers and police officers.
At one of the settlement’s synagogues, men, singing prayers and weeping, gather for the last time. Even as the settlements are being abandoned, diggers and bulldozers move in to destroy all the homes.
“I don’t think it’s fully appreciated that the religious right in Israel have their own calendar, and that there are traumatic events marked in that calendar,” said Daniel Seidemann, an Israeli attorney specializing in Israeli-Palestinian relations in Jerusalem and the founder of the NGO Terrestrial Jerusalem.
“Trauma number one came in 1967, when Moshe Dayan (then Israel’s defense minister) did not forcefully impose Israeli sovereignty over the Temple Mount, which they consider to be Israel’s biggest blunder.
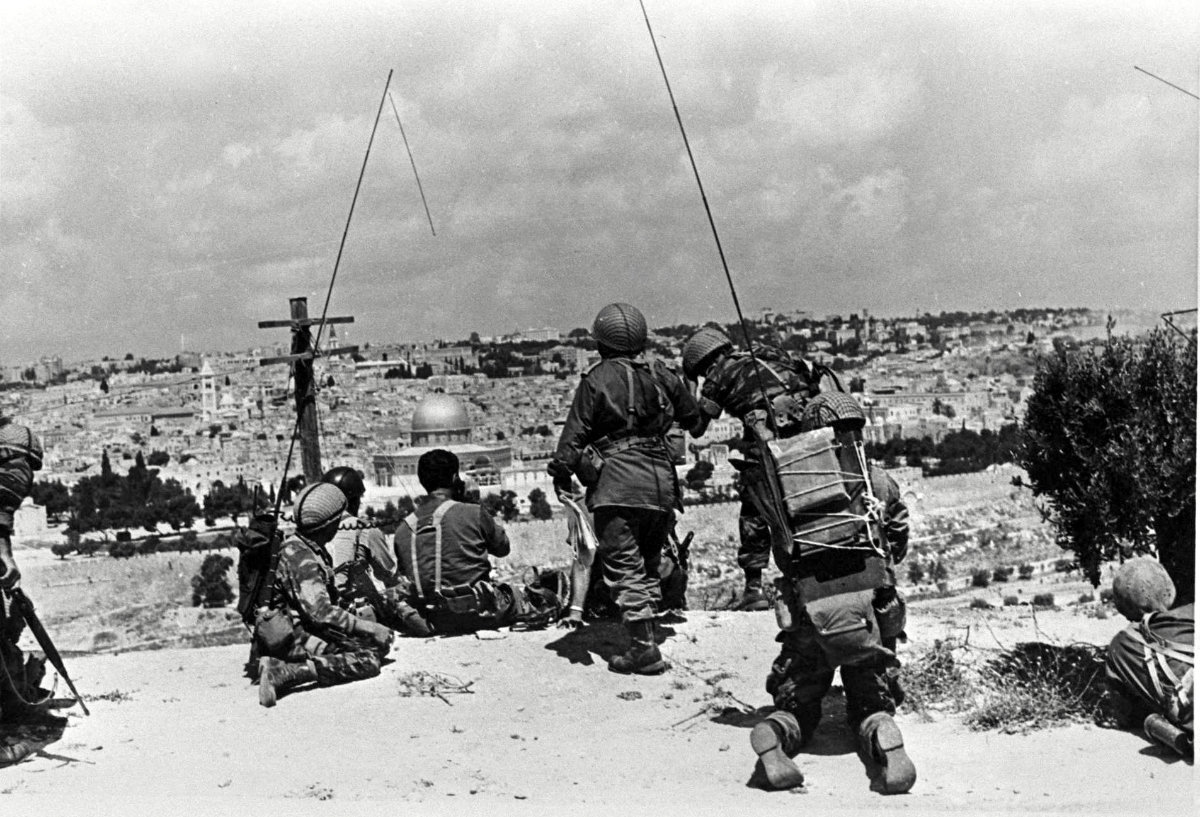

In this file photo, Israeli troops observe the old city of Jerusalem, home to the Dome of the Rock (C) in the Al-Aqsa Mosque Compound, Islam's third holiest site, known to Jews as the Temple Mount, the holiest site of Judaism, prior to their attack June 1967. (AFP)
“But the second-largest trauma for the religious right is the eviction from Gush Katif, a seminal, traumatic event for them.
