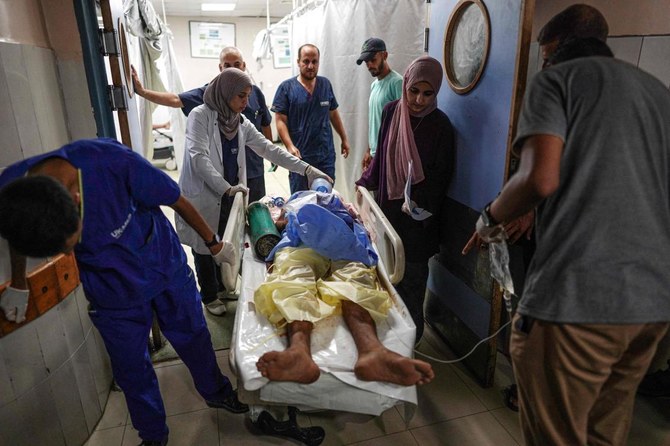
DEIR AL-BALAH: An Israeli airstrike on a school-turned-shelter in southern Gaza killed at least 25 Palestinians on Tuesday, as heavy bombardment in the north forced the closure of medical facilities in Gaza City and sent thousands fleeing in search of increasingly elusive refuge.
Israel’s new ground assault in Gaza’s largest city is its latest effort to battle Hamas militants regrouping in areas the army previously said had been largely cleared.
Large parts of Gaza City and urban areas around it have been flattened or left a shattered landscape after nine months of fighting. Much of the population fled earlier in the war, but several hundred thousand Palestinians remain in the north.
“The fighting has been intense,” said Hakeem Abdel-Bar, who fled Gaza City’s Tuffah district to the home of relatives in another part of the city. He said Israeli warplanes and drones were “striking anything moving” and that tanks had moved into central districts.
The strike at the entrance to the school killed at least 25 people, according to an Associated Press reporter who counted the bodies at Nasser Hospital in Khan Younis. Hospital spokesperson Weam Fares said the dead included at least seven women and children and that the toll was likely to rise.
Earlier airstrikes in central Gaza killed at least 14 people, including a woman and four children, according to two hospitals that received the bodies. Israel has repeatedly struck what it says are militant targets across Gaza since the start of the war nine months ago.
The military blames civilian deaths on Hamas because the militants fight in dense, urban areas, but the army rarely comments on individual strikes, which often kill women and children. The Israeli army said the airstrike near the school and reports of civilian casualties were under review, and claimed the strike targeted a Hamas militant who took part in the Oct. 7 attack on Israel.
There was also no immediate word on casualties in Gaza City. Families whose relatives were wounded or trapped were calling for ambulances, but first responders could not reach most of the affected districts because of the Israeli operations, said Nebal Farsakh, a spokesperson for the Palestinian Red Crescent.
“It’s a dangerous zone,” she said.
After Israel on Monday called for an evacuation from eastern and central parts of Gaza City, staff at two hospitals — Al-Ahli and the Patients Friends Association Hospital — rushed to move patients and shut down, the United Nations said. Farsakh said all three medical facilities run by the Red Crescent in Gaza City had closed.
Scores of patients were transferred to the Indonesian Hospital in northern Gaza, which itself was the scene of heavy fighting earlier in the war. “We do not know where to go. There is no treatment and no necessities for life,” said Mohammad Abu Naser, who was being treated there. “We are dying slowly.”
The Israeli military said Tuesday that it told hospitals and other medical facilities in Gaza City they did not need to evacuate. But hospitals in Gaza have often shut down and moved patients at any sign of possible Israeli military action, fearing raids.
The Episcopal Church in the Middle East, which operates Al-Ahli, said the hospital was “compelled to close by the Israeli army” after the evacuation orders and a wave of nearby drone strikes on Sunday.
In the past nine months, Israeli troops have occupied at least eight hospitals, causing the deaths of patients and medical workers along with massive destruction to facilities and equipment. Israel has claimed Hamas uses hospitals for military purposes, though it has provided only limited evidence.
Only 13 of Gaza’s 36 hospitals are functioning, and those only partially, according to the United Nations’ humanitarian office.
