NEW YORK CITY: Conflict and mass displacement in Sudan pose a threat to South Sudan’s limited humanitarian resources and brittle peace, Akuei Bona Malwal, the country’s permanent representative to the UN, has told Arab News.
Twelve years after gaining independence from its northern neighbor, South Sudan continues to face challenges of its own, with millions displaced to neighboring countries, including Sudan, to escape poverty and instability.

Akuei Bona Malwal, Sudan's permanent representative to the UN. (AN photo)
Now the violent power struggle in Sudan is forcing hundreds of thousands of South Sudanese living there to return en masse, alongside huge numbers of Sudanese and other nationalities, piling pressure on South Sudan’s already stretched humanitarian resources.
“There are two aspects to the humanitarian crisis,” Malwal told Arab News during a special interview in New York City.
“First, we have close to 2 million South Sudanese citizens who are in Sudan, and in Khartoum, in particular. They are now trying to come back to South Sudan. And this has taken people by surprise.

A violent power struggle in Sudan is forcing people, both locals and foreigners, to flee the country every day, piling pressure on neighbor South Sudan’s already stretched humanitarian resources. (AFP)
“Our authorities in the country don’t have the facilities to accommodate them quickly, and repatriate them to their villages. So, that is actually exhausting the meager facilities that we have.