“There is a yearning for returning now that that has been spoken about for years, but always by people who were perceived as on the fringe. Now, there are people in government who are also talking about it.”
GAZA STRIPTIMELINE
• Belongs to Ottoman Empire from 16th to 20th century.
• Taken by British troops in 1917 during the Second World War.
• British rule ends in 1918.
• Under Egypt’s military rule in 1950s and 1960s.
* Captured by Israel in 1967 Middle East war.
• Palestinians gain limited control under 1993 peace accord.
• Israel evacuates troops and settlers in August 2005.
• In 2006, Hamas scores victory in Palestinian parliamentary vote.
• In 2007 Hamas ejects political rivals and becomes sole ruler.
And not just talking about it. Rightwing politicians, including some in Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s cabinet, are joining forces with settler groups and calling for the lost homes of Gush Katif, and many more besides, to be rebuilt.
On Sunday Jan. 28, no fewer than a dozen government ministers and 15 members of the Israeli parliament joined 3,000 people at the Jerusalem International Convention Center for a “Resettle Gaza Conference,” a boisterous, noisy affair with a distinctly celebratory atmosphere.
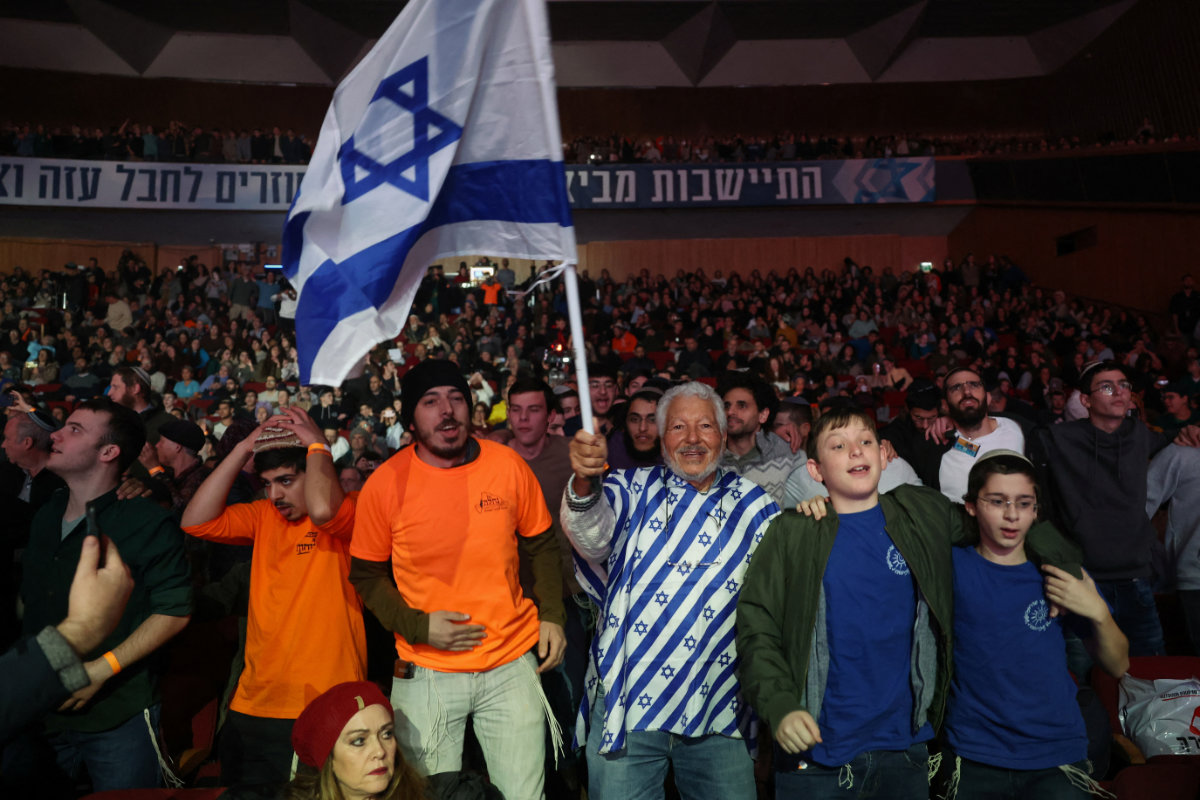

Jewish settlers gather at a convention in Jerusalem on January 28, 2024, calling for Israel to rebuild settlements in the Gaza Strip and the northern part of the Israeli-occupied West Bank. (REUTERS)0
Among the high-profile conference-goers was Netanyahu’s security minister Itamar Ben-Gvir, the darling of Israel’s religious right.
