LONDON: As Palestinian Authority President Mahmoud Abbas marks 20 years in office, his leadership remains a complex chapter in the Palestinian national story, characterized by division, disillusionment, but also dogged determination.
Having succeeded Yasser Arafat in 2005, Abbas’ lengthy tenure has been shaped by challenges that have profoundly impacted the Palestinian people, the pursuit of statehood, and the prospects for peace with Israel.
“Ever since taking office, President Abbas has focused all his attention on the realization of an independent Palestinian state using diplomatic and political means,” Daoud Kuttab, an award-winning Palestinian journalist and author, told Arab News.
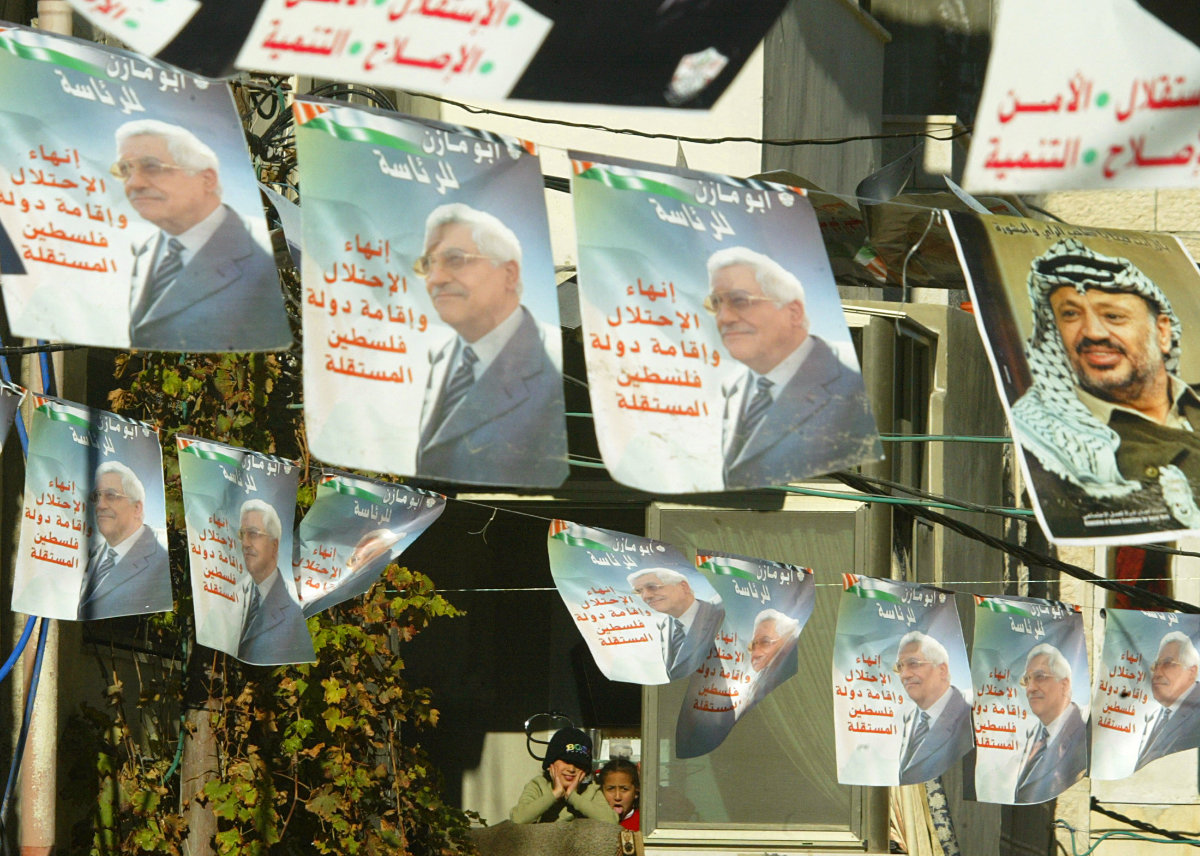

Posters of presidential candidate Mahmoud Abbas and the late Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat are seen at the Al-Amaari refugee camp in the West Bank city of Ramallah on January 2005 during the election for Arafat's successor. (AFP)
Abbas’s term was originally meant to last four years, meaning elections should have been held in 2009. However, no presidential elections have taken place since, primarily due to political rivalries between the main parties.
