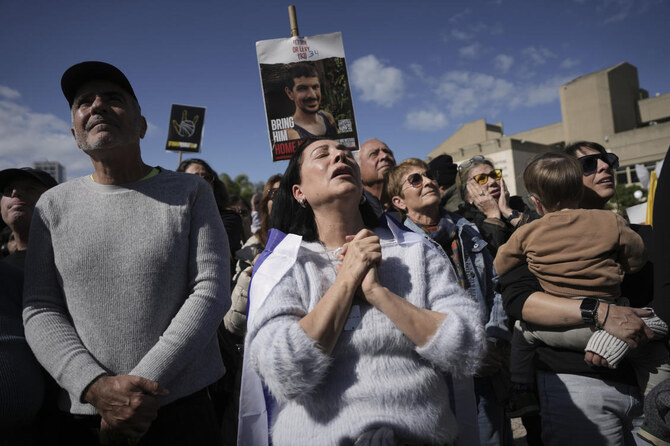
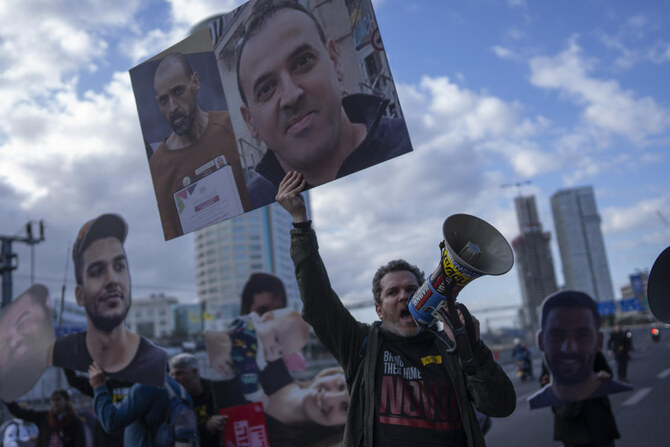RAMAT GAN, Israel: After 484 days of captivity in Gaza, Keith Siegel had many questions. Was his 97-year-old mother still alive? Which of his neighbors was killed in Hamas’ Oct. 7, 2023, attack? Why did it take so long to free him?
With minimal access to media, the dual American-Israeli citizen only learned months after he was captured that his son had survived the attack that launched the war in Gaza. He had heard that his family and others’ were advocating for hostages’ freedom. But beyond that, he knew very little about life outside his confines in Gaza.
“He really wanted to know everything as soon as possible, just to put all the question marks away and to know what happened,” said his daughter, Elan Siegel.
Hostages freed as part of a tenuous ceasefire in Gaza are confronting a flood of information about loved ones and destroyed communities, and are still figuring out their place in a changed world. Their families are grappling with how to fill them in on what they missed without potentially deepening their trauma.
Experts say it is important to be cautious.
“The information is definitely traumatic so you have to really be sensitive, careful and monitor the pace in which you expose the information,” said Einat Yehene, who heads the rehabilitation division at the Hostages and Missing Families Forum.
Paraded by Hamas, then by shattered reality
For many freed captives, catching up has been excruciating.
Eli Sharabi, 52, had no exposure to media during his 16-month ordeal, according to his brother, Sharon Sharabi.
Forced to speak at a staged Hamas ceremony before his release, a gaunt Sharabi told a crowd of masked militants and journalists that he was looking forward to seeing his wife and two teenage daughters back in Israel.
Then he learned the crushing reality shortly after his arrival in Israel: all three had been killed at home during the Oct. 7 attack.
“Beyond the emotional burden and difficult experiences he faced in captivity, he had to bear this horrible loss on the first day that he left from there,” his brother told Israeli Army Radio.
Or Levy, 34, was dealt a similar blow upon being freed. That is when he learned that his wife, Einav, was killed on Oct. 7.
“For 491 days, he held onto hope that he would return to her,” his brother, Michael Levy, told reporters.
Levy was reunited with his young son, who hit key developmental milestones, like being potty trained, while his father was in captivity. “It took you a long time to come back,” the 3-year-old told his father, according to Israeli media.
Facing uncertainty even after being freed
The first person Keith Siegel asked about upon returning home was his mother, Gladys. When his wife’s eyes welled up, he immediately understood she had died, his daughter recounted.
Siegel picked up some information about his family while in captivity. Months into the war, he heard his daughter on the radio, speaking about how his son had survived Hamas’ attack. Other freed hostages have also reported hearing messages from their families through the news media.
Yarden Bibas, who was freed earlier this month, was told by his captors that his wife, Shiri, and their two young sons, Ariel and Kfir, were dead. But he was also told they were spotted in Tel Aviv, according to Israeli media.
Now that he is out, he still lacks clarity. They remain in Gaza, and the Israeli government has said it has “serious concern” for their lives.
A relentless need to know more
Beyond their personal lives, freed hostages are also taking in more than a year’s worth of world events: President Donald Trump is back in the White House; Israel and Iran engaged in their first direct attacks; Israel killed the longtime chief of the militant group Hezbollah, Hassan Nasrallah.
Keith Siegel’s family is sharing information sparingly, as one might with a child. “You answer only what he asks and not more than that,” his daughter, Elan, said.
But the questions are relentless.
Siegel wanted to know what happened to his community of Kfar Aza. Was anyone watering the plants? Who was killed in Hamas’ attack?
“We asked him if he’s sure that he’s ready. And he said ‘yes,’ that he just wants to know. So I read him the list of 64 people” who were killed, his daughter said. She said his reaction to the news has been muted because “it’s almost like he forgot how to feel” while in captivity.
Siegel’s photo has been a mainstay at protests and on banners highlighting the plight of hostages, making him recognizable across Israel. Ahead of his release, dozens of Israelis posted videos of themselves on social media making his favorite pancake recipe.
Siegel’s wife, Aviva, who was freed from captivity in the early weeks of the war, prepared a book for him that includes notes from the important figures she had lobbied on his behalf — from Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to former US President Joe Biden.
Siegel was especially befuddled by the revelation that world leaders knew about his captivity.
His daughter, Elan, recalled him saying: “If they knew, how can it be that I was there for so long?”
Hostages freed from Gaza painfully piece together a changed world
https://arab.news/vunn6
Hostages freed from Gaza painfully piece together a changed world

