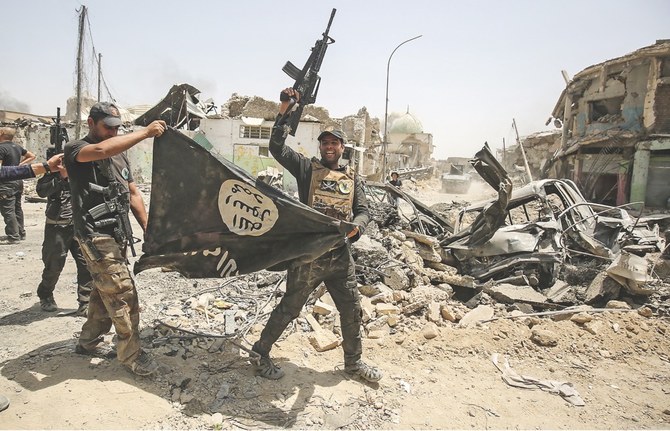
IRBIL, KURDISTAN: Having once controlled roughly a third of the country at the height of its power, including several major cities and oilfields, there are now growing signs that what remains of the Daesh terrorist organization in Iraq is in terminal decline.
Unable to attract new recruits to shore up its dwindling numbers, nor able to mount significant offensive operations, the group that had in 2014 proclaimed its own “caliphate” today looks like a spent force — in Iraq at least.
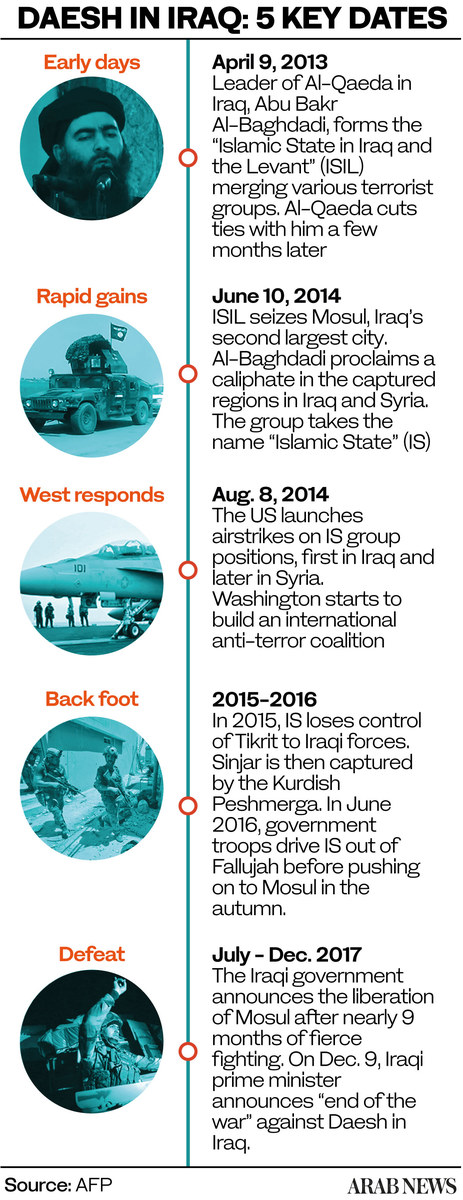
On March 12, Iraqi General Qais Al-Mohamadawi revealed that Daesh has about 500 active militants remaining in the country. However, he stressed that they are confined to remote desert areas and mountains and have lost their “ability to attract new recruits.”
The following day, the US-led coalition tweeted that Daesh networks “remain under intense pressure,” with the Iraqi Security Forces and the Kurdish Peshmerga having “removed from the battlefield at least 55” of the militants in February alone.
Joel Wing, author of the “Musings on Iraq” blog and who tracks security incidents in Iraq attributed to Daesh, recently wrote that recorded incidents from the start of March are a reminder that Daesh is in its “death throes in Iraq” and “remains barely active in the country.”
Only three incidents were attributed to Daesh in the first week of March, down from eight in the last week of February. Furthermore, since the start of 2023, eight out of nine weeks have witnessed security incidents in the single digits, which Wing says continues a trend that began in 2022, when the majority of weeks saw fewer than ten attacks.
