LONDON: Tech giant Meta recently announced it would start removing social media posts that use the term “Zionist” in contexts where it refers to Jewish people and Israelis rather than representing supporters of the political movement, in an effort to curb antisemitism on its platforms.
Facebook and Instagram’s parent company previously said it would lift its blanket ban on the single most moderated term across all of Meta’s platforms — “shaheed,” or “martyr” in English — after a year-long review by its oversight board found the approach was “overbroad.”
Similarly, TikTok, X and Telegram have long promised to step up efforts to curb hate speech and the spread of disinformation on their platforms against the backdrop of the ongoing war in Gaza.

Activists accuse social media giants of censoring posts, including those providing evidence of human rights abuses in Gaza. (Getty Images)
These initiatives are intended to create a safer, less toxic online environment. However, as experts have consistently pointed out, these efforts often fall short, resulting in empty promises and a worrying trend toward censorship.
“In short, social media platforms have not been very good at avoiding censorship or curbing hate speech and disinformation about the war on Gaza,” Nadim Nashif, founder and director of 7amleh, a digital rights and human rights activist group for Palestinians, told Arab News.
“Throughout the conflict, censorship and account takedowns have jeopardized efforts to document on-the-ground human rights violations as well.”
Nashif says hate speech and incitement to violence remain “rampant,” particularly on Meta’s platforms and X, where antisemitic and Islamophobic content continues “to spread widely.”
Since the Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack that sparked the conflict in Gaza, social media has been inundated with content related to the war. In many instances it has served as a crucial window into the dramatic events unfolding in the region and has become a vital source of real-time news and accountability for Israeli actions.
Profiles supporting the actions of both Hamas and the Israeli government have been accused of sharing misleading and hateful content.
FASTFACT
1,050
Takedowns and other suppressions of content on Instagram and Facebook posted by Palestinians and their supporters, documented by Human Rights Watch during October-November 2023 period.
Even so, none of the social media platforms — including Meta, YouTube, X, TikTok, or messaging apps such as Telegram — has publicly outlined policies designed to mitigate hate speech and incitement to violence in relation to the conflict.
Instead, these platforms remain flooded with war propaganda, dehumanizing speech, genocidal statements, explicit calls to violence, and racist hate speech. In some cases, platforms are taking down pro-Palestinian content, blocking accounts, and sometimes shadow banning users voicing their support for the people of Gaza.
On Friday, Turkiye’s communications authority blocked access to the Meta-owned social media platform Instagram. Local media outlets said access was blocked in response to Instagram removing posts by Turkish users that expressed condolences over the recent killing in Tehran of Hamas political chief Ismail Haniyeh.
The previous day, Malaysia’s Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim accused Meta of cowardice after his Facebook post on Haniyeh’s killing was removed. “Let this serve as a clear and unequivocal message to Meta: Cease this display of cowardice,” wrote Anwar, who has repeatedly condemned Israel’s war on Gaza and its actions in the occupied West Bank, on his Facebook page.
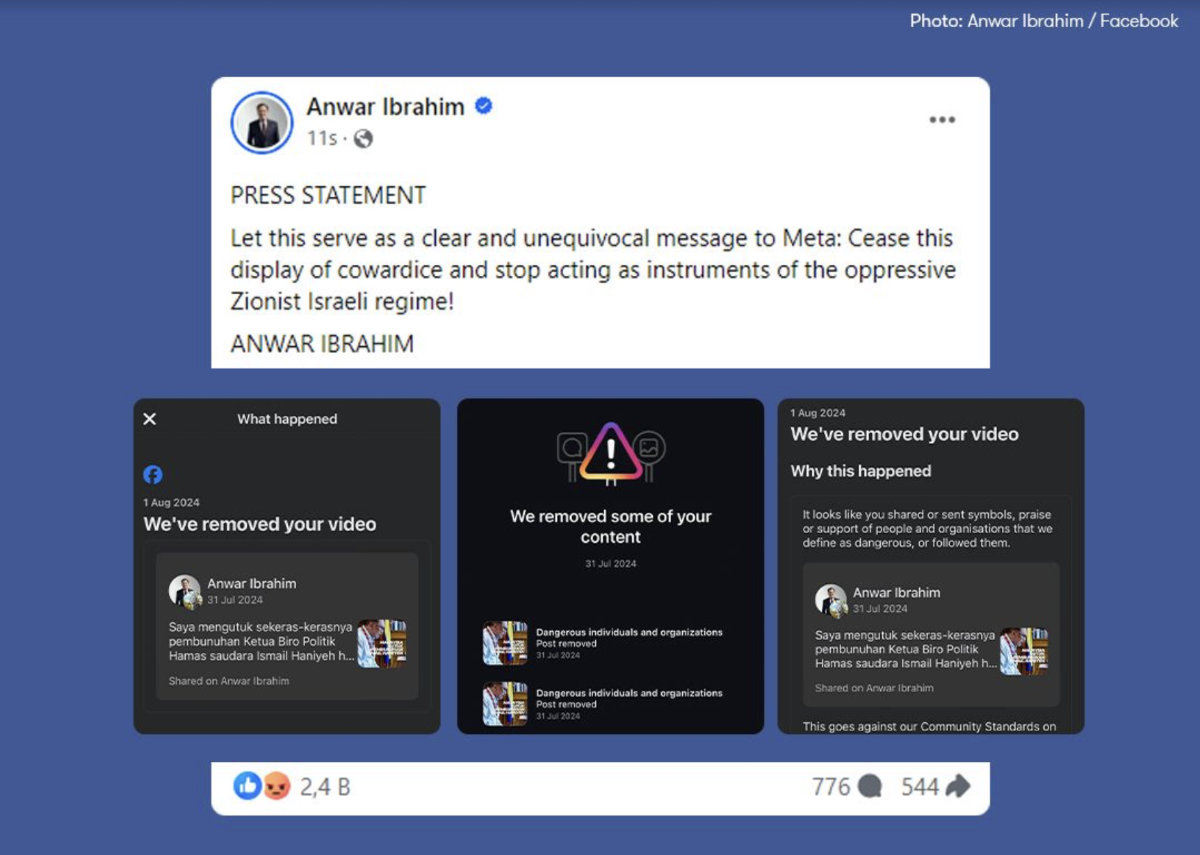
Screenshot of Malaysian Prime Minister Anwar Ibrahim's post denouncing Meta's censorship of his post criotical against Israel's assassination policy.
Meanwhile, footage of Israeli soldiers purportedly blowing up mosques and homes, burning copies of the Qur’an, torturing and humiliating blindfolded Palestinian detainees, driving them around strapped to the bonnet of military vehicles, and celebrating war crimes remain freely available on mobile screens.
“Historically, platforms have been very bad at moderating content about Israel and Palestine,” said Nashif. “Throughout the war on Gaza, and the ongoing plausible genocide, this has simply been exacerbated.”
A report by Human Rights Watch titled “Meta’s Broken Promises,” published in December, accused the firm of “systematic online censorship” and “inconsistent and opaque application of its policies” and practices that have been silencing voices in support of Palestine and Palestinian human rights on Instagram and Facebook.
The report added that Meta’s behavior “fails to meet its human rights due diligence responsibilities” due to years-long failed promises to address its “overbroad crackdowns.”
Jacob Mukherjee, convenor of the political communications MA program at Goldsmiths, University of London, told Arab News: “I’m not sure to what extent you can really even call them efforts to stop censorship.
“Meta promised to conduct various reviews — which, by the way, it has been promising for a good couple of years now since the last upsurge in the Israel-Palestine conflict in 2021 — before Oct. 7 last year.
“But as far as I can see, not a great deal has changed, substantially speaking. They have had to respond to suggestions that they’ve been engaged in censorship, of course, but that’s mainly been a PR effort in my view.”

