LONDON: On Sept. 13, Mahsa Amini, a 22-year-old Iranian woman, was arrested in Tehran for violating the Islamic republic’s strict dress code for women. In the custody of the Gasht-e Ershad — the “Guidance Patrol,” or morality police — she suffered a catastrophic head injury and, after three days in a coma, died in hospital.
Her death was the trigger for hundreds of protests across the country, which have seen men and women take to the streets in vast numbers, with women openly shunning the obligatory wearing of the hijab and cutting their hair in public in a gesture of defiance.
Now a new report from the Tony Blair Institute for Global Change — TBI — backed by two consecutive polls of thousands of Iranians, has concluded that the widespread rejection of the hijab is nothing less than a symbol of a nationwide yearning for regime change.
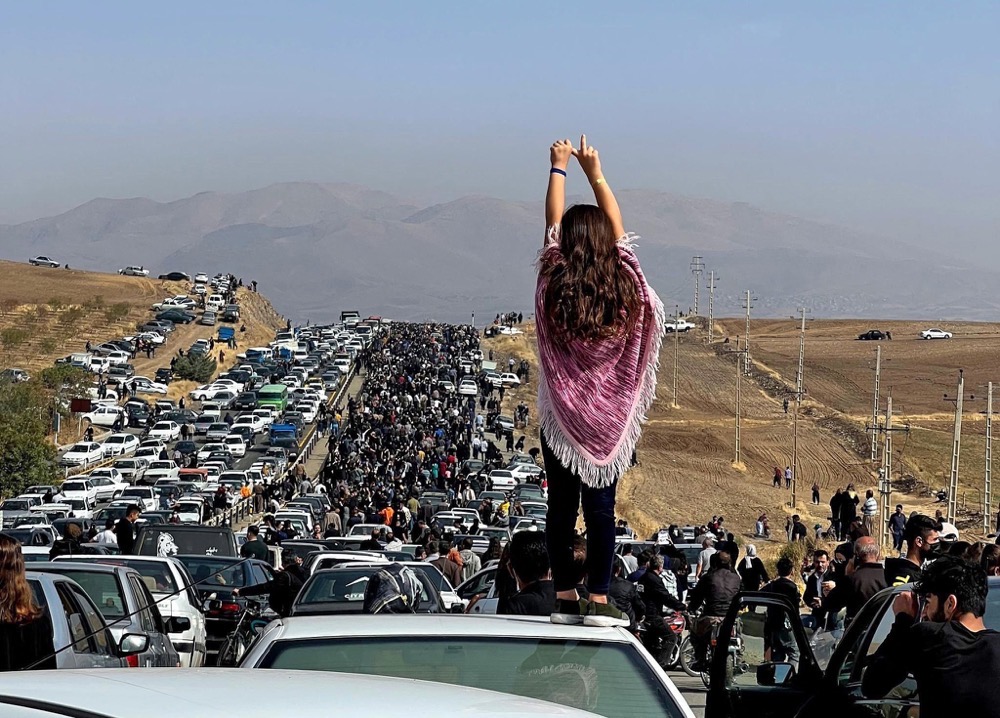

Such is the “unprecedented secularization” sweeping Iran that the TBI concludes that “Iran’s society is no longer religious.” (AFP)
The current protests are “no flash-in-the-pan moment,” says Kasra Aarabi, co-author of the report and the Iran Program lead at TBI’s Extremism Policy Unit.
“The protests we are seeing now are unprecedented in their longevity, and in their size. But they are a continuation of the trend for unrest that emerged in 2017, since when we’ve seen Iranians consistently taking to the streets.”
Aarabi, a non-resident scholar at the Middle East Institute in Washington and a native Farsi speaker, believes that the current unrest, some of the worst seen in Iran since the revolution in 1978 replaced the modernizing regime of the Shah, is a pivotal moment for Iran.
“This is the beginning of the end of the Islamic Republic,” he said.
“It’s been clear for years that the Iranian people don’t want reform, they want regime change, the downfall of the Islamic Republic in its entirety and the creation of a secular democracy.”