This 20-year milestone invites a reflection on Abbas’ legacy, the ongoing divisions within Palestinian politics, and whether his 20th year in power since succeeding Arafat might see tangible progress toward an independent Palestinian state.
When Abbas assumed the presidency on Jan. 15, 2005, he inherited a fractured political landscape. Arafat’s death in November 2004 left a void in Palestinian leadership, particularly given his unique ability to unite diverse factions under the umbrella of the Palestine Liberation Organization.
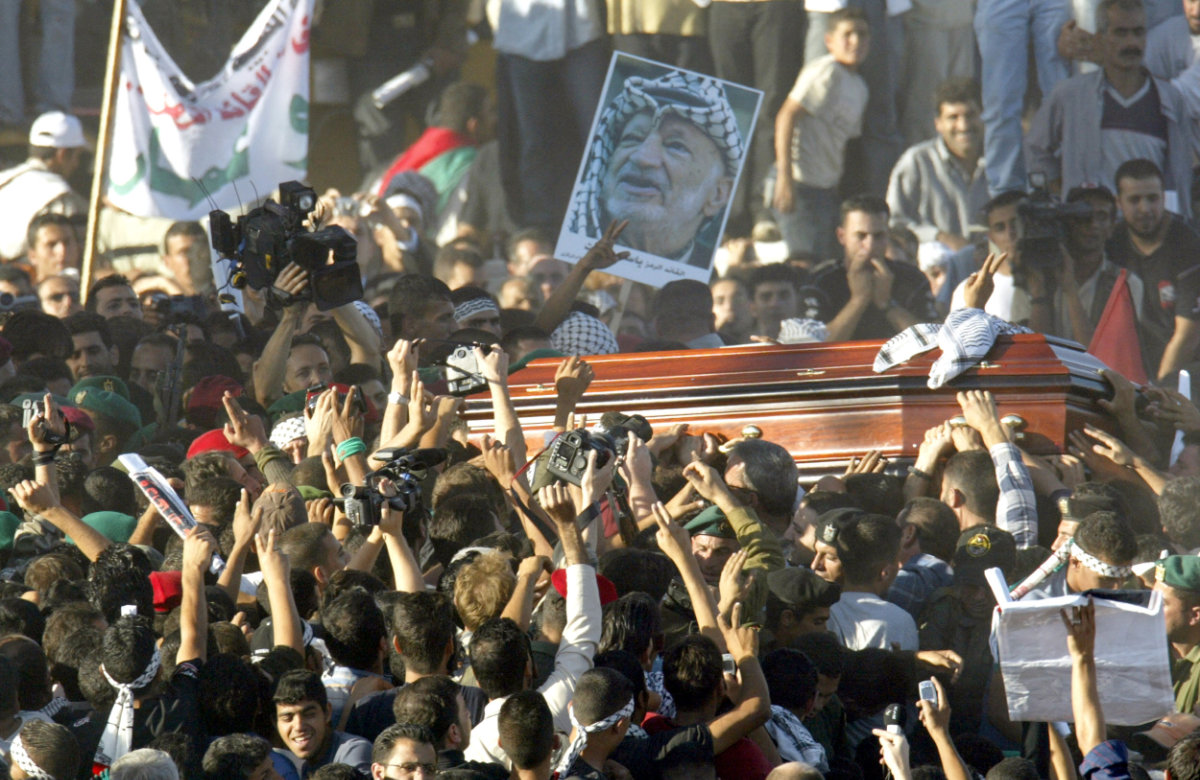

Palestinians crowd around the coffin of Fatah Chairman Yasser Arafat after it arrived from Cairo in the West Bank city of Ramallaha on November 12, 2004, for a burial ceremony. (AFP)
Abbas, known for his more pragmatic and diplomatic approach, was seen as a leader who could gain international credibility and potentially re-ignite peace talks with Israel. However, Arafat’s departure also brought long-simmering divisions among Palestinians to the fore.
“Abbas followed a revolutionary leader in Yasser Arafat and had to confront an Islamic movement that is focused on armed resistance,” said Kuttab, referring to the Palestinian militant group Hamas that controls Gaza.
“He attacked Hamas for their rocket attacks on Israel and has been silently disapproving of the Oct. 7, 2023, cross-border Hamas act that has caused huge loss of life as a result of the brutal Israeli revenge response.”
