DUBAI: Saudi doctors and volunteers are expected to play a key role in a newly launched initiative to allow health professionals in Yemen, Bangladesh, Sudan, Nigeria and Pakistan to intervene quickly to save people’s vision.
The initiative, the result of a partnership between the King Salman Humanitarian Aid and Relief Center (KSrelief) and Al-Basar International Foundation, envisages 41 medical campaigns, during which an estimated 205,000 examinations will be conducted, 16,400 operations will be carried out, and 41,000 medical glasses will be distributed.
The 262,400 individuals expected to benefit from this initiative are among the estimated 2.2 billion people worldwide affected by blindness or vision impairment, according to World Health Organization (WHO) data. The WHO figure includes an estimated one billion that have a preventable vision impairment or one that has yet to be addressed.
The leading causes of vision impairment and blindness are uncorrected refractive errors and cataracts, especially among the over-50s. The issue is especially prevalent in the developing world, where facilities and specialists are scarce.
“The highest prevalence of blindness that we see is in countries where there are limited resources for healthcare and in lower income countries,” Dr. David Gritz, a vision specialist and staff physician at Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi’s Eye Institute, told Arab News.
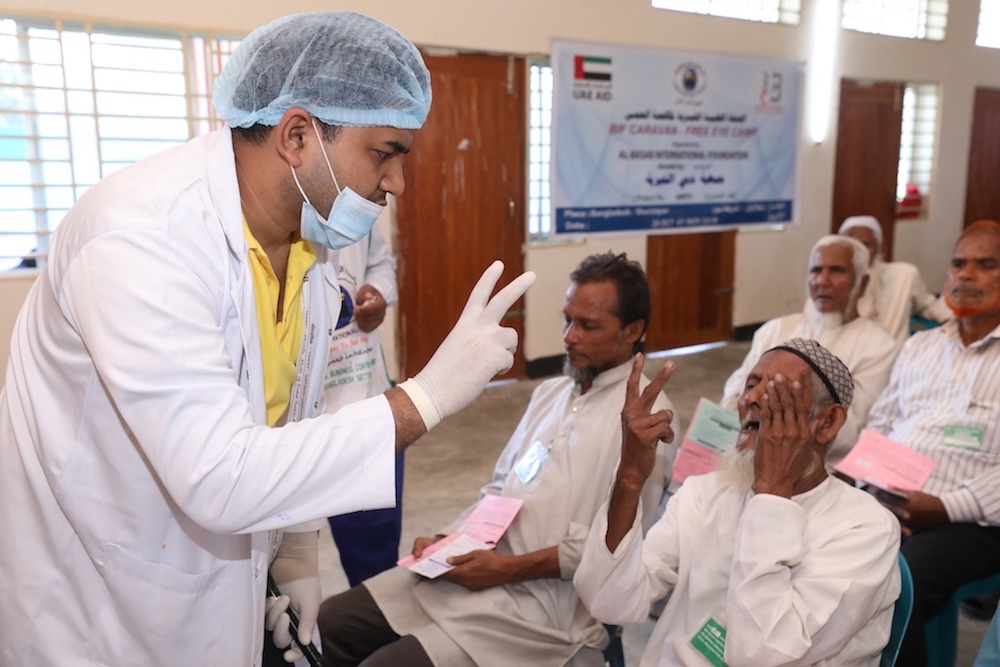
The Al-Basar International Foundation was first launched in Pakistan in 1989. (Supplied)
Gritz, who was previously head of the Cornea Division at the King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital in Riyadh, said prevalence of vision impairment is also linked to environmental factors, age distribution and population.
Referring to the KSrelief-Al-Basar joint initiative, he said: “This campaign is very exciting because anything we can do to make an impact is helpful.
“It is not just helpful for individuals that we are treating but it impacts the family, the community, and the economics of the entire country, because visual impairment and blindness affects people’s quality of life and how productively they can live. It also affects their general health.”
Al-Basar International Foundation launched its first medical campaign in Pakistan in 1989 before setting up a sister organization in the UK in 2005. Today it fights preventable sight loss in 46 countries.
Many more can now be reached thanks to its latest partnership with KSrelief. The Saudi aid agency has implemented 1,475 projects of its own worth nearly $4.9 billion in 59 countries, covering everything from landmine clearance to the rehabilitation of child soldiers.
INNUMBERS
KSrelief - Al-Basar partnership
* 16,400 - Operations set to take place.
* 41,000 - Medical glasses to be distributed.
* 205,000 - Eye examinations planned.
* 262,400 - People who will benefit.
The main causes of moderate to severe distance-vision impairment or blindness are unaddressed refractive error, cataract, glaucoma, and corneal opacities, as well as diabetic retinopathy, trachoma and near vision impairment caused by unaddressed presbyopia. In many cases, timely intervention can stop people needlessly losing their sight.
