ATACORA, Benin: The insurgents pressured Zackari to join their movement, and he turned them down.
Now he’s frightened of their revenge. He has been on the run from the jihadi fighters for more than a year. They regularly call the 33-year-old, warning: “We haven’t forgotten about you.”
Groups linked to Al-Qaeda and the Daesh group have been spreading for years from the vast arid expanse south of the Sahara Desert — the Sahel — into wealthier West African coastal states like Benin. Militants once were believed to want to use coastal nations like Benin, Togo and Ghana as bases for attacks on Sahel governments. Now militancy is taking root.
Benin has been the hardest hit. This year it had more than ten times the number of violent incidents involving jihadis than Togo did, according to the Armed Conflict Location & Event Data Project.
Attacks by jihadis against civilians in Benin nearly tripled from last year, from more than 30 to approximately 80. The overall number of incidents involving jihadi groups rose by more than 70 percent.
“There’s full expansion, regular preaching. They’re establishing cells, they have a lot of presence,” said Kars de Bruijne, senior research fellow and head of the Sahel program at the Clingendael Institute.
The jihadis’ activity in Benin is concentrated in the north of the country, where they try to recruit people or get them to be informants, creating division within local populations. Residents of one small town tucked behind lush hills and windy unpaved roads told The Associated Press last month that civilians can no longer move freely.
People in Materi live in constant fear because of the jihadi threat. The fighters are planting explosives and carrying out abductions in the area, instilling fear among the population while eroding state legitimacy. The government has imposed a curfew and a ban on gatherings.
“I can’t sleep at night, we’re not free to travel, to move,” Materi resident Florence Bati said. “People are too afraid.”
Kidnappings by jihadis in Benin surged from zero in 2021 to 33 this year, according to the Global Initiative Against Transnational Organized Crime, which analyzed the Armed Conflict Location & Event Data Project data and other sources. Explosions have also increased, residents say.
Several months ago, a woman was killed by an explosive while fetching wood, said locals. Women have stopped going into the forest, instead finding kindling closer to home, they said. In October, one aid group distributed portable ovens, which require less wood.
People are being displaced from their homes as attacks increase, sparking concerns of a humanitarian crisis.
In August, more than 12,000 people were displaced from their homes in the Atacora and neighboring Alibori departments, up from about 5,000 in March, according to the United Nations. Violence is also pushing people from their farms. The UN estimates that tens of thousands of people could face crisis levels of food insecurity.
The government is trying to stem the problem by reinforcing the military along the borders and recruiting thousands of soldiers. Locals in the north say they’ve seen a surge of soldiers but say the army is underequipped and sometimes responds hours late when called about an attack.
The government denies that.
The military is well-equipped, able to respond to the incursions that occur and is conducting advanced training while trying to acquire more ground and airborne resources, said Col. Faizou Gomina, commander of the Mirador operation, which is dedicated to fighting the jihadis.
Unlike neighboring Burkina Faso, Niger and Mali, which are being overrun by violence, and which ousted French troops after undergoing military coups and seeing surging anti-French sentiment, Benin is still open to help from its former colonial power, which left in 1960. The French don’t have a permanent base in the country, but at the behest of Benin, its troops deployed in the region can participate in training programs with Beninese soldiers, French military spokesman Col. Pierre Gaudilliere said.
While Benin’s government is shoring up its borders, it’s also trying to conceal the scale of the crisis to maintain its image, say residents in the north. It’s cracked down on freedom of speech and arrested journalists who report on insecurity.
Local officials insist the problem doesn’t extend beyond the border with Burkina Faso.
“There is no terrorist, no movement, no organization, no group that has settled or tried to settle in our department,” said Robert Wimbo Kassa, the mayor of Materi.
An agricultural nation of 13 million people, Benin has invested billions of dollars in propping up culture and tourism and is building a $1.5 billion industrial zone 27 miles (45 kilometers) outside of the city of Cotonou aimed at creating 300,000 jobs by 2030.
The information gap has left people in other parts of the country unaware of the security issues in the north. People in Cotonou said that they didn’t know about the jihadi problem, believed it was fake news, or that it was a problem limited to neighboring countries.
