WASHINGTON: The Myanmar military, which has been accused of ethnic cleansing against the country’s Muslim Rohingya minority, has been invited back as an observer in a major multinational military exercise next year led by the United States and Thailand.
Lt. Col. Christopher Logan, a Pentagon spokesman, told Reuters that Thailand had invited Myanmar to take part in the annual Cobra Gold exercise, which involves thousands of USand Thai military personnel and participants from other Asian countries.
Myanmar had been invited to observe the humanitarian assistance and disaster relief portion of the exercise, Logan said.
A senior officer at the Directorate of Joint Intelligence of the Royal Thai Armed Forces told Reuters it was unclear whether Myanmar had accepted the invitation but Thailand was eager for them to join.
Asked why Thailand decided to invite Myanmar despite concerns over the crackdown against the Rohingya and whether this issue was part of their deliberations, the official said: “That never came up in the discussions. We separated that issue (the Rohingya). We focus on training, on education, on military cooperation. That is our wish, to have Myanmar involved.”
“That is politics. We are soldiers. This is a military exercise,” added the official, who declined to be named because he was not authorized to speak to the media.
The Myanmar military did not respond to several requests for comment.
When asked whether the US military had attempted to apply pressure on Thailand not to invite Myanmar because of the international condemnation of its crackdown, the Pentagon declined to comment on internal deliberations.
Myanmar’s military cracked down on Muslim Rohingya from Rakhine state following Rohingya militant attacks on an army base and police posts in August. The crackdown has caused around 650,000 Rohingya to flee to Bangladesh in recent months.
The United States and the United Nations have described the campaign as ethnic cleansing of the stateless Rohingya people.
The Myanmar military has said its own internal investigation had exonerated security forces of all accusations of atrocities in Rakhine.
But earlier this week, the United States imposed sanctions on 13 “serious human rights abusers and corrupt actors” including Myanmar general Maung Maung Soe, who oversaw the crackdown against the Rohingya.
Zachary Abuza, a professor at the US National War College, said inviting Myanmar to the exercise was “outrageous” and sent the wrong message.
“To invite them after what the US government has labeled ethnic cleansing, when the Treasury Department just yesterday designated the commander for these egregious violations of human rights, just seems wrong, and that is putting it too mildly,” said Abuza, who focuses on Southeast Asia and security issues, including human rights.
In the 2017 Cobra Gold exercise, 29 nations either participated or observed the exercise, including Myanmar. It included about 3,600 US personnel. Cobra Gold is an annual exercise in Thailand. The 2018 war games are expected to be held in February.
The United States and Thailand have carried out joint war games for decades, even though Bangkok’s record on human rights and democracy has often been criticized in Washington.
The US-Thai relationship cooled when the Thai military took power in a 2014 coup but has improved under President Donald Trump.
Two Reuters journalists were arrested in Myanmar on Dec. 12 and on Thursday appeared in court and have been remanded in custody.
Reporters Wa Lone and Kyaw Soe Oo have been in detention for nine days with no detail on where they are being held. They have not had access to visitors or lawyers.
Myanmar, accused of crackdown, invited to US-Thai military exercise
Myanmar, accused of crackdown, invited to US-Thai military exercise

International peacekeepers killed as fighting rages around eastern Congo’s key city

