DUBAI: The fact that Israel and the Palestinian militant group Hamas are both uncomfortable with the Gaza peace plan presented by US President Joe Biden means that “the deal is a good one,” said Samuel Zbogar, Slovenia’s representative to the UN Security Council.
On June 10, the council adopted Resolution 2735 — a ceasefire proposal to end the conflict in Gaza. However, according to reports, Hamas has refused to accept the plan without amendments, which Israel has rejected.
Appearing on the Arab News current affairs program “Frankly Speaking,” Zbogar said the world should not lose hope in the Biden peace plan and should allow time for negotiators to help bring about a ceasefire.
“I wouldn’t give up on the Biden plan yet,” he said. “We understand the talks are still ongoing, mediated by Qatar, by Egypt, and the US, of course.
“I think the US put its authority behind this plan, so we hope that we will see it implemented. We want to give peace a chance. We haven’t been discussing in the council this week the situation in Gaza precisely to give negotiators time to finally come to a ceasefire.”
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has said Israel will not agree to a ceasefire without the destruction of Hamas’s military and governing capabilities. Zbogar, however, believes compromises are required on both sides.
“I believe that problems are on both sides,” he said. “I wouldn’t say that it’s one side that is rejecting the deal. I would think that both sides somehow are not comfortable, which means that the deal is a good one.
“We really hope that it’s implemented to stop this killing and suffering of civilians in Gaza.”
Asked whether the Security Council could be applying more pressure on the Israeli government to halt its operation in Gaza, which threatens to spill over into Lebanon and other countries in the region, Zbogar said only a unified position would prove effective.

Appearing on the Arab News current affairs program “Frankly Speaking,” Samuel Zbogar said the world should not lose hope in the Biden peace plan and should allow time for negotiators to help bring about a ceasefire. (AN Photo)
“The Security Council is the most effective, or maybe the only time that it’s effective, really, is when it is completely united,” he said. “When we have 15 votes in favor, I think then, maybe, it will be a strong enough message to Israel and to Hamas that enough is enough.
“But so far, in the last resolution, Russia abstained. In the previous resolutions the US abstained. And this is always a message to one or to the other side that, maybe, there is still room to maneuver.”
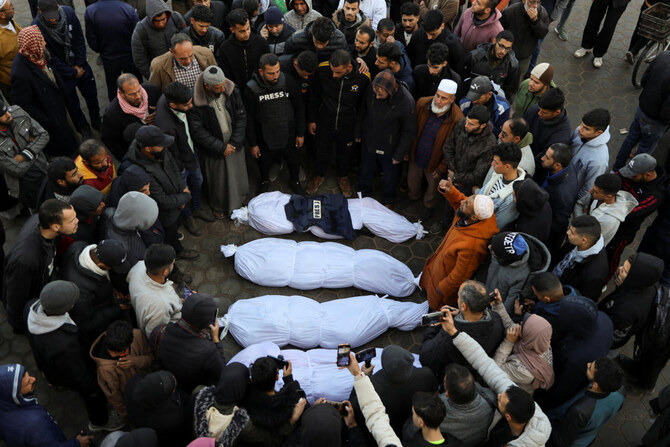
Ignoring the protests of numerous governments, Israel mounted an offensive on May 6 against Gaza’s southernmost city of Rafah, where about 1.4 million Palestinian refugees had sought shelter having fled the bombardment in the north.
Asked whether institutions like the European Union could have done more to prevent the Rafah assault, Zbogar said it was another example of a failure of unity.
“The Rafah assault is really something that will be haunting us, I think, as members of the council and as a human society in the future,” Zbogar told “Frankly Speaking” host Katie Jensen.
“All council members in the chamber, as well as in consultations, were saying Rafah should not happen. I was warning Israel not to go against Rafah. And yet we witnessed that it happened.
“This is something that is difficult to live with, to see the neverending suffering of people, of Palestinians, of Gazans.
“Couldn’t the EU do more? Yes, it could, it should. But unfortunately, we are not united. The EU is strong when it’s united. Then really we can be a strong player in international relations. On this topic, unfortunately, we have different views inside the EU.
“There are a lot of countries inside who are supportive of the Palestinian cause and who recognize Palestine, but still we are not united.”
Elaborating the point, Zbogar said: “As the Gaza crisis continued and deepened, there was more and more understanding on the European side that maybe supporting Israel and its right to self-defense, which we did at the beginning, was not appropriate anymore. So, we don’t hear that anymore from European leaders. Josep Borrell, the EU high representative for foreign and security affairs, took a very clear position all along the crisis. But, yes, we are not united and that’s why we are not the real player in this crisis.”
Since the Israeli military launched its operation in Gaza in the wake of the Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack on southern Israel, aid convoys sent to the embattled enclave have faced blockades and thorough inspections by Israeli authorities, delaying the relief response.
Once inside the Gaza Strip, aid convoys have been mobbed by crowds of starving Palestinians and come under intense Israeli fire, despite assurances by Israeli forces they would be permitted to pass.