Young people in Iran, he says, are witnessing the great changes taking place elsewhere in the region, from the bridge-building of the Abraham Accords to the great modernizing reforms in Saudi Arabia, “and they’re thinking, ‘Why can’t we have that?’”
The TBI report draws on two polls carried out among tens of thousands of Iranians, which demonstrate the extent to which Iran has become a secular society, despite more than 40 years of life under a hard-line Shiite theocracy.
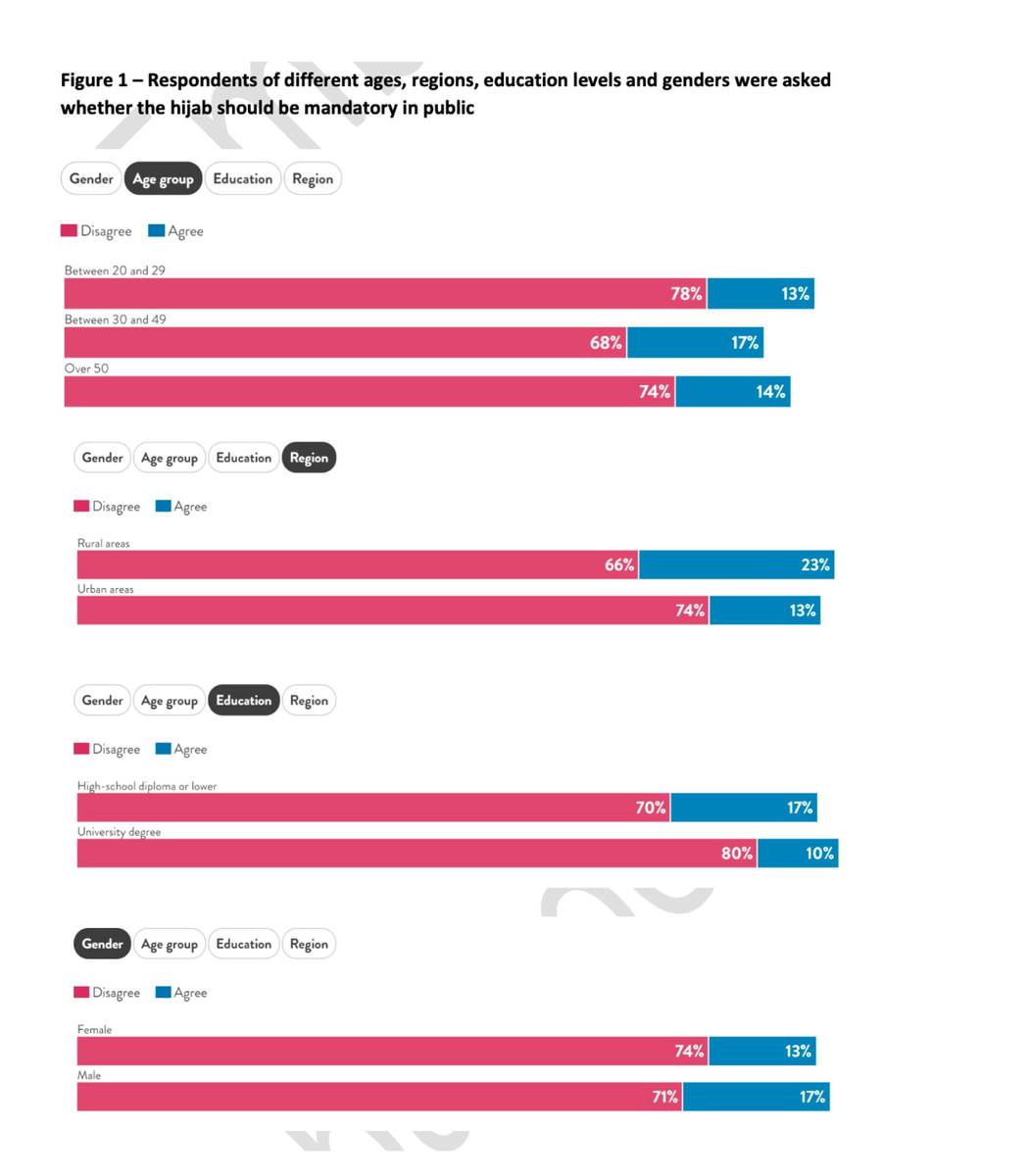
Key findings include that men and women in Iran are almost equally opposed to the mandatory wearing of the hijab, rejected by 70 percent of men and 74 percent of women.
