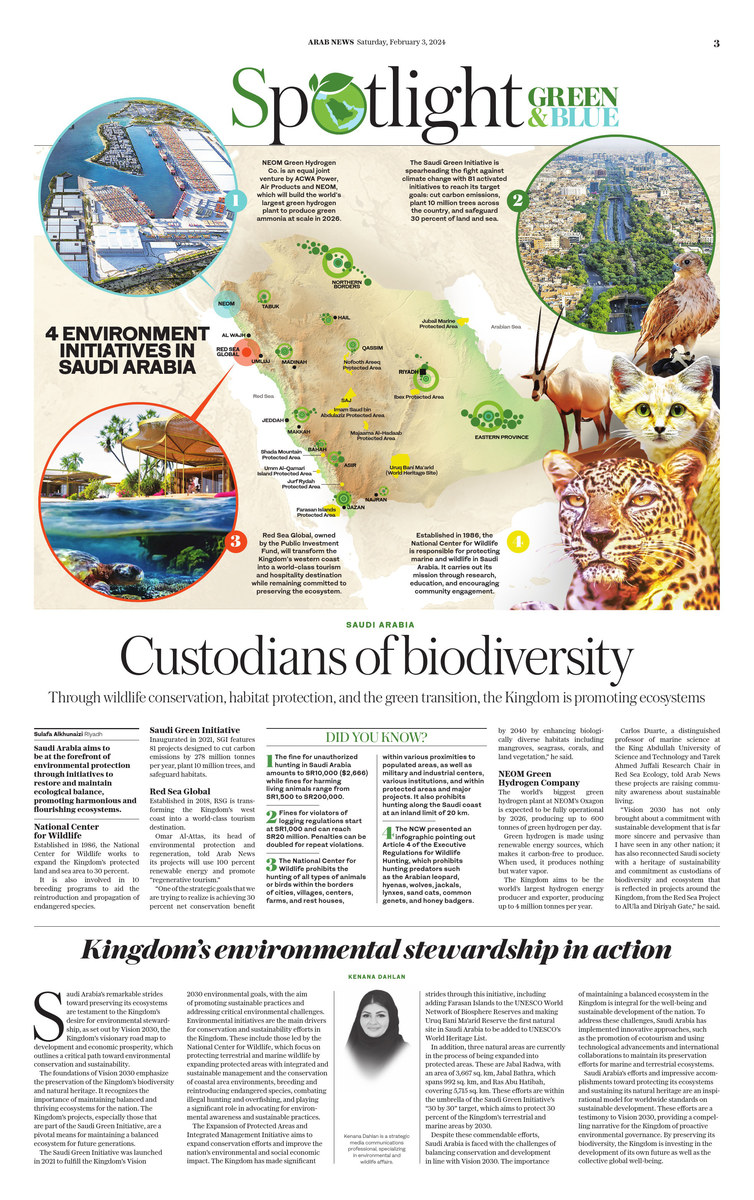
RIYADH: Saudi Arabia aims to be at the forefront of environmental protection through initiatives aimed at restoring and maintaining the ecological balance, which promotes harmonious and flourishing ecosystems.
Climate action, clean energy, and preserving habitats are just some of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals incorporated into Saudi Arabia’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
The SDGs serve as a blueprint for achieving a balanced ecosystem for wildlife, water, and the environment in the Kingdom.
Without balance, ecosystems face major challenges from global warming, water shortages, and the loss of biodiversity.
Carlos Duarte, a distinguished professor of marine science at the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology and Tarek Ahmed Juffali Research Chair in Red Sea Ecology, has spent 40 years researching ocean ecosystems.
“Loss of biodiversity reduces the capacity of ecosystems to maintain their functions under stress, such as under climate change,” Duarte told Arab News. “It directly impacts food security, but also by undermining pollination, the nursery role of many ecosystems for fisheries, and pest and disease control.
“It also represents the loss of natural products and genes of potential interest in pharma, cosmetic, food, energy, and environment applications before we have even discovered them.
“These are the major consequences of biodiversity loss, climate change and the impact of widespread pollution on our societies, economies, and well-being. The emerging concept is one of ‘one health,’ which recognizes that our health and that of our ecosystems are intimately linked, so that there are no healthy people on a sick planet.”
