DUBAI: Tit-for-tat exchanges between Israel and Lebanon’s Iran-backed Hezbollah militia have continued to escalate since violence along the shared border first erupted in the wake of the Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack on southern Israel that sparked the Gaza conflict.
In the absence of a diplomatic breakthrough, the low-intensity conflict has expanded both in scope and intensity in recent weeks, leading to fears of an imminent full-scale war.
The violence since early October has killed at least 455 people in Lebanon, mostly fighters but including 88 civilians, according to an AFP tally. On the Israeli side, at least 14 soldiers and 11 civilians have been killed, according to the army.
INNUMBERS
• 4,900 Attacks launched by Israel against southern Lebanon since Oct. 7.
• 1,100 Attacks by Hezbollah against Israel and Israeli occupied territories in Lebanon. Source: ACLED
Israel has carried out nearly 4,900 attacks in southern Lebanon since Oct. 7, according to the Armed Conflict Location & Event Data (ACLED) Project.
ACLED says Hezbollah has launched around 1,100 attacks on Israel as well as territories it has occupied in Lebanon over the same period.
Israeli strikes have made the entire border area in southern Lebanon a no-go zone, leading to the displacement of some 90,000 people, according to the UN migration agency, IOM. The same is true in northern Israel, where Hezbollah attacks have displaced 80,000 residents.
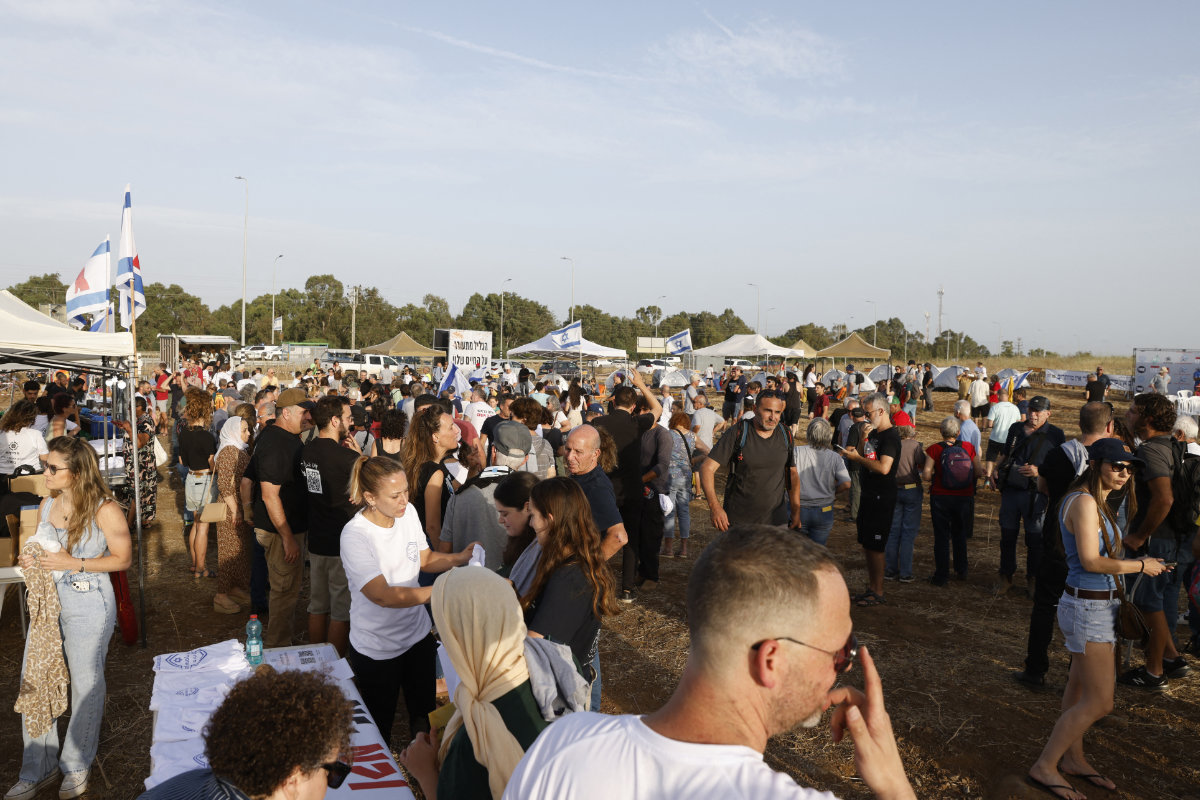

Israelis evacuated from northern areas near the Lebanese border due to ongoing cross-border tensions, rally near the northern Amiad Kibbutz, demanding to return home on May 23, 2024. (AFP)
Since the tit-for-tat attacks began, Lebanese officials and communities living along the border have been braced for a potential escalation into a conflict of a scale not seen since the 2006 war.