“And then we also have the Sudanese taking refuge in our country (along with) other Africans and other nationalities who are coming to South Sudan because we have opened the door for people to come in to take refuge. So that’s also a burden on the government.”
Fighting in Sudan began on April 15 between the Sudanese Armed Forces, headed by Sudan’s de-facto leader Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan, and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces, led by Al-Burhan’s deputy turned rival, Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo, also known as Hemetti.
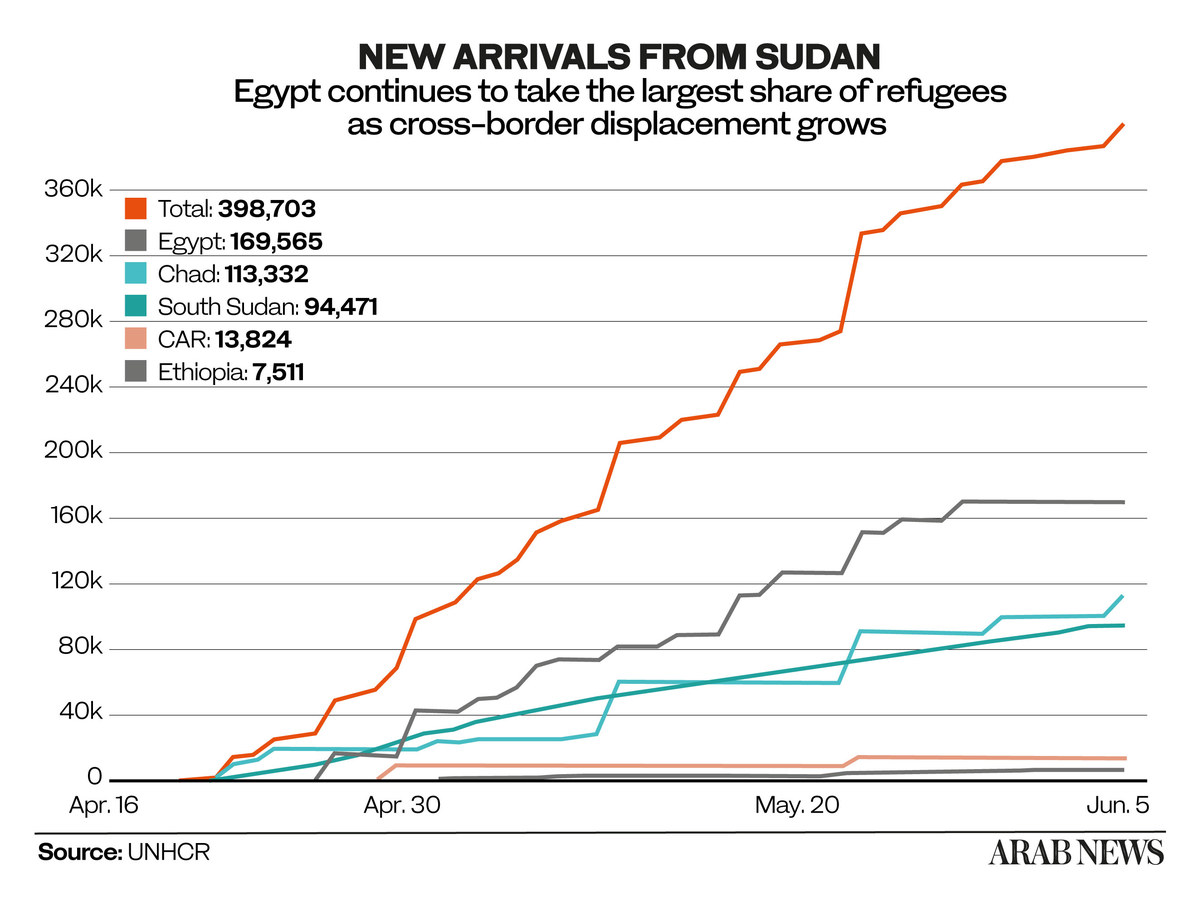
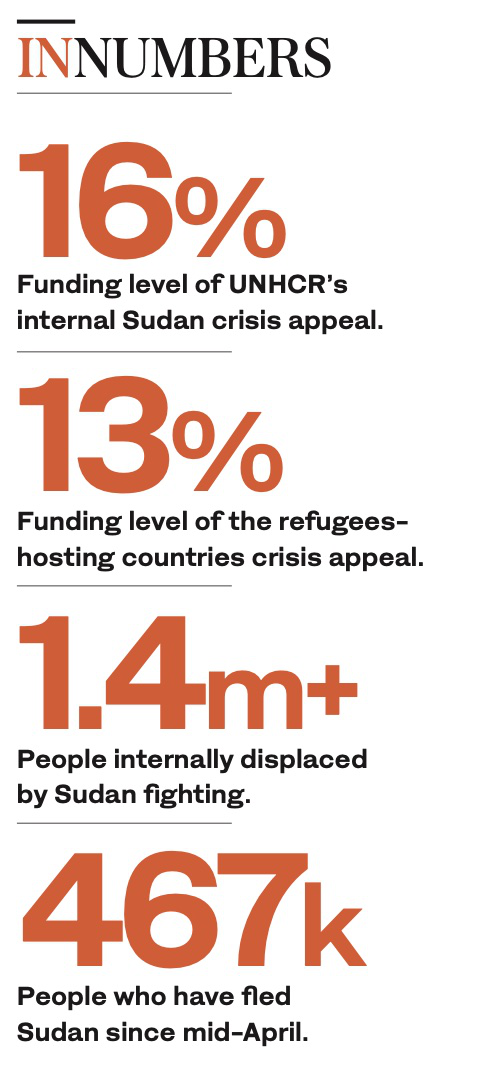
The clashes have plunged the country into a humanitarian crisis, with up to 3,000 people killed, according to Sudan’s minister of health, and more than 1.8 million displaced within Sudan or across its borders, according to the UN. Many have fled to Egypt, Chad and South Sudan, which have issues of their own.
Fueled by intercommunal violence, crime, public health challenges, climate and economic shocks, and poor governance, poverty in South Sudan is ubiquitous. Now it being aggravated by conflict and insecurity.
About 70 percent of South Sudanese live below the poverty line. On the global human development index, South Sudan ranks last. On top of this, the country is also facing its worst flooding in years, and continues to face very high levels of food insecurity.

