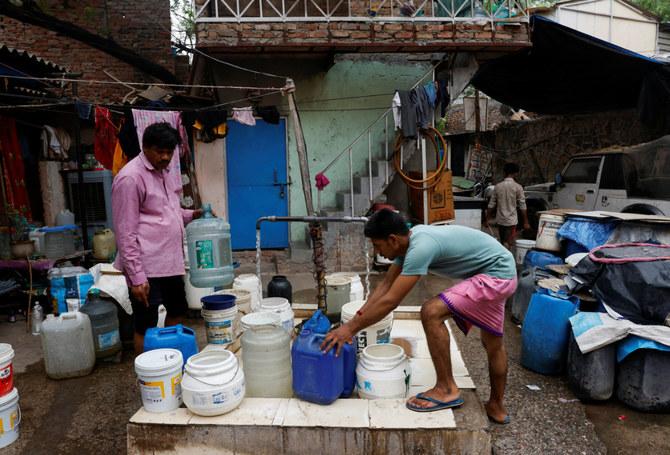
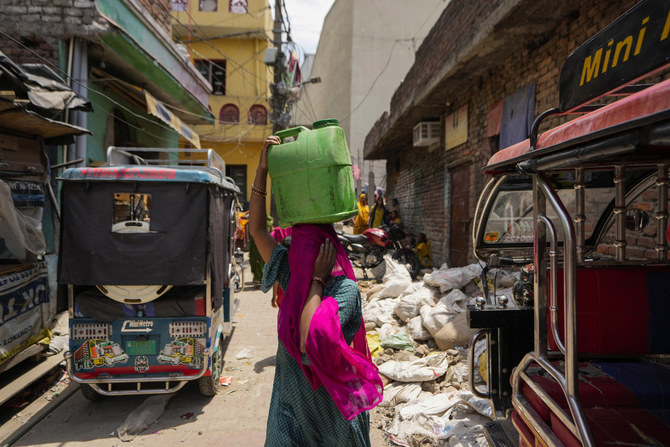NEW DELHI: In the Vivekananda Camp slum, adjacent to the US embassy in New Delhi, communal taps supply brackish water for about two hours a day. Water delivered by tankers provides one additional bucket to each of its 1,000 residents for drinking and cooking.
In parts of the arid state of Rajasthan, southwest of the Indian capital, tap water is available once every four days for an hour. In rural areas near Mumbai, women and children travel more than a mile to get water.
Bengaluru, India’s tech hub of 14 million people, reeled under a water shortage this year and had to rely on tanker deliveries.
“We don’t wash the floor or do the laundry for days sometimes,” said Sampa Rai, a 38-year-old in Delhi’s Vivekananda Camp, who scrambles before dawn every day to meet the first tanker delivering water. “Not even the dishes. We have to manage with what we have.”
The world’s most populous nation has suffered from water shortages for decades, but crises are coming around with increasing frequency. This year, for example, the summer has been one of the hottest on record and the crunch has worsened with rivers and lakes drying up and the water table falling.
The shortages are affecting rural and urban Indians alike, disrupting agriculture and industry, stoking food inflation and risking social unrest. Contaminated water kills about 200,000 Indians each year, according to the government. People and the economy are suffering.
That is adding urgency to public and private-sector efforts to conserve the resource, find ways to recycle waste water and reduce the country’s over-reliance on the annual monsoon, especially in the agricultural sector.
Ratings agency Moody’s warned last week that India’s growing water stress could affect its growth, which at a projected 7.2 percent this April-March fiscal year is the highest among major economies.
“Decreases in water supply can disrupt agricultural production and industrial operations, resulting in inflation in food prices and declines in income for affected businesses and workers, especially farmers, while sparking social unrest,” Moody’s said.
The government plans to more than triple waste water recycling by the end of the decade to 70 percent, according to a federal government policy document dated Oct. 21, 2023 that listed priorities for the next five years.
Krishna S. Vatsa, a senior official at the state-run National Disaster Management Authority, confirmed the targets in an interview last week.
