ISLAMABAD: Following days of political uncertainty after general elections on Feb. 8, the party of Pakistan’s former prime minister Nawaz Sharif and its allies have announced they will jointly form a coalition government.
According to official results, the allied parties together hold 152 general seats in the National Assembly and are expected to surpass the simple majority mark of 169 members after securing their share of reserved seats. Along with the 266 directly elected seats in the National Assembly, parties are allocated 70 reserved seats — 60 for women, 10 for non-Muslims — in proportion to the number of seats won. This completes the National Assembly’s total 336 seats. Independents are not eligible for reserved seats.
The specifics of the new government will emerge in the coming days but it is clear that former prime minister Imran Khan’s Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf (PTI) party will be in opposition, despite candidates backed by it winning the largest number of seats, 92, in the National Assembly.
The following people are expected to play a key role in the next administration:
Nawaz Sharif
Having buried a long-running feud with the country’s powerful military, most independent analysts believed three-time former prime minister Nawaz Sharif was the front-runner to lead the country.
However, after his Pakistan Muslim League-Nawaz (PML-N) did not win enough seats to form a simple majority in parliament — it got 79 seats — it announced it would form a coalition government with allies, including the Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP), which got 54 seats. Sharif stepped aside and his younger brother Shehbaz was announced as the coalition set-up’s prime minister candidate. Analysts say the decision reflects Nawaz’s reluctance to navigate the complexities of a coalition government with a limited mandate for his PML-N.
However, despite stepping back from the top slot, Sharif, as the PML-N’s founding leader and a key figure in the coalition, is expected to wield significant influence in shaping policies and guiding the coalition’s direction from behind the scenes.
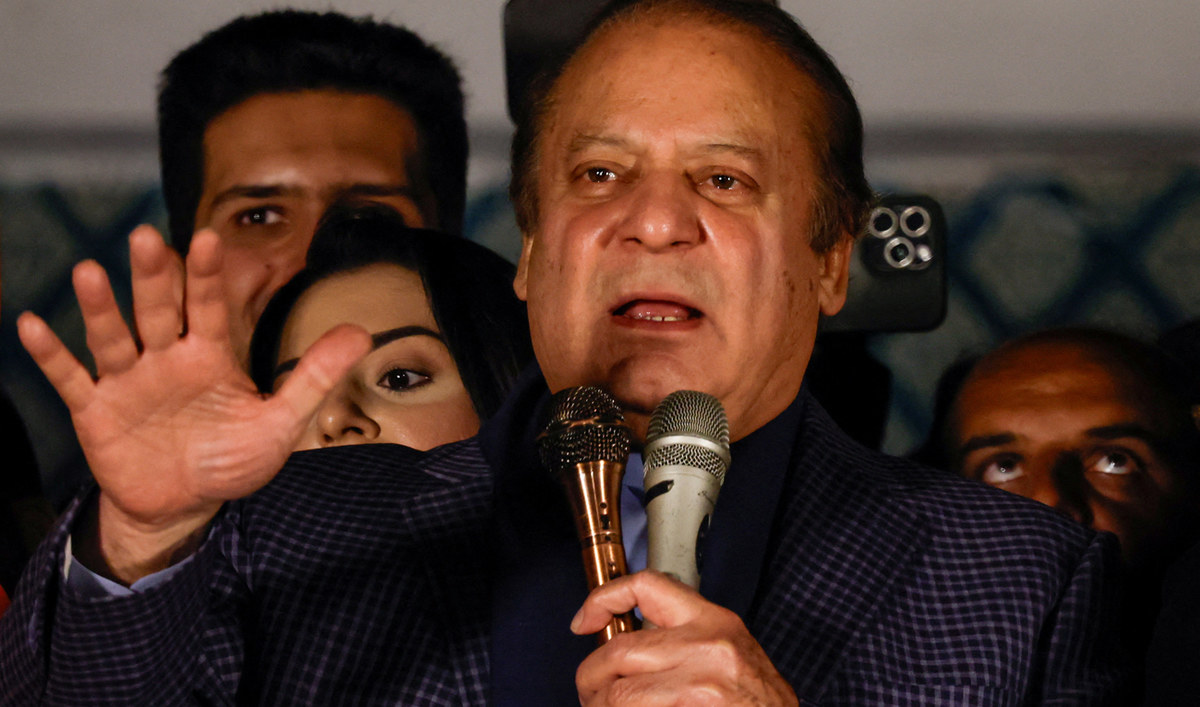
Former Prime Minister of Pakistan Nawaz Sharif speaks at the party office of Pakistan Muslim League (N), at Model Town in Lahore, Pakistan, February 9, 2024. (REUTERS)
“If it is being deduced that Nawaz Sharif is avoiding politics by not accepting the post of Prime Minister, then there is no truth in it. In the next 5 years, he will not only do vigorous politics, but will patronize his governments in the Federation and Punjab, God willing,” his daughter Maryam Nawaz Sharif, the candidate for chief minister Punjab, said on X.