- Hostages freed as part of a tenuous ceasefire in Gaza are confronting a flood of information about loved ones and destroyed communities
- Their families are grappling with how to fill them in on what they missed without potentially deepening their trauma
Does military’s recapture of Khartoum mark a crossroads in Sudan’s conflict?

- General Al-Burhan’s forces control key sites in the capital, including the airport, which will be critical for humanitarian relief
- Despite the losses in Khartoum, his foes have entrenched themselves in Darfur, maintaining a power base and foreign backing
LONDON: Sudan’s de-facto military ruler visited the presidential palace in Khartoum on Wednesday after his forces recaptured the city from a rival paramilitary group. Whether the development will prove to be a decisive moment in the conflict that has devastated the country since April 2023 remains to be seen.
Khartoum, once one of East Africa’s fastest-growing capitals, is today a ghost city, its residents displaced and its basic infrastructure in ruins. “It’s heartbreaking to see people dying in huge numbers from hunger in Sudan, once the breadbasket of East Africa,” Mathilde Vu, a Sudan-based aid worker with the Norwegian Refugee Council, told Arab News.
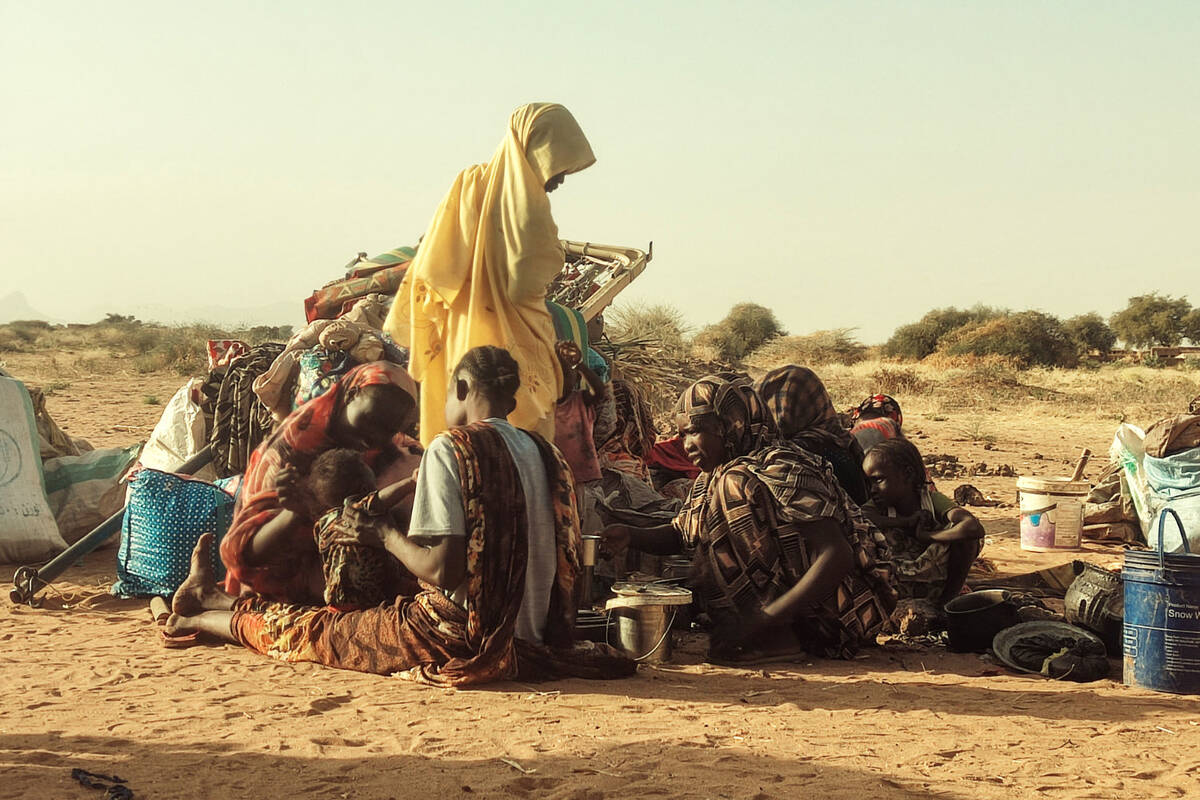