- M23 has made significant territorial gains in recent weeks, encircling the eastern city of Goma, which has around 2 million people
- Congo, the US and UN officials accuse Rwanda of backing M23, which is mainly made up of ethnic Tutsis who broke away from the Congolese army
GOMA, Congo: Fighting with M23 rebels in eastern Congo has left at least 13 peacekeepers and foreign soldiers dead, United Nations and army officials said Saturday.
M23 has made significant territorial gains in recent weeks, encircling the eastern city of Goma, which has around 2 million people and is a regional hub for security and humanitarian efforts.
The UN Security Council moved up an emergency meeting on the escalating violence to Sunday morning (10 am EST). Congo requested the meeting, which had originally been scheduled for Monday.
On Saturday, Congo’s army said it fended off an M23 offensive toward Goma with the help of its allied forces, including UN troops and soldiers from the Southern African Development Community Mission, also known as SAMIDRC.
“The Rwandan-backed M23 is clearly exploiting the presidential transition in the US to advance on Goma — putting thousands more civilians at risk,” Kate Hixon, advocacy director for Africa at Amnesty International US, told the Associated Press.
Congo, the United States and UN experts accuse Rwanda of backing M23, which is mainly made up of ethnic Tutsis who broke away from the Congolese army more than a decade ago.
Rwanda’s government denies the claim, but last year acknowledged that it has troops and missile systems in eastern Congo to safeguard its security, pointing to a buildup of Congolese forces near the border. UN experts estimate there are up to 4,000 Rwandan forces in Congo.
The burning wreckage of a white armored fighting vehicle carrying UN markings could be seen on a road between Goma and Sake on Saturday, where much of the fighting was concentrated in recent days.
Two South African peacekeepers were killed Friday, while a Uruguayan Blue Helmet was killed Saturday, a UN official told The Associated Press. The official spoke on condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to speak on the matter publicly.
Additionally, three Malawian peacekeepers were killed in eastern Congo, the United Nations in Malawi said Saturday.
Seven South African soldiers from the SAMIDRC were also killed during clashes with M23 over the last two days, South Africa’s department of defense said in a statement.
Uruguay’s military in a statement issued Saturday identified its member killed in Congo as Rodolfo Álvarez, who was part of the Uruguay IV Battalion. The unit, according to the statement, is working “uninterruptedly to comply with the United Nations mandate, as well as to guarantee the evacuation of non-essential civilian and military personnel from the city of Goma.”
“Various measures have been taken to improve the security of our troops, who are operating in adverse conditions,” the military said. It added that four Uruguayan peacekeepers were also injured. Three of them remained in Goma while a fourth one was evacuated to Uganda for treatment.
Since 2021, Congo’s government and allied forces, including SAMIDRC and UN troops, have been keeping M23 away from Goma.
The UN peacekeeping force, also known as MONUSCO, entered Congo more than two decades ago and has around 14,000 peacekeepers on the ground.
South Africa’s defense minister, Angie Motshekga, was visiting the country’s troops stationed in Congo as part of the UN peacekeeping mission the day the soldiers were killed.
Why child-killer diseases like dengue, cholera and mpox have surged worldwide

- Three child-killer diseases witnessed major resurgences in 2024, fuelled partly by climate crises and conflict
- Poor sanitation, displacement, and war-damaged infrastructure left millions vulnerable to fatal illnesses
DUBAI: When the UN launched the Sustainable Development Goals in 2015, it set out a bold action plan to eliminate premature death and needless suffering caused by preventable diseases by 2030.
With just five years to go, the world appears to be moving backwards. Indeed, 2024 actually witnessed an alarming surge in a triad of preventable or manageable child-killer diseases.
Dengue, cholera and mpox returned with a vengeance, claiming the lives of thousands of children. With their weaker immune systems, the young are particularly vulnerable to infection and often fatal complications.
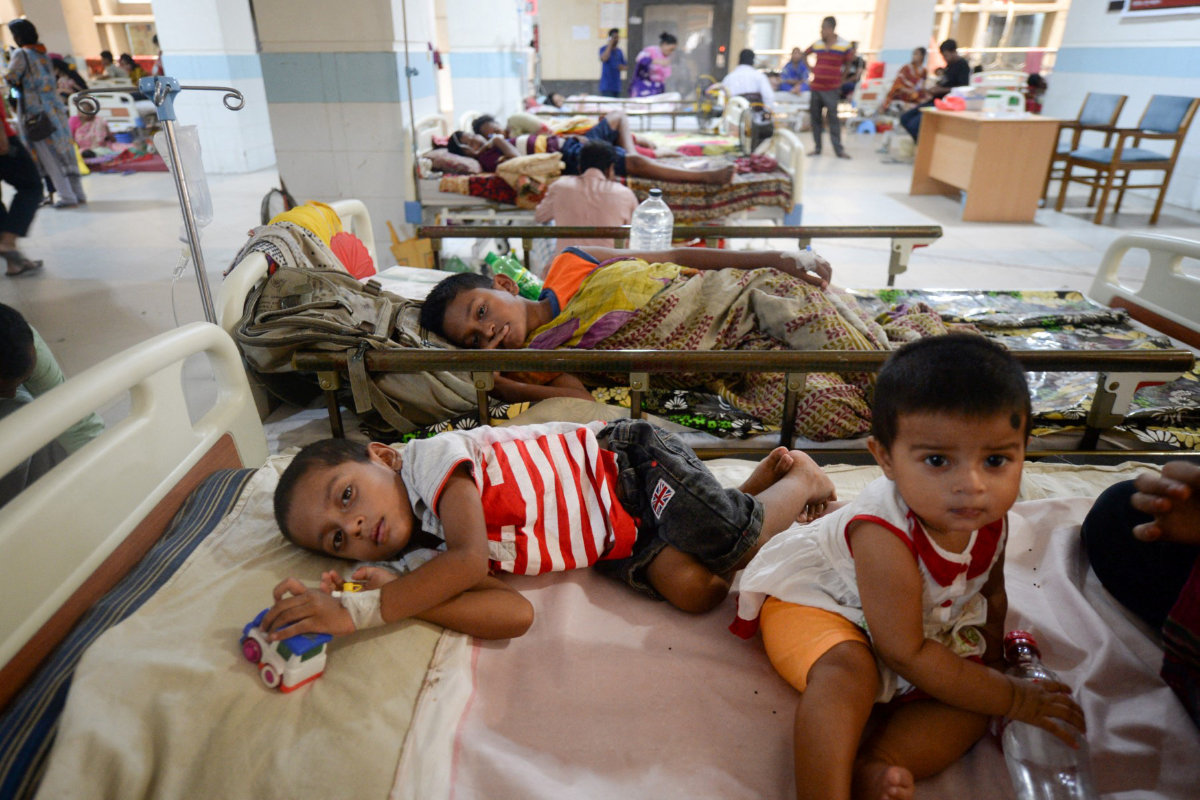