Israel’s campaign in Gaza, triggered by Hamas’ Oct. 7 attack, has killed or wounded more than 5 percent of Gaza’s 2.3 million Palestinians, according to the territory’s Health Ministry. Nearly the entire population has been driven from their homes. Many have been displaced multiple times. Hundreds of thousands are packed into sweltering tent camps.
The UN humanitarian office said the exodus in Gaza City was “dangerously chaotic,” with people instructed to flee through neighborhoods where fighting was underway.
“People have been observed fleeing in multiple directions, not knowing which way may be safest,” the agency said in a statement. It said the largest UN bakery in the city was forced to close, and that the fighting had blocked aid groups from accessing warehouses.
Maha Mahfouz, a mother of two, said she fled twice in the past 24 hours. She first rushed from her home in Gaza City to a relative’s house in another neighborhood. When that became dangerous, she fled Monday night to Shati, a decades-old refugee camp that has grown into an urban district where Israel has carried out repeated raids.
She described vast destruction in the areas targeted in the latest raids. “The buildings were destroyed. The roads were destroyed. All has become rubble,” she said.
The Israeli military has said it had intelligence showing that militants from Hamas and the smaller Islamic Jihad group were regrouping in central Gaza City. Israel accuses Hamas and other militants of hiding among civilians. In Shijaiyah, a Gaza City neighborhood that has seen weeks of fighting, the military said it had destroyed 6 kilometers of Hamas tunnels.
Hamas has warned that the latest raids in Gaza City could lead to the collapse of negotiations for a ceasefire and hostage-release deal.
Israel and Hamas had appeared to narrow the gaps in recent days, with the US, Egypt and Qatar mediating.
CIA Director William Burns met Tuesday with Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi in Cairo to discuss the negotiations, El-Sisi’s office said. More talks were to be held Wednesday in Qatar, where Hamas maintains a political office.
But obstacles remain, even after Hamas agreed to relent on its key demand that Israel commit to ending the war as part of any agreement. Hamas still wants mediators to guarantee that negotiations conclude with a permanent ceasefire.
Israel has rejected any deal that would force it to end the war with Hamas intact. Hamas on Monday accused Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu of “putting more obstacles in the way of negotiations,” including the operations in Gaza City.
Hamas’ cross-border raid on Oct. 7 killed 1,200 people in southern Israel, most of them civilians, according to Israeli authorities. The militants took roughly 250 people hostage. About 120 are still in captivity, with about a third said to be dead.
Israel’s bombardment and offensives in Gaza have killed more than 38,200 people and wounded more than 88,000, according to the territory’s Health Ministry, which does not distinguish between combatants and civilians in its count.
Airstrike kills 25 in southern Gaza as Israeli assault on Gaza City shuts down medical facilities
https://arab.news/gprzt
Airstrike kills 25 in southern Gaza as Israeli assault on Gaza City shuts down medical facilities

- Heavy bombardment in the north meanwhile forced the closure of medical facilities in Gaza City and sent thousands fleeing in search of increasingly elusive refuge
- Large parts of Gaza City and urban areas around it have been flattened or left a shattered landscape after nine months of fighting
Deal reached to release more Israeli hostages and allow Palestinians into north Gaza

- Netanyahu’s office says another six hostages to be released in coming week after talks with Hamas
- Israel confirms Qatar’s announcement, says Gazans can now return home from 7 a.m. Monday
DOHA/JERUSALEM/GAZA CITY: Mediator Qatar announced early Monday that an agreement has been reached to release an Israeli civilian hostage and allow Palestinians to return to northern Gaza, easing the first major crisis of the fragile ceasefire between Israel and Hamas.
Qatar’s statement said Hamas will hand over the civilian hostage, Arbel Yehoud, along with two other hostages before Friday. And on Monday, Israeli authorities will allow Palestinians to return to northern Gaza.
The office of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu in a statement said the hostage release — which will include soldier Agam Berger — will take place on Thursday, and confirmed that Palestinians can move north on Monday. Israel’s military said people can start crossing on foot at 7 a.m.
