JEDDAH: Already reeling from decades of conflict and political turmoil, the recent sudden outbreak of fighting in Sudan between rival military factions threatens to plunge swathes of the population into an even greater humanitarian disaster.
On April 15, after weeks of tensions, clashes broke out in the capital Khartoum, between the Sudanese Armed Forces of Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan and the Rapid Support Forces of Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, also known as Hemedti.
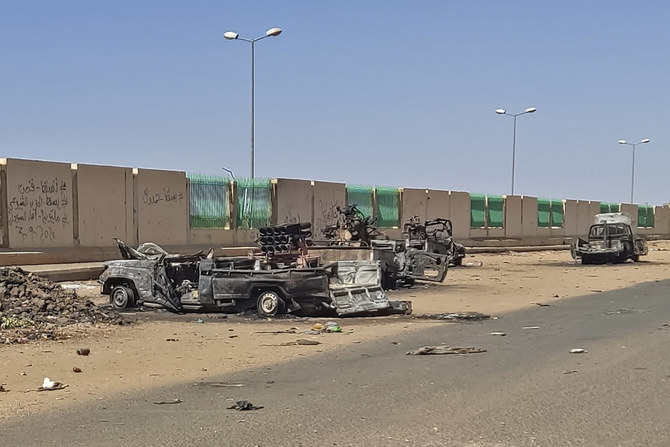
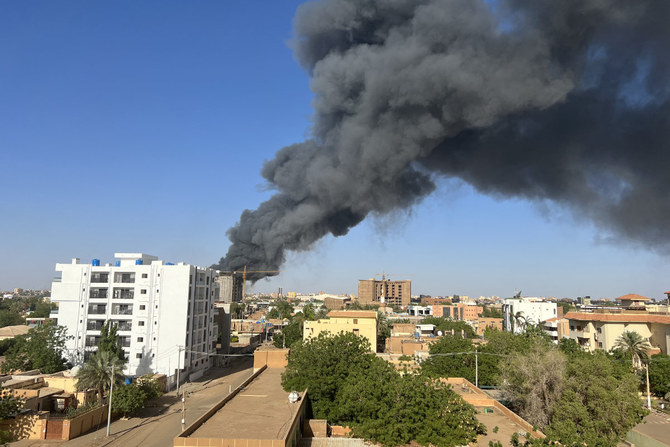
Videos have emerged showing passenger planes on fire on the aprons at the city’s international airport, while fighter jets fly overhead. Buildings can be seen riddled with bullet holes and the roar of artillery is heard across the capital.
“The sudden eruption has disrupted life in the capital city,” Abdullah Mukhtar, a resident of Khartoum, told Arab News. His family home has been without electricity since the fighting began.
He said: “Between 70 and 80 percent of people in the capital are daily wage workers, and if they lose their wages, they’ll have to provide somehow, and as we heard and saw, there’s much looting. The neighborhood is in total darkness as well as nearby areas.
“The supermarkets are deserted and looted, and the people are experiencing one suffering after another. Frankly, there is no assistance whatsoever provided anywhere in the city except through some citizen initiatives. It’s a war zone and it’s very dangerous.
“I haven’t seen any humanitarian assistance from either side, nor have I seen any international organizations, which is understandable. How can they reach the capital when the airport has been deemed technically not suitable for landing aircraft?”
Millions of Sudanese civilians, now caught in the crossfire between the two rival factions, were already in desperate need of humanitarian assistance, much of which has been suspended since the 2021 military coup.