Bangladeshi children suffering from dengue fever rest at a ward at the Mugda Medical College and Hospital in Dhaka on August 8, 2019. (AFP file)
This multifaceted health emergency has compounded the suffering of already stricken communities in impoverished countries and conflict zones, where climate change, inequality and underfunded health systems have left many without access to basic care or sanitation.
“Currently, about half of the world’s population is not fully covered by essential, quality, affordable health services, denying them their right to health,” said Dr. Revati Phalkey, global health and nutrition director at Save the Children International.
“Health systems are under enormous pressure to deliver universal health coverage, with the majority of countries experiencing worsening or no significant change in service coverage since the launch of the Sustainable Development Goals in 2015.”

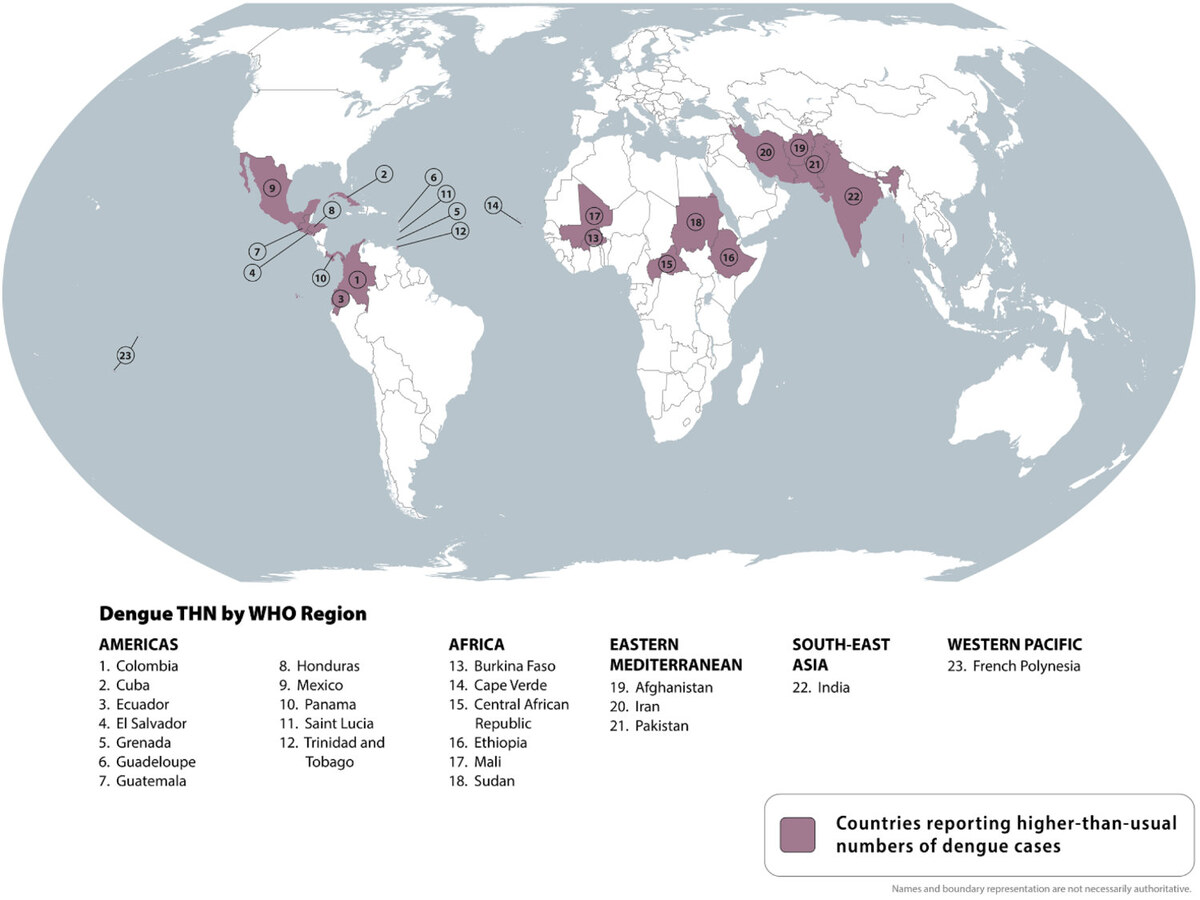
According to the World Health Organization, dengue fever — a mosquito-borne disease that causes severe fever, pain and in some cases death — saw an alarming spike in 2024.
