JEDDAH: Considering some 90 percent of Saudi Arabia’s territory is largely desert and ill-suited for farming, few might expect the Kingdom to be the site of a new agricultural boom designed to boost domestic crop production and reduce dependence on imported foodstuffs.
As large swathes of the Arab world struggle with food insecurity and supply-chain disruptions, the Kingdom’s initiatives, investments and technological innovations are redefining what it means to achieve self-sufficiency in many food items across one of the world’s most arid regions.
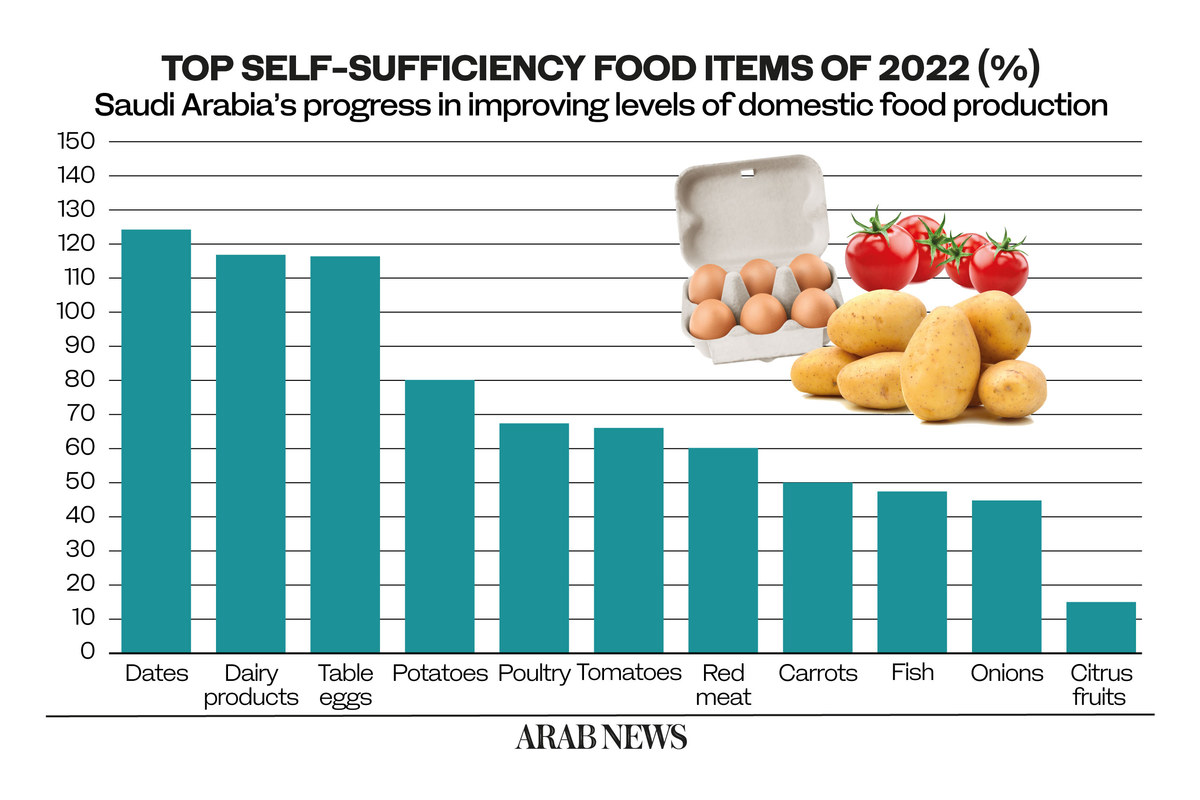
Today, Saudi Arabia has achieved complete self-sufficiency in the production of dates, fresh dairy products and table eggs, according to figures from the General Authority for Statistics’ Agricultural Statistics Publication.
These figures also show that Saudi Arabia produces more than enough of these three food items to meet local demand — 124, 118, and 117 percent, respectively — meaning it has excess capacity for export.