Last year Ben-Gvir led ultranationalist settlers on a series of provocative marches to the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound, which many Jewish religious extremists would like to see destroyed to make way for the construction of a third Jewish temple, replacing the two that the Jewish bible says were destroyed in antiquity.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
It was these marches, and an escalation in Israeli settler activities, that were cited by Hamas as the final provocation that triggered the Oct. 7 assault on Israel — an operation it named Al-Aqsa Flood.
Ben-Gvir has shown no remorse for his provocations. Indeed, on New Year’s Day he declared “we must promote a solution to encourage the migration of Gaza residents … a correct, just, moral, and humane solution.”
He added: “Make no mistake about it, we have partners around the world that can help, there are statesmen around the world to whom we can promote this idea.
“Encouraging the migration of the residents of Gaza will allow us to bring the residents of Gush Katif back home.”
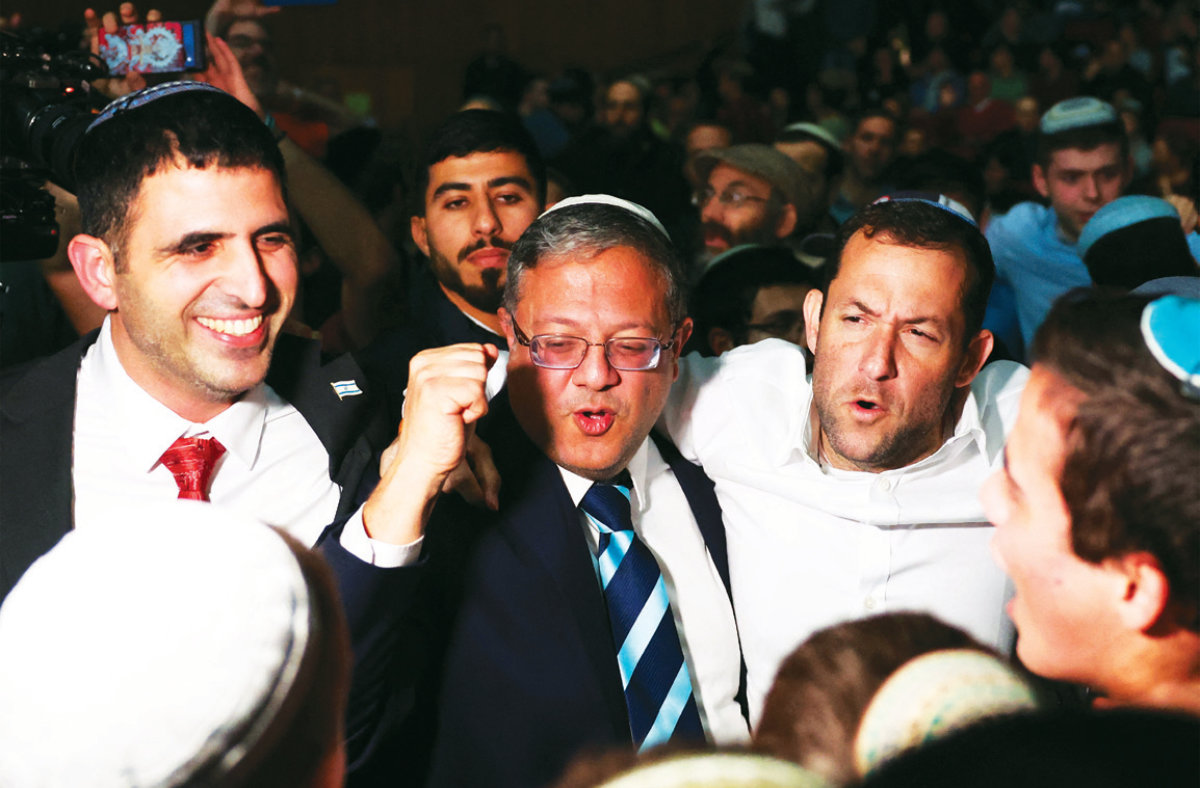

Israeli ministers, including national security minister Itamar Ben-Gvir, participated in a Resettle Gaza Conference in Jerusalem. (AFP)
His boss, Netanyahu, appears to share his sentiments.