Dengue cases doubled from 6.65 million in 2023 to 13.3 million in 2024. The total number of dengue-related deaths globally last year was 9,600. The WHO estimates some four billion people are now at risk of dengue related viruses.
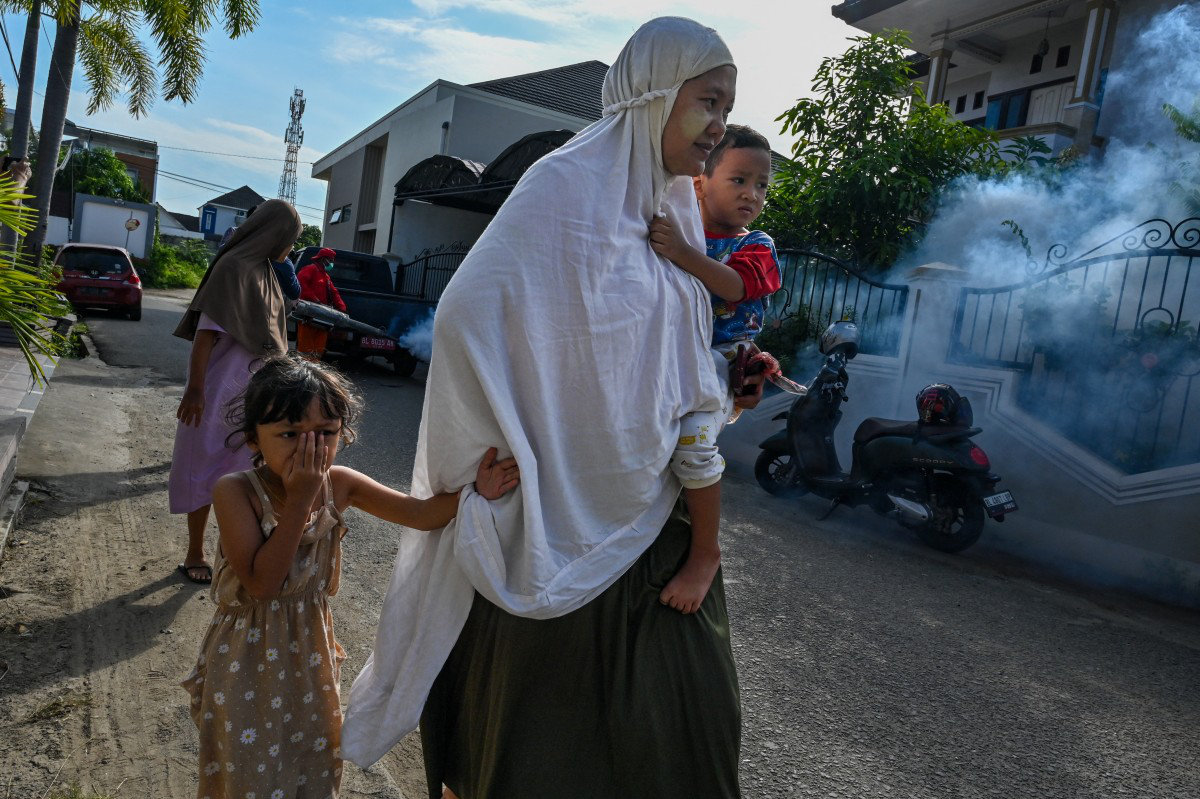
Children who play outside with limited protection against mosquitoes are often more exposed and therefore more vulnerable to the virus than adults. The absence of mosquito nets where children sleep is also a key contributing factor.
In developing countries in Southeast Asia, parts of Africa, Latin America and the Caribbean, dengue fever is especially prevalent. Informal settlements in these regions often lack basic infrastructure for waste management, sewage or clean water.
These conditions offer a fertile breeding ground for mosquitoes and for the disease to spread. Meanwhile, rising temperatures associated with climate change have expanded the range of mosquito habitats, allowing them to flourish across a wider region.