In recent months, influential Israeli officials have been calling on the government to mount a new military operation to push Hezbollah away from Israel’s northern border.
IDF Chief of Staff Lt. Gen. Herzi Halevi said on Tuesday that Israel is close to making a decision regarding Hezbollah’s daily attacks, according to the Times of Israel newspaper.
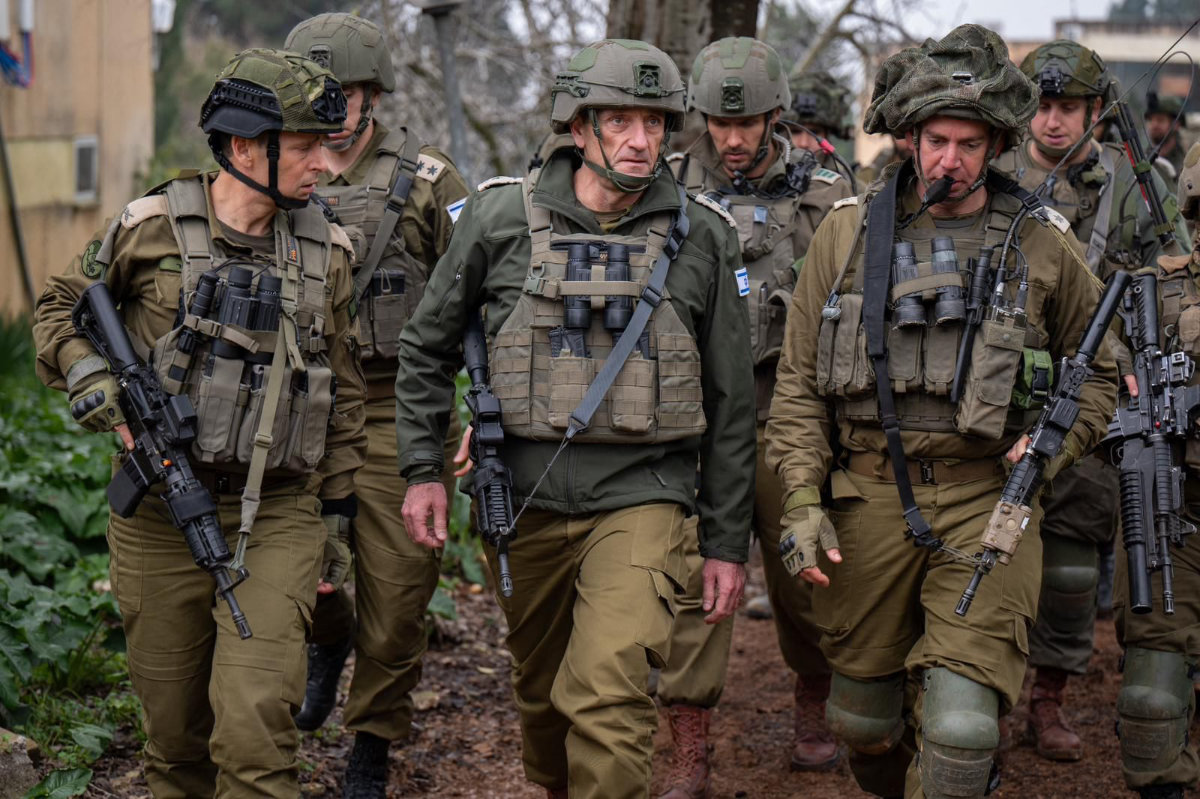

Israel's military Chief of the General Staff Herzi Halevi (C) walks among army officers during a situational assessment on the Lebanese border area on February 1, 2024, amid ongoing cross-border tensions between Israeli and Hezbollah forces. (Israeli Army handout via AFP)
“We are approaching the point where a decision will have to be made, and the IDF is prepared and very ready for this decision,” Halevi said during an assessment with military officials and Fire Commissioner Eyal Caspi, at an army base in Kiryat Shmona.