Under the ceasefire deal, Israel on Saturday was to begin allowing Palestinians to return to their homes in northern Gaza. But Israel put that on hold because of Yehoud, who Israel said should have been released on Saturday. Hamas accused Israel of violating the agreement.
Netanyahu's office said that another six hostages would be released in the coming week, after talks with Hamas. Three would be released on Thursday and another three on Saturday, said a statement from his office.
The breakthrough preserves a fragile ceasefire in the Israel-Hamas war, which has devastated the Gaza Strip and displaced nearly all its residents, paving the way for more hostage-prisoner swaps under a deal aimed at ending the more than 15-month conflict.
Israel had been preventing vast crowds of Palestinians from using a coastal road to return to northern Gaza, accusing Hamas of violating the truce agreement by failing to release civilian women hostages.
“Hamas has backtracked and will carry out an additional phase of releasing hostages this Thursday,” Netanyahu’s office said in a statement.
Trump’s plan meets mixed reactions
Palestinian leaders meanwhile slammed a plan floated by US President Donald Trump to “clean out” Gaza, vowing to resist any effort to forcibly displace residents of the war-battered territory.
Trump said Gaza had become a “demolition site,” adding he had spoken to Jordan’s King Abdullah II about moving Palestinians out.
“I’d like Egypt to take people. And I’d like Jordan to take people,” Trump told reporters.
Palestinian leader Mahmud Abbas, who is based in the Israeli-occupied West Bank, “expressed strong rejection and condemnation of any projects” aimed at displacing Palestinians from Gaza, his office said.
Bassem Naim, a member of Hamas’s political bureau, told AFP that Palestinians would “foil such projects,” as they have done to similar plans “for displacement and alternative homelands over the decades.”
Islamic Jihad, which has fought alongside Hamas in Gaza, called Trump’s idea “deplorable.”
For Palestinians, any attempt to move them from Gaza would evoke dark memories of what the Arab world calls the “Nakba,” or catastrophe — the mass displacement of Palestinians during Israel’s creation in 1948.
“We say to Trump and the whole world: we will not leave Palestine or Gaza, no matter what happens,” said displaced Gaza resident Rashad Al-Naji.
Trump floated the idea to reporters Saturday aboard Air Force One: “You’re talking about probably a million and half people, and we just clean out that whole thing.”
Moving Gaza’s roughly 2.4 million inhabitants could be done “temporarily or could be long term,” he said.
Israel’s far-right Finance Minister Bezalel Smotrich — who opposed the truce deal and has voiced support for re-establishing Israeli settlements in Gaza — called Trump’s suggestion of “a great idea.”
Tantamount to ‘ethnic cleansing’
The Arab League rejected the idea, warning against “attempts to uproot the Palestinian people from their land.”
“The forced displacement and eviction of people from their land can only be called ethnic cleansing,” the league said in a statement.
Jordanian Foreign Minister Ayman Safadi said “our rejection of the displacement of Palestinians is firm and will not change. Jordan is for Jordanians and Palestine is for Palestinians.”
Egypt’s foreign ministry said it rejected any infringement of Palestinians’ “inalienable rights.”
In Gaza, cars and carts loaded with belongings jammed a road near the Netzarim Corridor that Israel has blocked, preventing the expected return of hundreds of thousands of people to northern Gaza.
Israel had said it would prevent Palestinians’ passage until the release of Arbel Yehud, a civilian woman hostage. She is among those slated for return on Thursday, according to Netanyahu’s office.
Hamas said that blocking returns to the north also amounted to a truce violation, adding it had provided “all the necessary guarantees” for Yehud’s release.
Israeli army spokesman Avichay Adraee said Monday that residents would be allowed to return on foot starting at 07 a.m. (0500 GMT) and by car at 9 a.m.
Staggered releases
During the first phase of the Gaza truce, 33 hostages are supposed to be freed in staggered releases over six weeks in exchange for around 1,900 Palestinians held in Israeli jails.
The most recent swap saw four Israeli women hostages, all soldiers, and 200 prisoners, nearly all Palestinian, released Saturday — the second such exchange during the fragile truce entering its second week.
Dani Miran, whose hostage son Omri is not slated for release during the first phase, demonstrated outside Netanyahu’s office in Jerusalem on Sunday.