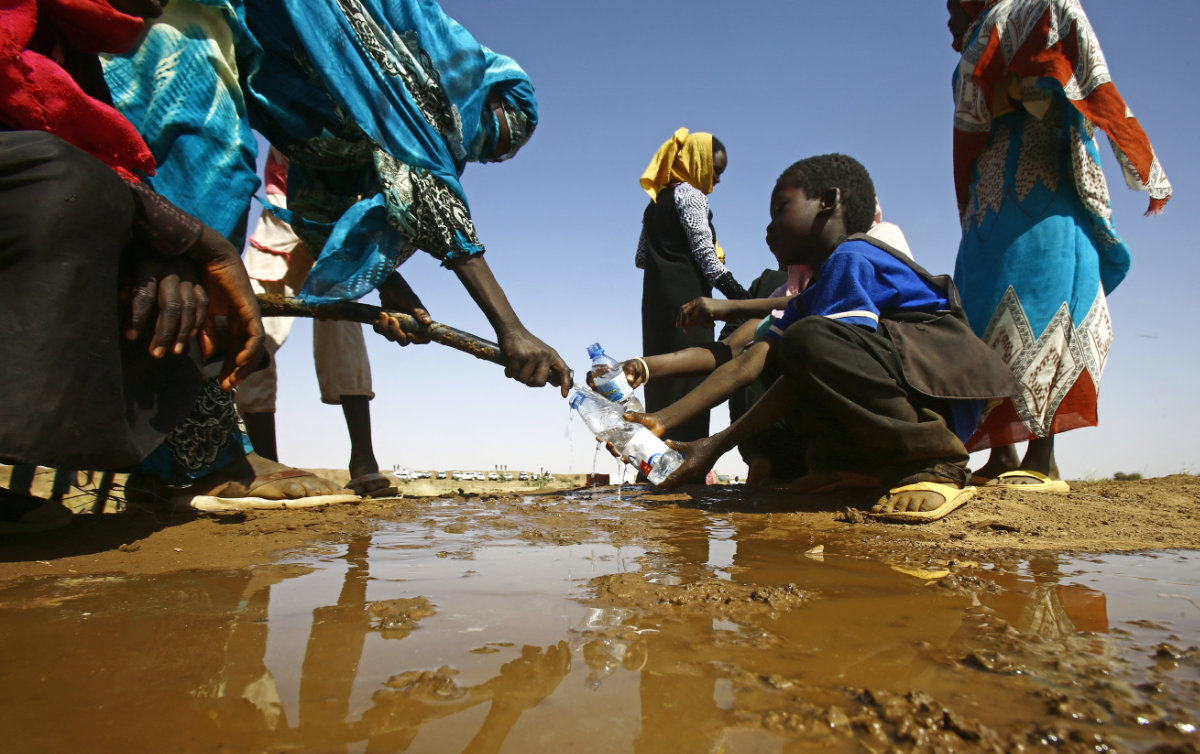

Sudan already faced acute humanitarian problems before the outbreak of violence late last week. (AFP)
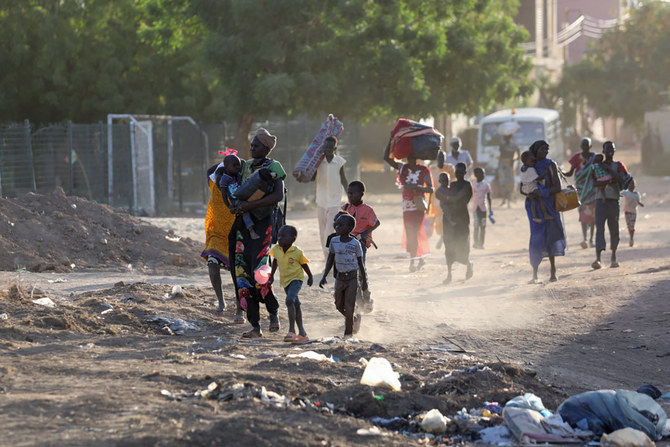
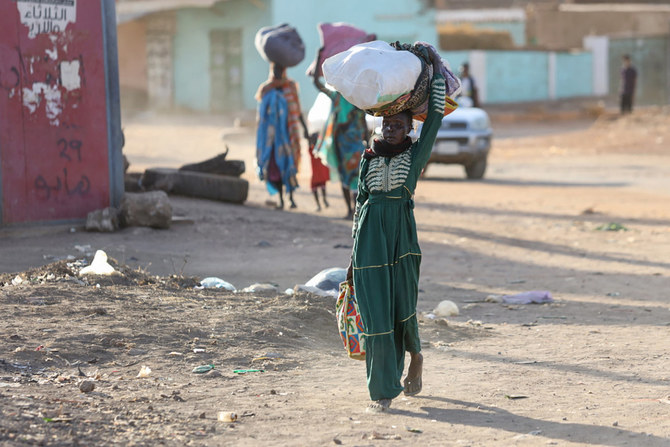
Thousands have left the capital and many are still trying to flee the violence. The UN refugee agency said on Thursday that between 10,000 and 20,000 people have fled Sudan’s western Darfur region in the past few days, seeking refuge in neighboring Chad, a nation that already hosts more than 370,000 Sudanese refugees from Darfur.