“We have been attacking for eight months, and Hezbollah is paying a very, very high price. It has increased its strengths in recent days and we are prepared after a very good process of training … to move to an attack in the north.”
Former Israeli prime minister Naftali Bennett tore into Benjamin Netanyahu’s government this week, claiming the north of Israel had been abandoned. “We must save the north,” he said in a statement. “The Galilee is going up in flames. The fire is spreading.
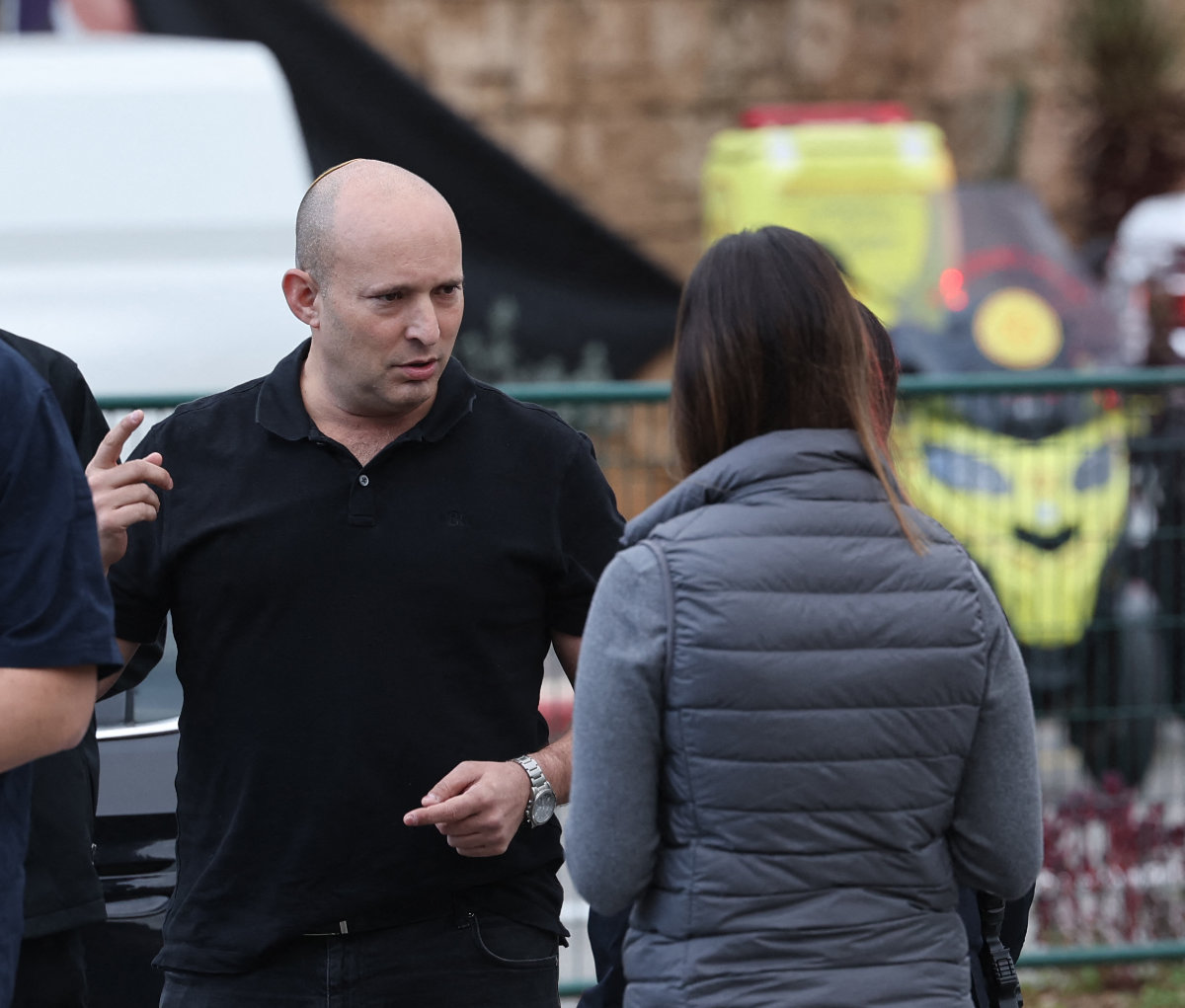

Former Israeli prime minister Naftali Bennett, shown in this photo taken on January 15, 2024, claims that the north of Israel had been abandoned by the Netanyahu government. (AFP/File photo)
“Beautiful and flourishing places have turned into heaps of rubble. Some residents who were evacuated are already planning their lives elsewhere. This is a grave strategic event and can in no way be normalized.”
