DUBAI: If the statements made by US President Joe Biden and his rival Donald Trump during Thursday’s election debate are anything to go by, it will be bad news for the Palestinian people no matter who wins the White House race in November.
Indeed, in the first televised head to head of the US election campaign, Biden reiterated his commitment to siding with Israel in the war in Gaza and accused Hamas of resisting efforts to end the conflict.
For his part, Trump called Biden “a weak and a very bad Palestinian” — using the name of the national group as a slur — and argued that Israel should be given a free hand to finish the job in Gaza.
Firas Maksad, a senior fellow at the Middle East Institute in Washington D.C., says the arguments posed by the candidates during the debate should not be considered their official stance.
“This is American electioneering at its worst,” Maksad said during an appearance on the Arab News current affairs show “Frankly Speaking.” “We all know that American elections tend to be the silly season.
“Candidates will say anything to get elected pretty much, only to turn around and change their position, or at least adjust their position, and in favor of a more nuanced one once they are in fact in the Oval Office. So, I think much of what was said (ought to be taken) with a grain of salt.”
Appearing on “Frankly Speaking,” Firas Maksad, a senior fellow at the Middle East Institute in Washington D.C., said the arguments posed by the candidates during the debate should not be considered their official stance. (AN Photo)
Maksad said it was “quite shameful” for Trump to use the term Palestinian in a “derogatory” way in a bid to undermine Biden by painting him as being relatively pro-Palestinian. “This, while both candidates were falling over themselves to demonstrate their support for Israel.”
Maksad, who is also the Middle East Institute’s senior director for strategic outreach, believes the style and tone of the debate is “just the reality of American electoral dynamics” and should not be considered a concrete policy position of either candidate.
“We can take our pick in terms of examples in the past where candidates have said one thing about nations in the Middle East, only to reverse course and even visit these countries once they become elected president,” he said.
One point that commentators were united on following the election debate was how poorly Biden performed — struggling to express his ideas clearly, fumbling over his words, and pausing for long periods, raising fresh doubts about his cognitive ability.
Although Trump is also prone to meandering speeches, commentators agreed the Republican nominee delivered a more concise and agile performance than the Democratic incumbent.
“I think it’s safe to say that most Americans were shell-shocked by the debate that they saw,” Maksad told “Frankly Speaking” host Katie Jensen.
“Going into this, the Democratic Party objective was to make this, first and foremost, about (Trump’s legal woes) rather than on the cognitive ability, or lack thereof, of President Biden.
“I think what we clearly saw was the Trump campaign had a great night, a celebratory night, whereas most of the Democratic operatives, fundraisers, and supporters of the president are left scrambling, wondering whether it’s too late in the game to try and draft in another last-minute, 11th hour candidate.”
Although many commentators said Biden offered more substance in his remarks, his poor delivery appears to have cost him in the eyes of voters.
“I very much had that debate with close friends in the Democratic circle, some of whom had served in the White House, as this debate was ongoing, and they kept pointing out to that very point, which is listen to the substance. Our candidate has much more substance,” Maksad said.
“Trump, in fact, rambles and says very little in terms of substance, not much in terms of specific policy focus and policy options being put on the table here. I think that’s true. I take the point, but I do think that in elections and American elections, how you come across to a voter is equally, if not more, important.
“And it was abundantly apparent that (former) President Trump was the more capable, confident, powerful in his presence on stage in this debate.”
If those watching the debate were hoping to learn more about where the rivals stood on the big foreign policy questions of the day, they would have been sorely disappointed as Biden and Trump focused mainly on domestic issues.
There were, however, some minor indications of similarities and differences on Middle East policy.
“President Biden — very much in favor of diplomacy. Some might say even accommodating Iran in the region, its aspirations,” said Maksad. “President Trump — much more confrontational when it comes to Iran, looking to contain its influence in the region.
“But that’s not to say that there aren’t similarities, too. I think, when it comes to regional integration, a possible normalization between Saudi Arabia and Israel, you see a bipartisanship on these issues here in Washington, D.C.”
Gaza, meanwhile, has become a deeply polarizing issue in the US, even beyond the Arab and Muslim communities, with protests taking place on university campuses across the country.
Asked whether the war is likely to influence the outcome of the election, however, Maksad said it was low down on the list of priorities for the majority of US voters.