In the face of growing international disquiet at Israel’s disproportionate military response in Gaza since Oct. 7, the man at the helm of the most rightwing government in Israel’s history, politically beholden to settler groups, has repeatedly rejected calls from allies, including the US, to pave the way for the long-awaited two-state solution.
Netanyahu’s position was made clear in a statement issued by his office on Jan. 21, the day after US President Joe Biden once again publicly urged him to seek peace by agreeing to the principle of Palestinian statehood.
“In his conversation with President Biden,” it read, “Prime Minister Netanyahu reiterated his policy that after Hamas is destroyed Israel must retain security control over Gaza to ensure that Gaza will no longer pose a threat to Israel, a requirement that contradicts the demand for Palestinian sovereignty.”
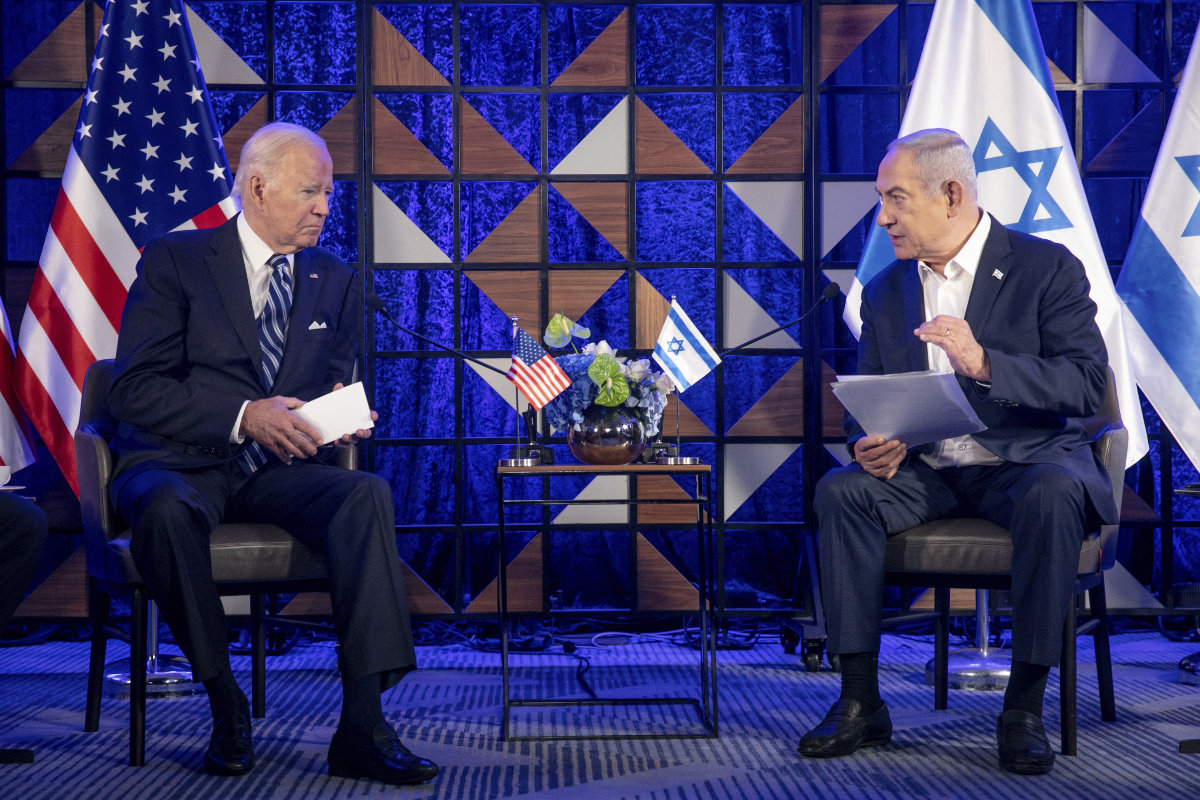

US President Joe Biden, left, meets with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu in Tel Aviv, Israel, on Oct. 18, 2023, to discuss the the war between Israel and Hamas. (Pool Photo via AP, File)
A return to Gush Katif, now being openly proposed by some in Netanyahu’s cabinet, would be compatible with this bleak vision of the future — but some want to go much further.
In a poll carried out in Israel in December, 68 percent of Israelis said they supported the idea of “voluntary migration” for the Arab citizens of Palestine. And on Dec. 25, the day after the poll results were published, Netanyahu told a meeting of his Likud Knesset faction that his government was already working on how to achieve this.