According to Vu, the humanitarian response in the capital depends heavily on grassroots efforts. “Local responders are the one hope of Sudan,” she said. “They operate without logos, without any resources, and yet they’ve organized evacuations, run soup kitchens, offered psychosocial support, even repaired water systems.”
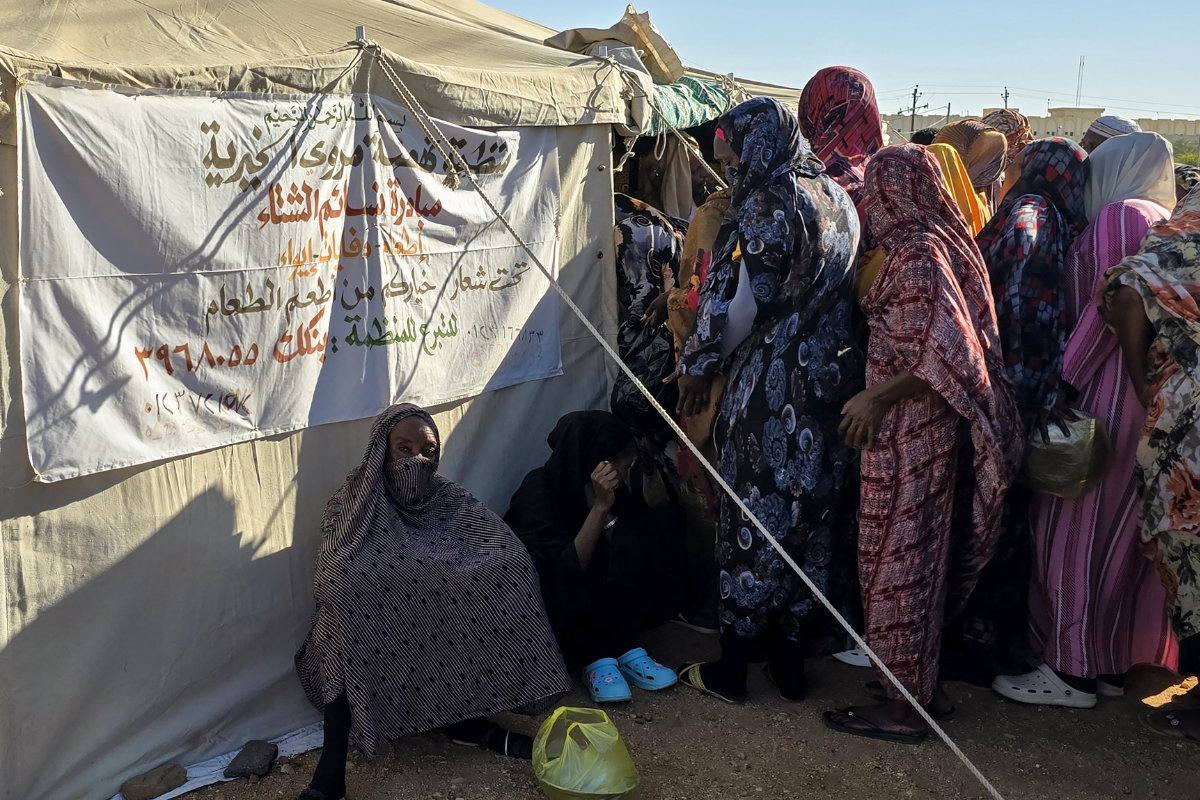

But these efforts are fragile and increasingly under threat, with at least 10 local responders killed during intensified fighting in March. “If one local responder dies, one kitchen is closed. And with that, entire families are left without food,” Vu said.
The Sudanese Armed Forces have in recent days consolidated control not just over the presidential palace, but also the central bank, the airport and the strategic Al-Yarmouk weapons manufacturing complex, having dislodged its adversary, the Rapid Support Forces.
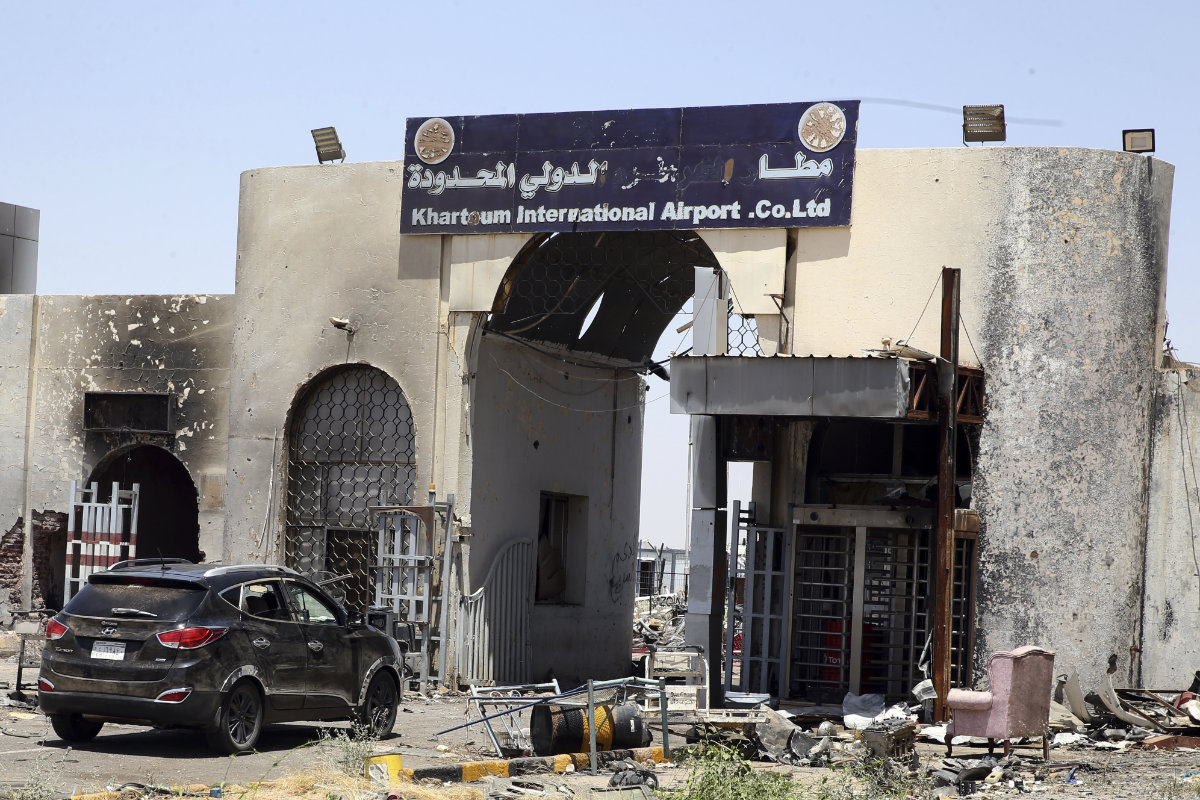