The spread of dengue, sometimes known as “breakbone fever” due to the severe fatigue it causes, represents “an alarming trend” according to WHO Director General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebereyesus, with 5 billion people at risk of being infected by 2050.
FASTFACT
13,600
Deaths from dengue, cholera, or mpox in 2024.
Dengue is not the only danger. In Yemen, Sudan and Gaza, where conflict has displaced thousands and destroyed critical civilian infrastructure, cholera has become a major threat to adults and children alike.
A deadly bacterial infection spread through contaminated water, cholera is another consequence of poor sanitation. The infection causes rapid dehydration through severe diarrhea and vomiting, which can quickly lead to death if left untreated.
The UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East released a statement in June warning of a cholera outbreak in the Gaza Strip amid severe water shortages and damage to sanitation services.
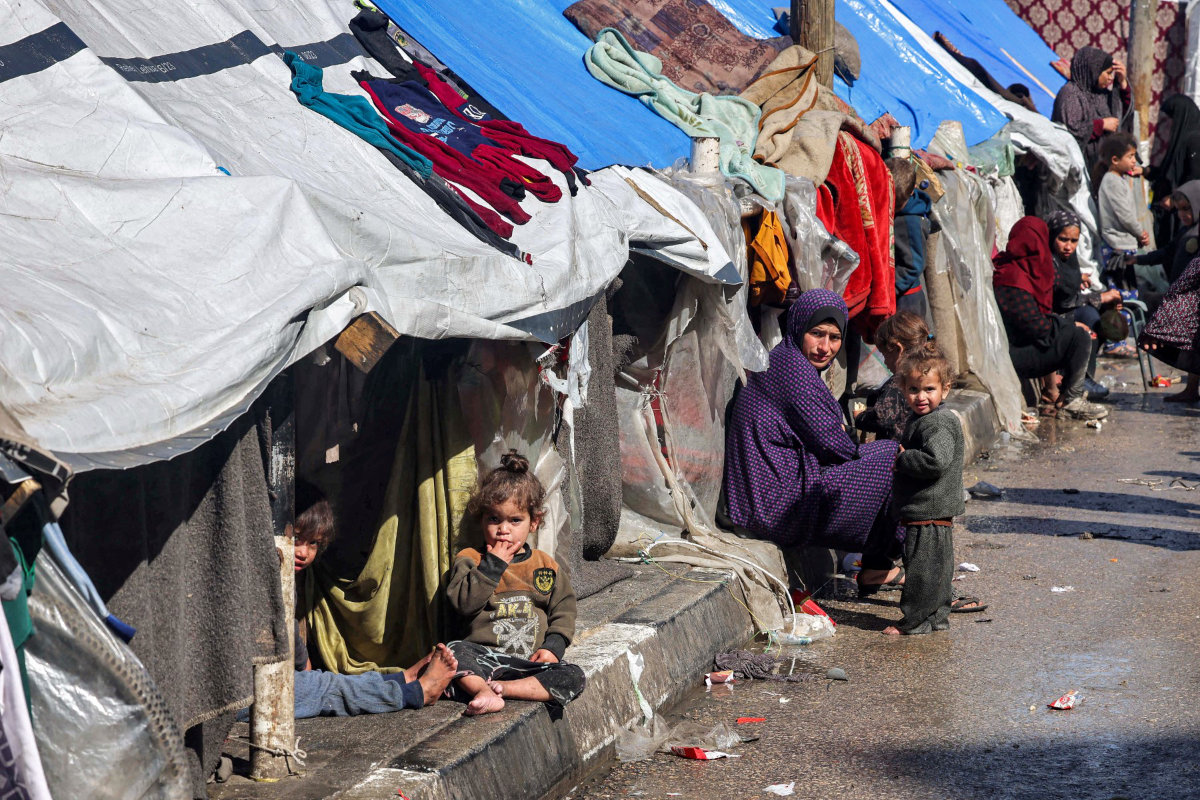