Hassan Nasrallah, the secretary-general of Hezbollah, has said the militia’s campaign will continue as long as the war rages in Gaza.
In a speech last week, he said the attacks are “pressuring Israel,” and that while the battle concerns Palestine, it also concerns “the future of Lebanon and its water and oil resources.”
Should a full-scale war break out, Nasrallah said Hezbollah has “surprises” in store for Israel. Indeed, many region watchers expect any conflict between Israel and Hezbollah to be far more devastating and costly for both sides than the war in Gaza.
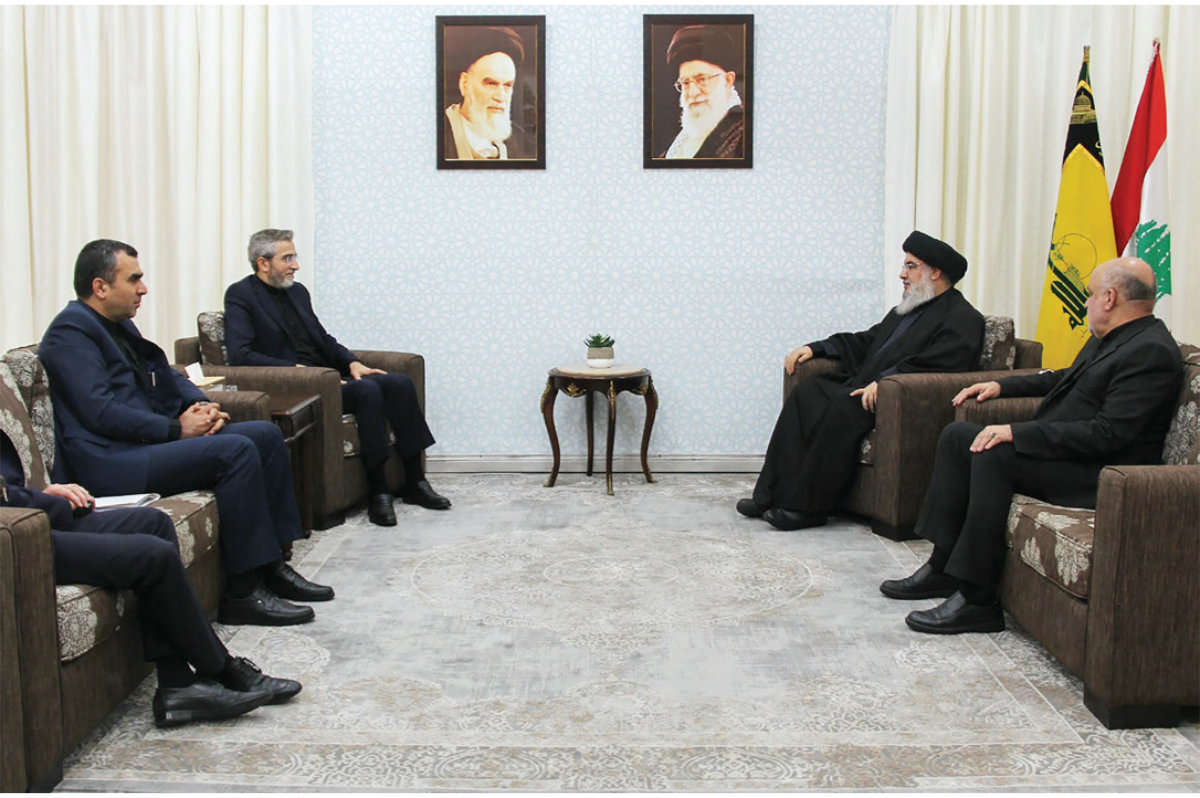

Hassan Nasrallah (2nd from R), leader of Lebanon's Hezbollah militia, met with Iranian officials as Hezbollah supporters braced for a spike, right, in Israeli reprisals. (AFP)
Nasrallah’s comments followed statements by Yaov Gallant, Israel’s defense minister, who warned Lebanon would “pay the price” for Hezbollah’s actions, saying “if you will continue, we will accelerate.”