Rights groups say the government’s attempts to control the information space, while arbitrarily arresting people believed to be working with the jihadis, is pushing people into the militants’ hands.
“The jihadists live with the populations, the citizens know them, but they refuse to denounce them because the government doesn’t encourage people to do so,” said Bertin Assogba, coordinator for Durable and Develop Reference, a local aid group focused on defending human rights.
The international community is trying to implement lessons from the Sahel by sensitizing people into not joining the jihadis, and organizing community dialogues with officials to foster trust. Diplomats and aid groups also say there’s been a rush of investment.
Last year, the World Bank invested $450 million in a five-year project aimed at reaching some 4,600 border communities in northern Benin, Ivory Coast, Ghana and Togo. It will be focused on preventing the spread of conflict by strengthening local institutions and economic opportunities. But residents say development projects take too much time to materialize.
In the meantime, militants are winning in the realm of public perception.
Jihadis enter impoverished villages promising to build roads and hospitals if they come to power, residents say.
“(The government) should hurry and bring infrastructure. It’s important because jihadists are around and their message is very clear: They want to change things,” said Raoufou Bandele, the coordinator for Action for Mutual Aid and Development, a local group. “Some families give their sons the blessing to go with the jihadists because of frustration with the government.”
Groups linked to Al-Qaeda and the Daesh take root on the coast of West Africa
https://arab.news/6dqyn
Groups linked to Al-Qaeda and the Daesh take root on the coast of West Africa

- Attacks by jihadis against civilians in Benin nearly tripled from last year, from more than 30 to approximately 80. The overall number of incidents involving jihadi groups rose by more than 70 percent
2 people killed and dozens wounded in Russian attack on Kharkiv