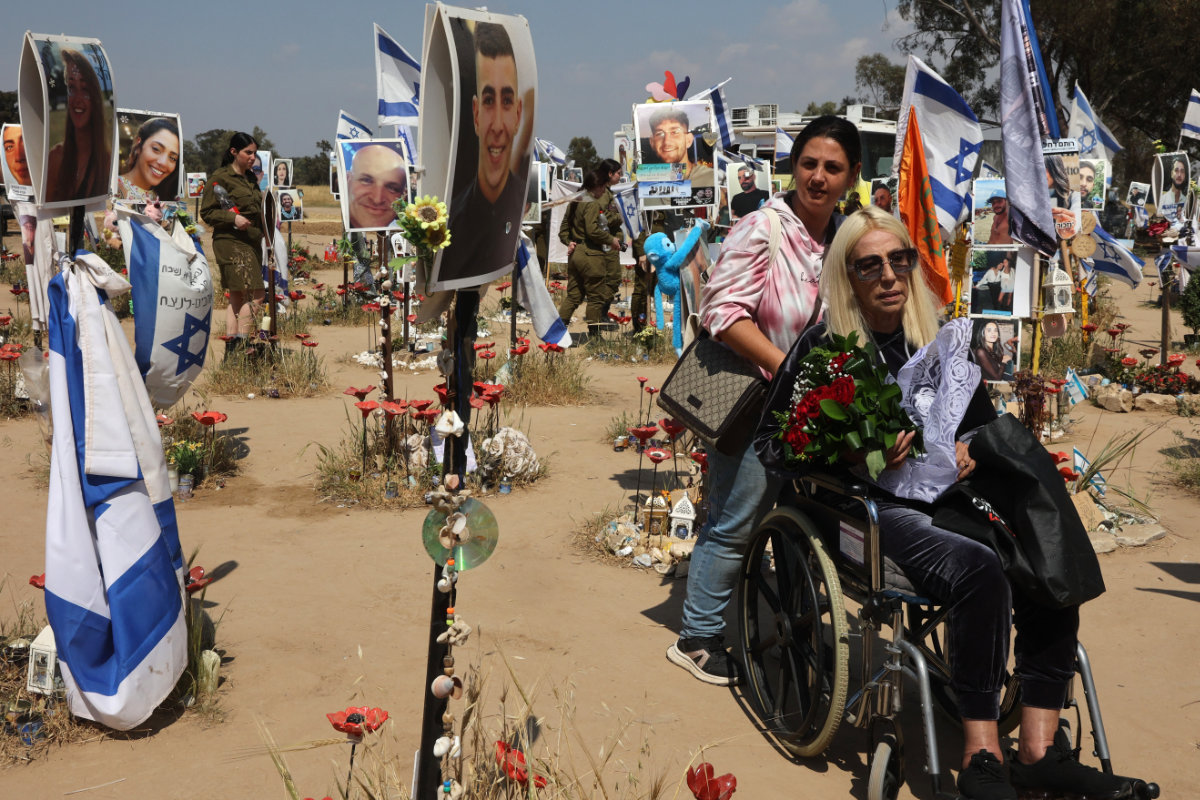

This April 7, 2024, photo shows near Israelis visiting a memorial at Kibbutz Reim in southern Israel, at the site of the October 7, 2023, Hamas attack on the Supernova music festival, which triggered Israel's genocidal Gaza invasion. (AFP)
The Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack on southern Israel left 1,200 people dead, the majority of them civilians, saw some 250 taken hostage, including many foreign nationals, and triggered Israel’s devastating retaliatory war in Gaza.
Fifteen months on, the war has cost the lives of more than 45,000 Palestinians, according to health officials in Gaza, although a new study published by the Lancet medical journal has placed the death toll at 64,260 as of last June.
The rivalry between Abbas’ Fatah and Hamas escalated into a full-blown schism in 2007. Following a short conflict, Hamas seized control of Gaza, leaving Abbas’ Fatah-dominated PA governing only parts of the West Bank.
This division has not only weakened the Palestinian cause but has also complicated efforts to present a unified front in negotiations with Israel.
