MISSOURI, USA: Every March, Kurds, Persians, Azeris, Tajiks, and others celebrate Newroz, the spring equinox festival of the new year. In the Kurdish version of Newroz, legends surrounding the festival focus on a mythical blacksmith of antiquity named Kawa, who saved normal people from a terrible tyrant. The Kurdish version of Newroz therefore comes replete with connotations of freedom from tyranny, oppression, and injustice.
If ongoing developments in Turkey serve as any indicator, it will take more than a couple of Newroz festivities to undo the Erdogan government’s myriad efforts to silence the country’s Kurdish population. Erdogan has, in recent years, turned the Turkish judiciary into his praetorian guard. Public prosecutors and sycophantic judges are now deployed to silence any and all dissent in Turkey.
The latest incident involves the country’s Court of Appeal, which upheld a two-and-a-half year prison sentence against Parliamentarian Omer Faruk Gergerlioglu. Gergerlioglu, of the pro-Kurdish People’s Democracy Party (HDP), was convicted of “making terrorist propaganda” for retweeting a T24 news story in 2016 about the Kurdish conflict and the collapse of the peace process.
With his conviction upheld, the Turkish Grand National Assembly — controlled by Erdogan’s party and its far-right ally, the Nationalist Action Party (MHP) — promptly stripped Gergerlioglu of his parliamentary immunity. Gergerlioglu was not even a member of parliament in 2016; he was elected in 2018, and the story he retweeted was never censored by the state or relied upon to punish the T24 news agency.
The story quoted a Kurdistan Workers’ Party leader, who called for a resumption of peace talks with Ankara and Turkey’s then-interior minister, who rejected such calls. To most observers, it would seem completely bizarre to accuse, much less convict, someone of “making terrorist propaganda” for retweeting a story.
The journalist who wrote the piece was not charged with anything, nor was the media company that ran it.
Today’s Turkey functions under different rules, however. Gergerlioglu’s real crime was his frequent criticisms of the Erdogan government and its human rights record. A former pulmonologist fired from his job as part of a broad emergency decree crackdown following the 2016 attempted coup in Turkey, Gergerlioglu also worked as the head of an Islamic human rights association.
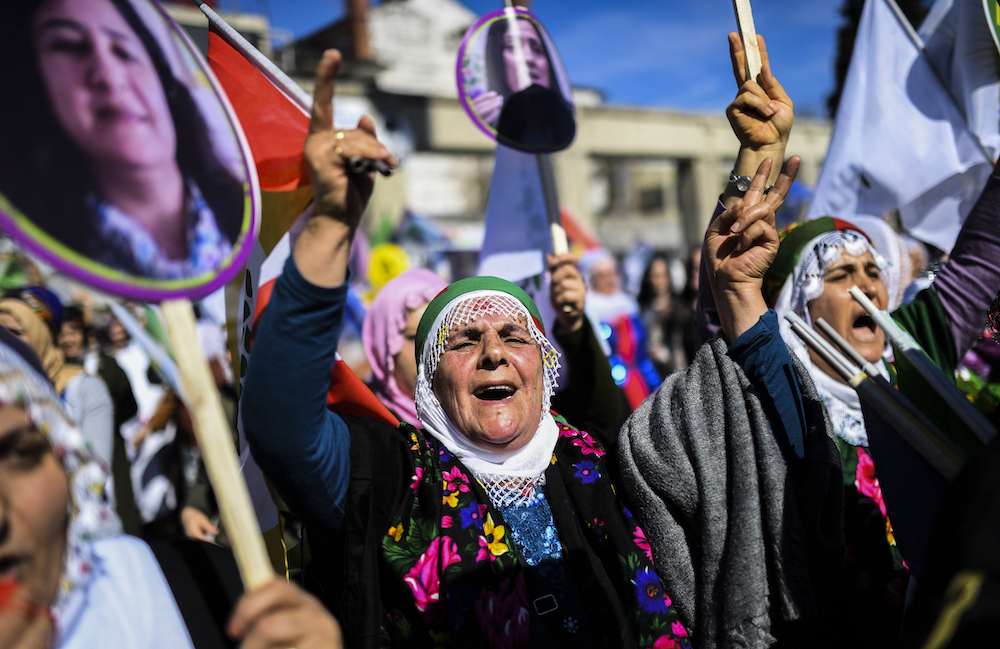

