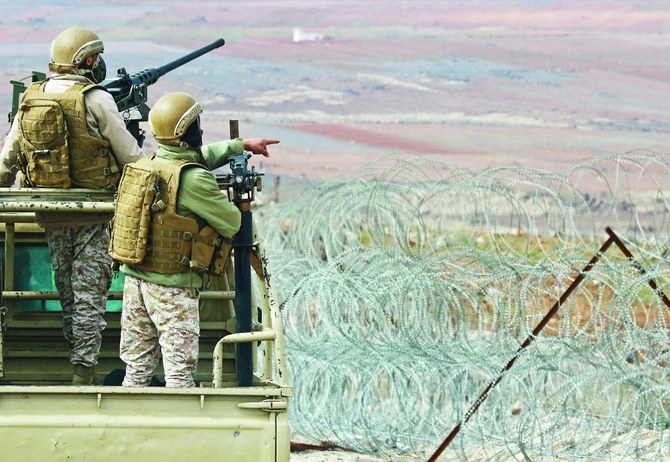
DUBAI/AMMAN: Just days after Ayman Safadi, Jordan’s foreign minister, warned in an interview with CNN that his country is “not taking the threat of drug smuggling lightly” and is ready “to do what it takes to counter that threat,” Merhi Al-Ramthan, a reputed Syrian drug kingpin, was killed when airstrikes targeted his house in the village of Shuab in the Sweida governorate.
Media reports quoting the Britain-based Syrian Observatory for Human Rights said a second airstrike targeted a suspected drug-manufacturing facility in Deraa, a governorate in Syria’s south. A Syrian opposition activist said the facility was used by Iran-backed groups to produce and store drugs before smuggling them to Jordan.
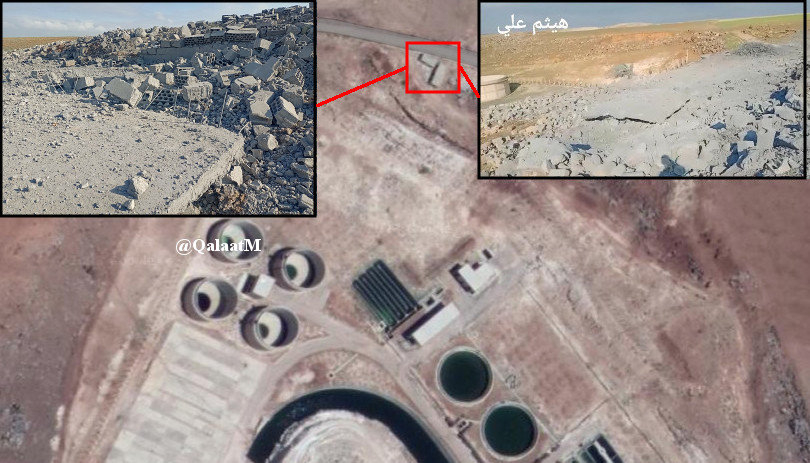

Illustration map showing a second site bombed by the Jordanian Air Force that was said to be an abandoned water station in west Deraa province, which was reportedly used by pro-Assad cartels to manufacture Captagon. (Social media)
Long known to be Jordan’s most wanted man, Al-Ramthan operated on the borders of the kingdom, using unemployed men to smuggle Captagon pills out of Syria through crossings and porous borders.
According to a report in the Jordanian newspaper Al-Ghad in July last year, the State Security Court gave Al-Ramthan and others 10 days to surrender. It said a Jordanian court had convicted him of importing narcotic substances with the intent of trafficking.

Captagon packets seized at Al Haditha port in Jordan. (Photo courtesy of ZATCA)
Captagon, a highly addictive amphetamine, works by stimulating the nervous system, allowing the user to have increased alertness and concentration with little sleep. The narcotic became very popular during the height of the Syrian civil war, when fighters on all sides were believed to be using it.
A report published in April 2022 by the New Lines Institute for Strategy and Policy on Captagon trade in the Middle East said Syria had become “the hub for industrial-sized production.”
It further claimed that “elements of the Syrian government are key drivers of the Captagon trade, with ministerial-level complicity in production and smuggling, using the trade as a means for political and economic survival amid international sanctions.”

Caroline Rose, a senior analyst with the Washington think tank, told Arab News in February that there was no doubt that “Captagon is being produced and trafficked by an array of individuals that are very close to the (Bashar) Assad regime, some of them cousins and relatives of regime members.”