“Our problem is finding countries that are ready to absorb them, and we are working on it,” the Jewish Press reported Netanyahu as saying.
The idea is also gaining traction among the Jewish lobby overseas.
On Jan. 2, a columnist for the Jewish Press, the largest independent weekly Jewish newspaper in the US, a self-proclaimed “tireless advocate on behalf of the State of Israel,” offered a sinister take on the calls for “voluntary migration.”
“It stands to reason that rather than engage in futile efforts to persuade the countries of the world to open their gates to the most militant Islamist population on the planet, Israel should invest efforts in making life in Gaza unbearable,” wrote David Israel in a deeply disturbing column.
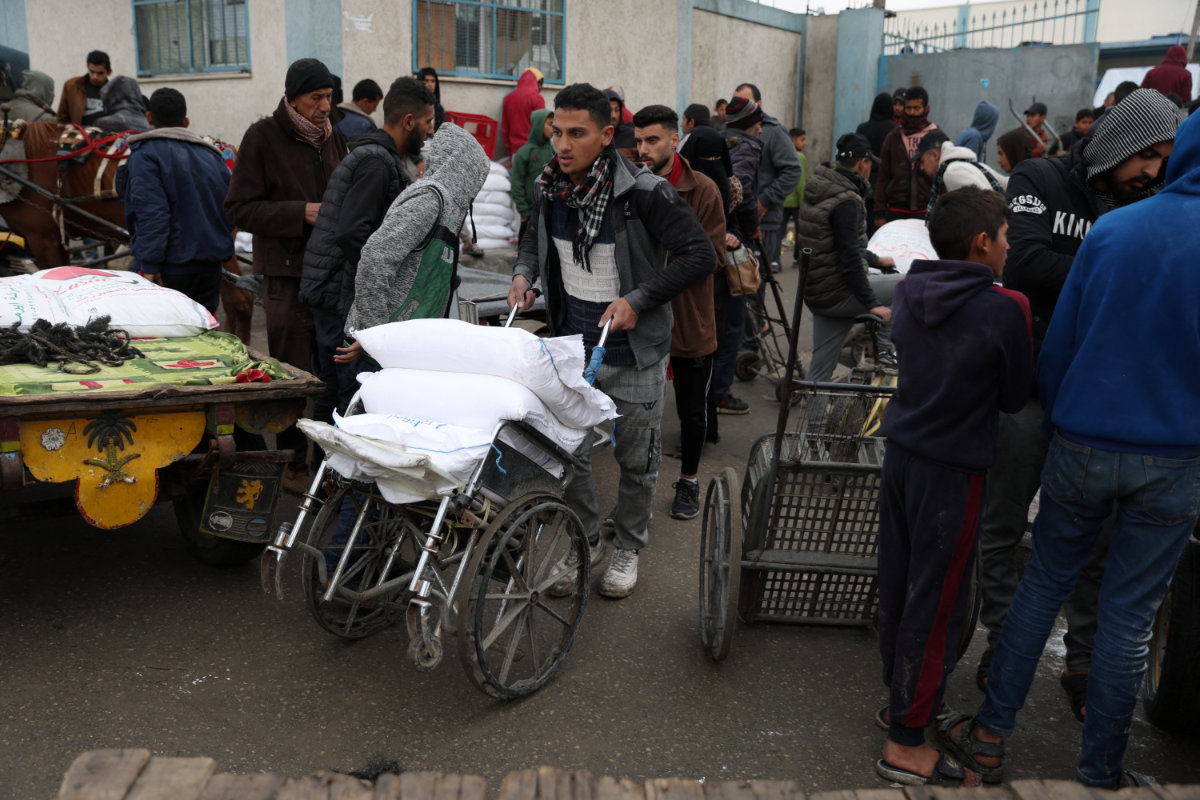

Palestinian man uses a wheelchair to transport bags of flour distributed by the United Nations Relief and Works Agency in Rafah, southern Gaza Strip, on January 29, 2024. If rightwing Israelis have their way, Palestinians should be sent to a country where they are welcomed. (REUTERS/File Photo)
He added: “The idea of tempting the Gaza Arabs onto large cruise ships that would take them to nicer places may be a romantic delusion, but the flight of thousands of starved individuals from a disease-ridden and ever-shrinking livable space would eventually bring down the Egyptian government’s barred gates.”