Several UN agencies have issued warnings about the high risk of infectious diseases in overcrowded refugee camps across the Middle East and North Africa, where displaced households have limited access to clean water and proper sanitation.
In Sudan, as of last November, the WHO reported more than 37,514 cholera cases across the country and at least 1,000 deaths. “We are racing against time,” Sheldon Yett, the UN children’s fund representative to Sudan, said in a statement in September.
“We must take decisive action to tackle the outbreaks as well as invest in the health systems underpinning the essential services vulnerable children and families in Sudan so desperately need.”
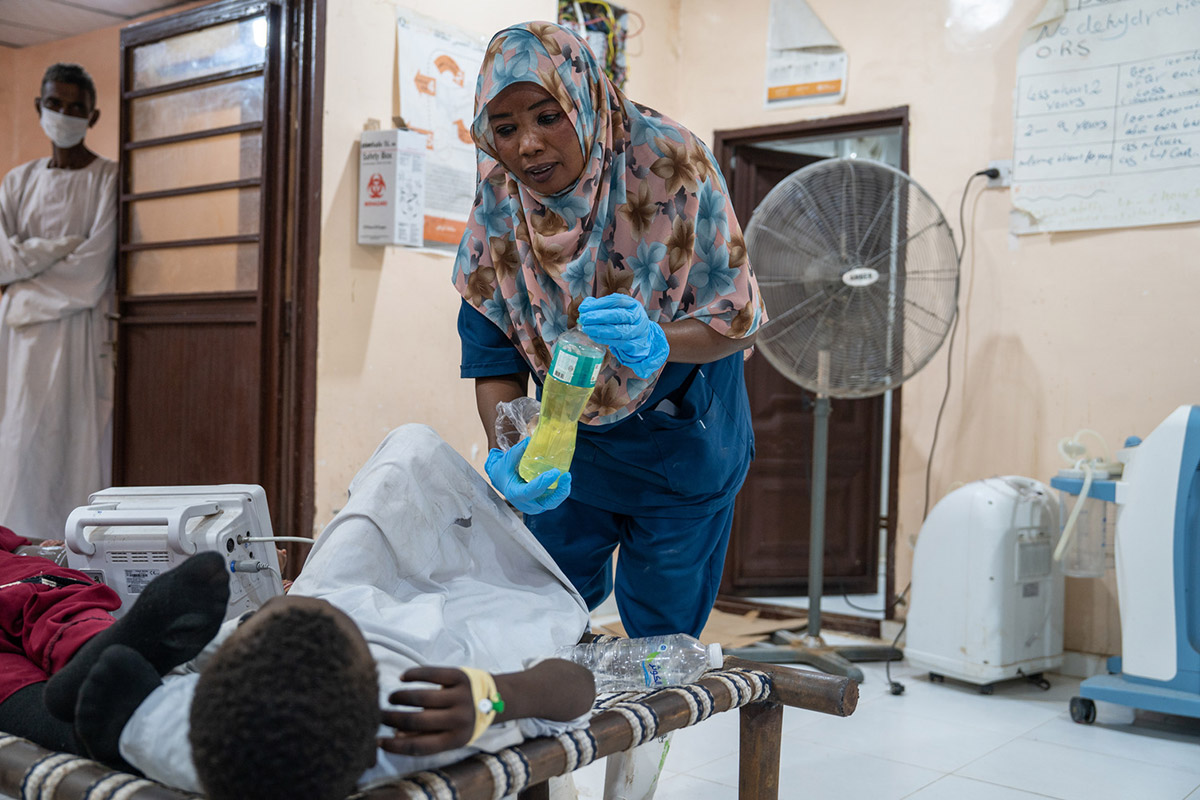