For years, Sudan’s humanitarian situation was in a precarious state due to decades of sanctions, economic deterioration, intercommunal violence, extreme weather events linked to climate change, and political turmoil.
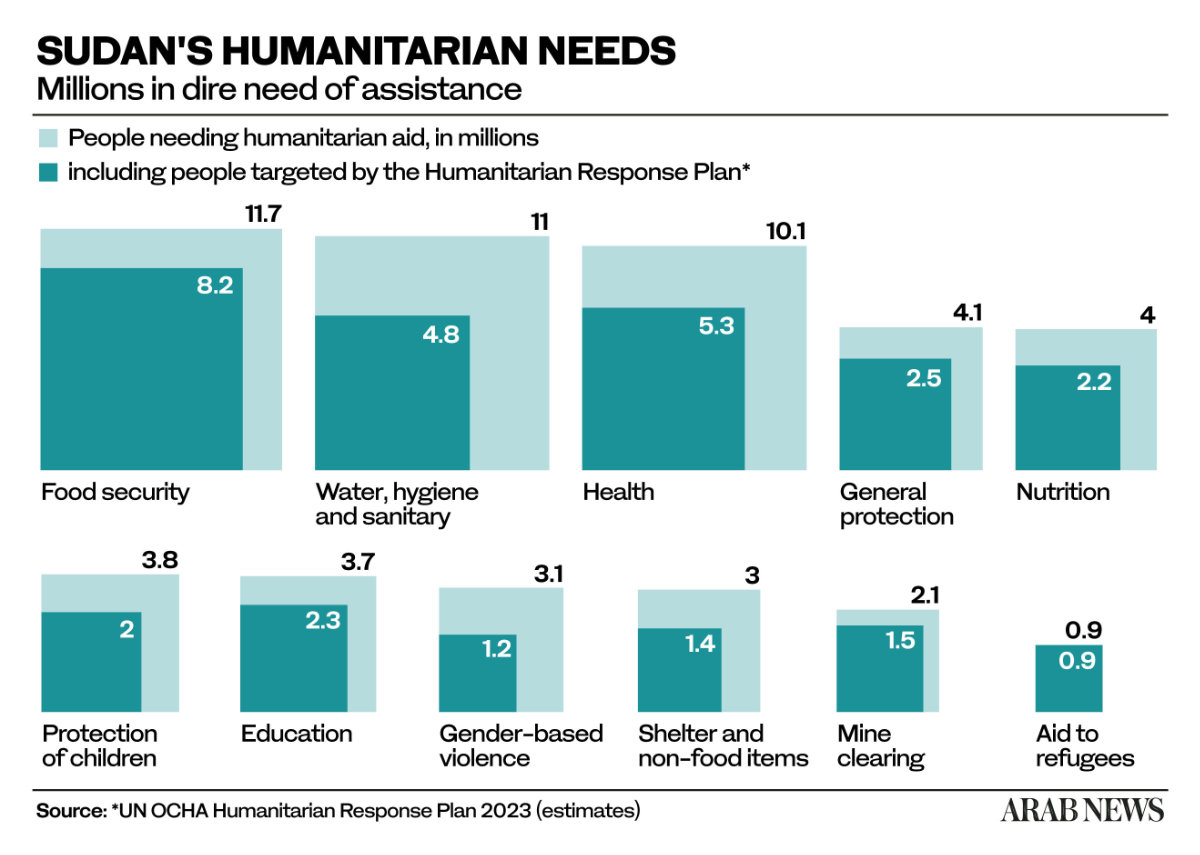
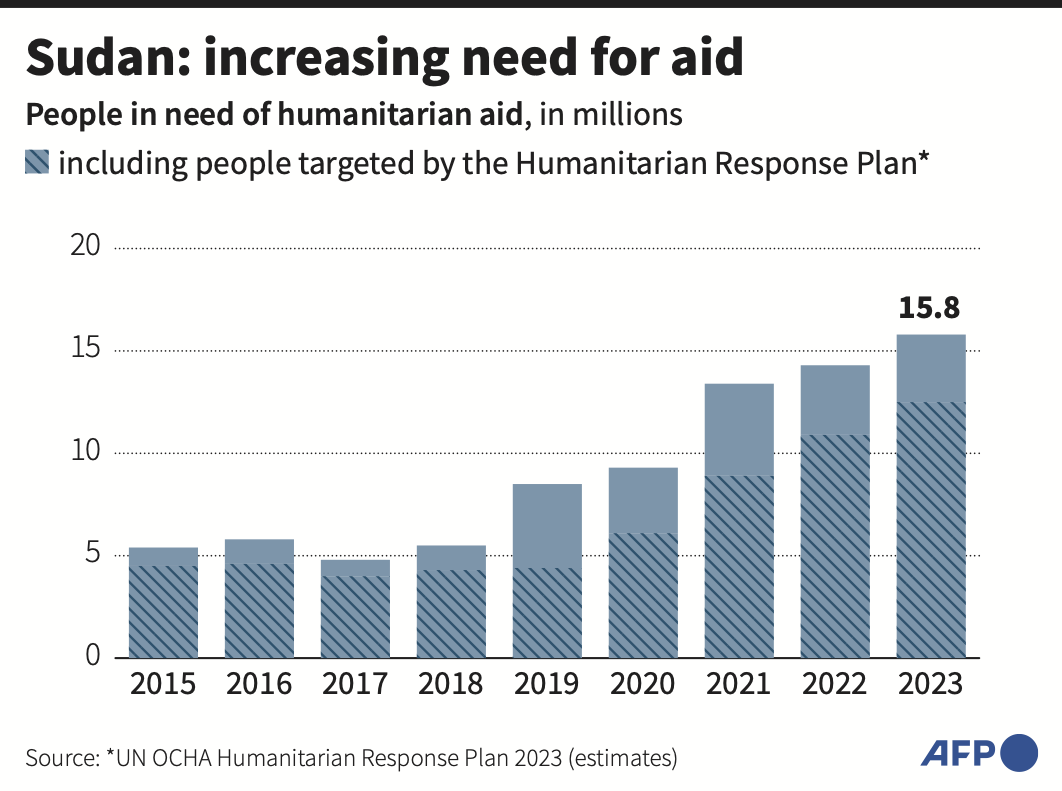
Even before the latest bout of fighting, the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs estimated around 15.8 million people among Sudan’s 45.6 million (2021) population would require humanitarian assistance in 2023, up from 1.5 million in 2021.
Of these, around 11 million required emergency assistance for life-threatening conditions related to physical and mental well-being.
Aid officials now fear the situation will grow even worse.
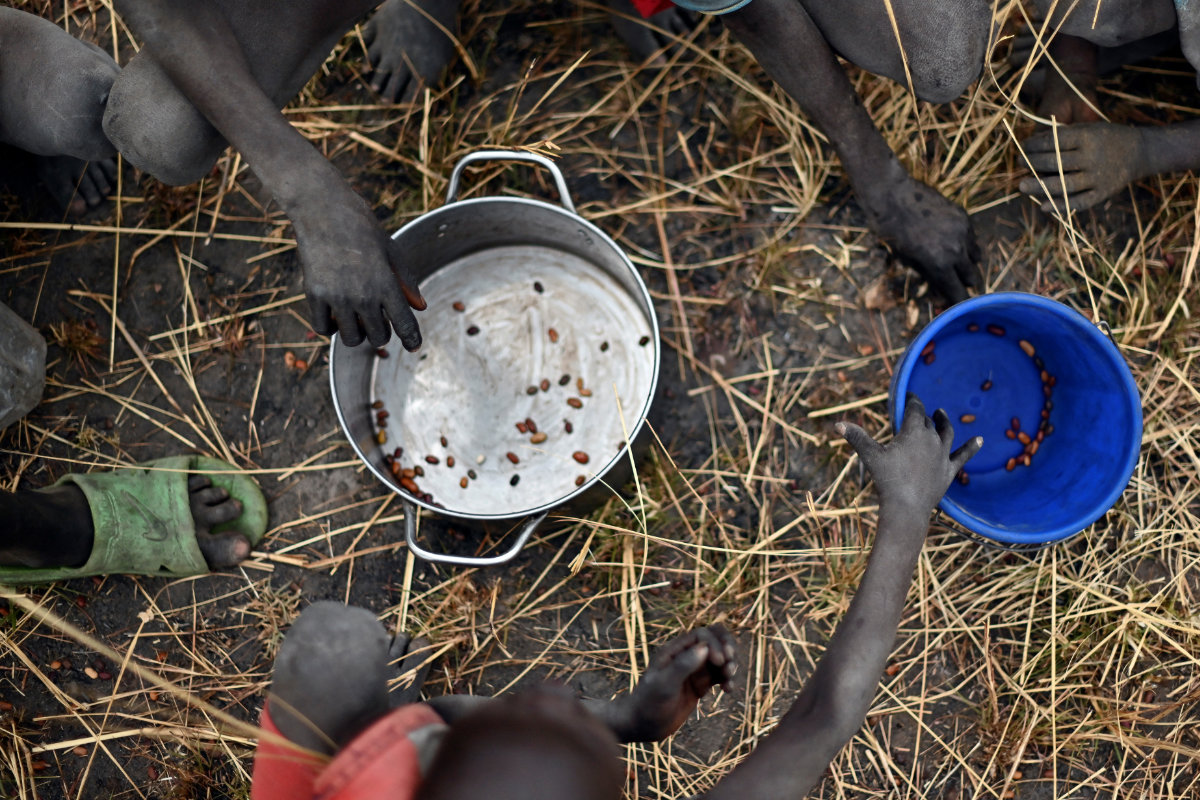

Sudan already faced acute food problems before the outbreak of violence late last week. (AFP)
“I am most concerned about the potential for the current conflict to spiral into a full-blown civil war with other regional actors getting involved and supplying further weapons. This would not only lead to more civilian deaths, but also cut off access to aid for millions already in need,” Daniel Sullivan, Refugees International’s director for Africa, Asia, and the Middle East told Arab News.