This opposition also spans what might otherwise be expected to be the divide between town and country, where people are traditionally considered to be more conservative in outlook.
Only 21 percent of urban Iranians believe in the practice, support that rises only to 28 percent among rural communities.
Predictably, rejection of the compulsory wearing of the hijab is strongest among younger people — 78 percent of respondents aged between 20 and 29 oppose it.
Yet the practice is also opposed by 68 percent of Iranians aged between 30 and 49, and 74 percent aged over 50 — the so-called revolution generation.
Only a small minority of Iranians support the practice — just 13 percent of women and 17 percent of men.
The hijab protests, says the TBI, are clearly about regime change: 84 percent of those who oppose the dress code also want to see an end to the Islamic Republic.
Furthermore, “the anti-regime protest movement in Iran is fundamentally secular,” said the report, adding that “76 percent of Iranians who want regime change, also consider religion unimportant in their lives.”
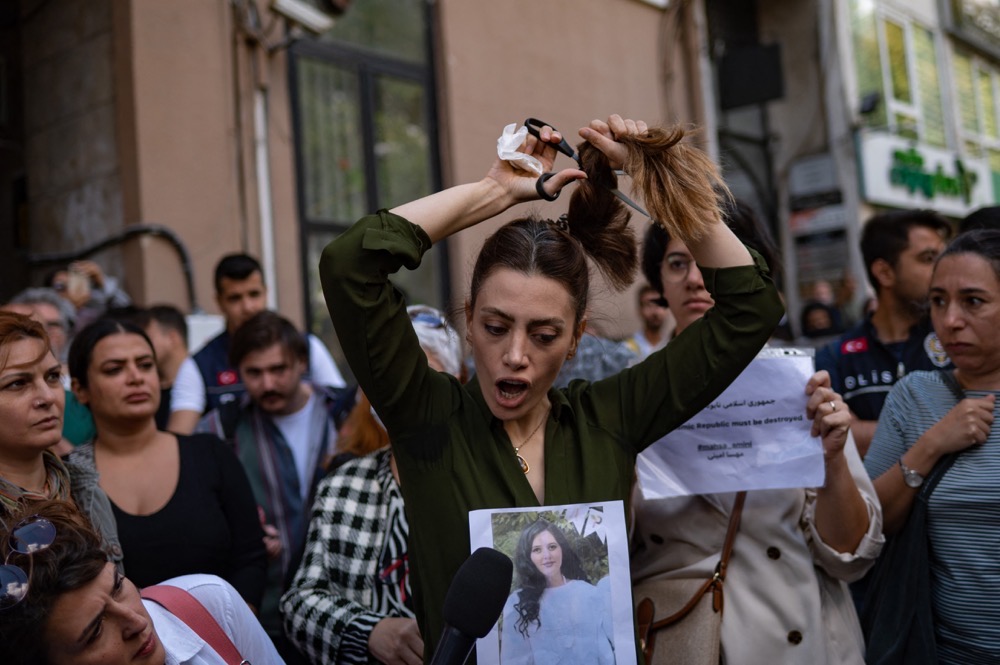

New report showes the widespread rejection of the hijab is nothing less than a symbol of a nationwide yearning for regime change. (AFP)
In fact, such is the “unprecedented secularization” sweeping Iran that the TBI concludes that “Iran’s society is no longer religious.”
Only a declining minority in the theocratic republic follows the Islamic obligation to pray five times a day, ranging from 33 percent of rural Iranians to only 26 percent of urbanites.
Analyzed in terms of education, only 26 percent of Iranians with a university degree pray five times a day, while the percentage for people with a high-school diploma or lower is little different, at 28 percent.

