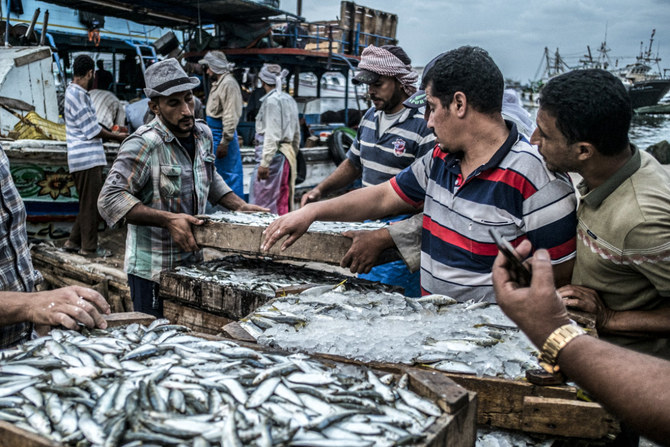
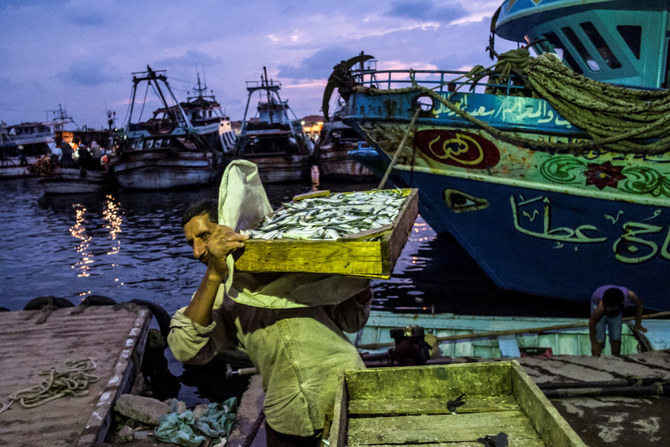
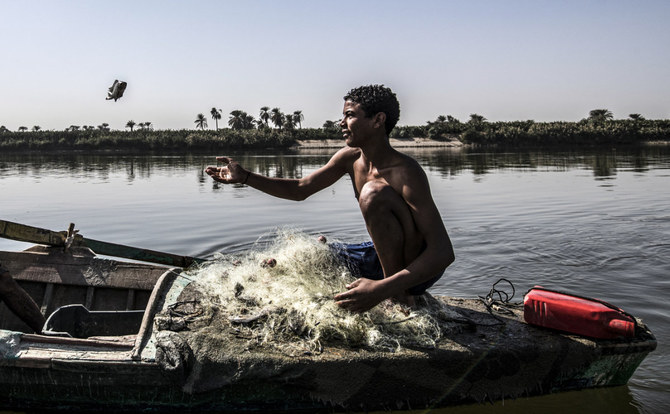
DUBAI: Dutch academics and the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization have launched a vital new project that is using state-of-the-art artificial intelligence technology to improve the identification and measurement of fish species and stocks in the Nile Basin.
It could become a key tool in the quest for sustainability and food security by improving the collection of vital data from fishing communities around the region.
The initiative, supported by Wageningen University and Research in the Netherlands, is the latest development in a decades-long effort launched in the 1970s by FAO to help countries carry out better identification of species for fisheries purposes, so that the collection of data about fish catches can be enhanced and the fishing industry improved.