Al-Ramthan was known to be a staunch supporter of President Assad and the Lebanese armed group Hezbollah. He was said to be operating freely with the security cover provided to him by the regime’s military branches and intelligence as well as Hezbollah.
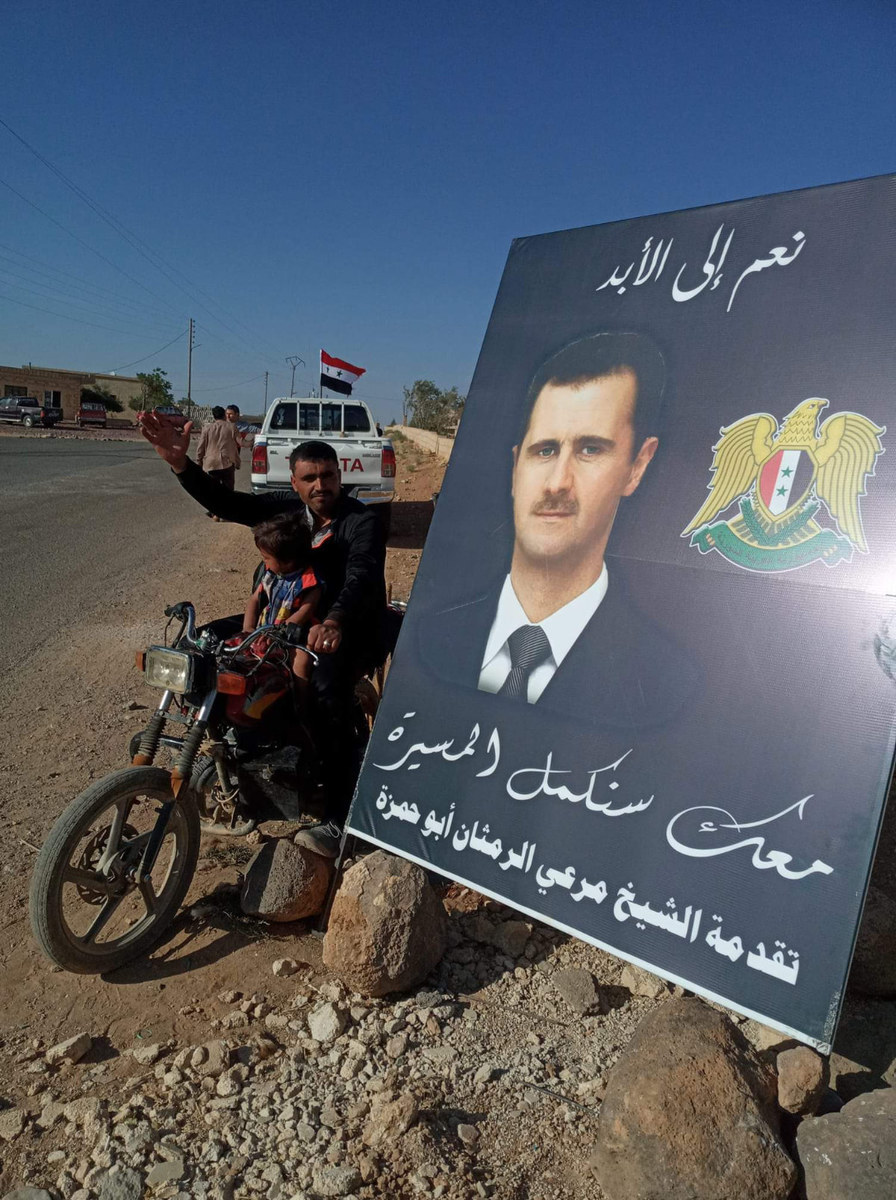

Captagon cartel leader Merhi Al-Ramthanwas known to support Syrian President Bashar Assad, even thanking him publicly in posters. (Social Media)
A cattle herder turned drug dealer, Al-Ramthan took advantage of the chaos that befell Syria after 2011 and formed his own militia to carry out pro-regime “security missions.”
As Captagon pills flooded the war-torn country, he transitioned into a manufacturer and trafficker of the drug, establishing production hubs in Sweida, where they were reportedly supervised by a man called Ali Bilan.
Sources said Al-Ramthan’s wealth grew steadily with his career switch, enabling him to purchase land and properties in his hometown as well as Damascus.