Sudanese refugees collect water from a tap at the Gorom Refugee near Juba, in South Sudan, on June 20, 2023. (REUTERS)
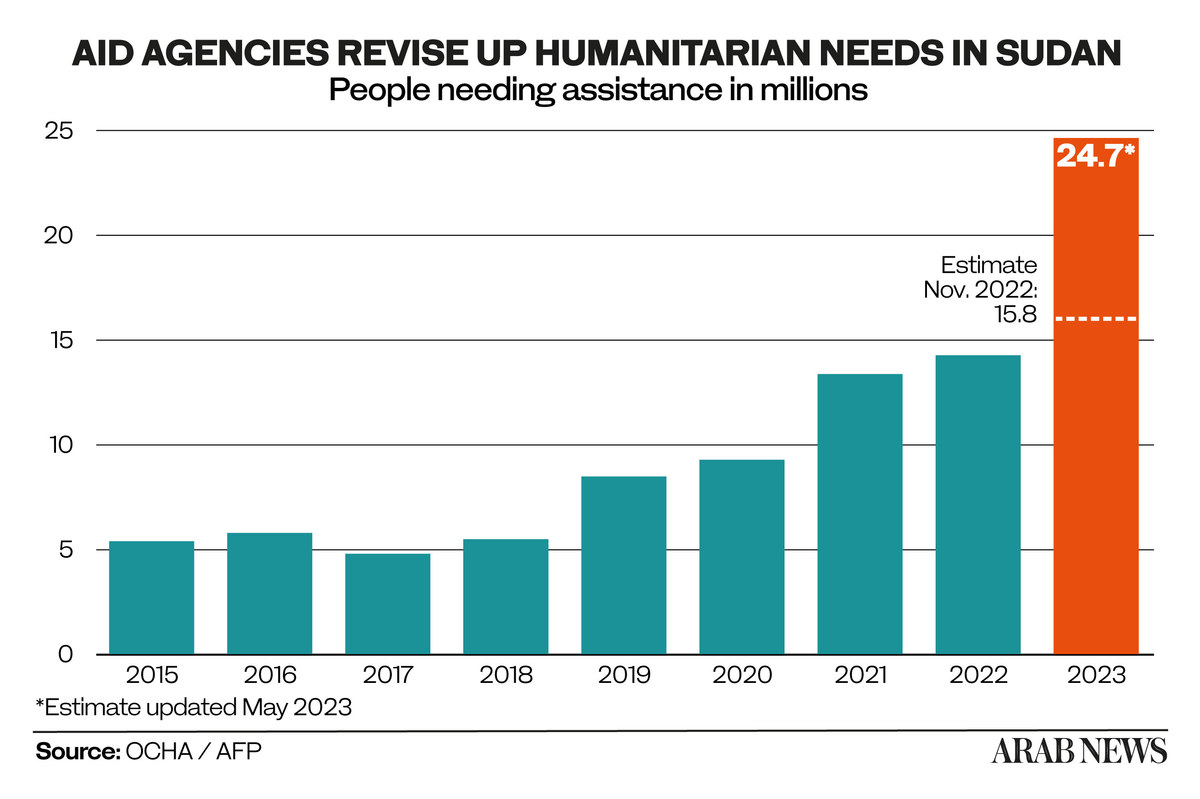
In 2023, around 10 million South Sudanese, or 76 percent of the population, will need humanitarian assistance in order to survive. And the number continues to increase.
South Sudan’s fragile stability is also in jeopardy. The country’s latest peace agreement was signed in 2018, leading to a delicate truce and the formation of the Transitional Government of National Unity in 2020.
Although hostilities between the government and the main opposition have eased, the very logic of the power-sharing agreement has actually contributed to the continuing violence.
The US, which last year suspended its assistance for the peace process monitoring mechanisms, has accused South Sudan’s leadership of failing to live up to its end of the deal by showing “a lack of political will necessary to implement critical reforms.”
The UN Security Council recently voted to extend the arms embargo on South Sudan, citing the country’s failure to meet the benchmarks stipulated in the peace process, related to security arrangements and disarmament.
Malwal described the extension as “ill-intentioned” and “counterproductive,” and said it had been handled in “bad faith.”