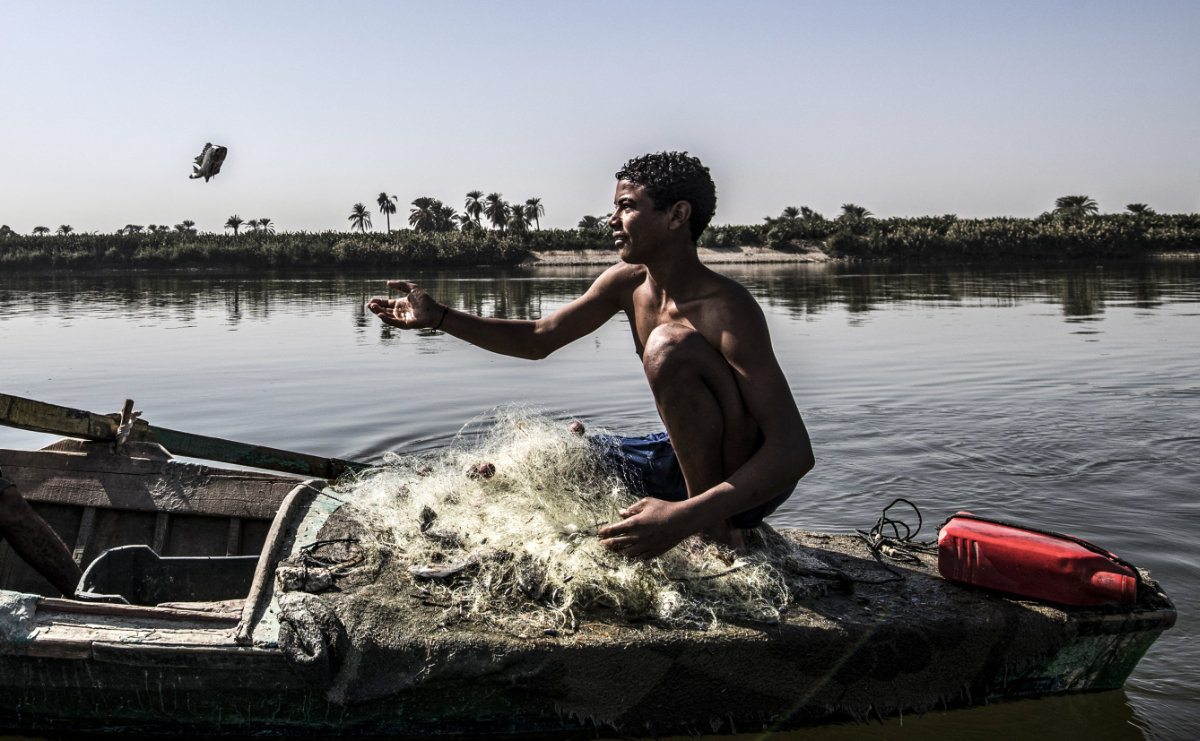

A fisherman on the Nile catches a tilapia. The river’s basin is the site of a new scheme using AI to track fish stocks, below, which, it is hoped, will improve the sustainability of fishing in the region. (AFP)
“This helps people to understand long-term trends in what is happening with fisheries through time,” said Kim Friedman, a senior fishery resources officer at FAO. “The initial push was mainly to do species identification guides and most of these were done with the museums of the world, so that a country could pick up a guide and know exactly which species it was. But then we started to also do posters and pocket guides so people could carry them in boats.”
The tools have evolved thanks to critical new work, supported by artificial intelligence, that could transform ocean-conservation efforts that are much needed given that many of the world’s fish species are in decline.
Once a very costly, time-consuming process carried out by observers on vessels, species tracking using advanced technology can now be so detailed that the data can even pinpoint the freshness of fish.
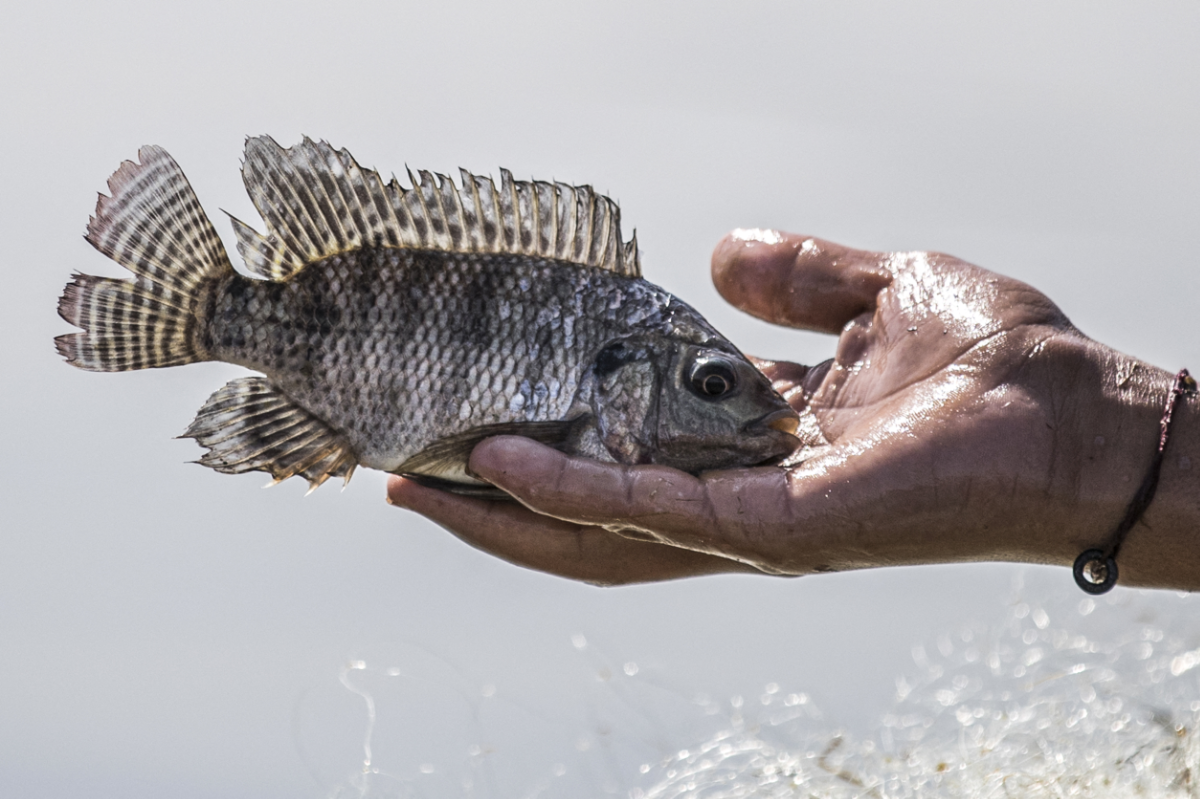