Officers of the Directorate of Narcotics Control of Saudi Arabia's Interior Ministry sort through tablets of Captagon (Fenethylline) seized during a special operation early this year. Insert, a close up of the pill inside a Captagon hidden inside a fake orange. (AFP)
For smuggling Captagon pills out of Syria, he was known to rely on homeless men and young boys, one of whom — a 14-year-old — was killed during clashes with Jordanian security last April.
The smugglers were paid handsomely, often in thousands of dollars, if they were able to carry out their mission successfully, the sources said.
The strike that killed Al-Ramthan, along with his wife and six children, came just days after Syria was officially welcomed back into the Arab League. Ahmed Aboul Gheit, the secretary-general, said the May 7 decision was the start of a process to resolve the crisis in Syria and that it was up to each state to resume its relations with the country.
The organization had removed Syria as a member in response to its crackdown on peaceful protesters at the start of the uprising in 2011.
Syria’s Foreign Ministry said it was treating the Arab League decision “with great attention” and called for “greater Arab cooperation and partnership.”
A meeting of the foreign ministers of Syria, Egypt, Iraq, Saudi Arabia and Jordan, which took place in the Jordanian capital Amman on May 1, had produced a statement in which Damascus pledged to identify the producers and transporters of the drug.
It added that Syria had agreed to “take the necessary steps to end smuggling on the borders with Jordan and Iraq.”
Jordan has not claimed responsibility for the strikes in Sweida and Deraa, but analysts say the probability is high that the Hashemite kingdom carried them out, pointing out that the Jordanian foreign minister had not ruled out the use of military force.
“Our country has suffered tremendously, and we will do what it takes to counter that threat including taking military action inside Syria to eliminate this extremely dangerous threat,” Safadi had said.
Following the strikes, he said, “Whenever we take any steps to protect our national security and (face) any threats towards it, we announce it at the appropriate time.”
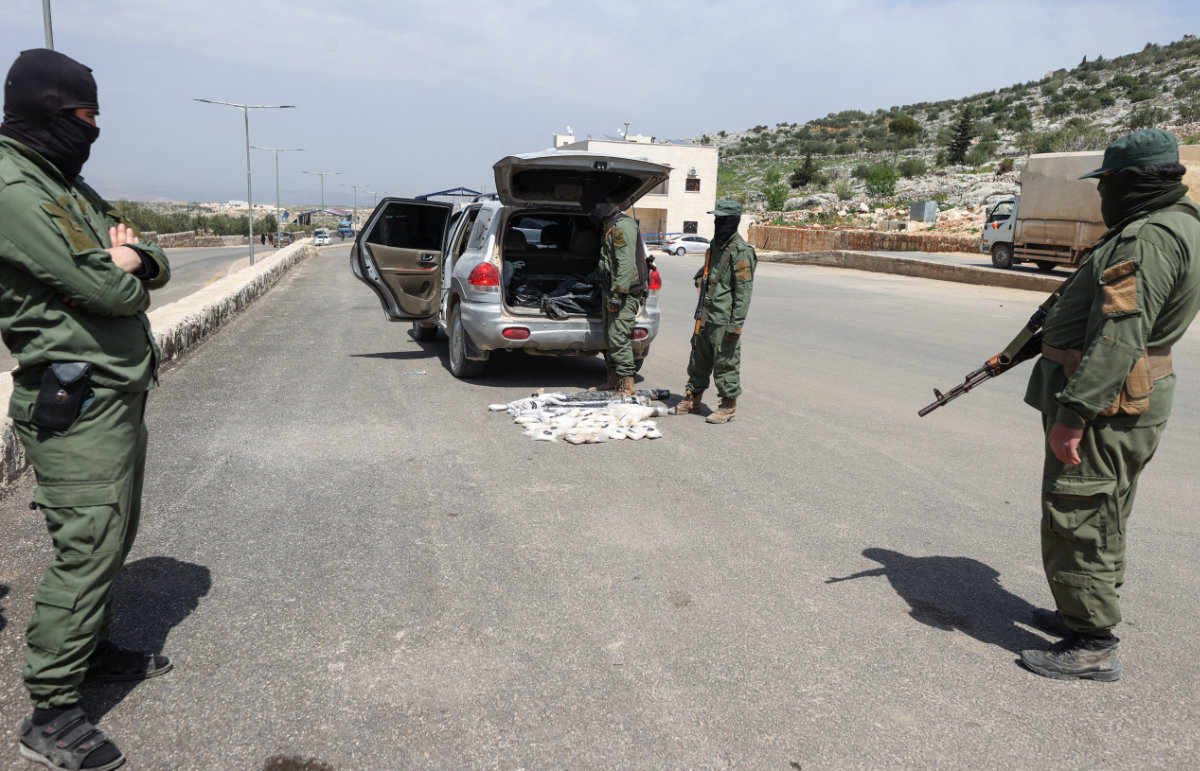

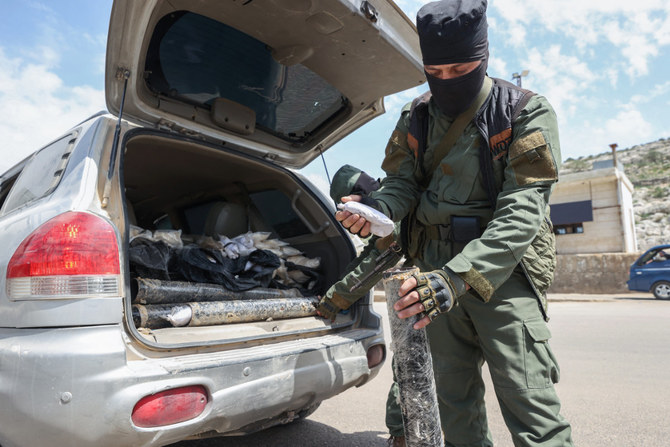
Fighters affiliated with Syria's "Hayat Tahrir al-Sham" (HTS) rebel-group display drugs previously seized at a checkpoint they control in Daret Ezza, in the western countryside of the northern Aleppo province, on April 10, 2022. (AFP)
In a series of tweets after Monday’s strikes, New Lines Institute’s Rose said: “Last week, we saw the carrot, but today these strikes may represent the ‘stick’ — an insurance policy to counter-balance increased interaction and cooperation with Damascus.