Zbogar said only an end to the fighting would create the security conditions needed to help stricken communities. “I think it’s one word — a ceasefire,” he said. “Nothing less than a ceasefire would allow enough distribution of humanitarian aid in Gaza.
“It’s very difficult to distribute aid at this moment when rockets are flying, where Israel is rejecting more than half of the trucks because of the dual use (issue), where there is public disorder now in Gaza after so many months and the desperate situation that people are in.
“We have seen so many times when the humanitarian workers had an approved road on which they could deliver the aid, and yet they were targeted.
“Like we were seeing with the World Central Kitchen a few weeks ago or months ago. How they had all the approvals, they were in touch with (the military coordinating unit) COGAT on the Israeli side, and yet they were targeted one after the other.
“How can you expect humanitarian workers to go into this situation even if they have promises from Israel that today we will not target? How do you expect people to sacrifice their lives when they see that 200 of their colleagues distributing aid were killed? And that’s why the ceasefire is the only way we can distribute more aid inside Gaza.”
It was because of this carnage and suffering in Gaza that on June 4 this year Slovenia followed Ireland, Norway and Spain in recognizing a Palestinian state, citing the need for two equally sovereign parties to negotiate future relations.
“We believe that after the destruction of Gaza, we see even more clearly that we need two equal parties,” he said.
“We need two sovereign, two parties that will be equally sovereign, Palestine and Israel, in order for them to be able to negotiate their future relations. Otherwise, as long as you have one party that is weaker, then it’s not a proper discussion. And that’s why that prevailed, then, in our reflection as well. We need a Palestine that is on the same level as Israel.”
Zbogar said Slovenian recognition of a Palestinian state was intended to send a message to the Palestinians that they are not alone, while telling the Israeli government it is on the wrong course.
“We are hoping for Palestine to open its embassy in Slovenia. And we already have a person on the ground in Ramallah who is representing Slovenia with the Palestinian Authority. So, officially we implemented the decision of the parliament,” he said.
“We’ve been discussing in Slovenia for years about this recognition. There was always a political process that we were waiting for. Now, since things began happening in Gaza, we thought it’s time for us to send a message.
“This is a message for Palestinians. It’s not a message to Israel. It’s not a message to Hamas. Neither of them really care for their citizens. They’re using Palestinians and hostages as an instrument of pressure on each other.
“This is, for us, a message to Palestinians that no matter how difficult it looks at the moment and that the world is abandoning them, that we do recognize their right to have a state, to live in their own state. And it’s time to do that.”
He added: “We have been friends, and we continue to be friends, with Israel. And we think this is a message to them as well, that what they’re doing is not right. I think they’re on the wrong course.
“But Israel is much more than the current government. And I believe that people in Israel will recognize that what we did was a good thing, to help bring peace to the region.”
Asked whether the Security Council could be applying more pressure on the Israeli government to halt its operation in Gaza, Zbogar said only a unified position would prove effective. (AN Photo)
Zbogar is concerned that a failure to respond to the carnage in Gaza will result in the youth of the region turning against the international community.
“You have the whole population in the region that might be turning against the international community, that we are not doing enough to stop the bloodshed in Gaza,” he said.
“I think we might be losing the whole young population across the region. That’s the message we are getting from all the countries, all the special representatives there, that it’s for the future relations between the West and these countries that is a very dangerous situation.”
Once the war ends in Gaza, the question will turn to who should govern the war-scarred territory — Hamas, the Palestinian Authority, Israel, an external power, or a multilateral agency.
Zbogar believes Gaza will need a transitional period to guarantee its own and Israel’s security and to rebuild. But he does not believe this is something the Palestinian Authority can do on its own, calling instead for UN involvement.
Indeed, a recent poll of Gaza and the West Bank by the Palestinian Center for Policy and Survey Research showed huge dissatisfaction with the Palestinian Authority, with more than 60 percent supporting its dissolution, and close to 90 percent wanting President Mahmoud Abbas to resign.
“I don’t think it’s surprising — this dissatisfaction — because the Palestinian authorities don’t have power to deliver to their people. And that’s why people are disappointed,” Zbogar said.
“They continue to see Israeli occupation. They continue to see what’s happening in Gaza. And, of course, they are disappointed that their authority is not protecting them and cannot do anything about it.
“But they really cannot do anything about it if you are serious. So, who should run Palestine or Gaza? I think it’s for Palestinians to decide. I don’t think it should be foreigners to decide. They should decide who should govern.
“Of course, there probably will be some transition period in Gaza after all this is over. There will need to be a transition period with regard to security, to re-establishment of security, to provide security to Israel. There will be a need to rebuild Gaza. There will be a lot of needs.
“But I don’t think Palestinian authorities can do that on their own. I think probably the UN should be involved, should be helping them, coordinating all the assistance and all the support that was coming from abroad, in re-establishing Gaza as a place to live.”




