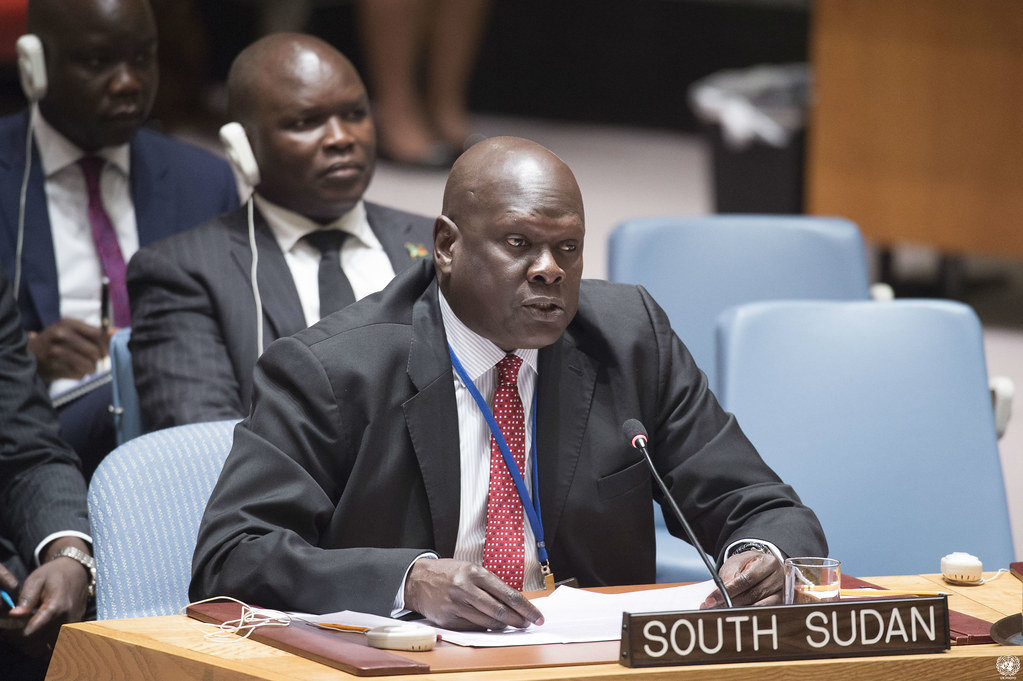

Akuei Bona Malwal. (Supplied photo)
“The Americans are angry with the South Sudanese leadership,” he said. “They keep using this word that I don’t like: ‘We midwifed you.’ Meaning they helped us become independent, which is true.
“We are not denying that. But, then, how do I become sovereign now in order to subordinate my independence and my sovereignty to the US, because they have helped us to become independent?
“Simply because we disagree on security, that doesn’t mean we no longer should be friends or partners. We still want to work with the US.”
 Malwal believes the situation unfolding in Sudan has undermined the political process in his home country.
Malwal believes the situation unfolding in Sudan has undermined the political process in his home country.
“Sudan being the current chair of IGAD, and the South Sudanese peace implementation is being monitored by IGAD, this has slowed things down,” he said, referring to the Intergovernmental Authority on Development, the eight-country African trade bloc headquartered in Djibouti.
“There are certain things that we are doing on our own. But it is always good to have a functioning regional organization that is actually verifying what we are doing, because certain (members) in the international arena do not think that we are faithfully implementing the peace process.”
Preventing further spillovers into the wider region means quickly resolving the crisis in Sudan. Malwal said his greatest fear is that the fighting will be prolonged, leading to further destruction and displacement.
“I grew up in Khartoum, and I went to school there,” he said. “It’s sad to see what is happening now. We thought Khartoum should be stable. It was moving forward, actually. And now it has gone back. And it’s very unfortunate. Sudan is an important country in the region and it should be stable as soon as possible.
“We knew there were some tensions. The signs were there. But we were hoping for a very smooth transition, because the two generals were actually together. They were allies. And we just didn’t know, in the last days before the eruption, why it had escalated to where it is. Nobody knows.
“That needs to be addressed quickly, because (the fighting) is unnecessary, really. The people of Sudan, and especially the citizens of Khartoum, and the city itself, shouldn’t be a battlefield.”
Multiple ceasefire agreements have been reached between the warring factions in Sudan, including what became known as the Jeddah Declaration — the outcome of negotiations led by Saudi Arabia and the US — who managed to bring the two generals to the negotiating table.
However, every truce to date has been violated.
Saudi Arabia and the US warned in a recent joint statement that “should the parties fail to observe the 24-hour ceasefire, facilitators will be compelled to consider adjourning the Jeddah talks.”