Although both sides have raised the rhetorical ante, Israeli analyst Ori Goldberg believes an all-out war with Hezbollah would be a disastrous overreach for Israel.
“Israel cannot afford a two-front war,” he told Arab News. “That is not sustainable. Hezbollah will be able to reach the Israeli heartland with its rockets. Israel is already imploding. More than 100,000 Israelis seem to have been permanently displaced.”
Nevertheless, if Prime Minister Netanyahu were to present a new war in Lebanon as the only viable option to allow displaced Israelis to return home, then “there is a good possibility that he can rally enough support,” said Goldberg.
“In a way, a war in Lebanon is something Israel’s professional warmongers have been pitching for years. Also, Israel is really hard up for solutions that would return people to the north. So popular support is there to be tapped.”
Map showing the border between Lebanon and Israel, where tit-for-tat bombardment between Israeli and Hezbollah forces had displaced tens of thousands of people on both sides. (AFP)
Amos Hochstein, a senior adviser to US President Joe Biden for energy and investment, who brokered the maritime boundary agreement between Lebanon and Israel in late 2022, recently proposed a road map to peace between Israel and Hezbollah.
“I’m not expecting peace, everlasting peace, between Hezbollah and Israel,” Hochstein said in an interview with the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace in March.
“But if we can reach a set of understandings and ... take away some of the impetus for conflict and establish for the first time ever, a recognized border between the two, I think that will go a long way.”
Hezbollah, however, has conditioned any agreement on a ceasefire in Gaza, arguing any deal would require the consent of both parties.
Michael Young, author and senior editor at Carnegie Middle East, believes that despite its continued provocations, Hezbollah does not want a full-scale war with Israel.
“Everything they’ve shown, up till now, proves that they are avoiding one at all costs,” Young told Arab News. “Sure, they have escalated in response to Israeli escalations, but clearly they are not looking for one.
“If there is war, I don’t think there will be support from large segments of Lebanese society, and Hezbollah knows this. Even though there is anger with Israel, they will not support one.
“There is criticism from outside the Shiite community. The reason why Hezbollah is careful not to engage in a full-scale war is that it knows support from society will dissolve very quickly.”
Hezbollah on Tuesday said one of its members who lived in the Naqoura area was killed in an Israeli strike, and that its fighters launched “a slew of explosive-laden drones” at Israeli positions in the annexed Golan Heights in retaliation for the attack on the coastal town.