Despite efforts by the international community to provide vaccines and clean water, outbreaks in conflict zones have proven difficult to keep under control. The collapse of sanitation services, in particular, has left millions of children vulnerable to the disease.
Although the overall number of cholera cases worldwide fell by 16 percent in 2024, there has been a 126 percent spike in the number of deaths as a result of the disease.
Another health crisis threatening the world’s children is mpox, formerly known as monkeypox. The virus reemerged in 2024 to devastating effect across parts of Africa, with children suffering the most severe consequences.

Once a rare disease confined to rural areas of Central and West Africa, mpox has now become a significant public health crisis with thousands of reported infections, particularly among children under the age of five.
Mpox, contracted through contact with infected people and animals, bodily fluids and contaminated objects, causes fever, rashes, and painful lesions that in turn can lead to other illnesses and afflictions such as pneumonia and blindness.
While it can be controlled using vaccines, such resources remain scarce in parts of Africa. Having already been overwhelmed by Ebola and malaria, the region’s health systems are stretched to the limit, leaving treatment out of reach for thousands of children.
Moreover, poor sanitation, crowded living conditions, and rapid urbanization have increased the risk of transmission.
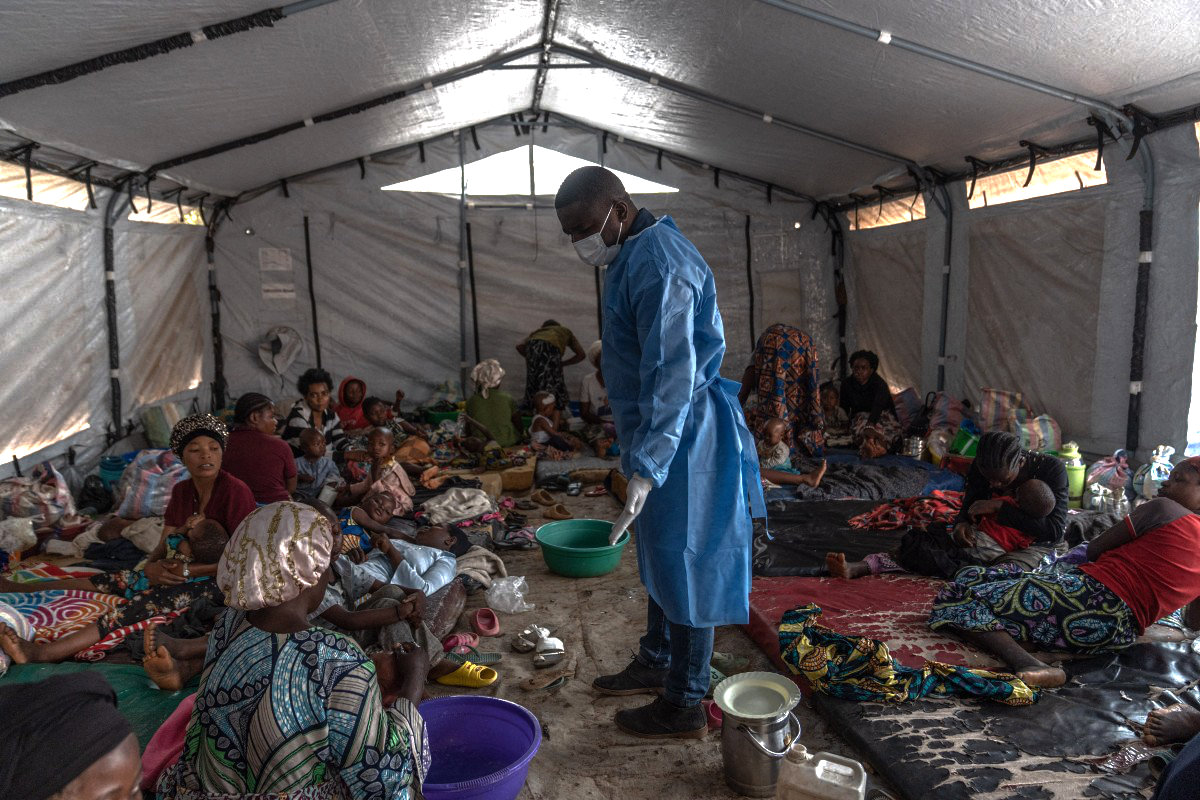

Children in the east of the Democratic Republic of Congo have been the worst affected by the mpox virus, with the WHO declaring the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern. Around 75 percent of cases are in children under the age of 10.
The surge in these diseases reflects the broader, interconnected crises faced by the world, where the most vulnerable populations are left with limited means to recover and adapt.
In wealthier countries, child deaths resulting from cholera and dengue have dropped significantly thanks to well-functioning sanitation services and accessible healthcare systems that have weathered the blows of the coronavirus pandemic.

However, in low income countries, particularly those in the midst of conflict, healthcare systems are extremely vulnerable, with medical staff overstretched, medicines in short supply, and wards overwhelmed by the sick and wounded.
The grim reality for millions of children across the world underscores the urgent need for global action.
“We need greater global investments to build strong health systems that are able to deliver essential health services, especially vaccines and essential medicines, while responding to global health emergencies including emerging issues like mpox,” said Dr. Phalkey.

“It is time for governments and the international community to step up and ensure all children are protected against disease and have access to adequate health services when they need them and where they need them.
“Every child has the right to survive and thrive, and it is our collective responsibility to deliver on this.”