- Ukrainian officials say two people were killed when Russian drones struck a military hospital, shopping center and apartment buildings in Kharkiv late Saturday
- The Ukrainian Air Force reported intercepting 65 of 111 Russian drones
Regional Gov. Oleh Syniehubov said that a 67-year-old man and a 70-year-old woman were killed in the attack on Ukraine’s second-largest city.
Ukraine’s General Staff denounced the “deliberate, targeted shelling” of the military hospital. Among the casualties were “servicemen who were undergoing treatment,” it said.
The Ukrainian Air Force reported that Russia fired 111 exploding drones and decoys in the latest wave of attacks overnight into Sunday. It said 65 of them were intercepted and another 35 were lost, likely having been electronically jammed.
Russia’s Ministry of Defense, meanwhile, said its air defense systems shot down six Ukrainian drones.
According to Ukrainian government and military analysts, Russian forces are preparing to launch a fresh military offensive in the coming weeks to maximize pressure on Ukraine and strengthen the Kremlin’s negotiating position in ceasefire talks.
The science behind the powerful earthquake in Myanmar and Thailand

- Myanmar lies on boundary between two tectonic plates, is one of world’s most seismically active countries
- Friday’s event was “probably the biggest” to hit Myanmar’s mainland in three quarters of a century, experts said
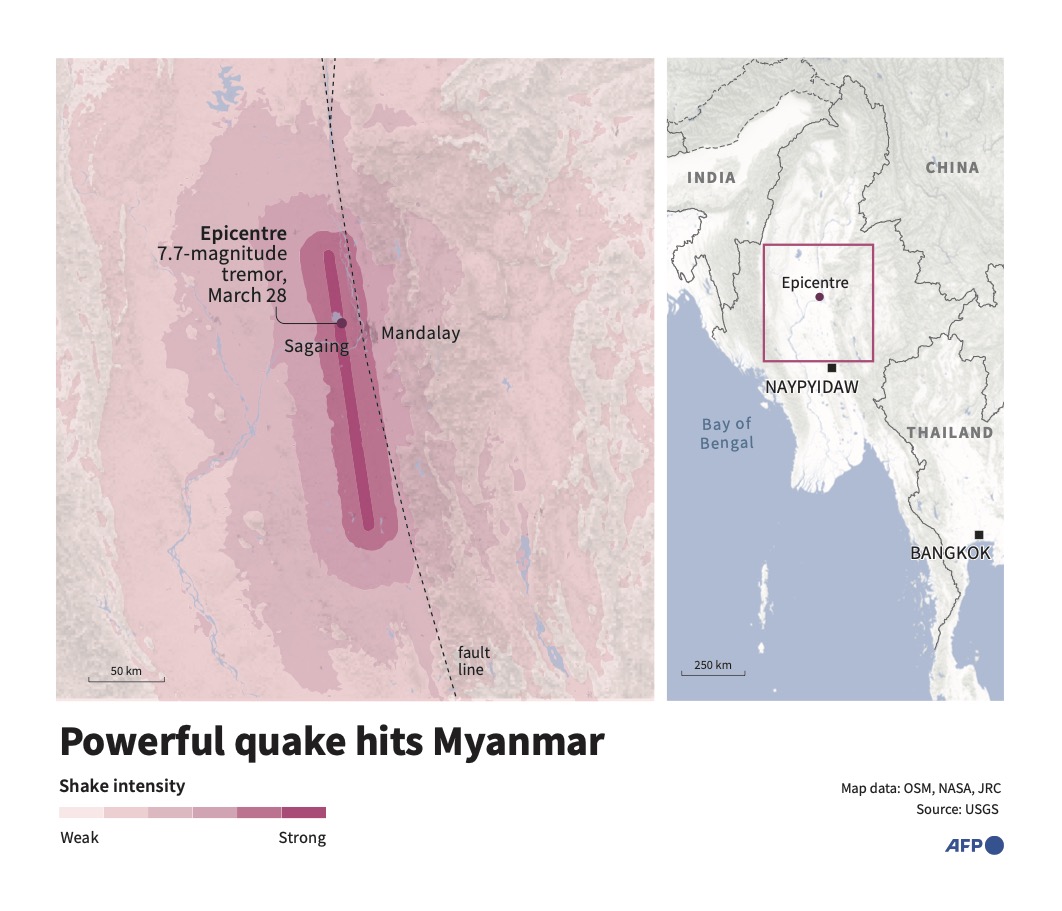
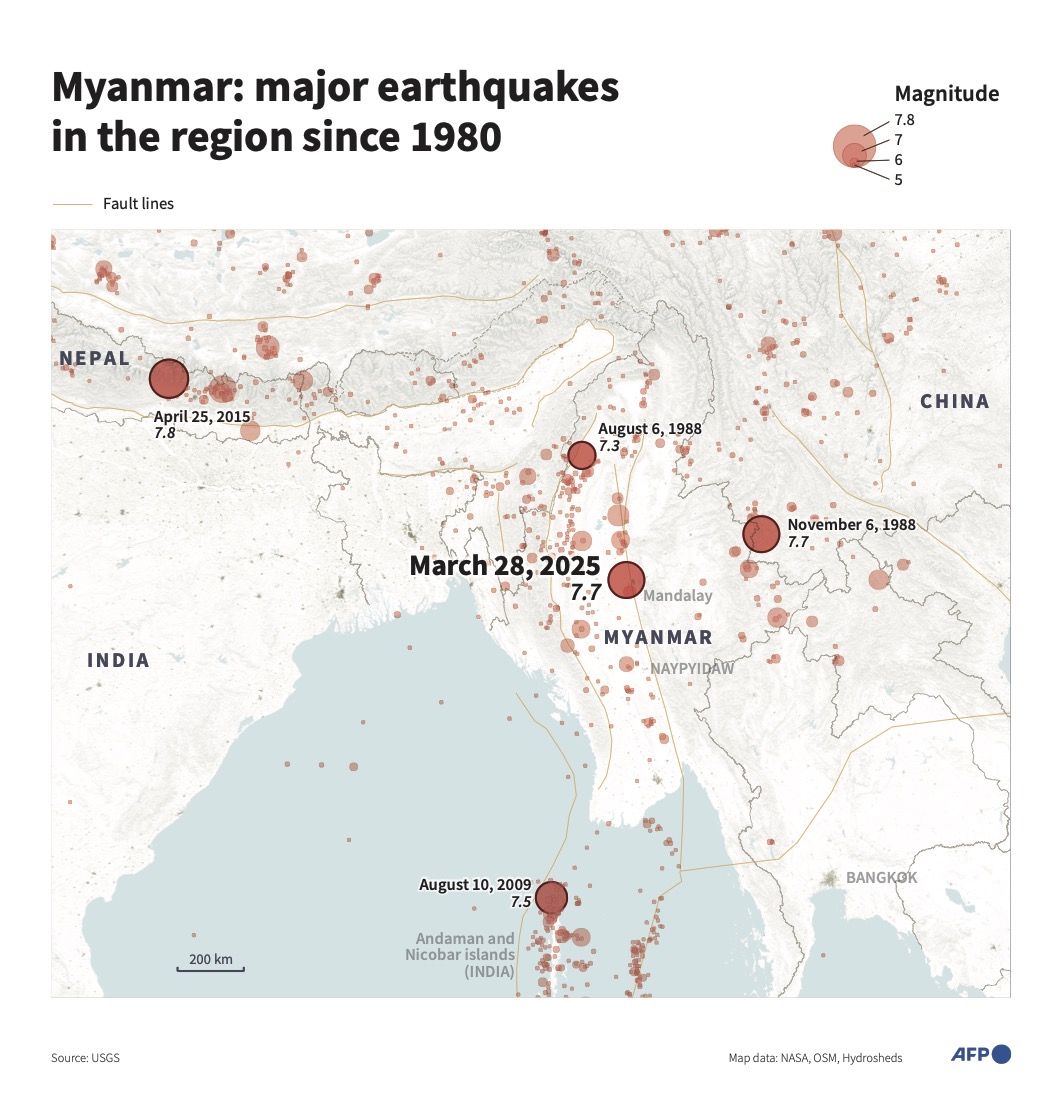
SINGAPORE: A powerful earthquake of magnitude 7.7 centered in the Sagaing region near the Myanmar city of Mandalay caused extensive damage in that country and also shook neighboring Thailand on Friday.
How vulnerable is Myanmar to earthquakes?
Myanmar lies on the boundary between two tectonic plates and is one of the world’s most seismically active countries, although large and destructive earthquakes have been relatively rare in the Sagaing region.
“The plate boundary between the India Plate and Eurasia Plate runs approximately north-south, cutting through the middle of the country,” said Joanna Faure Walker, a professor and earthquake expert at University College London.