“We want the agreement to continue and for them to bring our children back as quickly as possible — and all at once,” he said.
The truce has brought a surge of food, fuel, medicines and other aid into rubble-strewn Gaza, but the UN says “the humanitarian situation remains dire.”
Of the 251 hostages seized during Hamas’s October 7, 2023 attack that ignited the war, 87 remain in Gaza, including 34 the military says are dead.
The Hamas attack resulted in the deaths of 1,210 people, mostly civilians, according to an AFP tally based on official Israeli figures.
Israel’s retaliatory offensive has killed at least 47,306 people in Gaza, the majority civilians, according to figures from the Hamas-run territory’s health ministry that the United Nations considers reliable.
Bittersweet return for Syrians with killed, missing relatives

- “I thought that once I got to Syria, everything would be better, but in reality everything here is so very painful,” says Wafa Mustafa, whose father Ali was among the tens of thousands killed or missing in Syria’s notorious prison system
DAMASCUS: Wafa Mustafa had long dreamed of returning to Syria but the absence of her father tarnished her homecoming more than a decade after he disappeared in Bashar Assad’s jails.
Her father Ali, an activist, is among the tens of thousands killed or missing in Syria’s notorious prison system, and whose relatives have flocked home in search of answers after Assad’s toppling last month by Islamist-led rebels.
“From December 8 until today, I have not felt any joy,” said Mustafa, 35, who returned from Berlin.
“I thought that once I got to Syria, everything would be better, but in reality everything here is so very painful,” she said. “I walk down the street and remember that I had passed by that same corner with my dad” years before.
Since reaching Damascus she has scoured defunct security service branches, prisons, morgues and hospitals, hoping to glean any information about her long-lost father.
“You can see the fatigue on people’s faces” everywhere, said Mustafa, who works as a communications manager for the Syria Campaign, a rights group.

In 2021, she was invited to testify at the United Nations about the fate of Syria’s disappeared.
The rebels who toppled Assad freed thousands of detainees nearly 14 years into a civil war that killed more than 500,000 people and displaced millions.
Mustafa returned to Branch 215, one of Syria’s most notorious prisons run by military intelligence, where she herself had been detained simply for participating in pro-democracy protests in 2011.
She found documents there mentioning her father. “That’s already a start,” Mustafa said.
Now, she “wants the truth” and plans to continue searching for answers in Syria.
“I only dream of a grave, of having a place to go to in the morning to talk to my father,” she said. “Graves have become our biggest dream.”
In Damascus, Mustafa took part in a protest demanding justice for the disappeared and answers about their fate.

Youssef Sammawi, 29, was there too. He held up a picture of his cousin, whose arrest and beating in 2012 prompted Sammawi to flee for Germany.
A few years later, he identified his cousin’s corpse among the 55,000 images by a former military photographer codenamed “Caesar,” who defected and made the images public.
The photos taken between 2011 and 2013, authenticated by experts, show thousands of bodies tortured and starved to death in Syrian prisons.
“The joy I felt gave way to pain when I returned home, without being able to see my cousin,” Sammawi said.
He said his uncle had also been arrested and then executed after he went to see his son in the hospital.
“When I returned, it was the first time I truly realized that they were no longer there,” he said with sadness in his voice.
“My relatives had gotten used to their absence, but not me,” he added. “We demand that justice be served, to alleviate our suffering.”

While Assad’s fall allowed many to end their exile and seek answers, others are hesitant.
Fadwa Mahmoud, 70, told AFP she has had no news of her son and her husband, both opponents of the Assad government arrested upon arrival at Damascus airport in 2012.
She fled to Germany a year later and co-founded the Families For Freedom human rights group.
She said she has no plans to return to Syria just yet.
“No one really knows what might happen, so I prefer to stay cautious,” she said.
Mahmoud said she was disappointed that Syria’s new authorities, who pledged justice for victims of atrocities under Assad’s rule, “are not yet taking these cases seriously.”
She said Syria’s new leader Ahmed Al-Sharaa “has yet to do anything for missing Syrians,” yet “met Austin Tice’s mother two hours” after she arrived in the Syrian capital.