Women chant slogans and hold pictures of pro-Kurdish Peoples' Democratic Party's (HDP) co-leader Figen Yuksekdag, who is detained pending a trial on terror charges, on March 5, 2017, at Bakirkoy, in Istanbul. (AFP/File Photo)
As part of his work championing human rights, Gergerlioglu drew attention to the many abuses in Erdogan’s Turkey. His reports and statements regarding the police’s frequent strip-searches of female detainees seems to have particularly irked Erdogan and his government.
Unsurprisingly, foreign observers reacted negatively to the persecution of Gergerlioglu. Among others, the EU special rapporteur for Turkey stated that “stripping him of his parliamentary immunity was illegal, immoral and a cowardly act.”
Amnesty International issued a statement saying that “the lifting of the immunity of the opposition deputy Gergerlioglu because of his unjust conviction is a moment of shame.”
THENUMBER
97.1% of Turks do not believe the judiciary is independent
Also last week, the government arrested Ozturk Turkdogan, head of the Ankara-based Human Rights Association. Gergerlioglu and Turkdogan are only two of hundreds of peaceful opposition members in Turkey who now face Erdogan’s praetorian legal system.
Most, though not all, of those being imprisoned on trumped-up charges come from the HDP, including most of the HDP’s leaders such as Selahattin Demirtas, who has been imprisoned since 2016. Most recently, Erdogan’s Justice and Development Party (AKP) and MHP government began signaling its intention to completely close down and ban the opposition HDP party.
The HDP, after the last couple of elections, has become Turkey’s third-largest party, receiving close to 12 percent of the national vote and holding 55 seats in the Turkish Grand National Assembly. The US State Department spokesman called moves to close the HDP “a decision that would unduly subvert the will of Turkish voters, further undermine democracy in Turkey, and deny millions of Turkish citizens their chosen representation.”
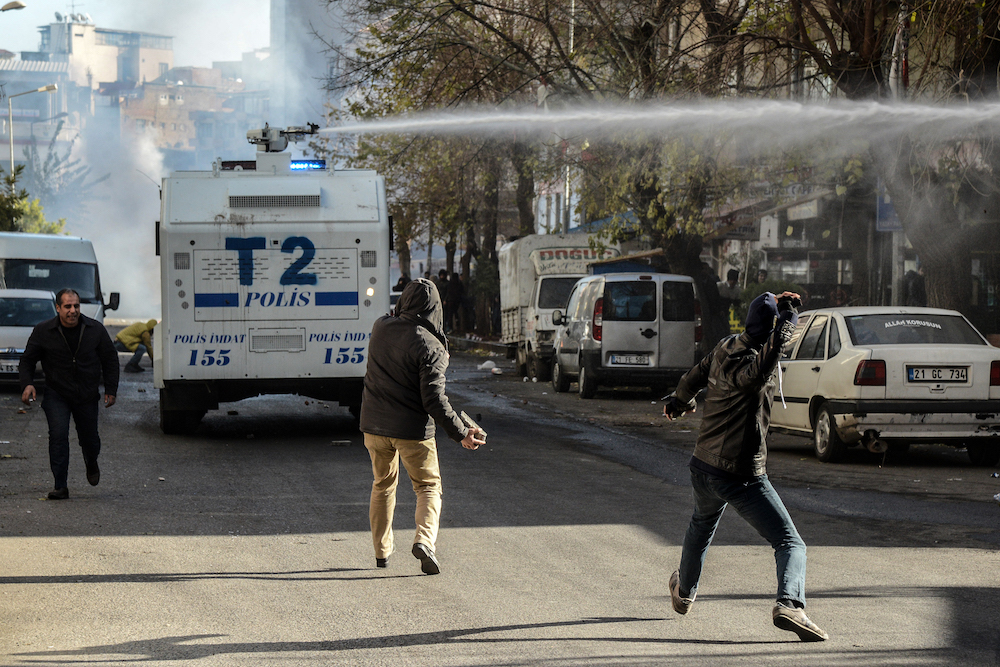

Protesters throws stones towards a water cannon during a demonstration in Diyarbakir on December 22, 2015 to denounce security operations against Kurdish rebels in southeastern Turkey. (AFP/File Photo)
Similarly, Nacho Sanchez Amor, the EU’s special rapporteur for Turkey, reacted to the possibility of the HDP’s closure negatively: “Unapologetically (moving) towards the end of pluralism. What reaction does Turkey expect now from the EU? A positive agenda?”
Erdogan’s government reacted to the criticism by rejecting “foreign interference” in Turkey’s domestic political concerns. Turkey’s Foreign Ministry said: “Everyone must wait for the ruling the Constitutional Court will make in this process. Commenting on an ongoing judicial process amounts to intervention in the judiciary.”
The statement added: “We call upon those who act inconsistently and attempt to interfere with our internal affairs to respect the legal processes conducted by the independent judiciary.”
These days, of course, almost no one thinks Turkey’s judiciary is actually independent. This includes Turks. A 2016 public opinion poll conducted by the Eurasia Public Opinion Poll Center, conducted before the worst of the Erdogan government’s moves to take over the judiciary, showed that “a total of 97.1 percent of Turks do not believe the judiciary in Turkey is independent and have no trust in the court system.”

Supporters of pro-Kurdish Peoples' Democratic Party (HDP) cheer around fire during a gathering to celebrate Nowruz, the Persian New Year, in Diyarbakir on March 21, 2021. (AFP)
The irony comes with the fact that in Turkey’s previous more secular incarnation before 2002, the courts closed the Islamist political parties that Erdogan belonged to and even imprisoned him in 1998 for a few months when he was the mayor of Istanbul for reading a poem at a rally that was deemed too Islamist.
Back in those days, both Islamists and Kurds suffered the state’s repression. A slew of both Islamist and pro-Kurdish political parties faced multiple closures since the 1970s until Erdogan’s new AK Party arrived on the political scene, promising to put an end to such repression. After some 20 years in power, that promise now seems long forgotten.
The system has instead become even more repressive while only the names of those running it have changed. Turkey’s rankings for civil and political liberties have fallen precipitously in the last several years. Freedom House gives Turkey 16 out of 40 points for “political rights” and 16 out of 60 for “civil rights.”
According to Freedom House, “after initially passing some liberalizing reforms, the AKP government showed growing contempt for political rights and civil liberties, and its authoritarian nature was fully consolidated following a 2016 coup attempt that triggered a dramatic crackdown on perceived opponents of the leadership. Constitutional changes adopted in 2017 concentrated power in the hands of the president.”
As a system, democracy is meant to promote social stability by giving people peaceful avenues to seek their political preferences. With mass incarcerations of political dissidents and looming closures of major opposition political parties, today’s Turkey seems to be eschewing such an arrangement. The current president and his political allies can no longer imagine losing power, and the price for this unwillingness to give the opposition a fair chance at taking over will have to be paid for years to come by Turkey.
* David Romano is Thomas G. Strong Professor of Middle East Politics at Missouri State University





