She said the plates move past each other horizontally at different speeds. While this causes “strike slip” quakes that are normally less powerful than those seen in “subduction zones” like Sumatra, where one plate slides under another, they can still reach magnitudes of 7 to 8.
Why was Friday’s quake so damaging?
Sagaing has been hit by several quakes in recent years, with a 6.8 magnitude event causing at least 26 deaths and dozens of injuries in late 2012.
But Friday’s event was “probably the biggest” to hit Myanmar’s mainland in three quarters of a century, said Bill McGuire, another earthquake expert at UCL.
Roger Musson, honorary research fellow at the British Geological Survey, told Reuters that the shallow depth of the quake meant the damage would be more severe. The quake’s epicenter was at a depth of just 10 km (6.2 miles), according to the United States Geological Survey.
“This is very damaging because it has occurred at a shallow depth, so the shockwaves are not dissipated as they go from the focus of the earthquake up to the surface. The buildings received the full force of the shaking.”
“It’s important not to be focused on epicenters because the seismic waves don’t radiate out from the epicenter — they radiate out from the whole line of the fault,” he added.
How prepared was Myanmar?
The USGS Earthquake Hazards Program said on Friday that fatalities could be between 10,000 and 100,000 people, and the economic impact could be as high as 70 percent of Myanmar’s GDP.
Musson said such forecasts are based on data from past earthquakes and on Myanmar’s size, location and overall quake readiness.
The relative rarity of large seismic events in the Sagaing region — which is close to heavily populated Mandalay — means that infrastructure had not been built to withstand them. That means the damage could end up being far worse.
Musson said that the last major quake to hit the region was in 1956, and homes are unlikely to have been built to withstand seismic forces as powerful as those that hit on Friday.