“The encouraging thing is that 90 percent of vision loss is preventable or treatable, so this is an area where we can make a huge impact in prevention, like glaucoma, where you need to find the disease and treat it to ensure prevention,” Gritz said.
“And some are treatable, like cataract, which is the number one cause of vision loss and blindness in the world, including in countries like the United States, and lower income countries.”
Global health inequalities are starkly reflected in the comparative rates of blindness and vision loss in wealthy countries and the developing world. According to WHO estimates, the prevalence of distance vision impairment in low- and middle-income regions is four times higher than in high-income regions.
In terms of unaddressed near vision impairment, rates are estimated to be greater than 80 percent in western, eastern and central sub-Saharan Africa, while rates in high-income regions of North America, Australasia, Western Europe and the Asia-Pacific are reported to be lower than 10 percent.
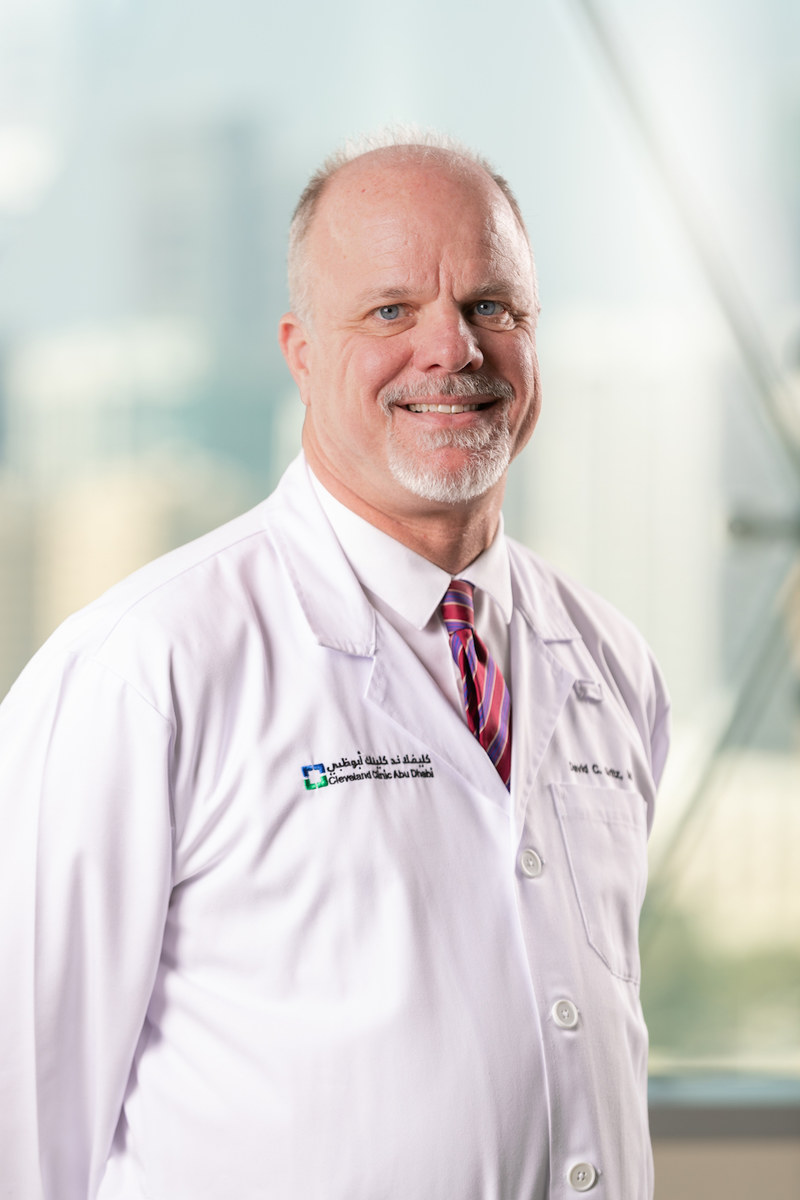

Dr. David Gritz, a vision specialist and staff physician at Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi’s Eye Institute, who spoke to Arab News. (Supplied)
“Population growth and ageing are expected to increase the risk that more people acquire vision impairment,” the WHO reports.
“One point is that the prevalence of blindness is decreasing, but that is based on the percentage of the population,” Gritz said.
“Because the population is increasing overall and it is ageing, the number of people with blindness and visual impairment is continuing to increase dramatically. Many organizations are doing great work out there to figure out how to effectively deliver care efficiently, so I am excited to see that the Saudi King is getting involved and is willing to contribute in this way.”
This is not the first time KSrelief and Al-Basar International Foundation have teamed up to address preventable blindness. An earlier agreement was signed in Sept. 2020 to provide assistance in Yemen, the Philippines, the Democratic Republic of Congo (correct?), Bangladesh, Sudan, Djibouti, Rwanda and Burundi.