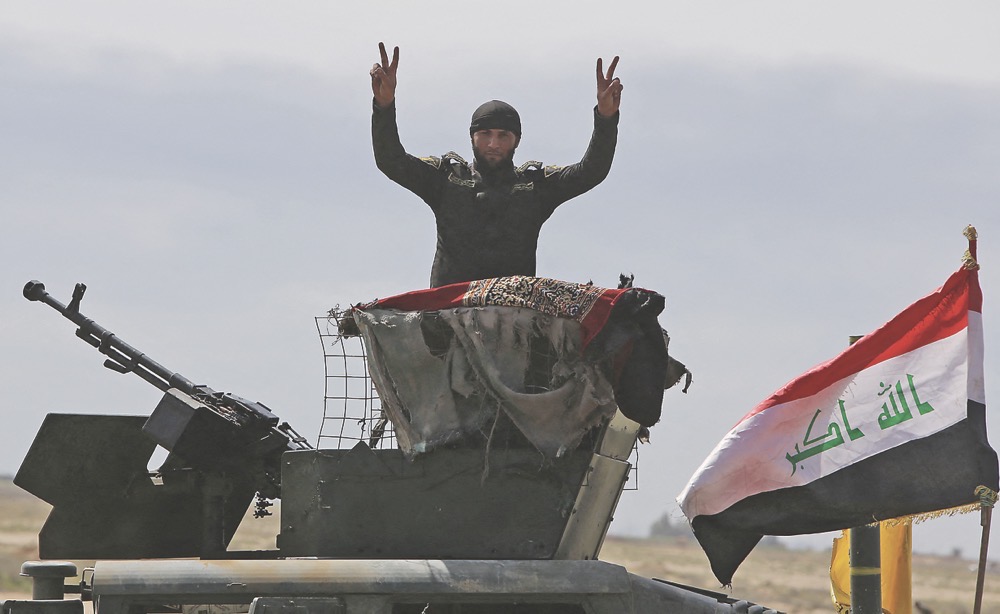

An Iraqi fighter flashes the sign for victory on top of an armed vehicle in the village of Albu Ajil, Tikrit, on March 8, 2015, during a military operation to regain control of the Tikrit area from Daesh militants. (AFP)
“I don’t see a Daesh revival any time soon,” Wing told Arab News, using another name for Daesh. “They’ve had five years to recover from their defeat in Mosul and all signs point to the group getting weaker, not stronger.”
Mosul is Iraq’s second city and the largest urban center the group annexed into its self-styled caliphate, which, at the height of its power in the mid-2010s, covered about one-third of Iraq and one-third of Syria.
Iraqi forces recaptured Mosul with the support of the US-led coalition in July 2017 after months of intense fighting. Iraq declared victory over the group the following December.
Having lost its territorial caliphate, Daesh mounted an insurgency from rural and mountainous redoubts. For years, there were fears that the group had reverted to its pre-2014 status as an insurgent threat and could one day retake significant swathes of territory.
It now seems that dire prospect is a remote one.
“They haven’t been able to recruit many new Iraqis to their cause,” Wing said. “Their main activities appear to be trying to smuggle members and their families from Syria into Iraq and protecting the rural areas they control. There are hardly any offensive operations and they are completely absent from Iraq’s urban centers.”
And while Daesh could feasibly continue in this state for years to come, since there are few people and a minimal government presence in the areas where they operate, Wing says that they have “little to no effect upon Iraq anymore.”
Michael Knights, the Jill and Jay Bernstein Fellow at The Washington Institute for Near East Policy, sees two different scenarios potentially unfolding.
“If current trends continue, Daesh is headed in the same direction as Algeria’s terrorist groups — disintegration into criminal gangs, inability to destabilize the country, and occasional terrorist outrages that are easy to quickly forget,” he told Arab News, using another acronym for Daesh.
“The question is whether — as in 2011-2014 — the Iraqi government will politicize the security forces and adopt a sectarian agenda, thus breathing life back into Daesh,” he said.
The government of former prime minister Nouri Al-Maliki adopted just such an agenda after the US withdrew the last of its troops from Iraq in 2011. Consequently, when Daesh entered Mosul in June 2014, the ISF infamously did not fight, despite having vastly superior numbers.