The Kingdom has also made progress in growing potatoes, meeting 80 percent of local demand. Domestic poultry comprises 68 percent, tomatoes 67 percent, red meat 60 percent, carrots 50 percent, fish 48 percent and onions 44 percent.
Improving food self-sufficiency has required the Kingdom to navigate the twin obstacles posed by climate change, bringing with it new record temperatures and soil degradation, and water scarcity, amid depleted rainfall and limited natural freshwater reserves.
Jamal Al-Saadoun, CEO and vice chairman of the Red Sea Farms Cooperative, or Tamala, an initiative aimed at developing agriculture in the Red Sea region, told Arab News the Kingdom reached its level of food self-sufficiency “through planning and over a long period.”
Saudi Arabia’s journey to food self-sufficiency started in the 1980s. During that decade, Riyadh “began developing agricultural plans and focusing on important sectors and products such as dairy, dates, poultry and table eggs,” said Al-Saadoun.
It was supported by investors, assisted by consultations and boosted by a good domestic market for homegrown products. Some of these goods were even exported to the Kingdom’s neighbors, demonstrating the oil-rich country’s potential to become an exporter of foodstuffs rather than a mere importer and consumer.
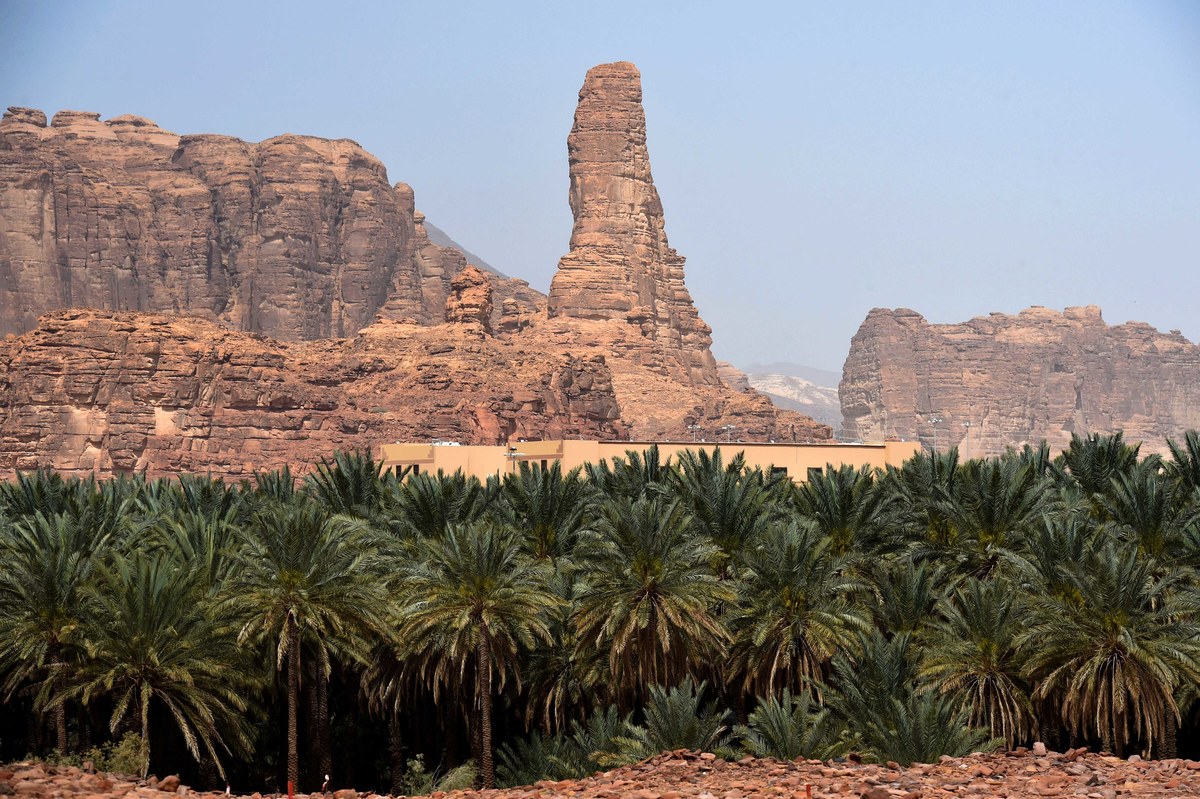

A picture taken on March 31, 2018 shows a date farm amidst sandstones in the Khuraiba archaeological site near Saudi Arabia’s northwestern town of AlUla. (AFP)
Now Saudi agri-businesses and investors have adopted modern technologies to improve quality and yields, learning and exchanging best practices with counterparts in the industry around the world.