“Fighting, shelling, and aerial bombardments in urban areas have caused scores of civilian deaths and cut people off from food, water, and access to medical care. Some progress had been made in providing aid and addressing accountability and preparations for return to civilian rule, but the latest violence has destroyed any positive momentum. Perhaps most worrying, the fighting has cut off aid groups from reaching millions of people already in need of assistance,” added Sullivan.
INNUMBERS
45.6 million Population of Sudan (2021).
15.8 million Facing acute food insecurity.
3.6 million Internally displaced people.
As an advocacy group, Refugees International does not have humanitarian operations in Sudan. Sullivan said there was some concern for local and international partner groups which had been forced to suspend activities and, in some cases, had come directly under fire.
He added: “The fighting in Sudan has cut off food delivery and driven aid organizations to suspend their activities and could put millions more in danger of food insecurity.”
On April 19, Sudanese Ministry of Health officials warned of a “total collapse” as 16 hospitals went out of service. According to OCHA, hospitals in Khartoum were running out of medical supplies because of looting and resources not being delivered.
“The government, the state, provides 1 percent of the population with the necessary services, medical and health, because the state itself is in a very fragile state, we cannot say a failed state. It doesn’t provide the necessary needs to the Sudanese people,” Ahmed Gurashi, a senior editor at Al Arabiya News channel, told Arab News.
“The shortage and the deficiency in the system was there before. But now, we do anticipate a crisis after this. I mean, Allah knows when the Sudanese could overcome this crisis. After the crisis, things will be revealed. (It will be) huge, it is a catastrophe in the making.”
Asma Yassin, a Sudanese medical volunteer in Khartoum, told Arab News that the situation was challenging as “most hospital staff evacuated the hospitals and patients were returned to their families.”
Meanwhile, all volunteer operations have been halted due to the streets being deemed unsafe.