“In the three governments of Nawaz Sharif, the people gave a clear majority and he has made it clear in his election speeches that he will not be a part of any coalition government. Those who are devoted to Nawaz Sharif’s temperament know the principled stand of Nawaz Sharif. Shehbaz Sharif [Sharif’s younger brother] and I are his soldiers, bound by his orders and will work under his leadership and supervision.”
The 74-year-old chief of the PML-N returned from a four-year self-imposed exile in the United Kingdom late last year to lead his party in elections. His convictions for corruption — which he denies — and a lifetime ban from politics were overturned by courts after his return.
Shehbaz Sharif
Shehbaz Sharif, 72, is the younger brother of Nawaz Sharif, and led a coalition government for 16 months following the ouster of Imran Khan in 2022 until parliament was dissolved and a caretaker government took over in August to prepare for national elections.
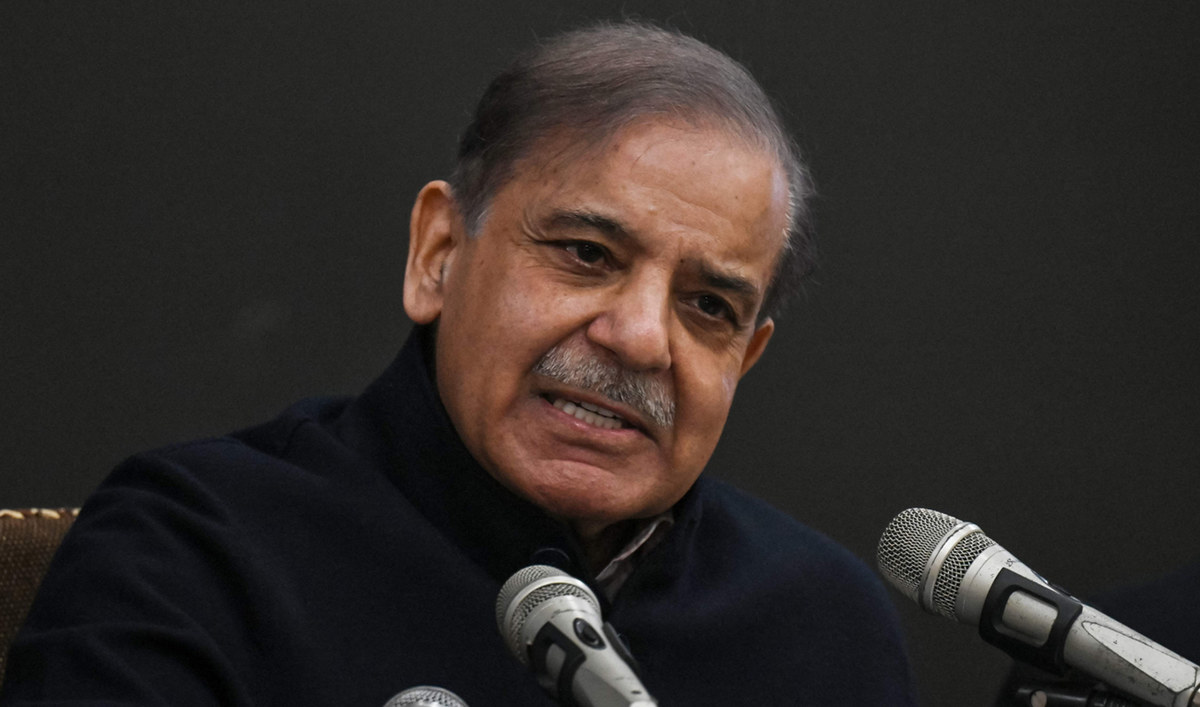

Pakistan's former Prime Minister and leader of the Pakistan Muslim League-Nawaz (PML-N) party Shehbaz Sharif speaks during a press conference in Lahore on February 13, 2024. (AFP)
He has previously served multiple times as chief minister of Punjab, Pakistan’s most populous province, cementing his reputation as an efficient administrator. He has worked closely with China on Beijing-funded projects in the last decade and helped Pakistan avert a financial crisis last year by striking a deal with the International Monetary Fund after tenuous, delayed negotiations for another bailout package.