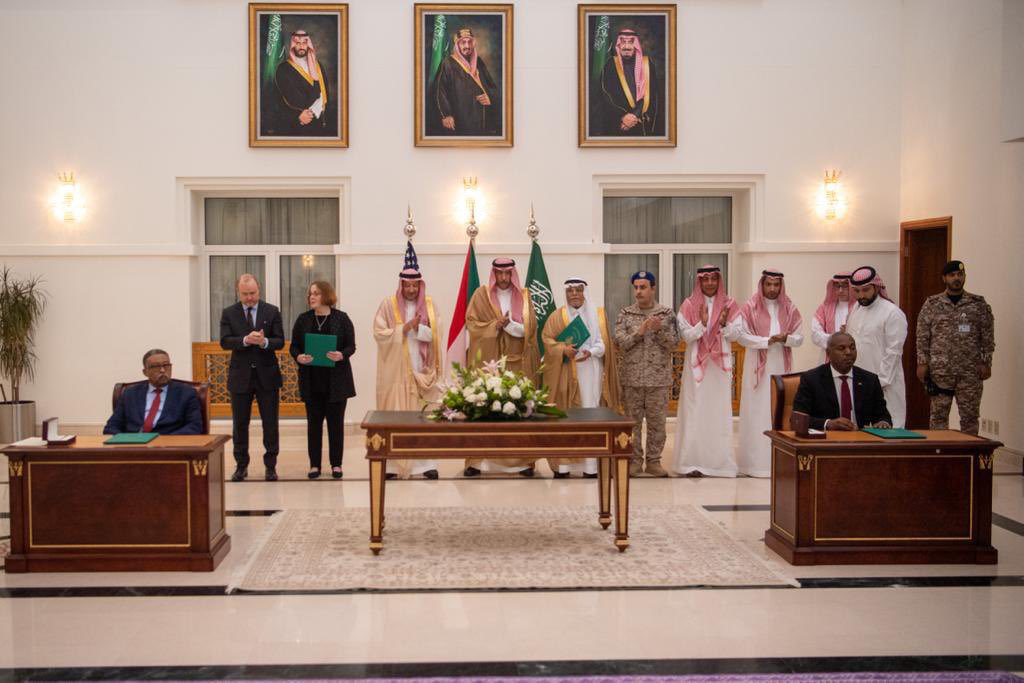

Representatives of the Sudanese Armed Forces and its rival Rapid Support Forces prepare to sign the Jeddah Declaration, witnessed by Saudi and US officials, during a ceremony in Jeddah on May 11, 2023. (Supplied)
Malwal echoed the African Union’s call to unify international peace efforts in order to avoid multiple overlapping initiatives, which could be a “complicating factor.”
“You don’t need to have so many forums for peace negotiations,” he said. “When the US and the Saudis managed to bring the generals to the negotiating table, everybody was waiting to see how they would fare, including the UN and IGAD.
“That’s why South Sudan President Salva Kiir has said let’s work behind the scenes while we wait and see what will happen from Jeddah.
“Now, maybe there is a need for the UN to come in and give IGAD instead the means to deal with the situation and see what happens. Maybe the situation needs a lower approach, rather than a high-profile approach.
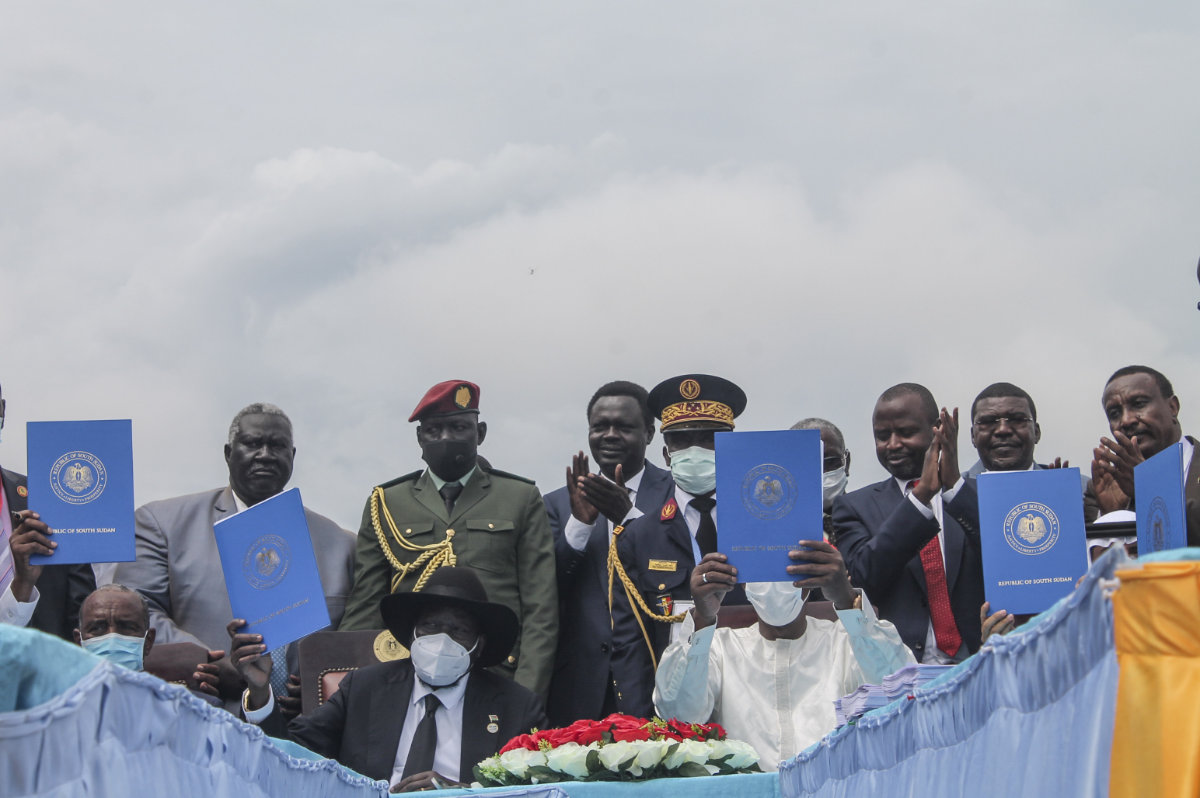

This Oct. 3, 2020, photo, shows South Sudan's President Salva Kiir (C) with Sudan's Sovereign Council chairman Abdel Fattah al-Burhan Chad President Idriss Deby during the signing of the South Sudan peace deal in Juba . (AFP)
“And that’s what I think IGAD would be best suited for, because Sudan is a member of IGAD. These are people who know the two generals very well. President Salva Kiir knows the two generals personally.