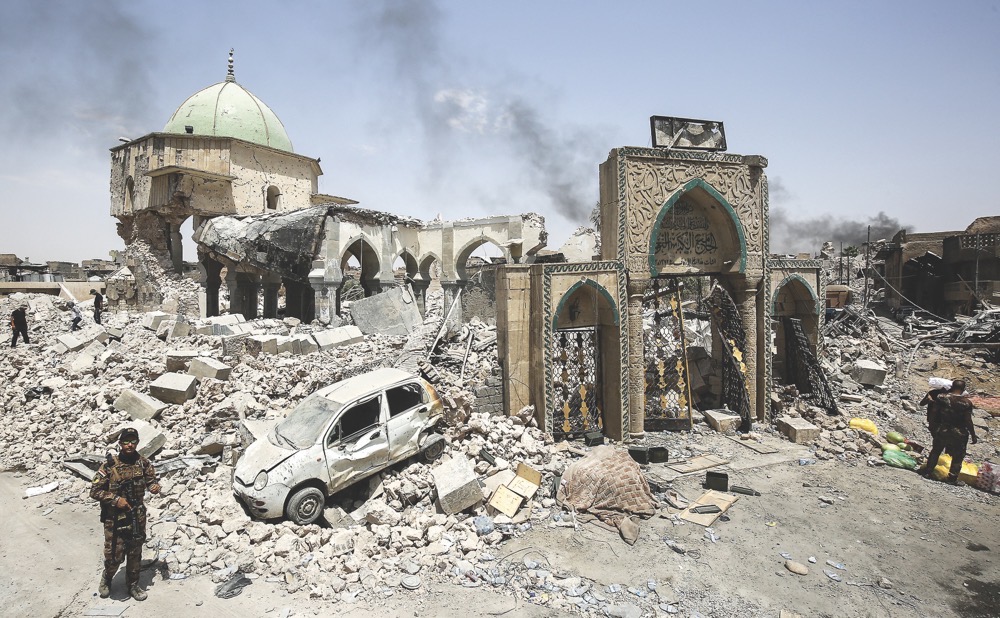

The destroyed Al-Nuri mosque in the Old City of Mosul. (AFP)
Daesh invaded northern Iraq in 2014 after gaining a sizable foothold in Syria amid the chaos of that country’s brutal civil war. If the security situation in eastern Syria again deteriorates, there are fears this could reenergize diminished Daesh remnants in Iraq.
After visiting prisons holding thousands of Daesh militants in northeast Syria earlier this month, General Michael Kurilla, head of the US military’s Central Command, CENTCOM, warned of a “looming threat” posed by these detainees.
“Between those detained in Syria and Iraq, it is a veritable ‘ISIS army in detention,’” he said in a CENTCOM statement. “If freed, this group would pose a great threat regionally and beyond.”
The Al-Hol camp in eastern Syria also houses tens of thousands of the relatives of alleged Daesh militants, roughly half of whom are Iraqi citizens.
In January 2022, Daesh detainees in Ghwayran prison in the northeast Syrian city of Hasakah rioted in coordination with an external attempt to free them, igniting 10 days of bitter fighting with Kurdish-led security forces. Daesh reportedly had similar plots for Al-Hol.
“Sneaking people out of Al-Hol and getting them into Iraq is a major priority because they haven’t been able to bring many new people to their cause in Iraq,” said Wing. “So they’re relying upon getting their current members out of the Syrian camp to try to bolster their numbers, but it hasn’t added to their capabilities at all.”
Ryan Bohl, a senior Middle East and North Africa analyst at the risk intelligence company RANE, emphasizes the importance of recalling the context in which Daesh initially emerged to “better understand the conditions that would allow it to return in the future.”
“ISIS emerged in a power vacuum, one first caused by the US invasion of Iraq and then the Syrian civil war that began in 2011,” Bohl told Arab News. “It was best able to grow and exploit local grievances for its radical agenda when its rivals were split and when it was not the focus of a major power, like the US, Turkiye, or Russia.
“Today, Iraq, despite deep political dysfunction and violence, is not nearly as divided as it was during the run-up to the Daesh blitz in 2014 into Iraq. Syria’s civil war has stabilized, leaving little room for them to grow there as well.”
Nevertheless, completely eradicating a group such as Daesh will remain a difficult, if not impossible, task for Iraqi authorities.
“There will always be online recruitment and localized grievances that can turn into small cells or radicalized individual attackers,” Bohl said. “Iraq’s social contract also remains fractured, and until there is a strong, sustained governing consensus, radicalism of all stripes will find a home there.”