In Israel, not everyone is comfortable with the talk of resettling Gaza, a prospect that has alarmed even politically center-right newspaper The Jerusalem Post. In an editorial on Jan. 30, it labelled the Resettle Gaza Conference “disturbing” and condemned the calls to resettle Gaza as “divisive.”
But, given the support of a growing number of ministers and others, the paper concluded, “we can no longer say the resettlement of Gaza is a fringe idea that has no teeth or staying power.”
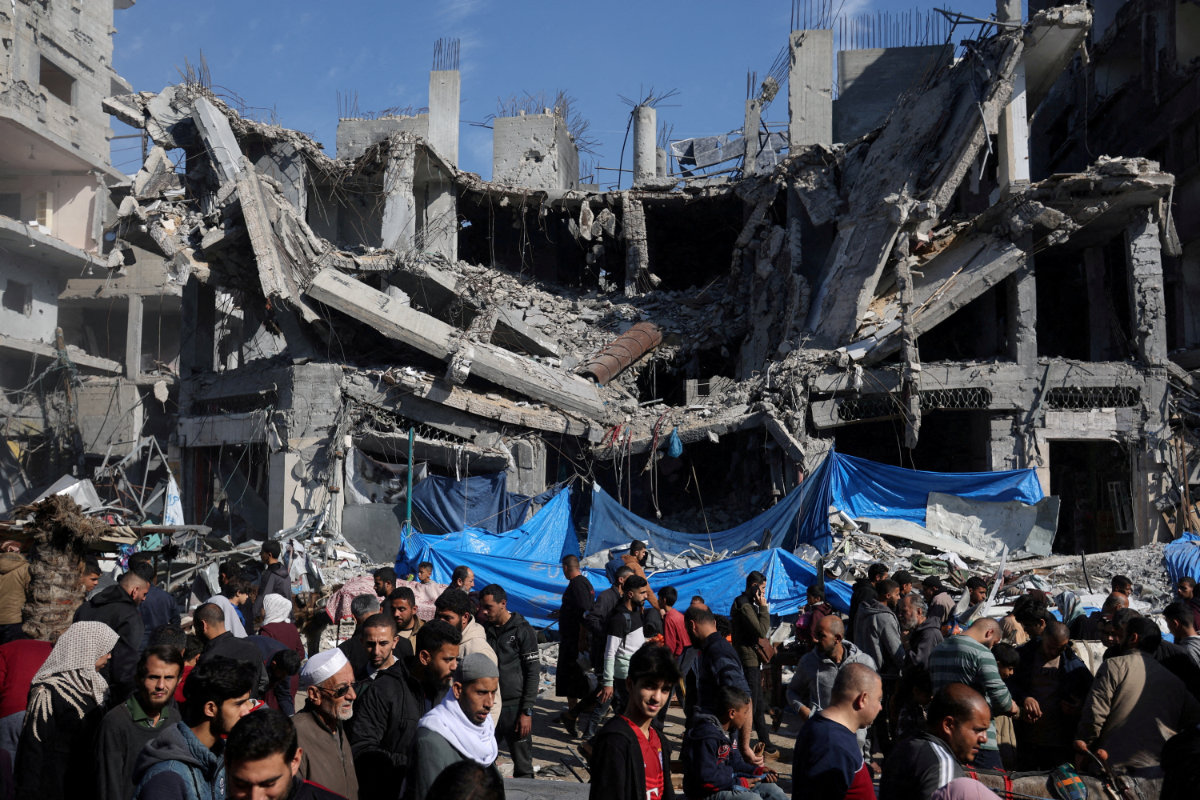

Palestinians shop in an open-air market near the ruins of houses and buildings destroyed in Israeli strikes during the conflict in Nuseirat refugee camp in the central Gaza Strip on November 30, 2023. Rightwing Israelis are toying with the idea of letting Palestinians leave Gaza "voluntarily" and migrate to other countries. (REUTERS/File Photo)
Omer Bartov, professor of Holocaust and genocide studies at Brown University’s Watson Institute for International and Public Affairs in Providence, Rhode Island, cautions against the use of euphemisms in the current situation.
“When speaking of a reoccupation of Gaza and the ‘voluntary’ removal of Palestinians, Ben-Gvir and followers are in fact speaking about the ethnic cleansing of Gaza, and then its settlement by Jews,” he said.