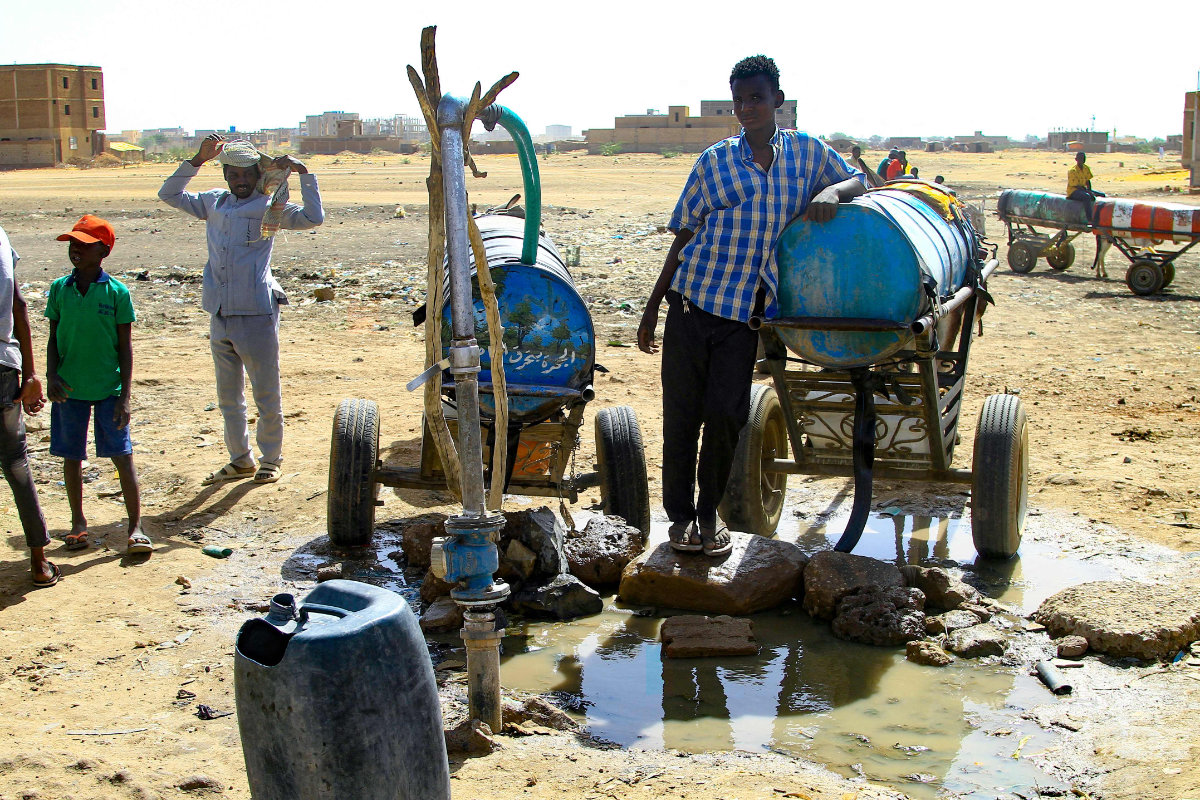

People fill barrels with water in southern Khartoum on April 22, 2023, amid water shortages caused by ongoing battles between the forces of two rival Sudanese general. (AFP)
“We hear that there’s shortage in vital medicines such as insulin and Ventolin, and a shortage of ventilators and oxygen.
“Several makeshift clinics at private homes were erected that supply these medicines to patients, and some Sudanese abroad have even transferred money to supply the medication.
“But it’s very difficult as most districts (in Khartoum) have been left without electricity or water since Saturday as the water stations have been hit and workers are not able to reach the stations to get them operational again,” Yassin said.
Despite the efforts of aid agencies and nongovernmental organizations, Yassin pointed out that Sudanese volunteers were doing their best to provide relief to some neighborhoods by delivering water by truck. “But not everyone is lucky,” she added.
“When you say a catastrophe, sometimes people will say it is an exaggeration, describing the very reality of the Sudanese people,” said Gurashi. “If the injured don’t have access (to services), they will die. When you want to describe the very necessary needs there, (even) if you have money, you cannot get it, you cannot obtain it.
“If this conflict is going to end in Khartoum, in the heart of Khartoum, we will find too many, literally, old people who have died of lack of access to medicine, lack of access to healthcare. Other people who were injured or needed help during this time will definitely pass away because no service will be provided to them, and no access to services will be possible. This is the most awkward problem.”
International aid distribution was disrupted this week after three World Food Programme employees were killed during the fighting, which caused the UN-backed body to halt operations.
In a statement following the deaths, the WFP’s executive director, Cindy McCain, said: “Aid workers are neutral and should never be a target.”

Cindy McCain
For much of its history, Sudan has been wracked by internal strife, including two of the longest-running civil wars on the African continent and the conflicts in Darfur, South Kordofan, and the Blue Nile.
These conflicts have shattered the nation’s infrastructure, disrupted its agricultural sector, and undermined public health, particularly in relation to nutrition and food security.
Long before the fighting broke out on April 16, the availability of food, medicine, and social development projects was limited, requiring external emergency assistance every year since 1984.
The situation has been made worse by the yawning inequality in the distribution of wealth and power between the center and the periphery, routine mass displacements, and the almost constant blight of drought.
Sudan has endured repeated and prolonged droughts from 1980 to 1984, 1985 to 1993, 1996, 2001, and most recently last year, which have led to severe shortages of food and destroyed livelihoods in farming, a sector that not only provides food but also alleviates poverty.