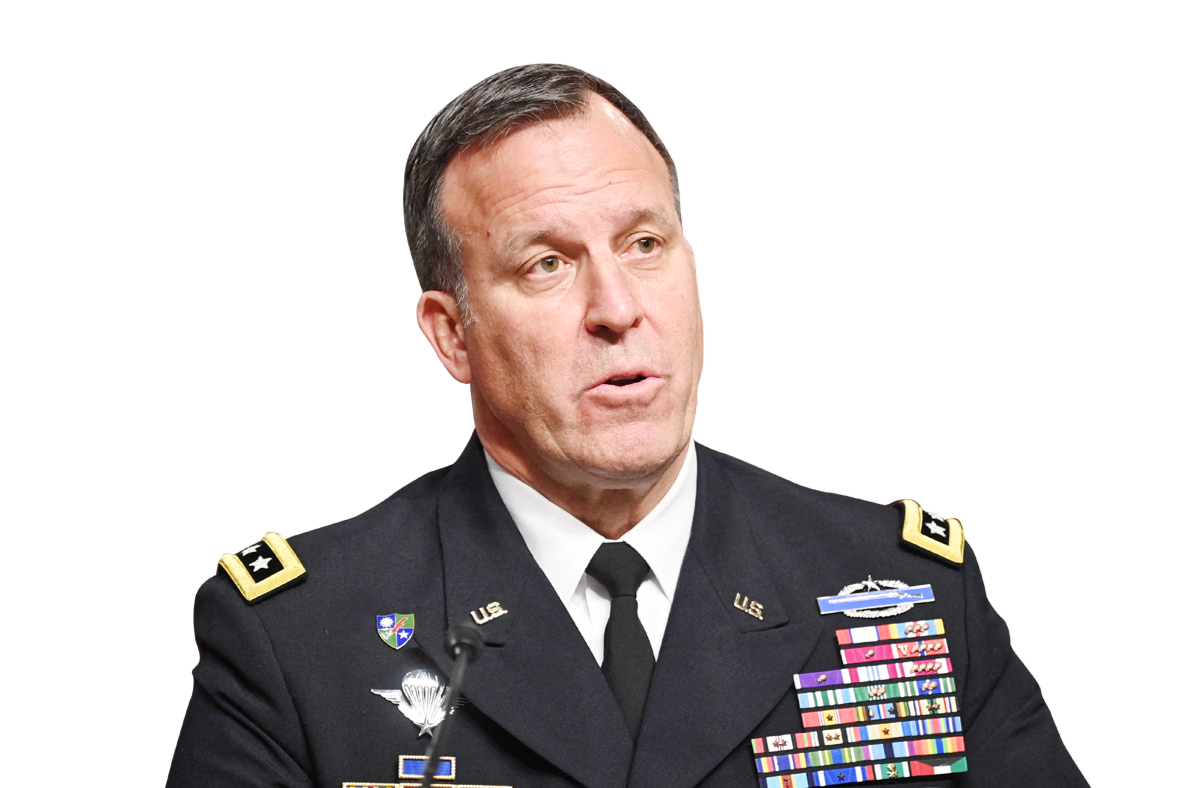

“Between those detained in Syria and Iraq it is a veritable ‘ISIS army in detention,’” said Gen. Michael Kurilla, Commander of US Central Command. (Supplied)
While he believes Syria is the most likely place from which Daesh can make a resurgence in the region, there would first have to be a strategic shift, such as a US withdrawal or some power vacuum caused by Damascus forcibly reestablishing its rule over the area.
“Under those conditions, it would become possible for Daesh to retake some initiative in that area and use Syria’s northeast to attack Iraq,” he said.
“However, it shouldn’t be entirely ruled out that Daesh could resurge in Iraq, particularly if political problems there grow so severe that it reignites sectarian war.
“Under those (more remote) circumstances, Daesh would once again have a shot at restoring territorial control within Iraq, even if Syria remained stable.”
Knights also stresses that any chance of Daesh making a successful resurgence in Iraq depends on Baghdad’s management of its security forces.
“Syria is like a freezer in which Daesh can hibernate, waiting for it to experience a springtime in Iraq,” he said. “If the Iraqi government mismanages the security file, then a cross-border pollination could start again.”





