Shehbaz’s expected return to the prime ministerial role may involve balancing the demands of coalition partners and ensuring cohesive governance while also leveraging his diplomatic skills and administrative experience to foster unity and progress within the multiparty setup. He will take over a country faced with a crippling economic crisis, record high inflation, slow growth and a surge in militancy.
Asif Ali Zardari
Asif Ali Zardari, the co-chairman of the Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP) and the widower of the late prime minister Benazir Bhutto, is widely expected to become the new president.
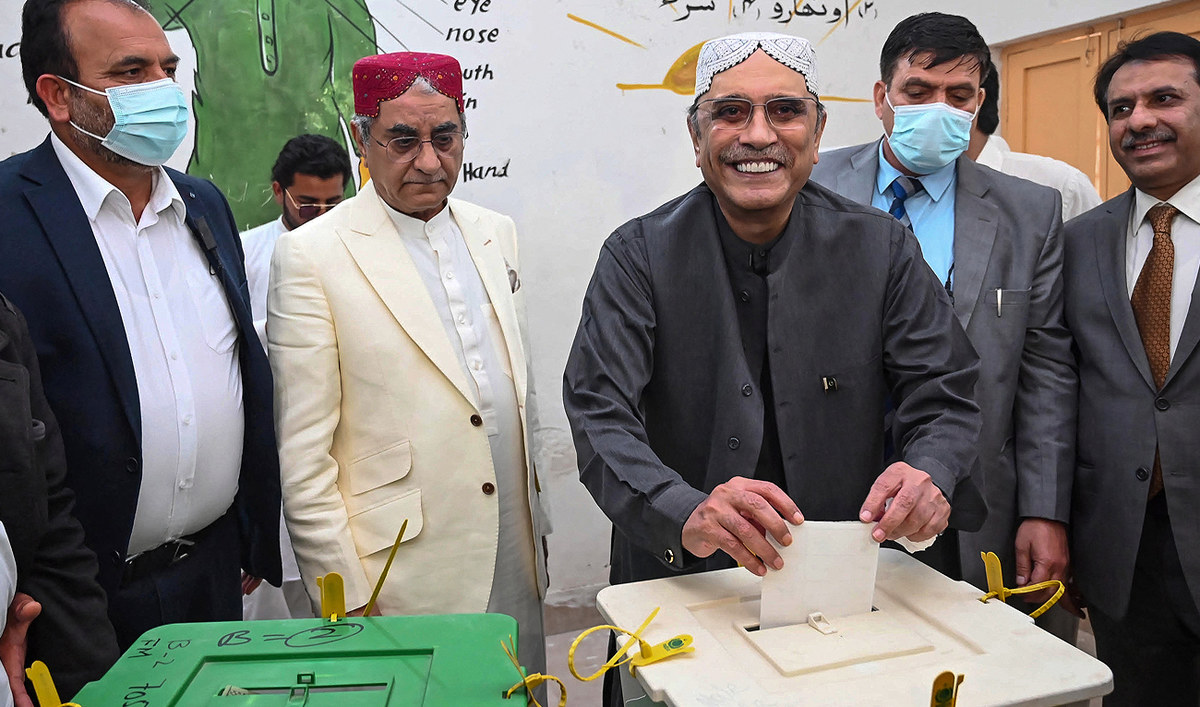

Pakistan's former President Asif Ali Zardari (3R) of Pakistan Peoples Party (PPP) casts his ballot to vote during the country's national elections at a polling station in NawabShah of Sindh province on February 8, 2024. (AFP)
Zardari, previously behind the scenes of Pakistani politics, came into the political centerstage after the assassination of his wife in 2007, leading him to the presidency of Pakistan from 2008-2013. Known for political maneuvering, he is expected to play a pivotal role in the new set-up and ensure that the PPP party’s interests are well-represented.