Authorities also plan to cut the extraction of fresh water — ground water and surface water from rivers and lakes — to less than 50 percent by the end of the decade from 66 percent, the highest rate in the world, said the document, which has not been made public and was reviewed by Reuters.
It will also launch a national village-level program this year to recommend crops to farmers based on local water availability, Vatsa said.
Details of plans to address the water crisis have not been previously reported.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has already ordered authorities to build or refurbish at least 75 lakes in each of the 785 districts of the country. The government says work has been started or completed on more than 83,000 lakes. Experts say such lakes can help recharge the water table.
Modi launched a near $50-billion program in 2019 to provide all rural households with tap water. The government says it has now covered 77 percent of more than 193 million such families, up from 17 percent five years ago, but residents and experts say not all pipes have water.
“It makes the issue of conservation far more urgent,” Vatsa said. “You cannot sustain such a national pipeline without the availability of water. The pipes will run dry.”
He agreed some taps could already be dry.
Water stressed
India relies substantially on the annual monsoon for its 1.42 billion people and its largely rural-based economy, where water-intensive crops like rice, wheat and sugarcane take up more than 80 percent of the overall supply.
The monsoon itself is prone to severe and extreme weather conditions. Catchment areas are getting scarce because of rapid urbanization, so even in a good monsoon, much of the rainwater drains off into the sea.
India’s annual per capita water availability, at about 1,486 cubic meters, is set to fall to 1,367 cubic meters by 2031 as its population grows, government projections show. The country has been “water stressed,” defined as per capita availability of less than 1,700 cubic meters, since 2011.
“We have a crisis now every year,” said Depinder Singh Kapur at Indian research body Center for Science and Environment.
“Earlier it used to be drought years versus normal years, now a water crisis is happening every year and with more intensity.”
There are pockets where private enterprise is addressing the crisis.
In Nagpur, a city of 3 million people, the Vishvaraj Group said it helped build a $100 million plant in 2020 that treats 200 million liters of sewage per day, extracting 190 million liters of treated water that it sells to two thermal power plants.
Founder Arun Lakhani said the freed up fresh water will be enough to take care of the expected population growth of the city for the next 35 years.
Some industries are investing in waste water recycling and rain harvesting to cut their dependence on fresh water.
Tata Steel plans to cut its fresh water consumption to less than 1.5 cubic meters per ton of crude steel produced at its Indian operations by 2030, from about 2.5 cubic meters now. JSW Steel also has similar plans.
“At least to plug the gaps in urban areas, treated waste water is going to be one important resource that we need to start acknowledging,” said Nitin Bassi at Indian think-tank The Council on Energy, Environment and Water.
Experts say nearly 90 percent of water supplied to homes can be recycled, but infrastructure for water distribution and sewage treatment has failed to match the growth of major cities and untreated waste ultimately flows into rivers.
Modi’s administration is adding sewage treatment capacity to lift the current rate of 44 percent in urban areas so more water can be recycled and used in industries, agriculture and other areas.
Between 2021 and 2026, it plans to invest about $36 billion to ensure equitable water distribution, reuse of waste-water and mapping of water bodies, the government has said.
Thirsty farmers
The cultivation of crops like rice in semi-arid states has led to rampant extraction of groundwater through borewells and steep falls in water tables, according to government and industry officials.
“The elephant in the room is agriculture,” said Lakhani of Vishvaraj. “We still use flood irrigation, we are not on drip or sprinkler irrigation. If we save just 10 percent water used in agriculture, it will take care of water problems of all the Indian cities.”
The government plans to implement a nationwide rural program on water use this year, said Vatsa, the disaster management official.
“For every village we need to have water budgeting,” he said. “How much water is available? How much should be used for irrigation? How much should be used for your domestic purpose? That would determine what kind of crops you are going to plant.”
Asked about possible resistance from farmers, who are a powerful voting bloc, he said: “There’s no other choice. The water table is just going down and at some point it becomes completely unviable. The borewells fail.”