“Most of the seismicity in Myanmar is further to the west whereas this is running down the center of the country,” he said.
US woman released by Taliban in Afghanistan

- Hall was detained in Feb. along with Peter and Barbie Reynolds, in their 70s
- Group was traveling to British couple’s home in central Bamiyan province
WASHINGTON: An American woman has been freed by the Taliban in Afghanistan after she, two Britons and their Afghan translator were detained earlier this year, Washington’s former envoy to Kabul, Zalmay Khalilzad, said Saturday.
“American citizen Faye Hall, just released by the Taliban, is now in the care of our friends, the Qataris in Kabul, and will soon be on her way home,” Khalilzad, who has been part of a US delegation working on Taliban hostage releases, wrote on X.
While at the Qatari embassy in Kabul, Hall “has been confirmed in good health after undergoing a series of medical checks,” said a source with knowledge of the release.
She was released on Thursday following a court order and with logistical support from Qatar, the source added.
Hall, who has been identified by the Taliban’s interior ministry as Chinese-American, was detained in February along with Peter and Barbie Reynolds, who are in their 70s, as they traveled to the British couple’s home in central Bamiyan province.
Their Afghan translator was additionally arrested.
Taliban officials have refused to detail the reasons for their arrest, but one report said Hall had been detained on charges of using a drone without authorization.
In his announcement, Khalilzad posted a picture of Hall smiling with Qatar representatives ahead of her departure from Afghanistan.
Khalilzad had been in the Afghan capital earlier this month on a rare visit by US officials to meet Taliban authorities, accompanying US hostage envoy Adam Boehler.
Following their visit, the Taliban government announced the release of US citizen George Glezmann after more than two years of detention, in a deal brokered by Qatar.
He and Hall are among several Americans to be released from Taliban custody this year.
In January, two Americans detained in Afghanistan — Ryan Corbett and William McKenty — were freed in exchange for an Afghan fighter, Khan Mohammed, who was convicted of narco-terrorism in the United States.
At least one other US citizen, Mahmood Habibi, is still held in Afghanistan.
The British couple detained with Hall remain in Taliban custody.
Their daughter has expressed grave fears for her father’s health and appealed to the Taliban authorities to free them.
The Reynolds, who married in Kabul in 1970, have run school training programs in the country for 18 years.
They remained in Afghanistan after the Taliban takeover in 2021 when the British embassy withdrew its staff.
The government in Kabul is not recognized by any country, but several, including Russia, China and Turkiye, have kept their embassies open in the Afghan capital.
Qatar, too, has maintained diplomatic channels with the Taliban and has facilitated negotiations for the release of US hostages.
Since US President Donald Trump’s reelection, the Kabul government has expressed hopes for a “new chapter” with Washington.
Pentagon chief says US will ensure ‘deterrence’ across Taiwan Strait

- Beijing has stepped up military pressure in recent years around Taiwan
Tokyo: The United States will ensure “robust, ready and credible deterrence” in the Asia-Pacific, including across the Taiwan Strait, US Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth said Sunday, calling Chinese actions “aggressive and coercive.”
Speaking in Japan, Hegseth also stopped short of publicly calling on Tokyo to increase military spending, saying he trusted the close US ally to “make the correct determination of what capabilities are needed.”
“America is committed to sustaining robust, ready and credible deterrence in the Indo-Pacific, including across the Taiwan Strait,” Hegseth said, using Washington’s term for the Asia-Pacific region.
“Japan would be on the frontlines of any contingency we might face in the western Pacific and we stand together in support of each other,” he told reporters after talks with Japanese counterpart Gen Nakatani.
“That is why today Minister Nakatani and I talked about the severe and urgent security environment around Japan, and we discussed what we are going to do about it.”
Beijing has stepped up military pressure in recent years around Taiwan, including near-daily air incursions, and has not ruled out using force to bring the island under its control.
Okinawa base
Japan and the United States are each other’s top foreign investors, and 54,000 US military personnel are stationed in Japan — mostly in Okinawa, east of Taiwan.
But Trump’s “America First” approach could mean weakening the US commitment for security in the region as well as more pressure — like in Europe — on allies to spend more.