These are symbolic gains. But whether they will translate into stability or reconstruction is far from certain.
Abiol Lual Deng, a South Sudanese-American political scientist, cautions against assuming that the SAF’s return to the city signals a new era. “This is a city where people died from starvation and infectious disease — not just bullets,” she told Arab News.
“The fighting disrupted every part of urban life. Shops closed, fuel ran out, water became contaminated, and no one could move because of snipers and shelling.”
She added: “Now that SAF has retaken key areas like the airport, we might see some humanitarian aid trickling back in, especially for the wounded and those in critical need. But the scale of need is just unfathomable. Two-thirds of Sudan’s population requires assistance. This is not something a few aid flights can solve.”
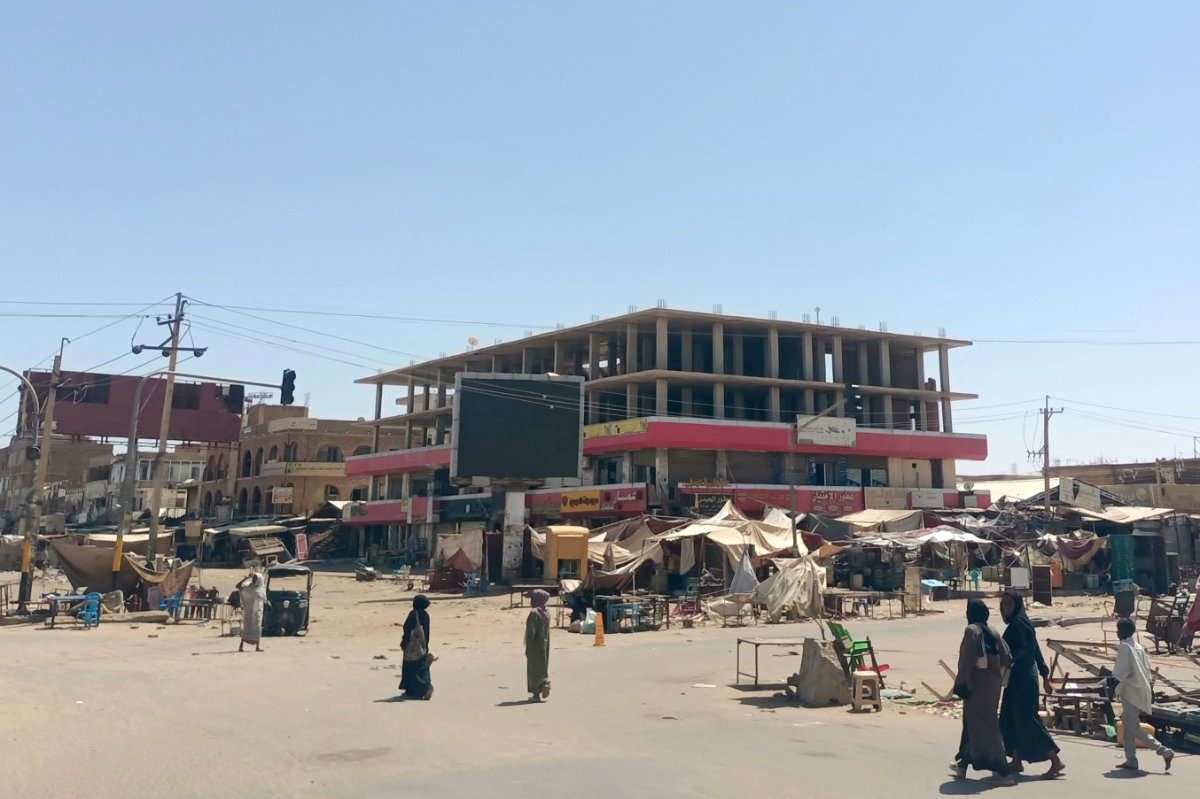