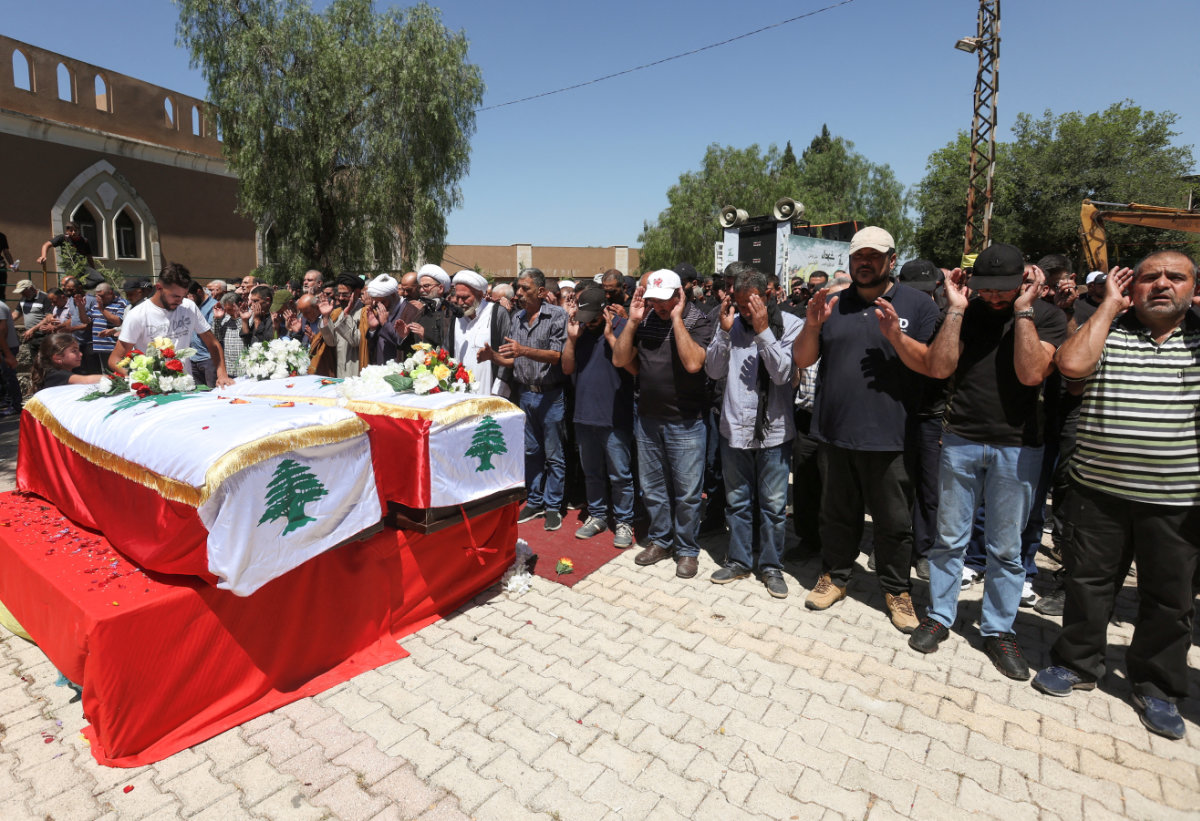

People pray during the funeral of the two brothers, Ali and Mohammed Qassem, who were killed by an Israeli strike in the Lebanese village of Houla near the border with Israel on June 2, 2024. (REUTERS)
It also claimed other attacks on Israeli troops and positions.
The Israeli army said in a statement that “fighter jets struck a Hezbollah terrorist” in Naqoura as well as hitting other sites.
Over the weekend, Hezbollah said its fighters had mounted a rocket attack against an Israeli army base in the border town of Kiryat Shmona, “scoring direct hits, igniting a fire and destroying parts of it,” according to militia statements.
The Israeli army confirmed the attack had taken place, with images of damaged infrastructure published by local media.
On Sunday night, the social media account of Green Southerners, a Lebanese civil society group dedicated to preserving national heritage, released videos purportedly showing massive fires around the border village of Al-Adisa.
The group claimed the fires were caused by Israel’s use of the incendiary weapon white phosphorus, and accused Israel of committing an act of “ecocide,” as the fires destroyed trees, farmland and animal habitats.