Hegseth said that he “did not talk specific numbers” about defense spending in his talks with Nakatani and Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba.
“We’re confident that Japan will make the correct determination of what capabilities are needed inside our alliance to make sure we are standing shoulder to shoulder,” he said.
“They have been a model ally, and we have no doubt that will continue. But we also both recognize everybody needs to do more.”
Japan has been shedding its strict pacifist stance, moving to obtain “counterstrike” capabilities and doubling military spending to the NATO standard of two percent of GDP.
But Washington could ask it to do more, with Trump’s nominee for a key Pentagon policy position, Elbridge Colby, calling for defense spending of three percent of GDP.
Nakatani said Sunday that he told Hegseth that spending should be “implemented based on Japan’s own judgment and responsibility.”
“I also explained Japan has continuously been working on a drastic strengthening of out defense capability... on which we received understanding from the US side,” he said.
Hegseth said the Tokyo meetings “affirmed the extraordinary strength of America’s alliance with Japan.”
“President Trump has also made it very clear, and we reiterate, we are going to put America first. But America first does not mean America alone,” he added.
“America and Japan stand firmly together in the face of aggressive and coercive actions by the Communist Chinese.”
Ukraine accuses Russia of ‘war crime’ with military hospital strike

- The latest deadly strikes come as US President Donald Trump’s administration pushes for a speedy end to the more than three-year war, holding talks with both Russia and Ukraine
KYIV: Ukraine accused Russia of committing a “war crime” during its weekend attack on the city of Kharkiv, as the US-backed ceasefire efforts continue to prove elusive.
Six strikes hit the northeastern border city overnight Saturday into Sunday, wounding personnel undergoing treatment at a military hospital and killing at least two people in a residential building, according to Ukrainian officials.
A spokesperson for the Kharkiv regional prosecutor’s office, Dmytro Chubenko, confirmed two deaths and said another 30 people were wounded, including children.
According to the emergency medical services, the “massive attack” reduced one home to a fiery ruin and damaged other houses, office buildings, cars and garages.
The Ukrainian army said that a military hospital building and nearby residential buildings “were damaged by a Shahed drone.”
“According to preliminary reports, there are casualties among the military personnel who were undergoing treatment at the medical center,” it added.
Kyiv does not typically reveal information on military casualties and did not say how many soldiers were wounded.
It accused Russia of having carried out a “war crime” and “violating the norms of international humanitarian law.”
'Real pressure'
The latest deadly strikes come as US President Donald Trump’s administration pushes for a speedy end to the more than three-year war, holding talks with both Russia and Ukraine.
Moscow has rejected a joint US-Ukrainian proposal for an unconditional and full ceasefire, while Ukraine has accused Russia of dragging out talks with no intention of halting its offensive.
“For too long now, America’s proposal for an unconditional ceasefire has been on the table without an adequate response from Russia,” Zelensky said in his evening address on Saturday.
“There could already be a ceasefire if there was real pressure on Russia,” he added, thanking those countries “who understand this” and have stepped up sanctions pressure on the Kremlin.
Both Moscow and Kyiv agreed to the concept of a Black Sea truce following talks with US officials earlier this week, but Russia said the deal would not enter into force until the West lifted certain sanctions.
Rapprochement between Washington and Moscow since Trump’s return to office and his threats to stop supporting Kyiv have bolstered Russian President Vladimir Putin’s confidence.
On the battlefield, his defense ministry claimed Saturday to have captured two Ukrainian villages: Shchebraki in the southern Zaporizhzhia region and Panteleimonivka in the eastern Donetsk region.
Putin has meanwhile called for a “transitional administration” as part of the peace process, reiterating his long-standing desire to oust Zelensky and install a more Moscow-friendly government in Kyiv.
Putin, in power for 25 years and repeatedly elected in votes with no competition, has repeatedly questioned Zelensky’s “legitimacy” as Ukrainian president, after his initial five-year mandate ended in May 2024.
Under Ukrainian law, elections are suspended during times of major military conflict, and Zelensky’s domestic opponents have all said no ballots should be held until after the conflict.