“The presence of many technical companies inside the Kingdom and regular participation in international exhibitions by the Ministry of Agriculture” are giving Saudis in the agricultural sector opportunities to meet specialists and learn about the latest technologies in their field, said Al-Saadoun.
Several economists have sought to emphasize the importance of food self-sufficiency in the face of chronic food insecurity, especially in countries that rely heavily on imports for domestic consumption.
As the global food system becomes more interconnected, the risk of food insecurity is on the rise. In this century alone, the importance of food self-sufficiency became evident during the 2007-08 world food price crisis.
More recently, destabilizing events such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the Russia-Ukraine conflict have again underlined the importance of food security and the need for many countries to pursue self-sufficiency to avoid price inflation and shortages.
FASTFACTS
- Saudi Arabia has implemented several innovative solutions to expand and improve its agricultural sector.
- Riyadh has invested in desalination technologies to avoid depleting its freshwater reserves vital for growing crops.
Driven by the need to achieve self-sufficiency in keeping with its food-security strategy, the Saudi government has invested in modern desalination technologies and advanced irrigation techniques.
Such investments enable it to utilize its water reserves more effectively and avoid unnecessary wastage, particularly given its limited natural freshwater resources, especially groundwater.
Across most of the Arabian Peninsula, there is precious little rainfall and much of what there is runs off into desert sand or quickly evaporates.
An area covering more than 1,000,000 square miles contains almost no perennial rivers or streams, and the Kingdom’s southern section is covered by one of the largest deserts in the world.