Although the report, “Protests and polling insights from the streets of Iran: How removal of the hijab became a symbol of regime change,” was published on Tuesday, it contains previously unpublished data from two surveys carried out in Iran in 2020 and 2022.
This, says the TBI, demonstrates that the issue of the hijab and the yearning for the secularization of Iranian society has been simmering for years.
“Today’s protests are the consequence of the huge gap between the regime and the people of Iran,” said Aarabi.
“Despite living under a hard-line Islamist theocracy, the Iranian people are the most secular in the Middle East. There has been a gradual process of secularization and liberalization that began in the early 1990s, which has reached unprecedented levels in the past five years.”
The new report draws on polls conducted in June 2020 and February 2022 by the Group for Analyzing and Measuring Attitudes in Iran — GAMAAN — an independent, non-profit research foundation registered in the Netherlands.
Instead of conventional face-to-face or telephone-based polling methods, GAMAAN says it uses “digital tools and alternative methods to capture the real opinions of Iranians ... allowing Iranians to answer questions about sensitive subjects truthfully, without fearing for their safety.”
A survey conducted by GAMAAN in June 2020 polled 39,981 respondents on questions relating to religion. In February 2022, 16,850 Iranians responded to questions about political systems.
Analyzed by demographic breakdown, says the TBI, “the results reveal a steadily emerging consensus on the streets, which is anti-compulsory hijab and anti-regime at its core.”
Thousands of arrests have followed as the regime has clamped down on the protesters. Some have been charged with crimes punishable by death, such as “enmity against God” and “corruption on Earth.”
This month has seen at least five executions of protesters carried out and confirmed by the state, and unknown numbers of people, including children, have been killed in the protests.
The HRA News Agency, founded in 2005 to monitor human-rights abuses in Iran, says more than 400 protesters have been killed, and at least 17,250 people have been arrested.

“This is the beginning of the end of the Islamic Republic,” says Kasra Aarabi, co-author of the report. (AFP)
Last week UNICEF, the United Nations children’s agency, reported that “since late September an estimated 50 children have reportedly lost their lives in the public unrest in Iran.”
The latest was a 10-year-old boy, Kian Pirfalak, one of several people shot dead in and around protests last Wednesday (Nov. 16). He was hit by gunfire and died as he and his father were driving home in the western Iranian city of Izeh.
The protests, widely covered in the West, gained an even higher profile this week when the Iranian football team pointedly refused to sing the national anthem before their opening World Cup match against England in Qatar.
Before the game, skipper Ehsan Hajjsafi said the team supported those who had died in the protests, adding “we have to accept that the conditions in our country are not right and our people are not happy.”
The West, says the TBI’s Aarabi, had failed to recognize the transformation that has been taking place in Iranian society “because it was focused solely on viewing Iran, and the dissent in the country, through the lens of the 2015 nuclear agreement, and then Trump’s withdrawal from that agreement.
“But this dissent is not being driven by the nuclear deal, nor by the reimposition of sanctions. It’s being driven by life under a totalitarian, misogynistic, ideological regime, which has consistently prioritized the interests of its hard-line Islamist ideology over those of the Iranian people.”
Commenting on the report, Tony Blair, the former UK prime minister who founded his institute in 2016, said that “the people of Iran have shown extraordinary bravery and courage over the past two months. They should know they have the support of millions of people around the globe who admire the stand they have taken for freedom.
“I have always said, and I stand by this more so today, that the single most liberating event for the Middle East will come when the Iranian people finally have their freedom.
“For the ordinary people of Iran, the values that many may describe as ‘Western’ are in fact their own. Neither they nor their country should be defined by the Islamic Republic. As a great people, whose history and civilization are rich and varied, it is they and they alone who should define their own future.
“This is why I firmly believe it is in our interests today, in the West, to show our deep solidarity with the protesters risking their lives for what we so often take for granted.”
It was, he added, “time we in the West recalibrate our policy in a way that draws a clear distinction between the people of Iran and the Islamic Republic. Our efforts should serve the former.”



