“They are quite open about that. There is nothing voluntary about this.”
If this came about, he said, “this would first of all mean that the entire IDF (Israeli Defense Forces) operation in Gaza will be seen as one of forcible removal of population, which is a war crime and a crime against humanity under international humanitarian law.”
It might also “be a breach of the Genocide Convention, as it could be presented as the intentional destruction of the part of the Palestinian people living in Gaza. This would put Israel directly in the sights of the International Court of Justice.”
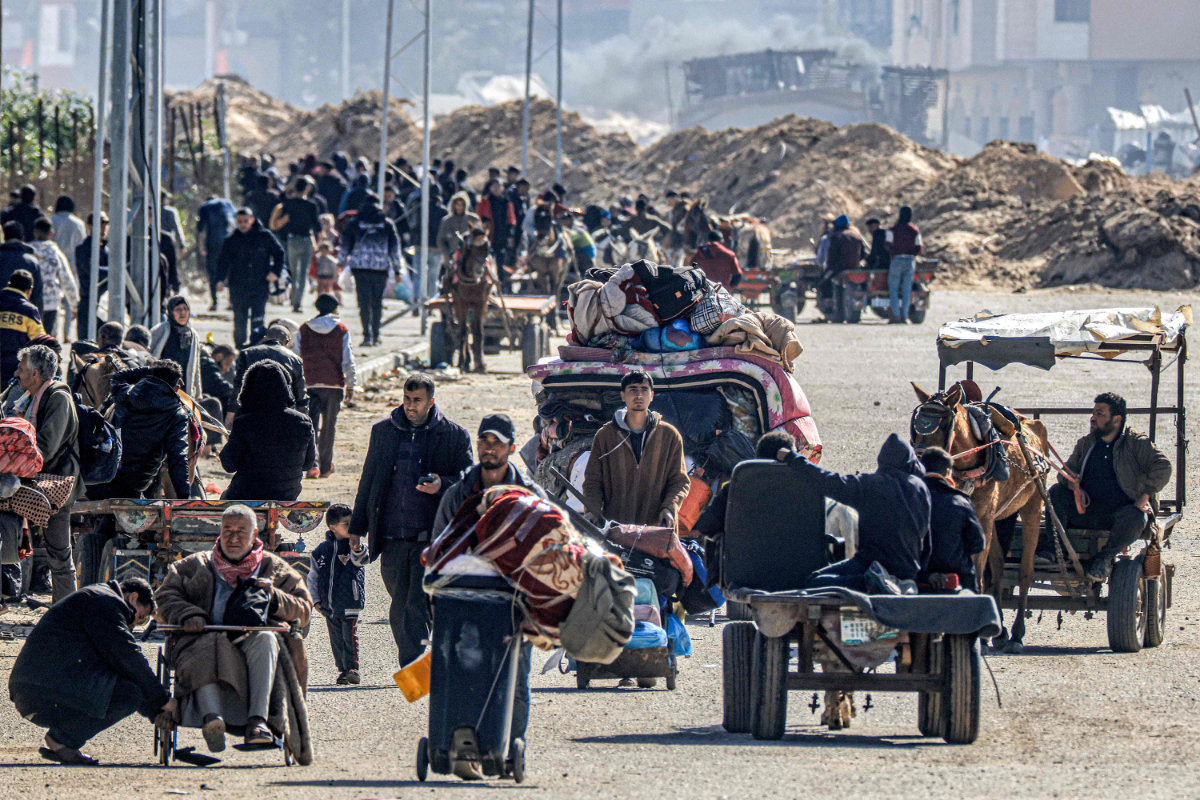

Displaced Palestinians flee from Khan Yunis in the southern Gaza Strip on January 30, 2024, amid the ongoing conflict between Israel and the Palestinian militant group Hamas. (AFP)
Bartov is, however, doubtful that “the radicals in the Israeli cabinet will manage to push this through. I don’t think there will be ethnic cleansing, but I do anticipate a major political crisis in Israel.
“This can be channeled in a positive direction only through massive pressure by the US and its allies, especially the UK, France and Germany, and then a regional agreement with Arab states, not least Saudi Arabia, to normalize relations with Israel on condition of the creation of an independent, possibly demilitarized, Palestinian state,” he said.