“Worth remembering that violent smuggling ops in fall 2021 and winter of 2022 (one of which killed a Jordanian officer) prompted the JAF (Jordanian Armed Forces) to loosen rules of engagement and for Amman to pump the brakes on normalization.
“Amidst all of these normalization efforts, there are lingering trust issues over counter-narcotics policies for Amman — particularly for the JAF which has shouldered an uptick in violent clashes with regime and Iran smugglers since the Nassib/Jaber crossing opened.
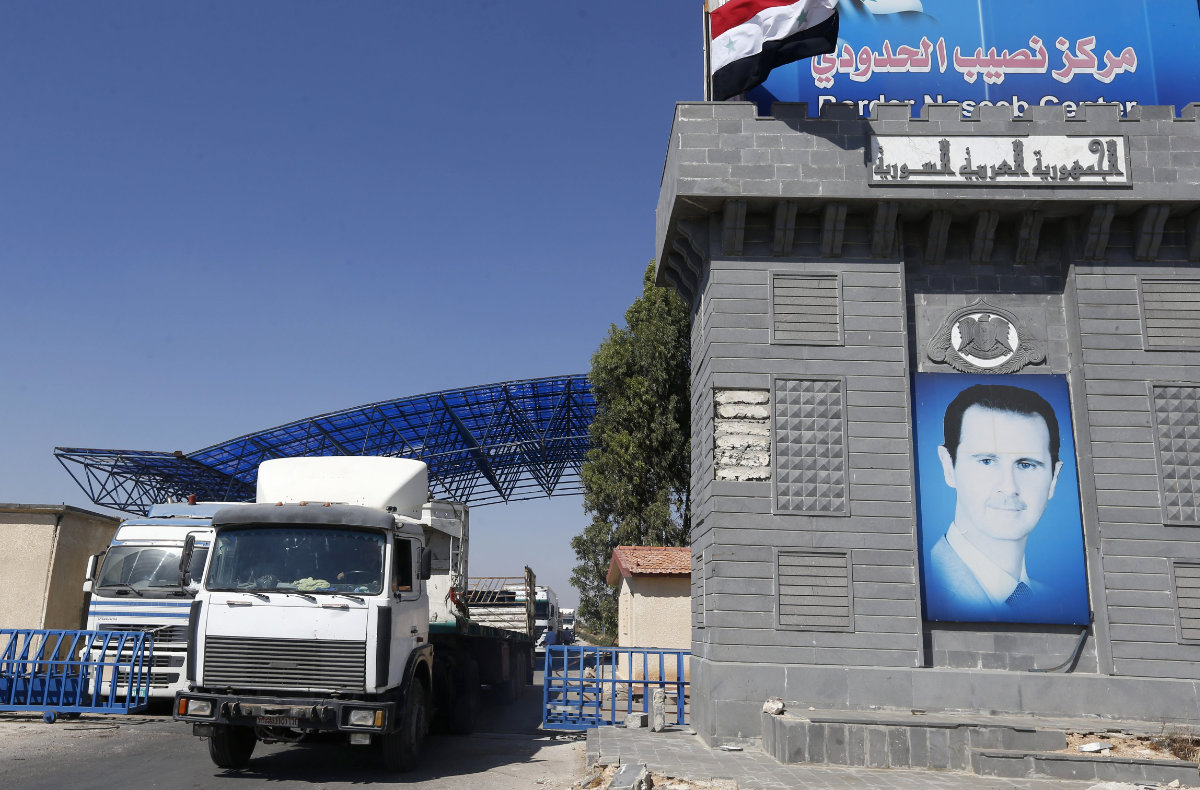

The opening of the Syrian-Jordanian border Nassib crossing on September 29, 2021. (AFP File Photo)
“These reported strikes could serve as a message to Damascus … that Amman not only has accurate intelligence on the southern, pro-regime networks that are producing/trafficking #captagon, but that it has the capacity to eliminate them when prompted.”
No official from the JAF or the Jordanian government was willing to comment on the strikes when contacted by Arab News on Wednesday. Security officials and politicians in Cairo told Arab News that they had no information of possible Egyptian involvement in the operations inside Syria.
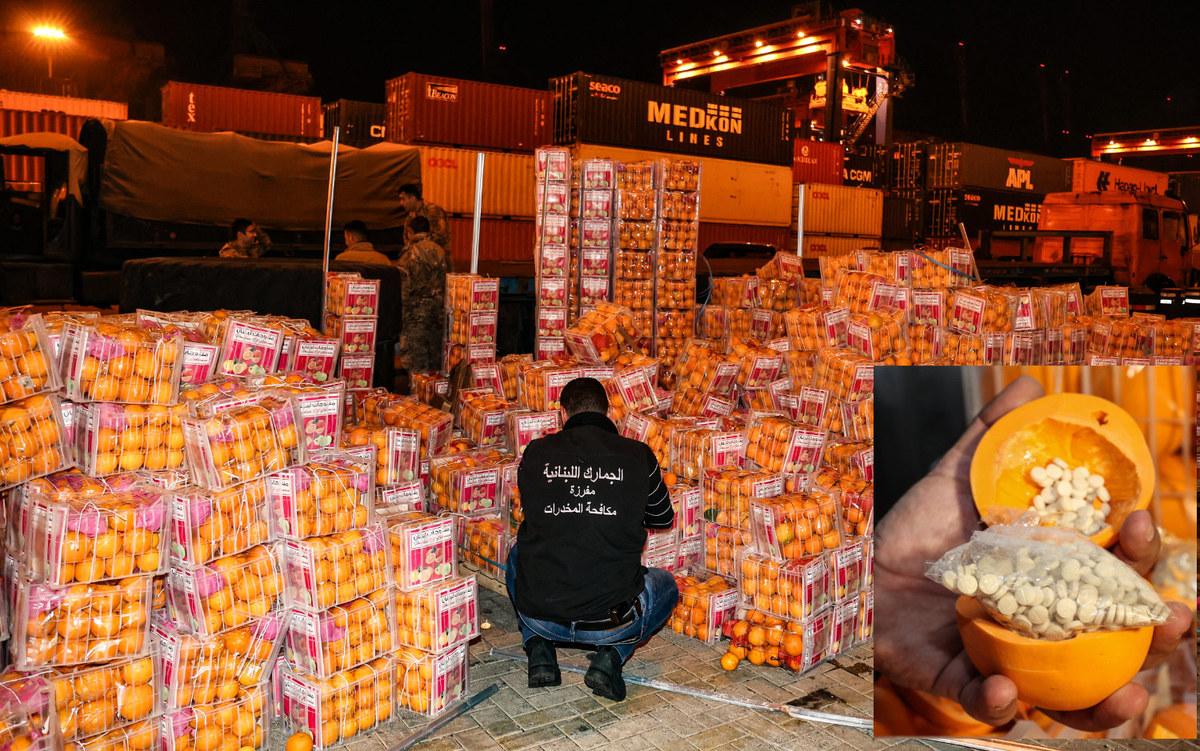
Intercepted shipments of Captagon from the region are typically headed for the Gulf countries, including a recent 10 million-pill transfer from Lebanon.