Tice is an American journalist missing in Syria since 2012.
Sharaa “did not respond” to requests from relatives of missing Syrians to meet him, Mahmoud said.
“The revolution would not have succeeded without the sacrifices of our detainees,” she said.
Deal reached to release more Israeli hostages and allow Palestinians into north Gaza

- Israel confirms Qatar's announcement, says Gazans can now return home from 7 a.m. Monday
- Netanyahu's office said that another six hostages would be released in the coming week, after talks with Hamas
DOHA/JERUSALEM/GAZA CITY: Mediator Qatar announced early Monday that an agreement has been reached to release an Israeli civilian hostage and allow Palestinians to return to northern Gaza, easing the first major crisis of the fragile ceasefire between Israel and Hamas.
Qatar’s statement said Hamas will hand over the civilian hostage, Arbel Yehoud, along with two other hostages before Friday. And on Monday, Israeli authorities will allow Palestinians to return to northern Gaza.
The office of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu in a statement said the hostage release — which will include soldier Agam Berger — will take place on Thursday, and confirmed that Palestinians can move north on Monday. Israel’s military said people can start crossing on foot at 7 a.m.
Under the ceasefire deal, Israel on Saturday was to begin allowing Palestinians to return to their homes in northern Gaza. But Israel put that on hold because of Yehoud, who Israel said should have been released on Saturday. Hamas accused Israel of violating the agreement.
Netanyahu's office said that another six hostages would be released in the coming week, after talks with Hamas. Three would be released on Thursday and another three on Saturday, said a statement from his office.
The breakthrough preserves a fragile ceasefire in the Israel-Hamas war, which has devastated the Gaza Strip and displaced nearly all its residents, paving the way for more hostage-prisoner swaps under a deal aimed at ending the more than 15-month conflict.
Israel had been preventing vast crowds of Palestinians from using a coastal road to return to northern Gaza, accusing Hamas of violating the truce agreement by failing to release civilian women hostages.
“Hamas has backtracked and will carry out an additional phase of releasing hostages this Thursday,” Netanyahu’s office said in a statement.
Trump’s plan meets mixed reactions
Palestinian leaders meanwhile slammed a plan floated by US President Donald Trump to “clean out” Gaza, vowing to resist any effort to forcibly displace residents of the war-battered territory.
Trump said Gaza had become a “demolition site,” adding he had spoken to Jordan’s King Abdullah II about moving Palestinians out.
“I’d like Egypt to take people. And I’d like Jordan to take people,” Trump told reporters.
Palestinian leader Mahmud Abbas, who is based in the Israeli-occupied West Bank, “expressed strong rejection and condemnation of any projects” aimed at displacing Palestinians from Gaza, his office said.
Bassem Naim, a member of Hamas’s political bureau, told AFP that Palestinians would “foil such projects,” as they have done to similar plans “for displacement and alternative homelands over the decades.”
Islamic Jihad, which has fought alongside Hamas in Gaza, called Trump’s idea “deplorable.”
For Palestinians, any attempt to move them from Gaza would evoke dark memories of what the Arab world calls the “Nakba,” or catastrophe — the mass displacement of Palestinians during Israel’s creation in 1948.
“We say to Trump and the whole world: we will not leave Palestine or Gaza, no matter what happens,” said displaced Gaza resident Rashad Al-Naji.
Trump floated the idea to reporters Saturday aboard Air Force One: “You’re talking about probably a million and half people, and we just clean out that whole thing.”
Moving Gaza’s roughly 2.4 million inhabitants could be done “temporarily or could be long term,” he said.
Israel’s far-right Finance Minister Bezalel Smotrich — who opposed the truce deal and has voiced support for re-establishing Israeli settlements in Gaza — called Trump’s suggestion of “a great idea.”
Tantamount to ‘ethnic cleansing’
The Arab League rejected the idea, warning against “attempts to uproot the Palestinian people from their land.”
“The forced displacement and eviction of people from their land can only be called ethnic cleansing,” the league said in a statement.
Jordanian Foreign Minister Ayman Safadi said “our rejection of the displacement of Palestinians is firm and will not change. Jordan is for Jordanians and Palestine is for Palestinians.”