Nile tilapia is one of the world's most popular cultured freshwater fish. (FAO photo)
Edwin van Helmond, a fisheries scientist at Wageningen Marine Research, which is part of WUR, said that the potential for the use of AI and other technologies in supporting fisheries management is huge.
“The fact that detailed catch information can be collected through algorithms, without the presence of experts, makes data collection available in remote areas,” he told Arab News. “Data can be sent or collected at a later stage or directly stored in a data cloud and made remotely available for experts.”
He believes such technology will also greatly benefit food security in the long term, which is a major challenge facing the Gulf region, and also the sustainable management of natural resources, which begins with the collection of sufficient data.
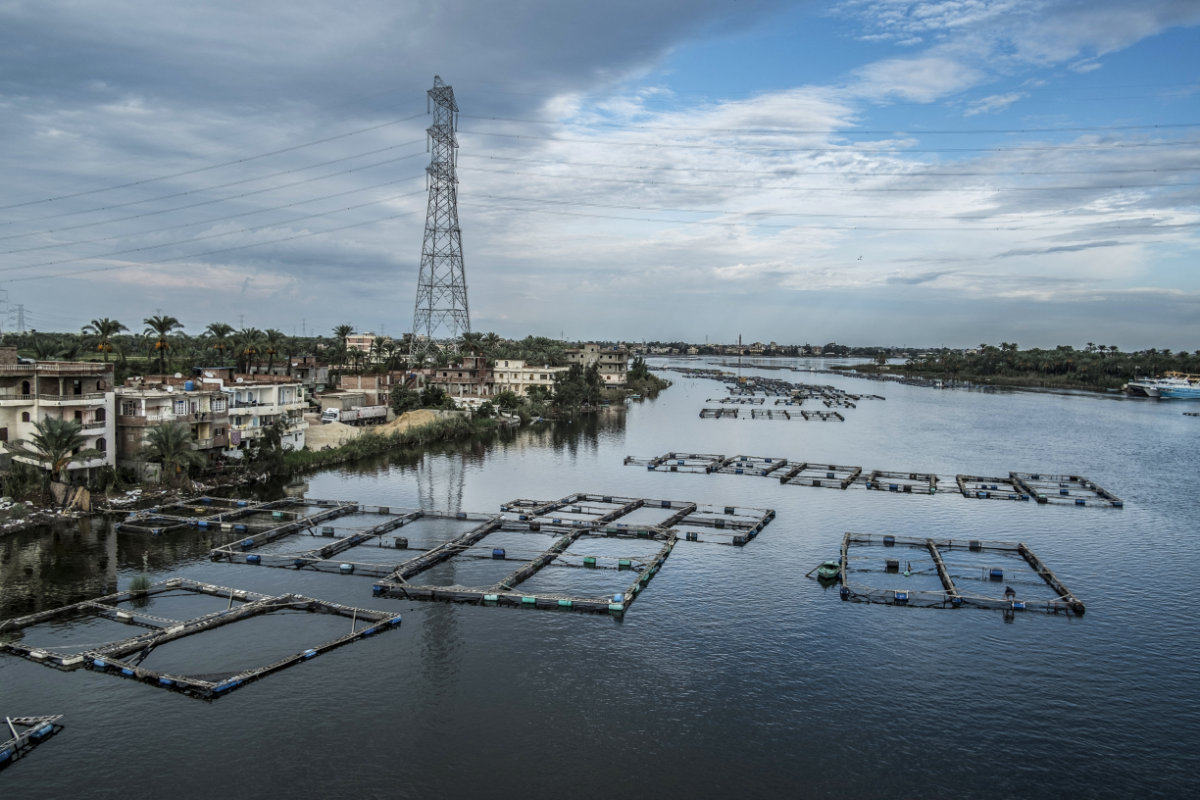

FAO is testing algorithms that can calculate sustainable harvest quantities without the danger of over exploitation. (Photo credit: FAO)
“To be able to perform a good assessment of the available resources, in this case local fish stocks, you need good data,” he said. “This includes detailed catch information by species, catch weight, and length frequencies.