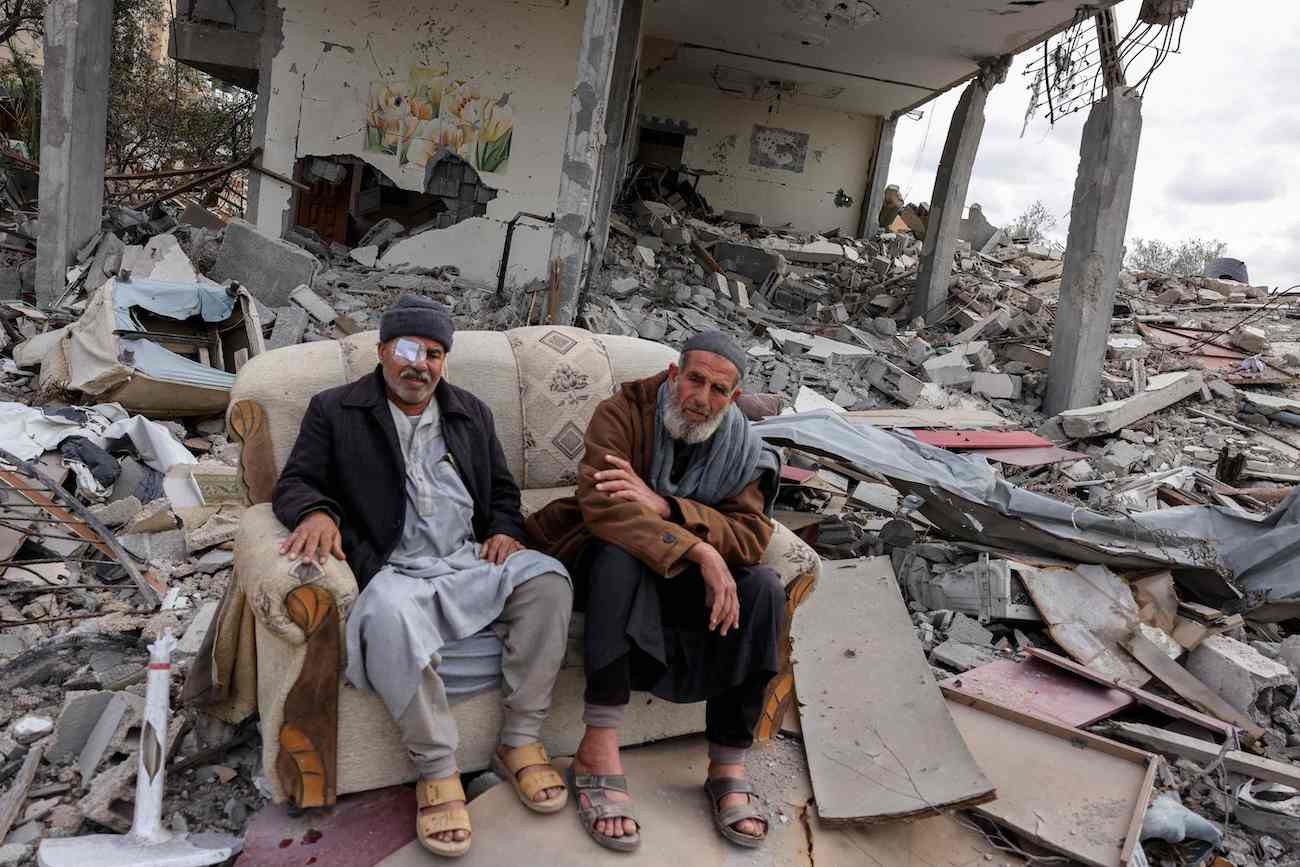
If the statements made by US President Joe Biden and his rival Donald Trump during Thursday’s election debate are anything to go by, it will be bad news for the Palestinian people no matter who wins the White House race in November. (AFP)
“I think it’s both unimportant but also very crucial,” he said. “If you take the laundry list of issues for most Americans that they care about, priorities, I don’t think Gaza features anywhere near the top.”
Since the conflict in Gaza began in the wake of the Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack on Israel, there have been fears that the war would spill over into the wider region. Lebanon, in particular, is seen as being especially vulnerable following months of tit-for-tat exchanges between Israel and Hezbollah.
Maksad, who is himself Lebanese and an expert on the nation’s troubled past, believes there are three likely scenarios, as all-out war appears increasingly inevitable.
“One is the current diplomatic efforts that are being spearheaded by Amos Hochstein, President Biden’s envoy on this issue, point person on this issue, who will be visiting areas and coordinating very closely with the French presidential envoy on this matter,” he said.