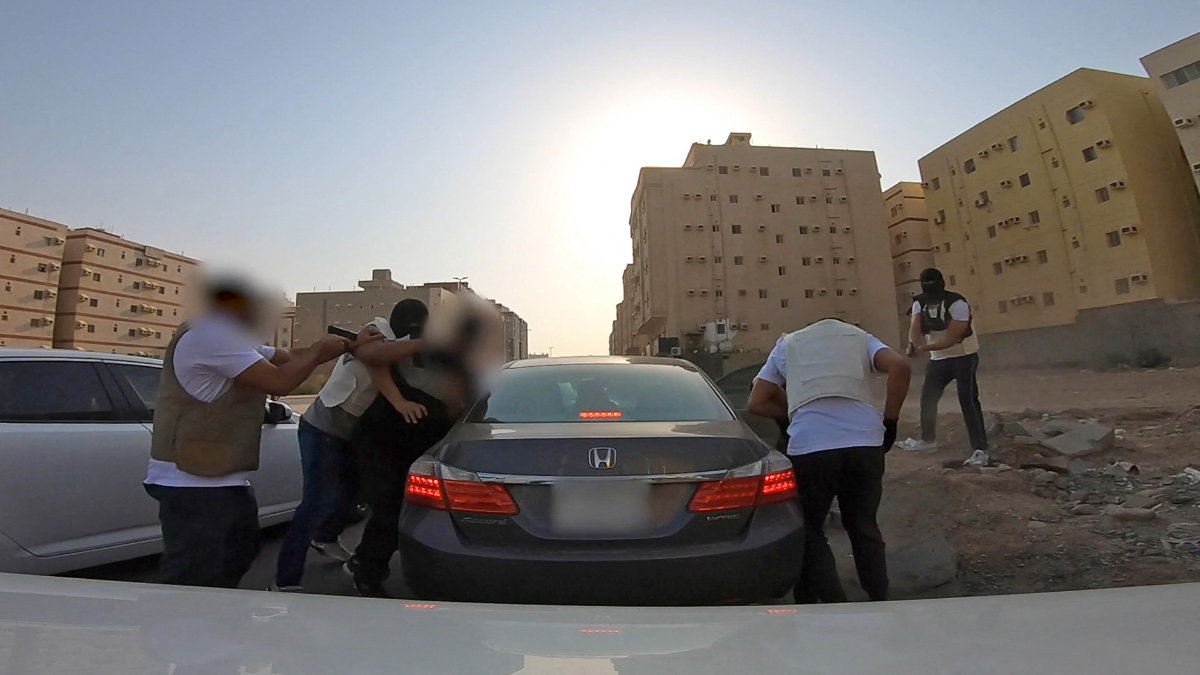

This image grab from a handout video on March 1, 2022 shows Saudi anti-narcotics agents arresting Captagon smugglers during a special operation in Tayseer district of eastern Jeddah. (Saudi Interior Ministry video via AFP)
Saudi Arabia has repeatedly voiced concern about attempts to smuggle Captagon into the Kingdom inside consignments of fruit and other food items. In September, authorities seized the largest shipment of illicit drugs in the Kingdom’s history after 47 million amphetamine pills were found hidden in a flour shipment. The Captagon pills were seized at a warehouse in the capital Riyadh.
In the past six years, Saudi authorities have intercepted an estimated 600 million Captagon pills at its borders.