“These variables form the input for any stock-assessment model, and with these models you can calculate sustainable harvest quantities without the danger of over exploitation, which equates to sustainable management of local fish stocks and long-term food security.”
FAO is now trying to make the technology more accessible so that more people in the industry can benefit from it, which in turn will help the organization expand its data sets. Comprehensive information about each species would be used to build algorithms that can identify species and their locations and recognize any changes.
FASTFACTS
Climate change, diminishing fish stocks and over-fishing are threatening coastal communities.
AI and mobile apps are helping fishermen worldwide engage in sustainable fishing practices.
Once such algorithms are developed, an app will allow users to search for specific species using imagery that can unlock information such as the features of the species, food values and other fisheries-related data.
“In the future, anyone, even a fisherman, could take pictures of his catch, send them off, get the species identification and, potentially, also some metrics like the size of the fish,” eventually developing a portfolio of trends in the waters in which they work, Helmond said.
The project in the Nile Basin, which will run for three to five years, will also look at certain country requirements in terms of languages, reporting and ensuring data sets meet the desired levels of security.
So far, e. The system mirrors recreational fishing identification efforts in European rivers and lakes, where communities fund systems that can identify catches and develop appropriate codes of practice among themselves.

Advances in technology are expected to play a leading role in the promotion of sustainable fisheries and aquaculture and ensure their growth. (AN file photo)
“This then feeds back into understanding how well the different rivers or lake systems are doing and which ones maybe need to be augmented with hatchery-reared fish,” Friedman said.
“It allows people to link up with others who would not have potentially linked up in the past.”
A key to success will be data gathering by as many stakeholders as possible, said Friedman. The resultant benefits for all those involved will be the best possible algorithms.
“There is also an ability for us to start to collect pictures from around the Nile to tell people they can catch this type of fish in good sizes and condition in a specific location,” he added. “So (this addresses) issues about sustainability and also looking for market opportunities.”
The Global Fishing Watch platform, a collaboration between Google, nonprofit environmental digital-mapping organization SkyTruth and conservation organization Oceana, was one of the first attempts to combine AI with satellite data to observe fishing activity.