The destruction of Khartoum’s civilian infrastructure has been especially devastating because of the city’s role in the national economy. Once home to the country’s key financial institutions, markets, and trade corridors, Khartoum’s paralysis has sent ripples across Sudan and beyond.
The SAF’s ability to maintain control over the capital will depend not just on military gains, but also on whether it can stabilize these essential services.
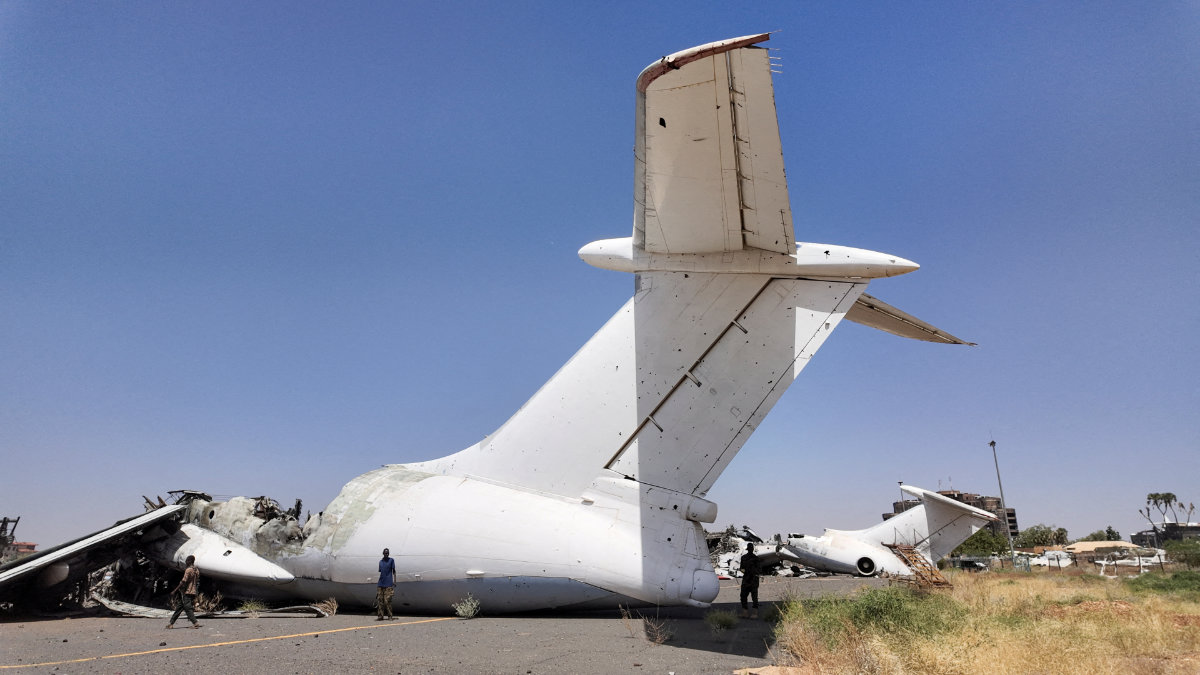

Dallia Abdelmoniem, a Sudanese analyst with deep experience in civil society networks, points out that many displaced civilians are already planning to return — despite the lack of security guarantees.
“For many Sudanese, they don’t have the privilege to wait for full reconstruction,” she told Arab News. “They’re returning to neighborhoods where there’s no running water, no banks, no healthcare. Civil society will be forced to fill the vacuum again.”
Yet any suggestion that the war is winding down would be premature. Having withdrawn from Khartoum, the RSF has entrenched itself in Darfur and other regions. There, it continues to function as a parallel authority, with reports of its leader, Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, making diplomatic overtures to regional leaders.

“The RSF has already established a parallel government,” said Deng. “They’re not disappearing. They have a base of power in Darfur, strong cross-border supply networks, and deep-rooted ethnic and regional dynamics backing them.”
She reminds observers that the RSF originated as a paramilitary force — evolving from the Janjaweed militias once backed by the central government — and has long been used to destabilize peripheries under the guise of counterinsurgency.
Abdelmoniem warns the SAF’s territorial gains may embolden it to pursue an outright military solution to the conflict. “Negotiations appear dead in the water,” she said. “SAF has political momentum now, and it would be naive to think that pushing the RSF into Darfur means an end to hostilities. We’re more likely to see Darfur become a sustained war zone again.”
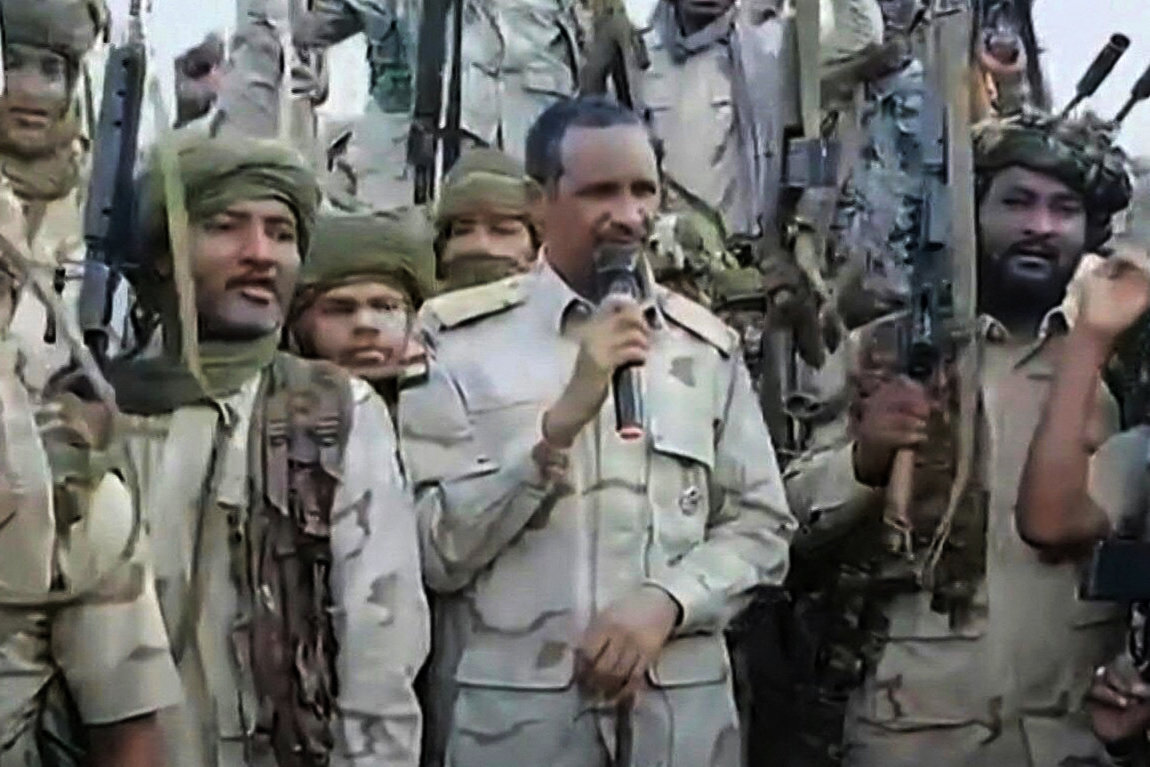