Saudi Arabia occupies about 80 percent of the Arabian Peninsula and is one of its driest countries. Water resources are scarce and climate conditions severe. The conditions cause groundwater salinization, which is a common problem affecting the Kingdom’s agricultural sector.
As part of its investment in desalination technologies, Saudi Arabia has built plants along its coastlines that convert sea water into freshwater, which is then used for irrigation and other agricultural needs.
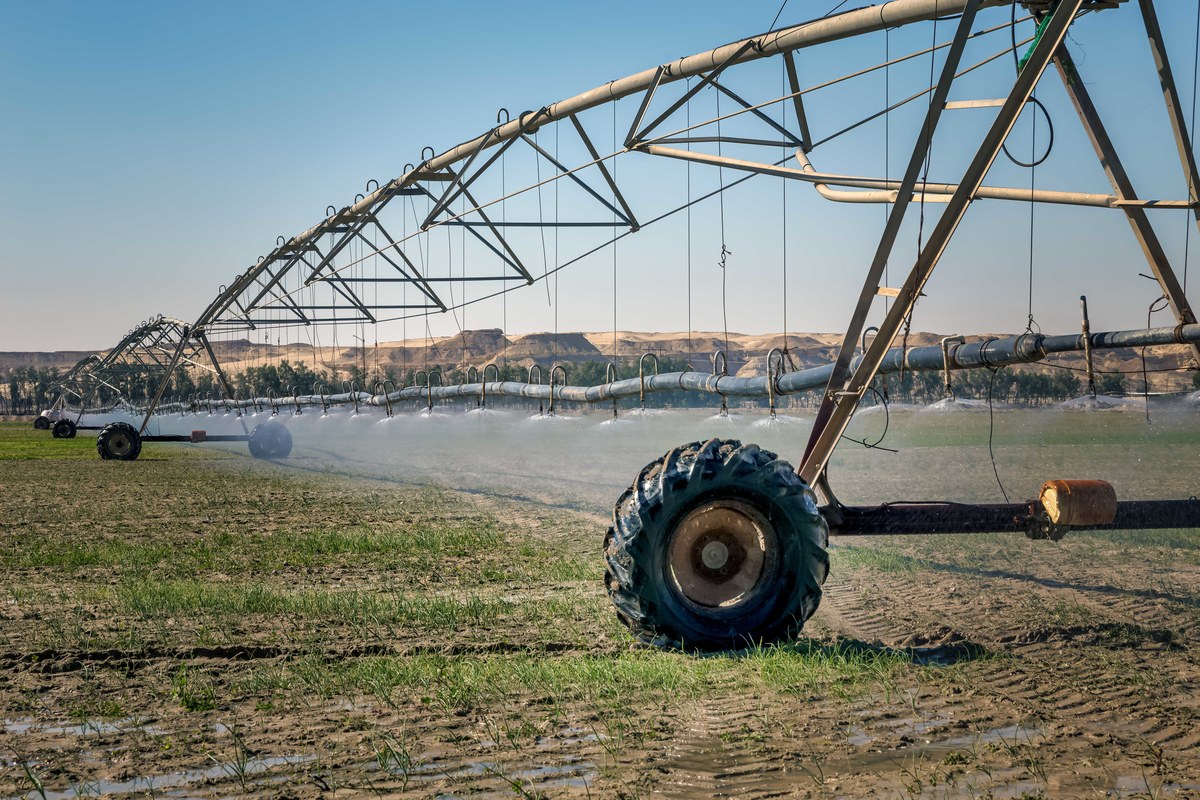

The Saudi government has invested in modern desalination technologies and advanced irrigation techniques. (Shutterstock)
In addition to reducing the use of its freshwater reserves, this process has made it possible to cultivate crops in drier, water-scarce regions, potentially giving the Kingdom more arable land for agriculture.
To prevent the exploitation of aquifers, Riyadh has also imposed strict regulations against groundwater extraction. By taking these proactive measures, Saudi Arabia is working to sustain and preserve this vital resource.
The Kingdom has achieved notable self-sufficiency in various crops, especially those requiring modern technologies, largely thanks to its integrated water management system. This approach has noticeably reduced the water consumption needed for agriculture from 86 percent to 70 percent.
Saudi authorities are also exploring the option of localized vertical-farming technologies and hydroponics — the science of growing plants without soil and with limited amounts of water.
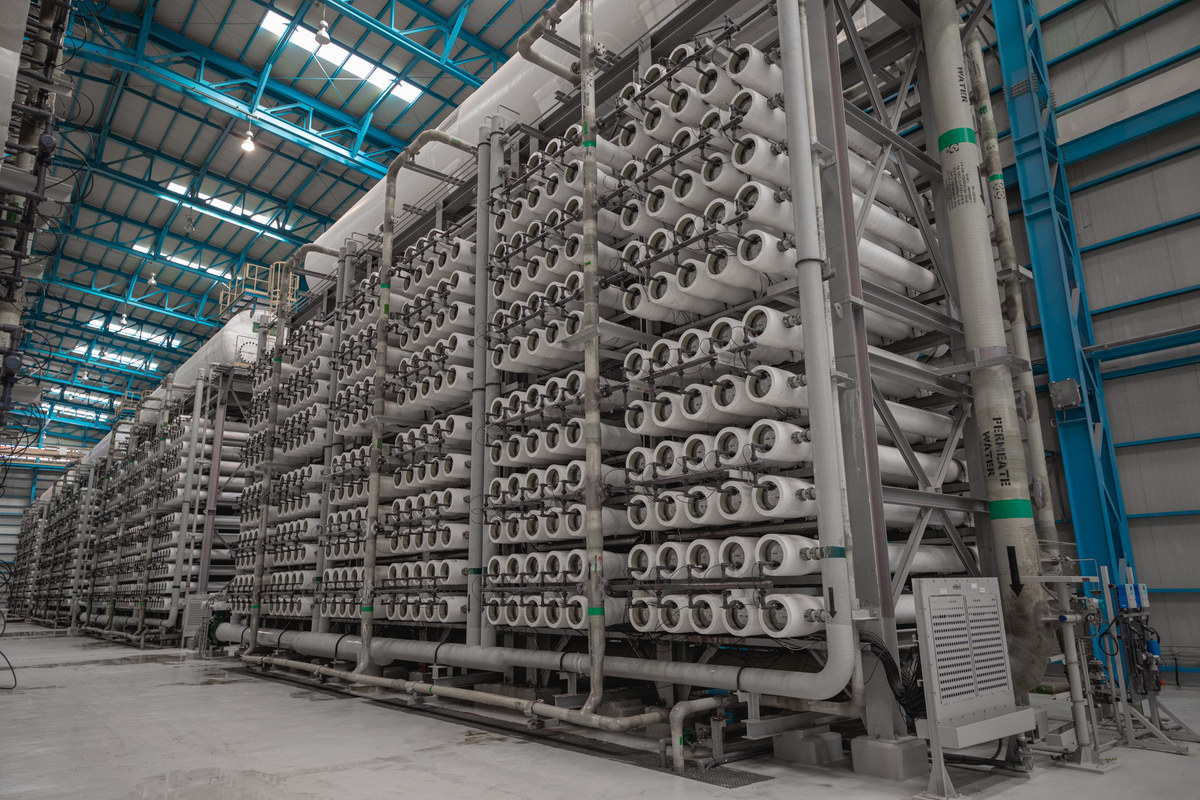

Saudi Arabia has built plants along its coastlines that convert sea water into freshwater, which is then used for irrigation and other agricultural needs. (Saudi Water Conversion Corporation)
These innovations boost the domestic cultivation of essential crops, such as wheat, barley and dates, and simultaneously reduce reliance on foreign sources for these staples.
Despite these successes, the Kingdom still relies heavily on imports for much of the food consumed by the Saudi public. However, authorities recognize that the Kingdom cannot achieve complete food self-sufficiency by remaining dependent on the international market.