A diplomatic breakthrough of this kind would mean finding a way for Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah to step back from his position of a permanent ceasefire in Gaza.
“That might be through some Israeli withdrawal from the disputed points along the Blue Line, the border between Israel and Lebanon, northern Gaza being something to watch out for,” Maksad said.
“But if the diplomatic breakthrough that we’re all looking, and hoping, for in the coming weeks does not materialize, scenario two here is a limited war … limited to the deep populated areas of northern Israel and southern Lebanon.
“And the US and French diplomacy would then kick in to try and bring things back with the diplomatic track. And that could help dislodge the current stalemate.”
The “catastrophic scenario,” meanwhile, would be a situation that “starts out as an attempt at a limited conflict, a limited war in northern Israel and south Lebanon, very quickly expands to population centers like Beirut and Haifa and beyond that. And we see the 2006 scenario on steroids where Israel is flattening entire blocks of southern Beirut.”
The UK’s Daily Telegraph newspaper recently suggested that Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut is being used by Hezbollah to store and smuggle weapons. Although Hezbollah has denied the allegation, there are fears Israel may use the claims as a justification to bomb the airport.
“I’m not too sure that Israel needs a justification to bomb Beirut International Airport,” said Maksad. “They have done so in the past. They’ve done so repeatedly. They’ve cratered the runways. They have done so as far back as the 1960s when the PLO was the major concern operating out of Lebanon.
“So, there’s a long track record there of Israel targeting Lebanese infrastructure. And I’m not too sure that this particular article in the Telegraph is what the Israelis are looking for.
“But that said, also given my Lebanese ancestry, I mean, I think every Lebanese knows that the airport is by and large under the influence and control of Hezbollah or Hezbollah’s allies.”
He added: “Whether in fact the Telegraph article is accurate in that it’s being used as a storage base for Hezbollah missiles is something that’s beyond my capability in terms of being able to assess that.”
Asked whether Hezbollah is likely to make good on Nasrallah’s threat to attack Cyprus — a country that could host Israeli jets should Israel launch an aerial campaign against Hezbollah — Maksad said he thought the comments were merely intended to signal the potential reach of Iran and its regional proxies in the event of war.
“There are multiple views as to why Hassan Nasrallah chose to include Cyprus in the list of threats he made in his recent speech,” he said.
“I do think that, first and foremost, he was thinking from a military perspective in terms of where Israel, and particularly the air force, might be able to operate from if Hezbollah rained missiles on Israeli airports in the north and hamstrings Israel’s ability to operate against it. And Cyprus is high on that list of alternatives for Israel.
“But I do think that he’s also sending a broader message … which is one about Hezbollah’s ability to intercept and contradict and complicate shipping in the Eastern Mediterranean.
“And so through Hezbollah, you have Iran here very clearly signaling its ability to interdict and disrupt global commerce, not only in Hormuz, not only in Bab Al-Mandeb, but also in the Eastern Mediterranean, arguably as far south as Suez.”

Firas Maksad, a senior fellow at the Middle East Institute in Washington D.C., says the arguments posed by the candidates during the debate should not be considered their official stance. (AN Photo)
He added: “This is part of Iran signaling its ability now to project influence and power into the Mediterranean, into the Red Sea and certainly within the Arab and Persian Gulf.”
As turmoil rages in the Middle East at the very moment that the US is turning its attention inward to the looming election, doubts have been raised about the possibility of securing the hotly anticipated deal between the US and Saudi Arabia.
“I see very low prospects of the Saudi-US deal being able to move forward,” said Maksad. “In fact, it will continue to be tethered to an Israeli leg with a precondition of a viable, non-reversible pathway towards a Palestinian state.
“But the politics is simply not there on the Israeli side, but also on the Palestinian side. This is the proposition that is entirely devoid of reality on the Israeli and Palestinian side.
“That said, the deal itself, the bilateral aspects of this deal, are largely negotiated and done. Whether it relates to a defense treaty or civil nuclear cooperation or commerce and AI and cyber, those issues have all been successfully negotiated by both the US and by Riyadh.
“But the issue is that if you are seeking a treaty which requires congressional, mainly Senate ratification, it is difficult to see that being passed in the Senate short of normalization with Israel.
“And normalization with Israel, given the very clear Saudi preconditions on the Palestinian state, or a pathway to a Palestinian state, are simply not there.”


