Even as the geography of the conflict shifts, the consequences remain grim for civilians. In Darfur’s Al-Fasher and Zamzam camp, where thousands are trapped in siege-like conditions, Vu describes haunting scenes of families trying to escape on donkeys under the cover of night — leaving everything behind.
“They’re too scared to take cars during the day because they could be arrested or attacked,” she said.
Access to these areas remains severely limited. “We must be realistic about the fact that both sides have obstructed aid,” said Deng. “But RSF-controlled areas are among the worst-hit. Famine conditions are spreading, and aid blockades are used as a weapon of war.”
Still, she says, international humanitarian organizations like the International Committee of the Red Cross and Medecins Sans Frontieres continue to engage with non-state actors.
“Groups like the ICRC or MSF operate based on neutrality, and the RSF knows that,” said Deng. “Sometimes access is possible — but it requires pressure, not just on the ground, but also on the states backing these groups with arms and logistics.”


That pressure, so far, has been uneven. The international response to Sudan’s war has been widely criticized as inadequate, both in scale and in coherence. Vu underlines that while the world debates political solutions, people are starving.
“Humanitarian access must prevail, whether there is peace or not,” she said. “Aid should have no side.”
Meanwhile, SAF’s internal cohesion remains uncertain. Analysts have long warned of leadership fractures within the army and its allied militias. Deng points out that the SAF and RSF were not always rivals — they once operated in concert, often carrying out atrocities in Darfur and the south together.

“Now they’ve turned those tactics on each other,” she said. “That a power vacuum would emerge inside the SAF is no surprise. Everyone wants to be seen as the legitimate inheritor of military authority.”
In the background looms a larger question: How much of Sudan’s war is about Sudan at all? “We’re entering an era where global geopolitics is less about rules and more about resources,” said Deng.
“Sudan manufactures its own weapons. It’s geographically pivotal. And it’s being drawn into the gravitational pull of multiple regional powers. That changes how this war plays out — and how it ends.”


For now, Khartoum remains in limbo. The SAF may have reclaimed the city, but it has not yet won the peace.
Displaced civilians are navigating shattered neighborhoods. Aid might be trickling in, but it is far from sufficient. Across the country, war rages on in new theatres. And a political resolution, however desirable, feels no closer.
“The international community must increase pressure on the warring parties and their backers,” said Vu. “Without strong engagement, especially from countries with influence over SAF and RSF, aid will remain politicized and civilians will keep paying the price.”

Hamas says it accepts a new Gaza ceasefire proposal but Israel makes a counter-offer

- It was not immediately clear whether the proposal changed before Khalil Al-Hayyah, the leader of Hamas in Gaza, announced it had been accepted
- Frustrated by the threat to remaining hostages in Gaza, families and others rallied again Saturday evening to call for a deal that would bring everyone home
CAIRO: The Hamas militant group said Saturday it has accepted a new Gaza ceasefire proposal from mediators Egypt and Qatar, but Israel said it has made a counter-proposal in “full coordination” with the third mediator, the United States.
Egypt early in the week made a proposal to get the troubled ceasefire back on track, following Israel’s surprise resumption of fighting.
It was not immediately clear whether the proposal changed before Khalil Al-Hayyah, the leader of Hamas in Gaza, announced it had been accepted.
Early in the week, an Egyptian official described the proposal to The Associated Press, saying Hamas would release five living hostages, including an American-Israeli, from Gaza in return for Israel allowing aid into the territory and a weekslong pause in fighting. Israel would release hundreds of Palestinian prisoners. The official spoke on condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to brief media on the closed-door talks.
On Saturday, the office of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu gave no details about Israel’s counter-proposal, which it said was offered after Netanyahu held consultations on Friday.
Israel a week and a half ago ended its ceasefire with Hamas by launching a surprise wave of strikes that killed hundreds of people. The White House blamed Hamas for the renewed fighting.
Israel has vowed to escalate the war until Hamas returns the 59 hostages it still holds — 24 of them believed to be alive. Israel also wants Hamas to give up power, disarm and send its leaders into exile. On Saturday, Israel widened its ground operations in Gaza’s southern city of Rafah near the border with Egypt.
Hamas has said it will only release the remaining captives in exchange for Palestinian prisoners, a lasting ceasefire and an Israeli withdrawal from Gaza.
Frustrated by the threat to remaining hostages in Gaza, families and others rallied again Saturday evening to call for a deal that would bring everyone home.
“The price of your war is the life of the hostages!” some protesters chanted in Tel Aviv. Minor scuffles broke out with police.
“War will not bring our hostages home, it will kill them,” Naama Weinberg, cousin of deceased hostage Itay Svirsky, told a weekly gathering of families in Tel Aviv.
The war in Gaza was triggered by Hamas’ Oct. 7, 2023, attack into Israel, in which Palestinian militants killed some 1,200 people, mostly civilians, and abducted 251.
Israel’s retaliatory offensive has killed over 50,000 people, according to Gaza’s Health Ministry, which does not say how many were civilians or combatants. Israel’s bombardment and ground operations have caused vast destruction and at their height displaced some 90 percent of Gaza’s population of over 2 million people.
Early this month, Israel again cut off all supplies to Gaza to pressure Hamas to accept new terms to the ceasefire that started in mid-January.
Israel had balked at entering negotiations over the truce’s second phase, which were meant to begin in early February. Under the agreement, phase two was meant to bring the release of the remaining 24 living hostages, an end to the war and full Israeli withdrawal from Gaza.
Misinformation, online hate speech fuels panic in South Sudan

