PARIS: The war in Ukraine has sparked an energy supply crisis and upset the global power balance, prompting a flurry of diplomatic activity. One nation that has been reaping the benefits of recent engagements is Saudi Arabia.
Concerns over energy have restored the Kingdom’s image in the eyes of European powers as a key player in this multipolar, post-COVID world order — one that could rebalance oil markets, and perhaps beckon the continent into a clean energy future.
The diplomatic circuit began in April when Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman met with the Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan in Ankara. This was followed in mid-July with US President Joe Biden’s visit to Jeddah.
On July 26, the crown prince was traveling once again, this time heading to Athens for talks with Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis and the country’s business community. Two days later, it was France’s turn to welcome the crown prince.
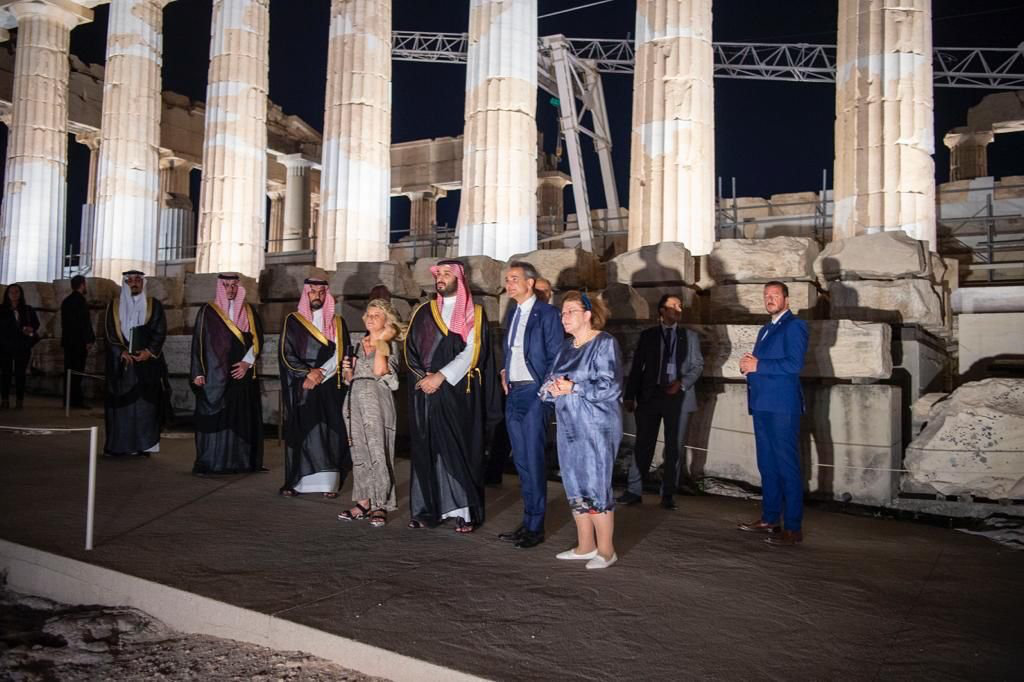

Greek Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis gives Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman a tour of the Acropolis during the Saudi leader's visit to Athens on Wednesday. (SPA)
These latest stops mark Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman’s first visit to the EU since 2018 when relations with Washington and the Kingdom’s European allies soured. Today, in the face of new economic realities, the past, it would appear, is well and truly in the past.
Boosting the supply of oil and gas to Europe has become a critical issue in the wake of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the resulting Western embargo on Russian hydrocarbons.
If Russian President Vladimir Putin is seen in Western capitals as the cause of this disruption, then Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman is viewed as the remedy. As a result, the crown prince entered into talks with Greek and French leaders from a position of strength.
Western capitals want to convince the world’s biggest oil exporter to open the floodgates and bring down prices, which have contributed to a cost of living crisis for many nations still emerging from the economic turmoil of the pandemic.
Riyadh has been reluctant to meet Western demands, however, in part because it has solid partnerships with Russia, such as the natural gas project in Siberia directed by the Russian group Novatek.
The stage is therefore set for Saudi Arabia to reap the benefits of Western reengagement.
Saudi delegations have not arrived empty-handed, however. While in Athens, the crown prince signed agreements on maritime transport, energy, defense, waste management and culture. Experts say that the joint project to install a cable connecting the two countries is especially important, promising to provide Europe with cheaper energy.
Saudi-Greek cooperation could transform Greece from a debt-burdened nation into a regional energy, trade, and communications hub connecting Europe and Asia, and into a gateway for new green hydrogen technologies to help the continent realize its net-zero aims.
Saudi Arabia, the world’s 19th largest economy, has initiated an economic and social reform agenda to reimagine its future and its place in the region — Vision 2030 — and is eager to attract outside investment.
The vision, launched in 2016, offers a new, diversified model for economic development that is more inclusive — especially for women and young people — and which will create jobs and wealth in sectors beyond hydrocarbons, from tourism, entertainment, and tech, to retail, renewables and smart city megaprojects.
By 2030, these new industries could create revenues equivalent to those now generated by oil — about $250 billion.

Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman has shown his determination to radically transform the Saudi economy and society by freeing it from its dependence on hydrocarbons, which make up 42 percent of its gross domestic product, 70 percent of its income and 90 percent of its exports.
Despite the economic setbacks of the COVID-19 pandemic, the transformation is already in motion. Within the next decade, the Kingdom will emerge as a major player in tourism (with 100 million visitors by 2030), in entertainment (with a market worth of $8 billion) and a cutting-edge defense industry thanks to technology transfers.
Then there is the prospect of growth in renewables, manufacturing and mining, the Kingdom’s ambitions in food security, biotechnologies and artificial intelligence, not to mention large-scale logistics and airport infrastructure plans.
To power this transformation, the Kingdom relies on its Public Investment Fund — a $2 trillion sovereign wealth fund — which recently acquired stakes in Starbucks, Marriott, Disney, Boeing, City Group, Facebook, Germany’s Signa Sports, the Dutch TMF Group, and also bought Newcastle United F.C.
With this wealth, Riyadh intends to build major national reference companies alongside Saudi Aramco — the world’s leading oil exporter — in transport, mining, renewable energies, digital and automotive.
And the cultural sector will not be left behind either. The Kingdom is a candidate to host the World Expo in 2030, having seen its pavilion awarded best exhibition venue at Expo 2020 Dubai.
Perhaps the most striking project the Kingdom has launched is NEOM — a contraction of the Greek word “Neo,” or “new,” and the letter “M” for mostaqbal, or “future,” in Arabic. This $500 billion smart city will be at the forefront of tech and sustainability, and promises to revolutionize the urban experience.
Last year, at the fifth edition of the Future Investment Initiative, also known as “Davos in the desert,” foreign investors learned the Arabic word Marhaba — “welcome.” It is a word that will shape relations with the Kingdom over the coming decade.
During the forum, the Saudi crown prince presented world leaders in finance and technology with a clear ambition — to establish the Kingdom as a key player in the global economy.
When he meets with French President Emmanuel Macron at the Elysee Palace in Paris this week, the crown prince will bring this same sense of ambition and purpose, strengthened, no doubt, by the Kingdom’s new economic clout.
• Azouz Begag is a writer and former minister (2005-2007), researcher in economics and sociology. He is a researcher at the CNRS. Twitter: @AzouzBegag
Disclaimer: Views expressed by writers in this section are their own and do not necessarily reflect Arab News’ point of view.





