CIA now says COVID-19 ‘more likely’ to have come from lab

- The agency had for years said it could not conclude whether COVID-19 was the result of a lab incident or it originated in nature
- The CIA says it has “low confidence” in its assessment that a “research-related origin of the COVID-19 pandemic is more likely“
NEW YORK: The Central Intelligence Agency has assessed that the COVID-19 pandemic is “more likely” to have emerged from a lab rather than from nature, an agency spokesperson said on Saturday.
The agency had for years said it could not conclude whether COVID-19 was the result of a lab incident or it originated in nature. But in the final weeks of the Biden administration, former CIA Director William Burns asked CIA analysts and scientists to make a clear determination, stressing the pandemic’s historical significance, according to a senior US official.
The CIA says it has “low confidence” in its assessment that a “research-related origin of the COVID-19 pandemic is more likely” and notes in its statement that both scenarios — lab origin and natural origin — remain plausible.
The Chinese embassy in Washington did not immediately respond to a request for comment.
It was unclear the extent to which the agency has collected new intelligence on COVID-19’s origins and whether that new evidence was used to formulate the latest assessment.
China’s government says it supports and has taken part in research to determine COVID-19’s origin, and has accused Washington of politicizing the matter, especially because of efforts by US intelligence agencies to investigate.
Beijing has said claims that a laboratory leak likely caused the pandemic have no credibility.
In an interview with Breitbart following his confirmation by the US Senate on Friday, CIA Director John Ratcliffe said one of his first priorities was getting his agency to make a public assessment on the pandemic’s origins.
“That’s a day-one thing for me,” he said. “I’ve been on record as you know in saying I think our intelligence, our science, and our common sense all really dictate that the origins of COVID was a leak at the Wuhan Institute of Virology.”
New Delhi probes mystery illness after 17 die in India-administered Kashmir

- The deaths, including those of 13 children, have occurred in the remote village of Badhaal in Rajouri area since early December
- All of the fatalities had damage to the brain and nervous system, said Amarjeet Singh Bhatia, who heads Rajouri’s medical college
SRINAGAR: Authorities in India-administered Jammu and Kashmir were investigating a mysterious disease that has claimed the lives of 17 people, local media reports said Saturday.
The deaths, including those of 13 children, have occurred in the remote village of Badhaal in Jammu’s Rajouri area since early December.
The village was declared a containment zone earlier this week with around 230 people quarantined, the Press Trust of India (PTI) news agency reported.
All of the fatalities had damage to the brain and nervous system, Amarjeet Singh Bhatia, who heads Rajouri’s government medical college, said.
“The winter vacations have also been canceled to deal with the medical alert situation,” PTI quoted Bhatia as saying.
The victims were members of three related families.
The federal government has launched an investigation with health minister Jitendra Singh saying an initial probe suggested the deaths were “not due to any infection, virus or bacteria but rather a toxin.”
“There is a long series of toxins being tested. I believe a solution will be found soon. Additionally, if there was any mischief or malicious activity, that is also being investigated,” PTI quoted Singh as saying.
In a separate medical incident, authorities in the western city of Pune recorded at least 73 cases of a rare nerve disorder.
Those infected with Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) include 26 women and 14 of the patients are on ventilator support, PTI quoted an official as saying.
In GBS, a person’s immune system attacks the peripheral nerves, according to the World Health Organization.
The syndrome can impact nerves that control muscle movement which may lead to muscle weakness, loss of sensation in the legs or arms and those infected can face trouble swallowing and breathing.
India is undergoing transformative change, says Indian CG in Republic Day message

- India celebrates 76th Republic Day on Sunday
- Relationship between Saudi Arabia and India continues to thrive
On the occasion of the 76th Republic Day of India, I extend my warmest greetings to all Indian nationals in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and to our esteemed friends in the country.
Republic Day is a time to reflect on the values that shape India, honor the sacrifices of our forebears, and celebrate our continued progress as a nation.
The Constitution of India beautifully outlines the principles that form the foundation of our nation’s remarkable journey. It is a source of pride for every Indian to be part of this ongoing story, one of hope, resilience and success.
Today, India is undergoing transformative change, with significant progress in infrastructure, technology and industrial development. Our economy, now the fifth-largest globally, is poised to become the third-largest in the next few years. We are expanding connectivity, supporting innovation and building a future-driven workforce, all while navigating global challenges.
The bilateral relationship between India and Saudi Arabia continues to thrive, with high-level bilateral visits and engagements becoming increasingly frequent; growing cooperation across trade, energy, defense, and cultural domains; and many new opportunities for collaboration.
We extend our sincere gratitude to King Salman, Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, the nation’s government and its people for their care and the warm hospitality extended to the 2.5 million Indians living in the Kingdom. The Indian community remains a vital bridge between our nations, contributing significantly to Saudi Arabia’s growth and prosperity.
We also express our sincere appreciation for the cooperation in facilitating the safe and enriching experiences of Indian pilgrims during Hajj and Umrah. We look forward to further strengthening this partnership to ensure the best experience and safety for our pilgrims during the upcoming Hajj 2025.
As we celebrate the 76th Republic Day, let us continue to work toward a future of peace, prosperity and deeper ties between India and Saudi Arabia.
Happy Republic Day to all. Jai Hind!
— Fahad Ahmed Khan Suri is India’s consul general in Jeddah.



