NAIROBI: Misinformation and online hate speech are fueling panic and division in South Sudan at a time of acute political tensions that observers fear could drive the country back to war.
Ethnic divisions, particularly between the largest communities, the Dinka and Nuer, fueled the brutal civil war of 2013-18 in which some 400,000 people died.
After years of relative calm, there are worrying signs of renewed ethnic polarization, said Nelson Kwaje, chair of Digital Rights Frontlines, an organization based in the capital Juba that monitors hate speech and misinformation online.
FASTFACT
After years of relative calm, there are worrying signs of renewed ethnic polarization, said Nelson Kwaje, chair of Digital Rights Frontlines, an organization that monitors hate speech and misinformation online.
It comes as the 2018 peace agreement between President Salva Kiir and his long-time rival, First Vice President Riek Machar — who are respectively of Dinka and Nuer ethnicity — is hanging in the balance after Machar’s arrest on Wednesday.
He said mobile phone penetration in South Sudan is only 40 to 50 percent, and social media use around 10 percent at a conservative estimate.
However, those with access are often “the loudest voices,” and their messages spread through communities by more traditional means, helping poison the atmosphere.
Kwaje, speaking from Juba, said life in the city was still “relatively calm.”
But “social media disinformation and hate speech, which is very intense,” is stoking fears.
“There are rumors of assassinations, talk of retaliatory violence ... warnings about ethnic violence,” he said.
First, the brutal killing of an army general captured by members of a predominantly Nuer militia known as the White Army, and then a video appearing to show a young Dinka man being savagely treated by people with Nuer accents.
Ethnic polarization had reduced considerably in recent years, said Kwaje, but those videos have once again “radicalized people.”
“The polarization is obvious,” he said.
“If more incidents go in this direction, it will go to the next level of people taking up arms.”
“South Sudan has limited access to good information and free media. It creates a vacuum,” said Kwaje.
“The people who fill the vacuum are not all nefarious; many just want to share information to protect their community.
“But then you have actors who want to engage in fan engagement, and a small section who are politically motivated.”
He said it was hard to identify who was behind these political messages, but they were consistent and well-designed.
“When we see that level, we know there’s someone on a payroll,” said Kwaje.
“We have better shock absorbers now,” said Kwaje.
When the civil war broke out in 2013, there was an evident tribal divide “from day one,” he said.
The peace agreement that ended the war in 2018, “for all its faults,” engaged the international community, partially unified and disarmed Kiir and Machar’s respective armies, and installed an arms embargo that limited the supply of weapons to some extent, said Kwaje.
“Young people are also aware of the dangers of dividing along tribal lines. There is a lot of messaging about peace.
“But what pushes people to the edge is sharing content showing someone from your tribe being mistreated. Whether that content is factual or not, that immediately radicalizes you.”
Hezbollah says it will act if Israel’s attacks on Lebanon continue

- “We fully complied and we have no presence south of the Litani but Israel did not abide,” Kassem said
- “These (Israeli strikes) are not violations. They are an aggression that crossed all limits”
BEIRUT: The leader of Lebanon’s Hezbollah group warned Saturday that if Israel’s attacks on Lebanon continue and the Lebanese state does not act to stop them, the group will eventually resort to other alternatives.
Naim Kassem’s comments came a day after Israel launched an attack on Lebanon’s capital for the first time since a ceasefire ended the latest Israel-Hezbollah war in November. The strike on Beirut came hours after two rockets were fired from Lebanon toward Israel and Hezbollah denied it fired them.
There was no immediate response from Israeli officials.
Kassem was supposed to give his speech on Friday to mark Jerusalem Day that is usually held on the last Friday of the Muslim holy month of Ramadan. However, it was postponed because of the Israeli airstrikes on different parts of Lebanon including a suburb of the capital.
Jerusalem Day is an annual international day launched by Iran’s first supreme leader Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini in 1979 in which Iranians and many of their allies show support for the Palestinians.
Under the US-brokered ceasefire that end the 14-month Israel-Hezbollah war, Israeli forces were supposed to withdraw from all Lebanese territory by late January while Hezbollah had to end its armed presence south of the Litani river along the border with Israel.
The deadline was extended to Feb. 18, but Israel has remained in five border locations while carrying out dozens of strikes on what it said were Hezbollah targets in southern and eastern Lebanon. Last week, Israeli airstrikes on several locations in Lebanon killed six people while an airstrike on a southern village on Friday killed three and wounded 18, most of them women and children.
“We fully complied and we have no presence south of the Litani but Israel did not abide. Israel is carrying aggressions every day,” Kassem said in his televised speech Saturday night.
“These (Israeli strikes) are not violations. They are an aggression that crossed all limits,” Kassem added. He said Israel appears to be pressuring Lebanon to normalize relations with it, a move the Hezbollah totally rejects.
“Israel will not get during peace time what it was not able to achieve by war,” he said. “Let everyone know that this resistance (Hezbollah) is present and ready and at the same time is committed to the agreement.”
But Kassem warned that if Israel does not abide by the deal and the Lebanese state is not able to impose the implementation of the deal through political means, then “we will have to resort to other alternatives.” It was an apparent reference that Hezbollah might resort to its weapons to fight Israeli troops inside Lebanon.
“We will not allow anyone to deprive us from using our force and capabilities to confront this enemy,” said Kassem. He added that Hezbollah “is not weak in facing the projects of America and Israel.”
“Our patience so far aims to give a chance to solutions that could reduce the pains and casualties,” Kassem said.
Hezbollah began launching rockets, drones and missiles into Israel the day after the Oct. 7, 2023, attack on southern Israel by its Hamas allies ignited the war in Gaza. Palestinian militants killed about 1,200 in Israel and abducted 251 others during the 2023 attack.
The Israel-Hezbollah conflict exploded into all-out war last September when Israel carried out waves of airstrikes and killed most of the militant group’s senior leaders. The fighting killed over 4,000 people in Lebanon and displaced about 60,000 Israelis.
Hundreds of thousands join Istanbul protest rally