Agriculture generates 35 to 40 percent of Sudan’s gross domestic product, according to the World Bank, and employs between 70 and 80 percent of the labor force in rural areas, where around 65 percent of the population lives.
Without oil revenues, growth has faltered, while the country’s debt problem remains unresolved. Poverty and malnourishment, which were already severe, have now worsened.
After the 2019 military coup that overthrew Omar Al-Bashir, a transitional government took over, carrying out ambitious economic and social reforms and engaging in peace negotiations with armed groups.
In 2021, Sudan received approval from the International Monetary Fund for relief on more than $56 billion in debt and new IMF funding worth $2.5 billion over a period of three years.
Saudi Arabia and the UAE also agreed to send $3 billion worth of aid, $500 million of which was deposited in the Sudanese central bank and the rest delivered in the form of food, medicine, and goods.
However, the promising start was soon disrupted in 2021 when the military launched another coup, resulting in the suspension of development and debt relief programs and a return to political deadlock.
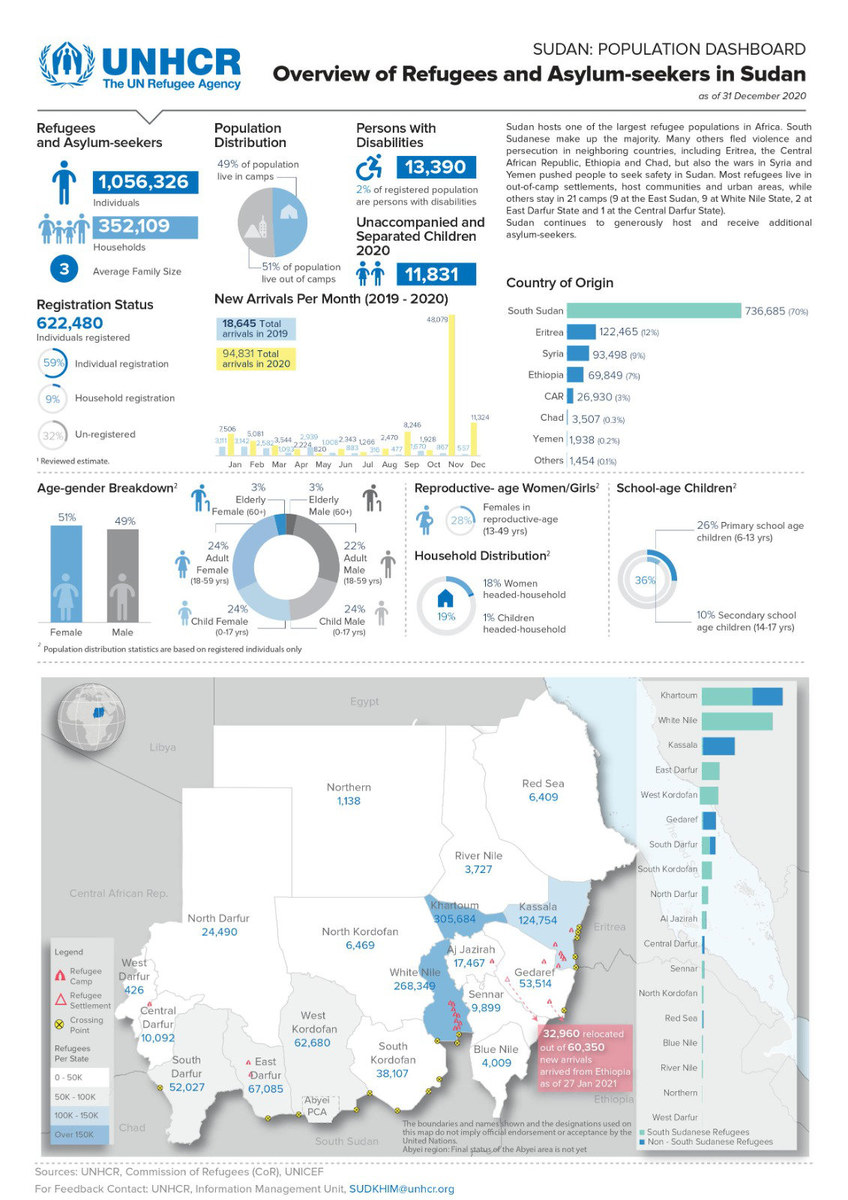
Aid agencies fear the latest violence will also lead to further displacement. According to OCHA, Sudan hosts around 1.1 million refugees from other countries — constituting one of the largest refugee populations in Africa.