Egypt’s foreign ministry said it rejected any infringement of Palestinians’ “inalienable rights.”
In Gaza, cars and carts loaded with belongings jammed a road near the Netzarim Corridor that Israel has blocked, preventing the expected return of hundreds of thousands of people to northern Gaza.
Israel had said it would prevent Palestinians’ passage until the release of Arbel Yehud, a civilian woman hostage. She is among those slated for return on Thursday, according to Netanyahu’s office.
Hamas said that blocking returns to the north also amounted to a truce violation, adding it had provided “all the necessary guarantees” for Yehud’s release.
Israeli army spokesman Avichay Adraee said Monday that residents would be allowed to return on foot starting at 07 a.m. (0500 GMT) and by car at 9 a.m.
Staggered releases
During the first phase of the Gaza truce, 33 hostages are supposed to be freed in staggered releases over six weeks in exchange for around 1,900 Palestinians held in Israeli jails.
The most recent swap saw four Israeli women hostages, all soldiers, and 200 prisoners, nearly all Palestinian, released Saturday — the second such exchange during the fragile truce entering its second week.
Dani Miran, whose hostage son Omri is not slated for release during the first phase, demonstrated outside Netanyahu’s office in Jerusalem on Sunday.
“We want the agreement to continue and for them to bring our children back as quickly as possible — and all at once,” he said.
The truce has brought a surge of food, fuel, medicines and other aid into rubble-strewn Gaza, but the UN says “the humanitarian situation remains dire.”
Of the 251 hostages seized during Hamas’s October 7, 2023 attack that ignited the war, 87 remain in Gaza, including 34 the military says are dead.
The Hamas attack resulted in the deaths of 1,210 people, mostly civilians, according to an AFP tally based on official Israeli figures.
Israel’s retaliatory offensive has killed at least 47,306 people in Gaza, the majority civilians, according to figures from the Hamas-run territory’s health ministry that the United Nations considers reliable.
Trump’s Palestinian refugee idea falls flat with Jordan and confounds a Senate ally

- Egypt and Jordan have made peace with Israel but support the creation of a Palestinian state in the occupied West Bank, Gaza and east Jerusalem, territories that Israel captured in the 1967 Mideast War
- Both Egypt and Jordan also have perpetually struggling economies and their governments, as well as those of other Arab states, fear massive destabilization of their own countries and the region from any such influx of refugees
DORAL, Florida: President Donald Trump’s push to have Egypt and Jordan take in large numbers of Palestinian refugees from besieged Gaza fell flat with those countries’ governments and left a key congressional ally in Washington perplexed on Sunday.
Fighting that broke out in the territory after ruling Hamas attacked Israel in October 2023 is paused due to a fragile ceasefire, but much of Gaza’s population has been left largely homeless by an Israeli military campaign. Trump told reporters Saturday aboard Air Force One that moving some 1.5 million people away from Gaza might mean that “we just clean out that whole thing.”
Trump relayed what he told Jordan’s King Abdullah when the two held a call earlier Saturday: “I said to him, ‘I’d love for you to take on more because I’m looking at the whole Gaza Strip right now, and it’s a mess.’”
He said he was making a similar appeal to Egyptian President Abdel Fattah El-Sisi during a conversation they were having while Trump was at his Doral resort in Florida on Sunday. Trump said he would “like Egypt to take people and I’d like Jordan to take people.”
Egypt and Jordan, along with the Palestinians, worry that Israel would never allow them to return to Gaza once they have left. Both Egypt and Jordan also have perpetually struggling economies and their governments, as well as those of other Arab states, fear massive destabilization of their own countries and the region from any such influx of refugees.
Jordan already is home to more than 2 million Palestinian refugees. Egypt has warned of the security implications of transferring large numbers of Palestinians to Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula, bordering Gaza.
Trump suggested that resettling most of Gaza’s population of 2.3 million could be temporary or long term.
Jordan’s foreign minister, Ayman Safadi, said Sunday that his country’s opposition to what Trump floated was “firm and unwavering.” Some Israel officials had raised the idea early in the war.