- Ozgur Ozel, leader of the main opposition party CHP which organized the rally, said there were 2.2 million people in the crowd
- The mass protests, which began with Imamoglu’s March 19 detention on contested fraud and “terror” charges, have prompted a repressive government response
ISTANBUL: Waving flags and chanting slogans, many hundreds of thousands of anti-government demonstrators rallied Saturday in Istanbul in defense of democracy after the arrest of mayor Ekrem Imamoglu which sparked Turkiye’s worst street unrest in over a decade.
Under a cloudless blue sky, vast crowds gathered in Maltepe on the Asian side of Turkiye’s biggest city on the eve of the Eid Al-Fitr celebration which starts Sunday, marking the end of Ramadan.
Ozgur Ozel, leader of the main opposition party CHP which organized the rally, said there were 2.2 million people in the crowd, but AFP was unable to independently confirm the figure.
The mass protests, which began with Imamoglu’s March 19 detention on contested fraud and “terror” charges, have prompted a repressive government response that has been sharply condemned by rights groups and drawn criticism from abroad.
Widely seen as the only politician capable of challenging President Recep Tayyip Erdogan at the ballot box, Imamoglu was elected as CHP’s candidate for the 2028 race on the day he was jailed.
As his wife, Dilek, arrived on stage, massive applause arose from the crowd which was a sea of Turkish flags and pictures of Mustafa Kemal Ataturk, modern Turkiye’s founding father.
Imamoglu was resoundingly re-elected mayor for the third time last year. The anger over his arrest which began in Istanbul quickly spread across Turkiye.
Nightly protests outside Istanbul City Hall drew vast crowds and often degenerated into running battles with riot police, who used teargas, pepper spray and rubber bullets to disperse the protesters.
“We are here today for our homeland. We, the people, elect our rulers,” insisted 17-year-old Melis Basak Ergun, a young protester who vowed they would never be cowed “by violence or tear gas.”
“We stand behind our mayor, Imamoglu.”
Turkish authorities did not comment on the latest mass protest. Erdogan has previously branded the demonstrations “street terror.”
In a letter read out to the crowd, Imamoglu addressed Turkiye’s youngsters, saying: “If young people are on the front line, it’s because they’re the ones who feel most anxiety about the future.
“The youth are telling Recep Tayyip Erdogan: Show the people respect. Don’t touch the nation’s will. Don’t cheat — compete fairly. But Erdogan is closing his ears to these voices,” he wrote.
“This is not about Ekrem Imamoglu, it’s about our country... It is about justice, democracy and freedom,” he said, as the crowd roared back: “Rights! Law! Justice!“
“Everywhere is Taksim, resistance is everywhere!” they chanted, referring to Istanbul’s iconic Taksim Square, site of the last massive wave of protests in 2013.
The last major demonstration called by CHP was Tuesday ahead of Saturday’s big rally, although students have continued to protest throughout the week.
Speaking to French newspaper Le Monde, Ozel said there would be weekly rallies every Saturday in different cities across Turkiye as well as a weekly Wednesday night demo in Istanbul.
“If we don’t stop this attempted coup, it will mean the end of the ballot box,” he said.
“I joined the rallies outside City Hall for four days together with university students. I told them not to give in,” protester Cafer Sungur, 78, told AFP.
“There is no other way than to keep fighting,” he said.
“I was jailed in the 1970s but back then there was justice. Today we can’t talk about justice anymore.”
Student groups have kept up their own protests, most of them masked, in the face of a police crackdown that has seen nearly 2,000 people arrested.
The authorities have also cracked down on media coverage, arresting 13 Turkish journalists in five days, deporting a BBC correspondent and on Thursday arresting a Swedish reporter who flew into Istanbul to cover the unrest.
Eleven journalists were freed Thursday, among them AFP photographer Yasin Akgul.
Swedish journalist Joakim Medin was jailed on Friday, his employer Dagens ETC told AFP.
Reporters Without Borders’ Turkiye representative Erol Onderoglu said Medin had been charged with “insulting the president” — a charge often use to silence Erdogan’s critics.
“The judicial pressure systematically brought to bear on local journalists for a long time is now being brought to bear on their foreign colleagues,” he told AFP, two days after the deportation of BBC correspondent Mark Lowen.
He said authorities had accused him of being “a threat to public order.”
Baris Altintas, co-director of MLSA, a legal NGO helping many of the detainees, told AFP the authorities “seem to be very determined to limit coverage of the protests.
“We fear the crackdown on the press will not only continue but increase,” she said.