About 30 medical campaigns were conducted, offering 12,000 operations and 30,000 medical glasses, benefiting 150,000 people.

The leading causes of vision impairment and blindness are uncorrected refractive errors and cataracts, especially among the over-50s. The issue is especially prevalent in the developing world. (AFP/File Photo)
Challenges to these projects include finding enough funding, resources and equipment to implement field programs, and cruicilly finding enough skilled professionals to carry out examinations and operations.
Interventions must be tailored to specific regions, where local diseases, rates of poverty and environmental factors have their own distinct impact on eye health. Local customs, beliefs and educational standards must also be taken into account.
“That is one of the important things whenever you are thinking about a program. It is how to best address the particular needs, and the environmental and cultural sensitivities, so many things need to be taken into account when designing an interventional program,” Gritz said.
“Other things like their openness to medical healthcare, particularly vision care. And for less educated people, people who have had different experiences in their life, blindness is viewed as an inevitability when you are old, so there is a part of it that is also educational. They think cataracts are part of getting old but, if they just seek treatment, they can get cataract treatment and see very well.”
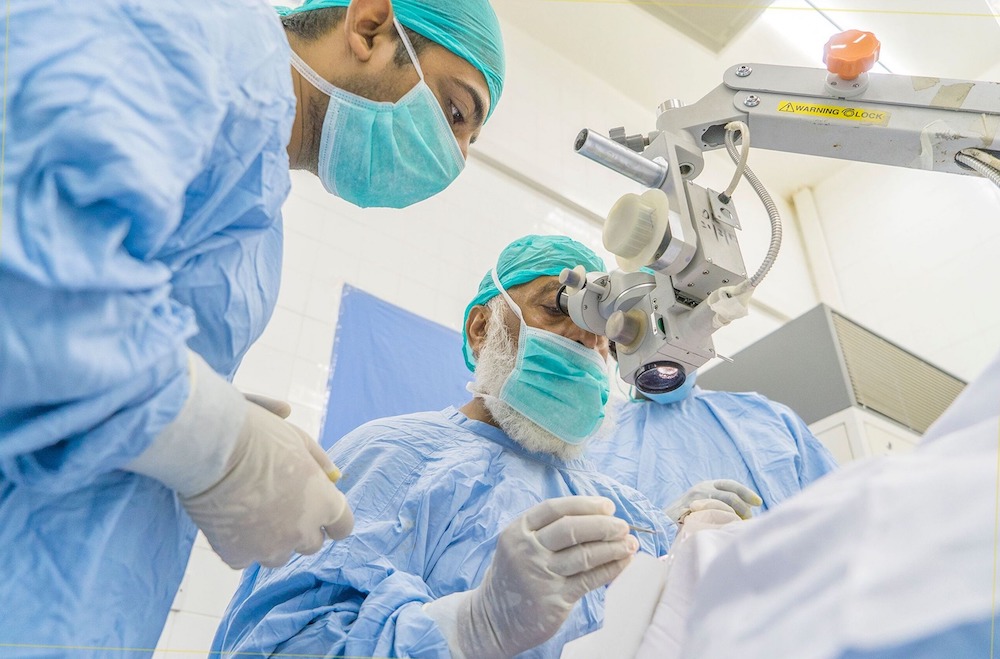
Al-Basar International Foundation fights sight loss in 46 countries. (Supplied)
Dr. Anurag Mathur, an ophthalmology specialist at Medcare Hospital in Sharjah, UAE, says vision loss is among the world’s foremost healthcare problems, with 90 percent of blindness occurring in developing nations, especially in Africa and Asia.
Within the developing world, the prevalence of blindness varies between countries, ranging from 0.9 percent of the population in Pakistan to upwards of 4 percent in Nigeria, often contingent upon living conditions and the socioeconomic situation of the country.
“The number of elderly people and children suffering from blindness is on the rise in developing nations, primarily because of improving life expectancy and more children surviving complicated births,” Mathur told Arab News.
With the right healthcare facilities and treatments made available, these individuals can be spared the encroaching darkness and isolation of preventable blindness.

Within the developing world, the prevalence of blindness varies between countries, ranging from 0.9 percent of the population in Pakistan to upwards of 4 percent in Nigeria. (AFP/File Photo)
“A simple comprehensive eye examination can detect all major eye issues leading to blindness,” Mathur said.
“Appropriate management can enable millions of people across the globe to see better, which can not only change their lives but can also empower societies.
“This campaign is a small but positive step in the right direction to fight avoidable blindness and we need more such initiatives to eradicate avoidable blindness from the face of the earth.”
------------------
Twitter: @CalineMalek





