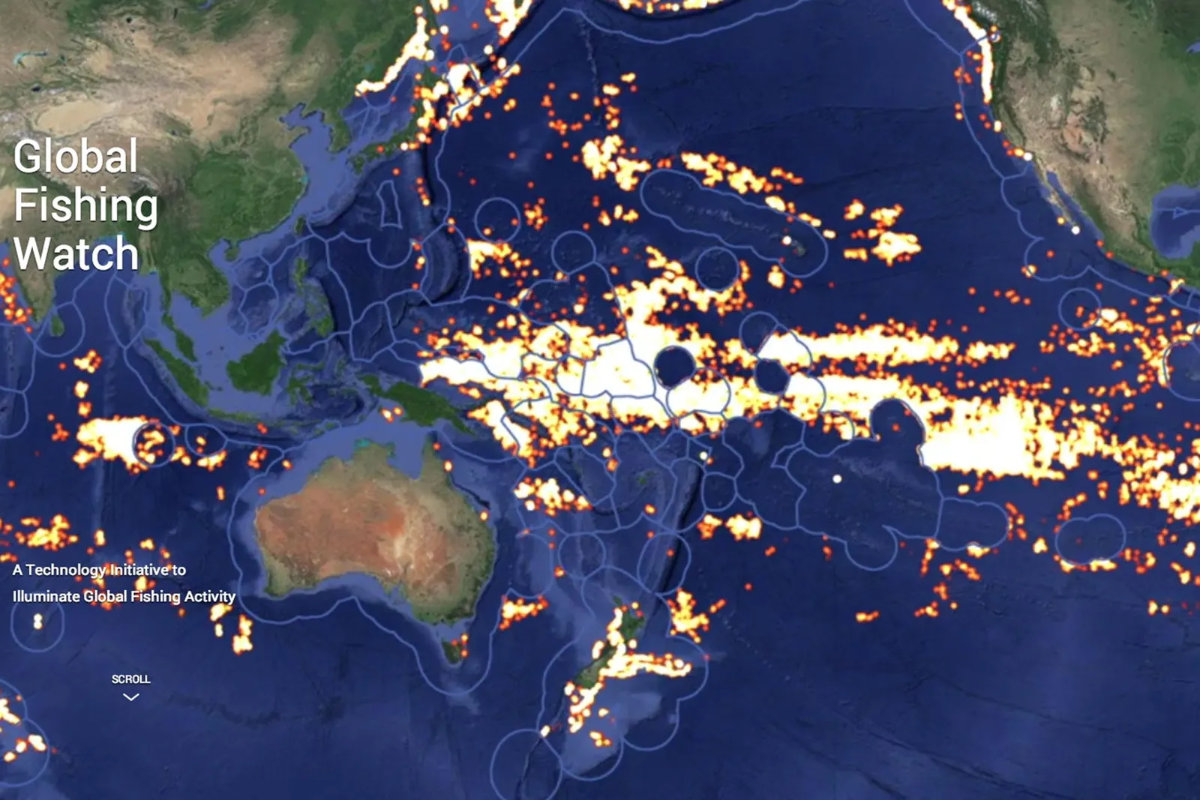
Google, along with the nonprofit environmental digital-mapping organization SkyTruth and conservation organization Oceana, are working on an AI project to combine studies with satellite data to observe fishing activity worldwide. (Global Fishing Watch)
The technology also offers hope for efforts to address diminishing freshwater resources across the region, which has some of the lowest levels of fresh water in the world, mainly in the form of underground, non-renewable stocks. Freshwater reserves have fallen by 60 percent in the past four decades, according to FAO, and what remains is expected to diminish by 50 percent by 2050.
Advances in technology are expected to play a leading role in the creation of international policies to promote sustainable fisheries and aquaculture and ensure their growth, with artificial intelligence helping to address what is now a global environmental concern. The data that is gathered will allow fish and seafood retailers and customers to be more aware of whether what they are selling and consuming is sustainable.
Innovation also holds the key to making farming and the entire agri-food value chain more attractive, creating business and employment opportunities and helping the region to achieve food security, sustainable agriculture and the objectives of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals.

Advances in technology are expected to play a leading role in the promotion of sustainable fisheries and aquaculture and ensure their growth. (AN file photo)
FAO Director-General Qu Dongyu believes the latest collaborative project is a vital step toward achieving this.
“A focused and strengthened framework between FAO and Wageningen University and Research will allow our partnership to better align efforts and resources for greater impact in meeting the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Goals,” he said.
In addition to the Nile project, FAO and WUR are collaborating on several other initiatives related to the sustainable development of fisheries and aquaculture value chains.
In the African, Caribbean and Pacific States, for example, a joint project called FISH4ACP is providing expertise on multi-stakeholder partnerships that is contributing to food security and increased nutrition, prosperity and job creation.
Just last month, authorities in Saudi Arabia, which is responsible for 49 percent of the Gulf’s aquaculture, announced they are working to establish a regional center for fisheries as part of wider goals to diversify the national economy and address food security.

Saudi Arabia is responsible for 49 percent of the Gulf region's aquaculture industry. (Supplied)
Friedman said that such initiatives have the potential to rapidly spread across the region and beyond.
“If we look back through time, all the regional guides that were put together to understand fisheries started off in certain regions and now are global,” he said.
“I suspect we will have the same thing happen not just for the Nile, but for inshore fisheries, pelagic (open sea) fisheries and so on, based on the opportunities that AI will offer us.”








