Maryam Nawaz Sharif
Maryam Nawaz Sharif, the daughter of Nawaz Sharif, plays an influential role in the PML-N party, and has been presented by her father as his political heir-apparent. She is senior vice president of the party.
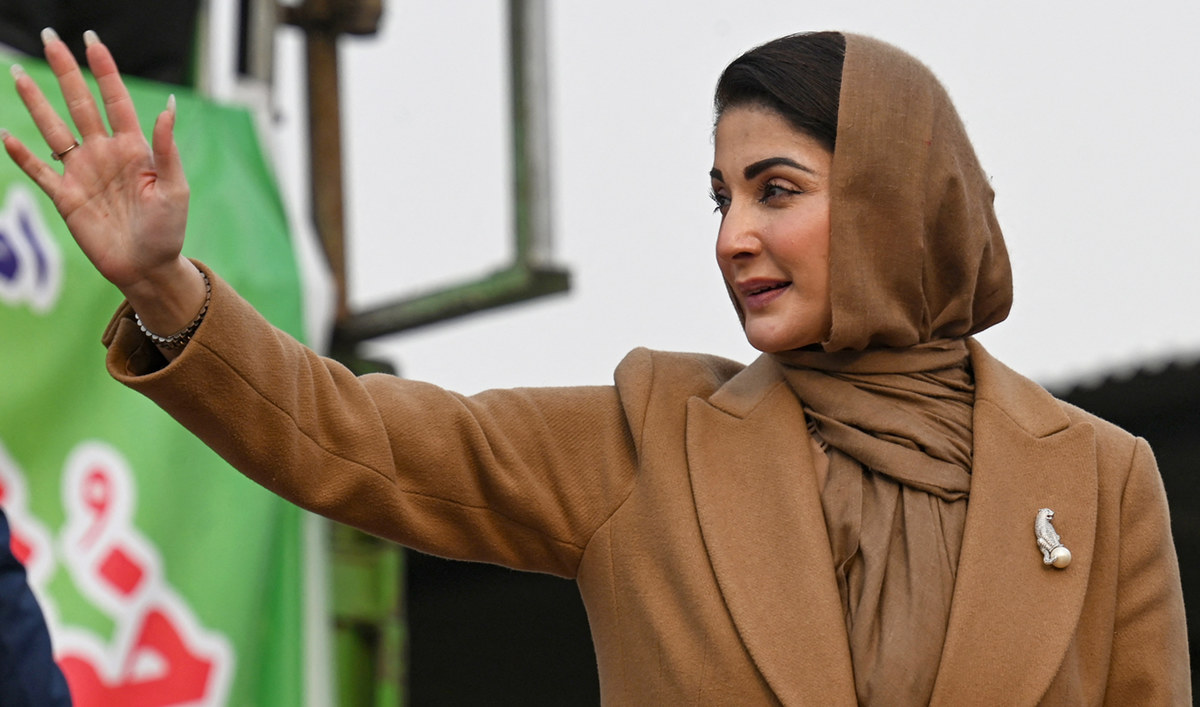

Maryam Nawaz, the daughter of Pakistan's former Prime Minister and leader of Pakistan Muslim League Nawaz (PMLN) party Nawaz Sharif waves to her supporters during an election campaign rally at Mansehra in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province on January 22, 2024. (AFP)
She is now set to chart a new course in her political career, potentially becoming the first woman chief minister of Punjab, arguably the most important political appointment in the country after the PM. However, Maryam’s lack of prior administrative experience presents challenges, but analysts say these can be overcome with the support of an experienced advisory team, which includes veteran politicians from the Sharif dynasty, including her father and uncle.