In the Gush Katif museum, among the artefacts on display, pride of place goes to a menorah, the traditional candelabra traditionally lit on the Jewish holiday of Hannukah. It was saved from the synagogue of Netzarim, the last of the Gaza settlements to be evacuated, and growing numbers in Israel would like to see it returned to what they believe is its rightful place.
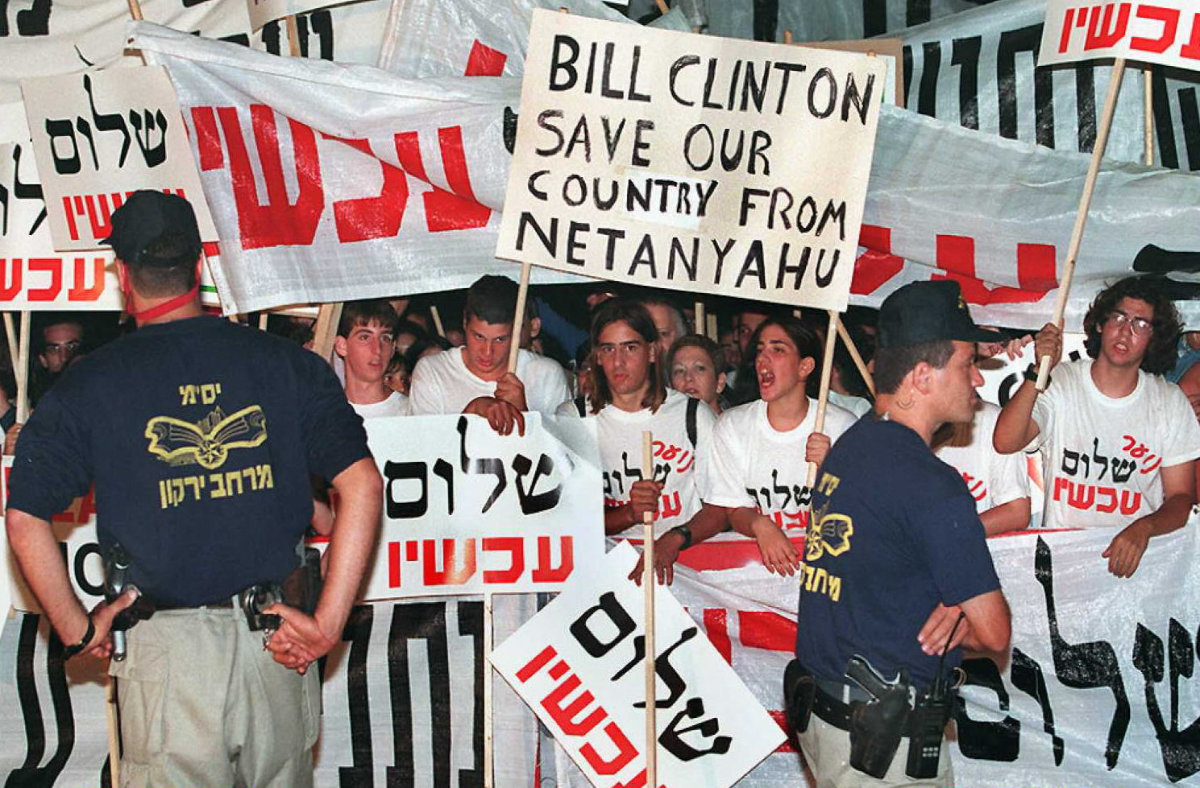

More than 20,000 Peace Now demonstrators gathered in Tel Aviv on October 1, 1996, calling for a continuation of the peace negotiations between Israel and the Palestinians. Twenty-seven years after, Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu is still in office, leading right-wing extremists in posing an obstacle to peace. (AFP/File)
In a film shown at the museum, Rivka Goldschmidt, one of the “Uprooted” from Gush Katif, speaks of her hopes for the future.
“It could be that our children will be able to return to Gush Katif and that will be a great comfort,” she says.
“I don’t know if it will happen, or when it will happen, but in the back of my mind that is an aspiration because there was something there that was great and tremendous, built by honest people.”
Gush Katif, she adds, “was vacated for no reason and it could be that our children, maybe our grandchildren, will return there one day.”
If Netanyahu and the rightwing ministers in his cabinet get their way, that day could be sooner than anyone could have predicted.
And if that happens, the prospects for a two-state solution and the peace for which so many Palestinians and Israelis have prayed for so long will likely have been dashed for generations to come.