Between October and November 2023, Human Rights Watch documented more than 1,050 takedowns and other suppressions of content on Instagram and Facebook posted by Palestinians and their supporters, including content about human rights abuses.
Of these, 1,049 involved peaceful content in support of Palestine that was censored or otherwise unduly suppressed, while one case involved the removal of content in support of Israel.
However, censorship appears to be only part of the issue.
7amleh’s violence indicator, which monitors real-time data on violent content in Hebrew and Arabic on social media platforms, has recorded more than 8.6 million pieces of such content since the conflict began.

Nashif says the proliferation of violent and harmful content, predominantly in Hebrew, is largely due to insufficient investment in moderation.
This content, which has primarily targeted Palestinians on platforms like Facebook and Instagram, was used by South Africa as evidence in its case against Israel at the International Court of Justice.
Meta is arguably not alone in bearing responsibility for what has been described by South Africa’s lawyers as the first genocide livestreamed to mobile phones, computers, and television screens.

Activists accuse social media giants of censoring posts, including those providing evidence of human rights abuses in Gaza. (Getty Images)
X too has faced accusations from both supporters of both Palestine and Israel of giving free rein to handles known for spreading disinformation and doctored images, which oftentimes have been shared by prominent political and media personalities.
“One of the major issues with current content moderation systems is a lack of transparency,” said Nashif.
“When it comes to AI, the platforms do not release clear and transparent information about when and how AI systems are implemented in the content moderation process. Policies are often opaque and allow a great deal of leeway for the platforms to do as they see fit.”
For Mukherjee, the issue of moderation happening behind a smoke screen of murky policies is strongly political, requiring these companies to adopt a “balanced” approach between political pressure and “managing the expectations and desires of the user base.”

Activists accuse social media giants of censoring posts, including those providing evidence of human rights abuses in Gaza. (Getty Images)
He said: “These AI tools can kind of be used to insulate the real power holders, i.e. the people that run the platforms, from criticism and accountability, which is a real problem.
“These platforms are private monopolies that are essentially responsible for regulating an important part of the political public sphere.
“In other words, they’re helping to shape and regulate the arena in which conversations happen, in which people form their opinions, from which politicians feel the pressure of public opinion, and yet they are completely unaccountable.”
Although there have been examples of pro-Palestinian content being censored or removed, as revealed by Arab News in October, these platforms made clear, well before the Gaza conflict, that it is ultimately not in their interest to take down content from their platforms.
“These platforms are not made for reasons of public interest or in order to ensure that we have an informed and educated populace that’s exposed to a range of perspectives and is equipped to properly make decisions and form opinions,” said Mukherjee.
“The fact (is) that the business models actually want there to be lots of content and if that’s pro-Palestine content, then so be it. It’s ultimately still getting eyeballs and engagement on the platform, and content that provokes strong sentiment, to use the industry’s terms, gets engagement, and that means data and that means money.”