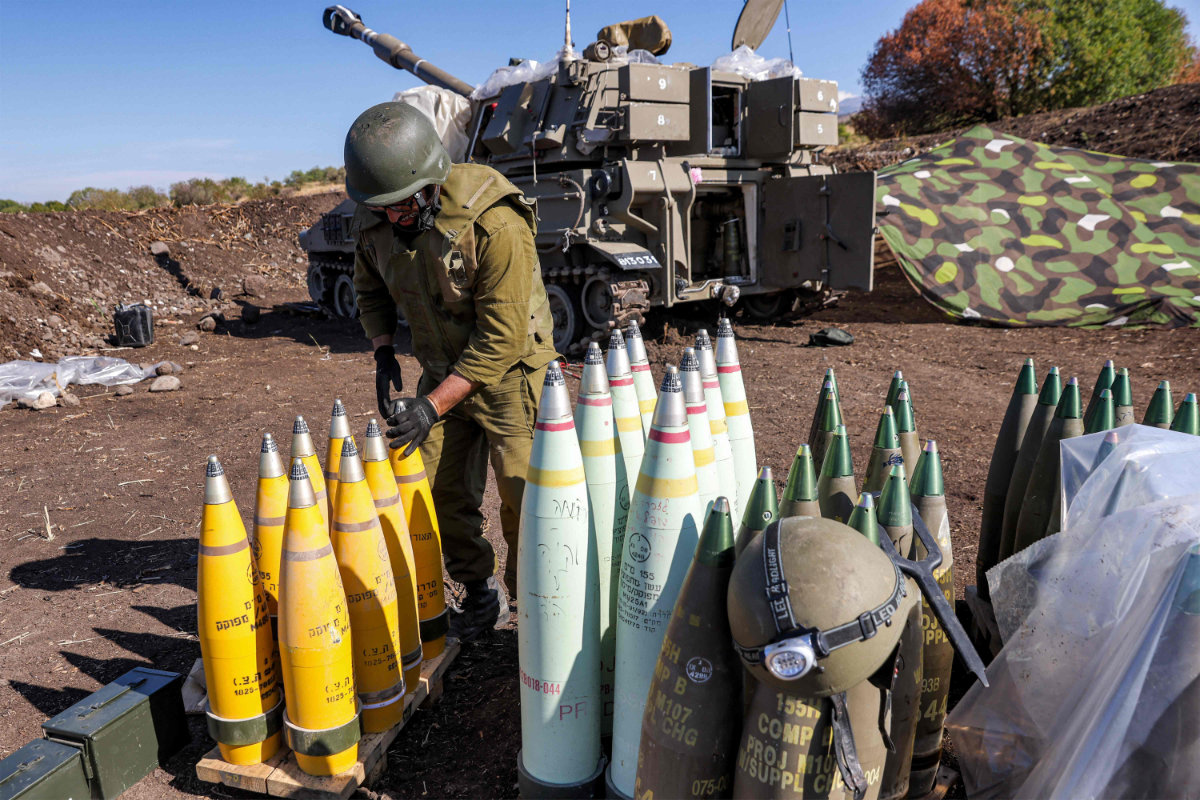

An Israeli army soldier artillery shells at a position near the border with Lebanon in the upper Galilee region of northern Israel . Lebanon has accused Israel of using controversial white phosphorus rounds, in attacks authorities say have harmed civilians and the environment. (AFP)
Twenty four hours later, massive fires were ignited by suspected Hezbollah attacks on the Israeli side of the border around Kiryat Shmona. Civilians were ordered to evacuate as firefighters battled the flames.
Israeli officials said more than 2,500 acres of land were affected by the fires, claiming it could take years for the land to recover.
On Monday, Hezbollah said it had fired Katyusha rockets toward Israeli bases in the occupied Golan Heights. For the first time since the outbreak of violence in October, the militia said it had launched a squadron of drones.
The Israeli military confirmed the attacks, stating it had intercepted one drone carrying explosives while two others fell in northern Israel.