Among these are more than 800,000 South Sudanese and around 126,000 Eritreans.
However, Sudan also counts about 3.6 million internally displaced people, mainly in the Darfur region, which has experienced volatility and bouts of ethnic cleansing for almost two decades. Some 4 million Sudanese live in neighboring Egypt.
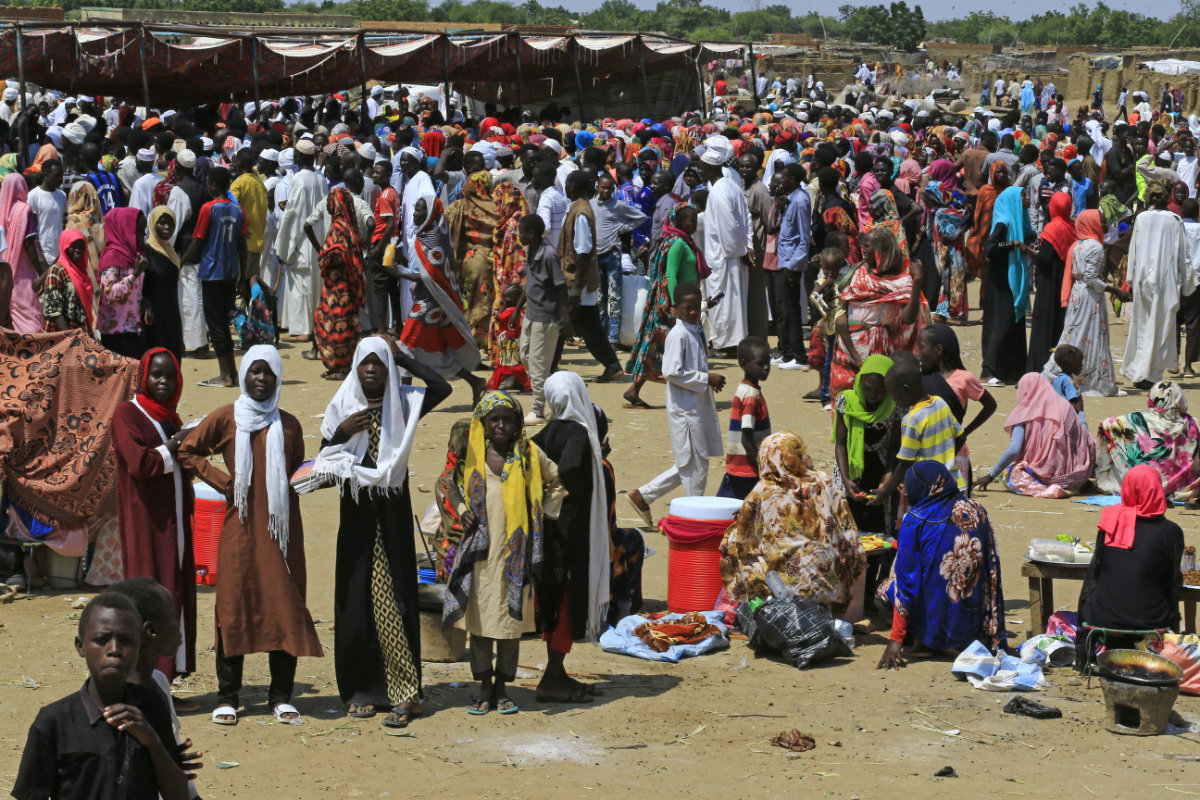

In this October 9, 2019 picture, Sudanese queue to receive humanitarian aid supplies at a camp for internally displaced people in Darfur's state capital Niyala. With workers from aid agencies fleeing the war in Sudan, the humanitarian crisis is feared to worsen. (AFP File)
According to reports in the New York Times, more than 15,000 people have already fled the Darfur region into Chad.
For Khartoum residents such as Mukhtar, who have found themselves caught in the crossfire, fleeing the country may be the only option to guarantee their safety — a luxury not everyone can afford, nor a risk everyone is willing to take.
With gunfire in the background, Mukhtar said: “Everyone is on edge, and the situation has reached boiling point for people in the city.
“Those who made it out are safer. It’s the ones who can’t leave, it’s the sick who will suffer most because of the lack of healthcare services, and the unprivileged.”


