Consequently, over the summer, the Kingdom’s Agricultural Development Fund approved funding for small farmers in greenhouse vegetable production, fish and shrimp farming, and poultry breeding. Under this scheme, farmers were loaned $400 million in funding to support what many call “local-for-local” goods.
Al-Saadoun of Tamala highlighted the government’s support for agricultural cooperatives and initiatives to develop agriculture and livestock farming with a view to employ modern technologies, sustainable irrigation systems and organic farming practices.
Such initiatives include developing agricultural and livestock farming in the Red Sea region. In recent years, multiple centers for agricultural development have emerged throughout the coastal area, with small local farms adopting more advanced practices to boost yields.

Saudi companies and associations are helping farmers to transition to modern and sustainable farming methods. (Shutterstock)
Companies and associations like Tamala are playing a crucial role in helping such farmers transition to modern and sustainable farming methods. They aim to facilitate the development of high-quality produce while conserving vital resources.
Although Saudi Arabia is boosting local production, this does not mean it is turning its back on foreign imports. Rather, the Kingdom is diversifying its sources of food to guard against future systemic shocks.
Indeed, in a 2017 paper, “Food self-sufficiency: Making sense of it, and when it makes sense,” published by the journal Food Policy, the author argues that “policy choice on this issue is far from a straightforward binary choice between the extremes of relying solely on homegrown food and a fully open trade policy for foodstuffs.”
Saudi Arabia’s experience is a striking example of a country vigorously pursuing its goal of achieving food self-sufficiency and tackling food insecurity in an unpredictable and uncertain world.