National Center for Wildlife
Established in 1986, the National Center for Wildlife is responsible for protecting and preserving plants and animals in Saudi Arabia.
The center is leading the initiative to expand the Kingdom’s protected land and sea area to 30 percent, to help rehabilitate ecosystems and enrich biodiversity.
DIDYOU KNOW
1
The fine for unauthorized hunting in Saudi Arabia amounts to SR10,000 ($2,666) while fines for harming living animals range from SR1,500 to SR200,000.
2
Fines for violators of logging regulations start at SR1,000 and can reach SR20 million. Penalties can be doubled for repeat violations.
3
The National Center for Wildlife prohibits the hunting of all types of animals or birds within the borders of cities, villages, centers, farms, and rest houses, within various proximities to populated areas, as well as military and industrial centers, various institutions, and within protected areas and major projects. It also prohibits hunting along the Saudi coast at an inland limit of 20 km.
4
The NCW presented an infographic pointing out article 4 of the Executive Regulations for Wildlife Hunting, which prohibits hunting predators such as the Arabian leopard, hyenas, wolves, jackals, lynxes, sand cats, common genets, and honey badgers.
5
Hunting endemic birds in the Kingdom is also prohibited, in addition to ungulates, including the Arabian oryx, the sandy-colored goitered antelope, the mountain gazelle (whether found in mountains or on the Farasan Islands), and the Nubian ibex.
It is also involved in 10 breeding programs to aid the reintroduction and propagation of endangered species including the Arabian oryx, sand gazelle, mountain ibex, bustards, and ostriches, as well as predators, such as the Arabian wolf, striped hyena, lynx, and cheetah.
The NCW recently collaborated with the Saudi Konoz Initiative, under Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Media’s Center for Government Communication, on “Horizon,” a Netflix documentary showcasing the Kingdom’s diverse wildlife.
Saudi Green Initiative
Inaugurated in 2021, the Saudi Green Initiative features 81 projects designed to cut carbon emissions by 278 million tonnes per year, plant 10 million trees across the country, and safeguard habitats.

Caption
The SGI uses the circular carbon economy, a framework focused on managing emissions. Saudi Arabia has implemented more than 30 CCE initiatives across the energy system to date.
One of the SGI’s focus areas is “whole-of-society action,” which encourages the public and private sectors to work together and enables citizens to participate.
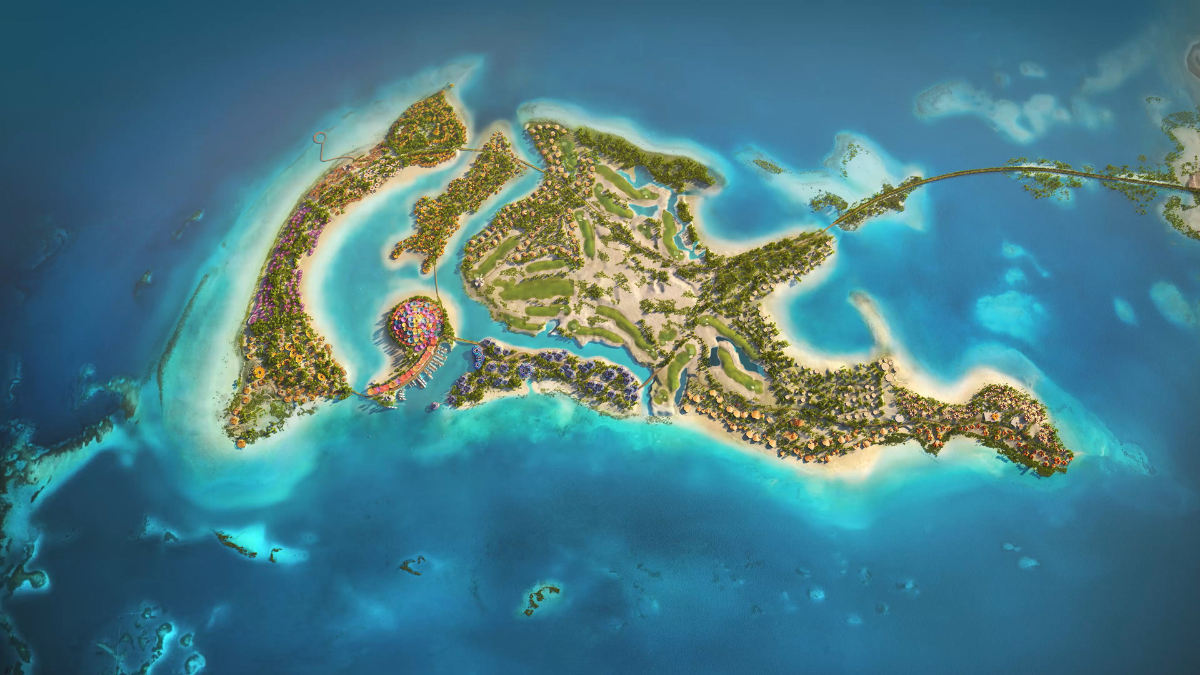
Red Sea Global
The Red Sea is home to the world’s fourth-biggest barrier reef, where marine life and coral thrive.