Egypt’s foreign minister issued a statement saying that the temporary or long-term transfer of Palestinians “risks expanding the conflict in the region.”
Trump does have leverage to wield over Jordan, which is a debt-strapped, but strategically important, US ally and is heavily dependent on foreign aid. The US is historically the single-largest provider of that aid, including more than $1.6 billion through the State Department in 2023.
Much of that comes as support for Jordan’s security forces and direct budget support.
Jordan in return has been a vital regional partner to the US in trying to help keep the region stable. Jordan hosts some 3,000 US troops. Yet, on Friday, new Secretary of State Marco Rubio exempted security assistance to Israel and Egypt but not to Jordan, when he laid out the details of a freeze on foreign assistance that Trump ordered on his first day in office.
Meantime, in the United States, even Trump loyalists tried to make sense of his words.
“I really don’t know,” said Sen. Lindsey Graham, when asked on CNN’s “State of the Union” about what Trump meant by the ”clean out” remark. Graham, who is close to Trump, said the suggestion was not feasible.
“The idea that all the Palestinians are going to leave and go somewhere else, I don’t see that to be overly practical,” said Graham, R-S.C. He said Trump should keep talking to Mideast leaders, including Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and officials in the United Arab Emirates.
“I don’t know what he’s talking about. But go talk to MBS, go talk to UAE, go talk to Egypt,” Graham said. “What is their plan for the Palestinians? Do they want them all to leave?”
Trump, a staunch supporter of Israel, also announced Saturday that he had directed the US to release a supply of 2,000-pound bombs to Israel. Former President Joe Biden had imposed a hold due to concerns about their effects on Gaza’s civilian population.
Egypt and Jordan have made peace with Israel but support the creation of a Palestinian state in the occupied West Bank, Gaza and east Jerusalem, territories that Israel captured in the 1967 Mideast War. They fear that the permanent displacement of Gaza’s population could make that impossible.
In making his case for such a massive population shift, Trump said Gaza is “literally a demolition site right now.”
“I’d rather get involved with some of the Arab nations, and build housing in a different location,” he said of people displaced in Gaza. “Where they can maybe live in peace for a change.”
Syria monitor says 35 people summarily executed in three days

- Most of those executed are former officers in the toppled Assad government who had presented themselves in centers set up by the new authorities, according to the Britain-based monitor with a network of sources inside Syria
DAMASCUS: Fighters affiliated with Syria’s new Islamist leaders have carried out 35 summary executions over 72 hours, mostly of Assad-era officers, a war monitor said Sunday.
The authorities, installed by the rebel forces that toppled longtime president Bashar Assad last month, said they had carried out multiple arrests in the western Homs area over unspecified “violations.”
Official news agency SANA said the authorities on Friday accused members of a “criminal group” who used a security sweep to commit abuses against residents, “posing as members of the security services.”
The Syrian Observatory for Human Rights monitor said that “these arrests follow grave violations and summary executions that had cost the lives of 35 people over the past 72 hours.”
It also said that “members of religious minorities” had suffered “humiliations.”
Most of those executed are former officers in the toppled Assad government who had presented themselves in centers set up by the new authorities, according to the Britain-based monitor with a network of sources inside Syria.
“Dozens of members of local armed groups under the control of the new Sunni Islamist coalition in power who participated in the security operations” in the Homs area “have been arrested,” the Observatory said.
It added that these groups “carried out reprisals and settled old scores with members of the Alawite minority to which Bashar Assad belongs, taking advantage of the state of chaos, the proliferations of arms and their ties to the new authorities.”
The Observatory listed “mass arbitrary arrests, atrocious abuse, attacks against religious symbols, mutilations of corpses, summary and brutal executions targeting civilians,” which it said showed “an unprecedented level of cruelty and violence.”
Civil Peace Group, a civil society organization, said in a statement that there had been civilian victims in multiple villages in the Homs area during the security sweep.
The group “condemned the unjustified violations” including the killing of unarmed men.
Since seizing power, the new authorities have sought to reassure religious and ethnic minorities in Syria that their rights would be upheld.
Members of Assad’s Alawite minority have expressed fear of retaliation over abuses during his clan’s decades in power.