For as long as Israel’s war against Hamas in Gaza rages and Hezbollah continues to pose a threat to the towns and villages of northern Israel, the potential for escalation remains high
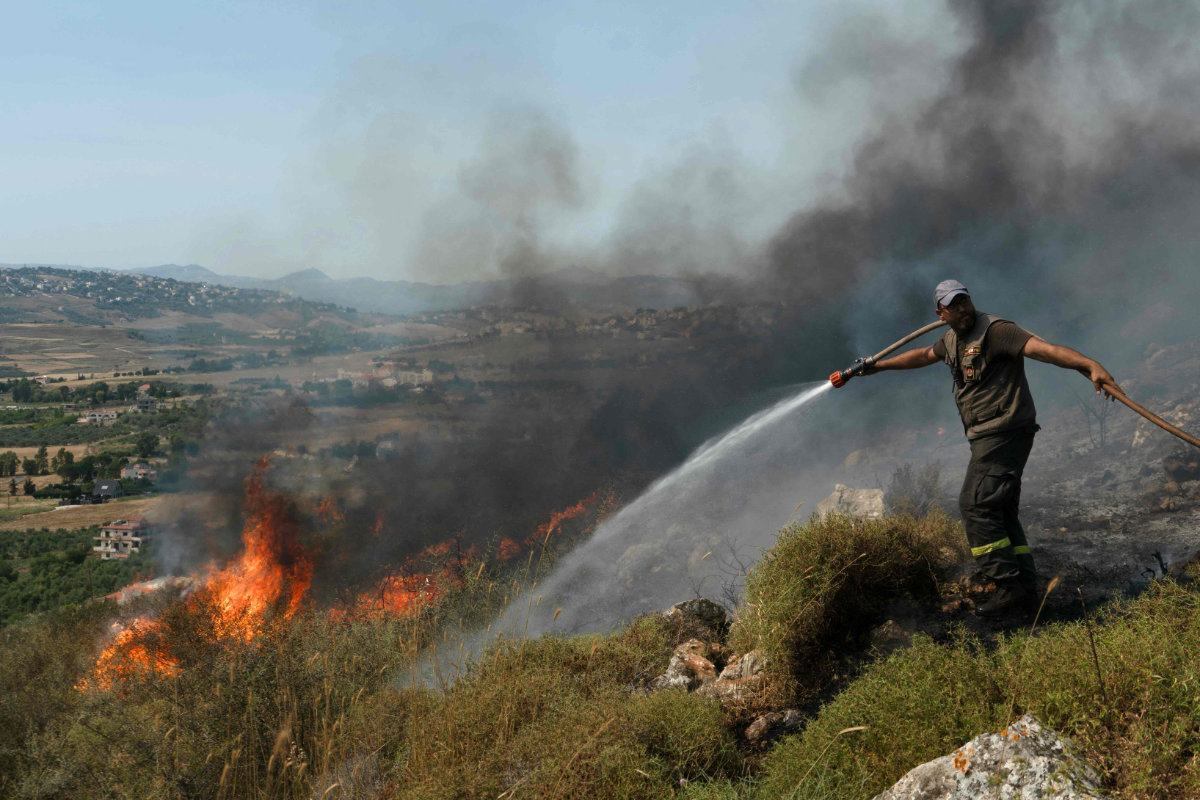

A Lebanese firefighter from the Islamic Sanitary Committee douses a fire that swept over fields hit by Israeli shelling in southern Lebanon near the border with Israel on June 3, 2024. (AFP)
The consequences, however, would be severe for all parties.
“I think Hezbollah has demonstrated it is committed to tit for tat,” said Israeli analyst Goldberg. “If Israel invades — and invade it must, if it wants a war — I think Hezbollah will likely retaliate in kind.”
And although Hezbollah has the means to cause significant damage to Israeli cities with its arsenal of Iranian-supplied weapons, it is crisis-wracked Lebanon that has the most to lose in the event of a full-scale war.
Indeed, the 2019 financial crisis and the failure to establish a new government has plunged much of the population into poverty, left public services and infrastructure in tatters, and even risked reopening old sectarian wounds.
“Should there be a war, it will be very difficult, if not impossible, to put Lebanon back together as it was or even as it is today,” said Young of Carnegie Middle East.
“Already the sectarian social contract is falling apart. How do you do this after a very destructive war?”





