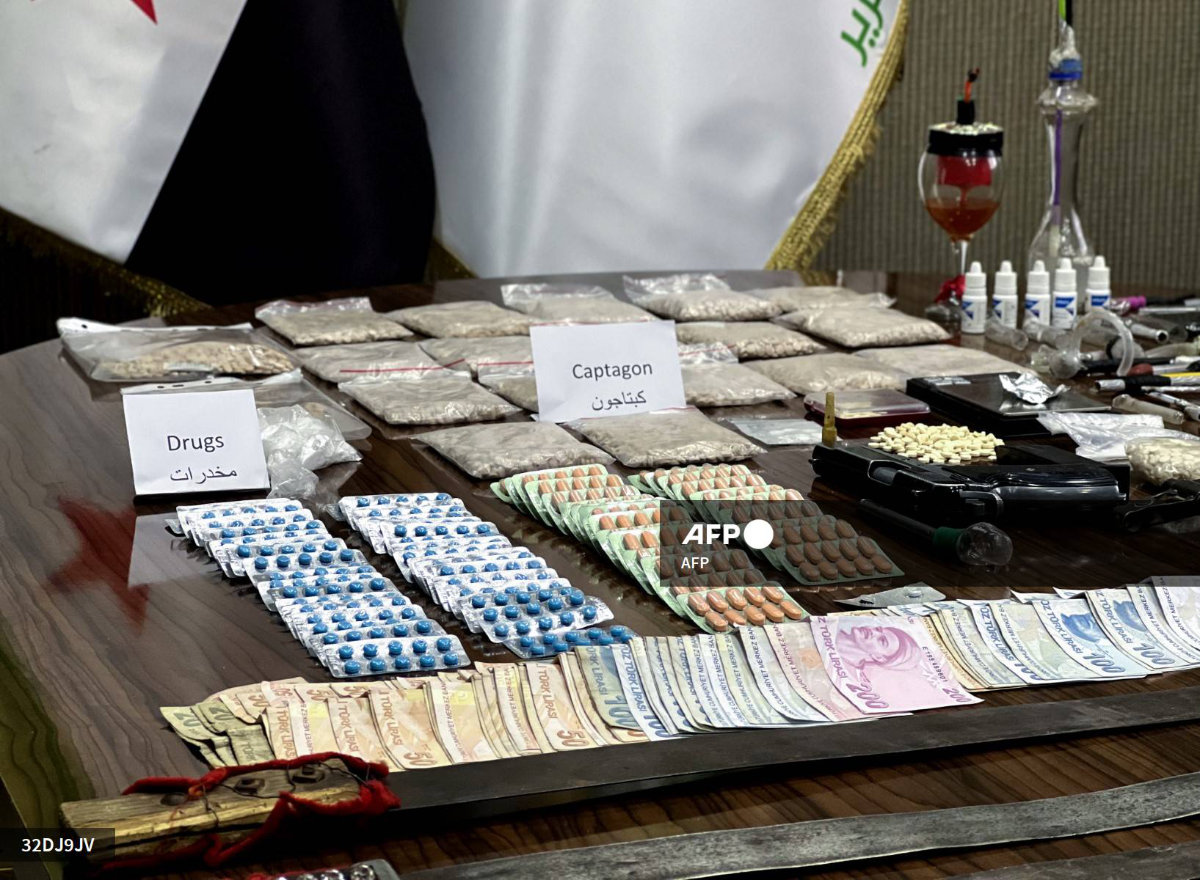
Saudi Narcotics Control officers sort through tablets of Captagon seized during a special operation early this year along the Jordan-Saudi border. (SPA file photo)
Western governments estimate that drug production has generated billions of dollars in revenue for President Assad, his associates and allies over the years.
In recent months, several relatives of Assad and top Syrian officials have found themselves on the sanctions lists of major Western powers for their involvement in the Captagon trade.
American, British and European authorities have formally blamed Syria’s government for the production and export of the drug, naming Maher Assad — the head of the army’s Fourth Division and the president’s brother — as a key figure.

A decade of appalling civil war has left Syria fragmented and in ruins but one thing crosses every frontline: the drug fenethylline, commercially known as Captagon. (AFP file photo)
Many experts describe Syria as a “narco state,” its government dependent on the export of Captagon and other drugs to stay afloat. Syria’s economy and infrastructure have been shattered by 12 years of war, which has pushed 90 percent of the population below the poverty line.
A Syrian activist who wished to remain anonymous told Arab News: “Al-Ramthan wouldn’t have been able to operate as long as he did without cover from the Assad regime, which could have delivered him within hours to Jordan, but instead chose to sell him out. His usefulness had come to an end.”
Other activists speculated that Al-Ramthan’s killing showed that, despite being a major drug dealer, he did not have the impeccable political connections that could have saved his life.



