Bilawal Bhutto-Zardari
Bilawal Bhutto-Zardari, the 35-year-old son of Benazir Bhutto and Asif Ali Zardari, was the country’s foreign minister until a caretaker government took over late last year. He became co-chairperson of the Pakistan Peoples Party in 2007 when he was still a teenager after his mother was assassinated in a gun and bomb attack at a rally.
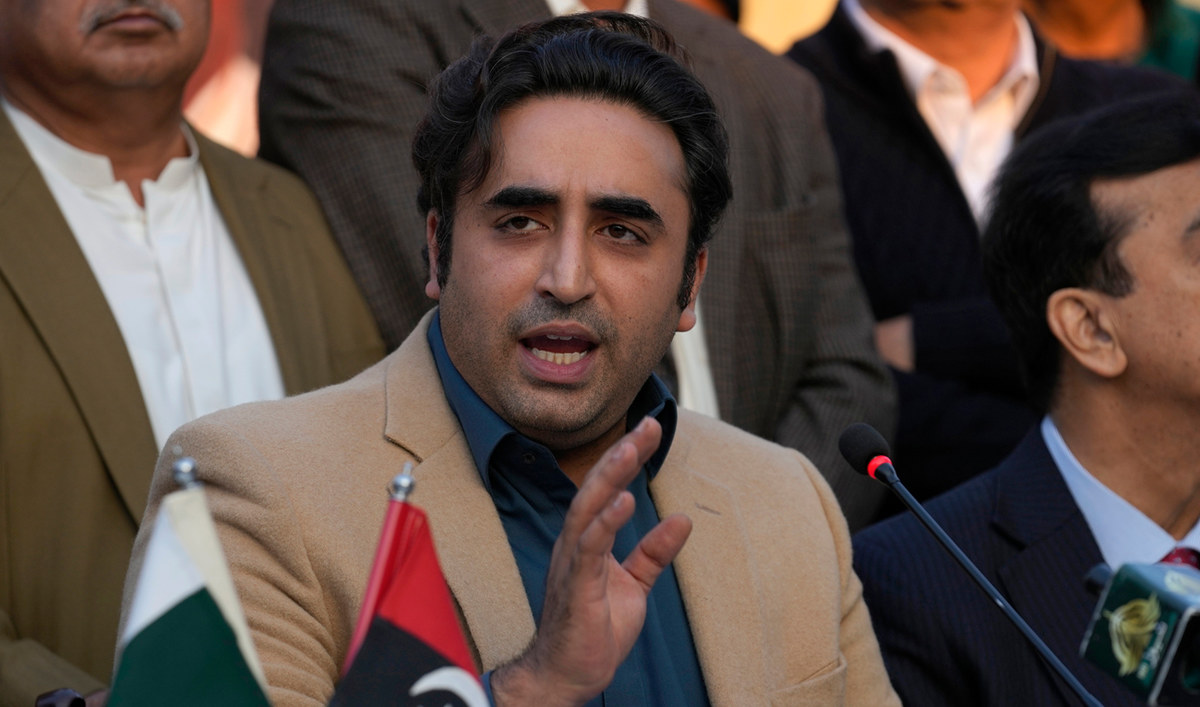

Bilawal-Bhutto Zardari, Chairman of Pakistan People's Party speaks during a press conference regarding parliamentary elections, in Islamabad on February 13, 2024. (AP)
Bhutto-Zardari ran one of the most prominent campaigns in Feb. 8 elections, appearing throughout the country, saying he was focusing the country’s huge youth population and addressing impacts of climate change, which have wreaked havoc in his southern Sindh province. His adept handling of diplomatic affairs as foreign minister has bolstered his reputation as a capable leader and he is expected to be a major player in the new coalition.




