“He would bring in Kenya, who is a member of that mediation team. It’s a very important country in the region. Djibouti is a good friend of Sudan and a member of IGAD. So these are three countries that know these people.
“I think if they are empowered more to take the lead and to see what they could do, maybe there would be a way of rescuing the situation faster.”
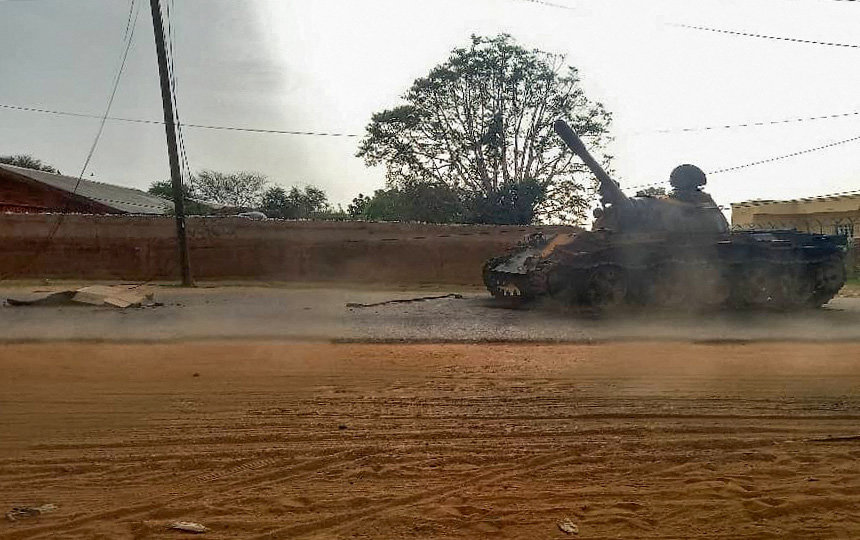

A picture taken on June 16, 2023, shows a covered body across from a military armored vehicle on a street in the West Darfur state capital El Geneina, amid ongoing fighting between two generals in war-torn Sudan. (AFP)
However, Malwal believes the authority of the African Union has been routinely undermined.
“We’ve been dealing with certain members of the Security Council who are not listening,” he said. “They don’t respect — and I wouldn’t use that word if I didn’t know what I’m talking about — the decision of the African Union vis-a-vis the issues that concerned African countries.
“You cannot say to the AU you’re a part of this process, and then, when the heads of African states say they are against sanctions on South Sudan and ask for the opportunity to deal with the issue of South Sudan or any other issue, you don’t say: ‘No, we have our own way of looking at it.’
“We have moral authority and we are imposing these because our way is the only way that’s going to resolve this issue. So, I don’t think the AU is being treated as an equally important organization when it comes to certain issues and, in particular, in South Sudan,” he said.



