Established in 2018, Red Sea Global aims to transform the Kingdom’s west coast into a world-class tourism and hospitality destination.
Rendering of a Red Sea Global project off Umluj and Al-Wajh in Tabuk province. (Supplied)
Located between Umluj and Al-Wajh, the project covers an area of 28,000 square kilometers.
Omar Al-Attas, head of environmental protection and regeneration at Red Sea Global, told Arab News the firm aims to protect ecosystems by using 100 percent renewable energy and promoting “regenerative tourism.”
“One of the strategic goals that we are trying to realize is achieving 30 percent net conservation benefit by 2040 by enhancing biologically diverse habitats including mangroves, seagrass, corals, and land vegetation,” he said.
The RSG is currently working on seven SGI projects, which include establishing the largest marine-protected area in the region. It also aims to limit development and visitor footfall to protect the environment

Launched in 2017, NEOM's Oxagon project in Tabuk features a floating industrial complex, global trade hub, tourist resorts and a linear city powered by renewable energy sources. (Supplied)
“We made the decision to develop only 22 of the more than 90 islands,” Attas said. “We limited our development to accommodate no more than 1 million visitors a year at the Red Sea and 500,000 at AMAALA,” two of RSG’s luxury projects.
However, Attas believes society as a whole has a role to play in environmental protection.
“Individuals can help promote a balanced ecosystem by reducing waste, conserving water and energy, planting native species, using sustainable transportation, supporting local and sustainable food, minimizing chemical use, protecting natural habitats, educating others about environmental issues, and supporting conservation organizations,” he said.

Society as a whole has a role to play in environmental protection, says Omar Al-Attas, head of environmental protection and regeneration at Red Sea Global. (Supplied)
NEOM Green Hydrogen Company
The world’s biggest green hydrogen plant at NEOM’s Oxagon is expected to be fully operational by 2026, producing up to 600 tonnes of green hydrogen per day.
Green hydrogen is made through a process of electrolysis using only renewable energy sources, which makes it carbon free to produce. When hydrogen undergoes combustion, it produces nothing but water vapor, so it is also carbon free to use.
The Kingdom aims to be the world’s largest hydrogen energy producer and exporter, producing up to 4 million tons of clean hydrogen per year.

Illustration showing the Oxagon's green hydrogen project. (X: @NGHC_)
Duarte says these projects are raising community awareness about the importance of sustainable living.
“We can only promote a balanced ecosystem if we are aware of the broader consequences of our choices and behavior,” he said. “Our choices of energy source and delivery systems for transport or illumination, our respect for water — essential for a Bedouin culture where the respect for scarce water resources was of absolute importance — and the responsible generation and disposal of waste are all key elements of our footprint on the environment.
“Vision 2030 has not only brought about a commitment with sustainable development that is far more sincere and pervasive than I have seen in any other nation; it has also reconnected Saudi society with a heritage of sustainability and commitment as custodians of biodiversity and ecosystem that is reflected in projects around the Kingdom, from the Red Sea Project to AlUla and Diriyah Gate.”