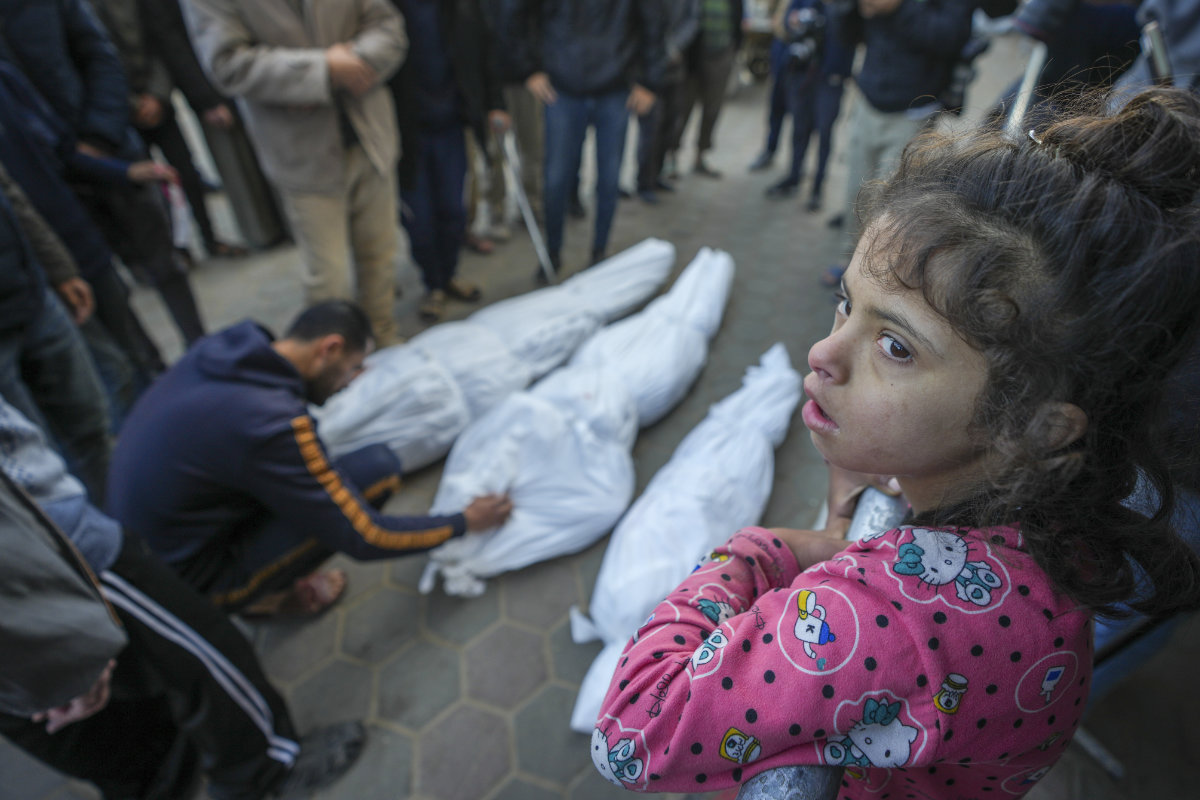

A Palestinian mourns his daughter and two other relatives who were killed in an Israeli airstrike on Jan. 11, 2025, in Deir al-Balah, central Gaza Strip. Fifteen months on, the Gaza war has cost the lives of more than 46,500 Palestinians and at least 109,660 wounded. (AFP)
Abbas began his presidency with optimism. His platform emphasized nonviolent resistance, institution-building, and a commitment to achieving a two-state solution through negotiations.
His efforts gained initial support from the international community, particularly the US and the EU. The 2005 Israeli withdrawal from Gaza was seen as a potential breakthrough, despite being unilateral and limited.
However, hopes for progress soon faded. The victory of Hamas in the 2006 legislative elections, coupled with the failure to reach a consensus on governance, exacerbated divisions.
Meanwhile, peace talks with Israel stalled repeatedly over issues such as settlement expansion, security arrangements, and the status of Jerusalem.

Palestinians rally in the West Bank city of Ramallah on June 13, 2007, calling for a stop to fighting between the Fatah and the Hamas movements in the Gaza Strip. Fatah and Hamas remain rivals to this day. (AFP)
The situation worsened after the 2008-09 Gaza war, further entrenching the divide between Hamas and Fatah. For many Palestinians, Abbas’ commitment to negotiations began to appear futile, especially as Israel’s settlement activity in the West Bank continued unabated.
Critics accused Abbas of presiding over a corrupt and ineffective administration, eroding public trust in the PA.
The split between the West Bank and Gaza remains one of the defining challenges of Abbas’ presidency. Efforts at reconciliation between Fatah and Hamas have repeatedly faltered, with each side blaming the other for the impasse.
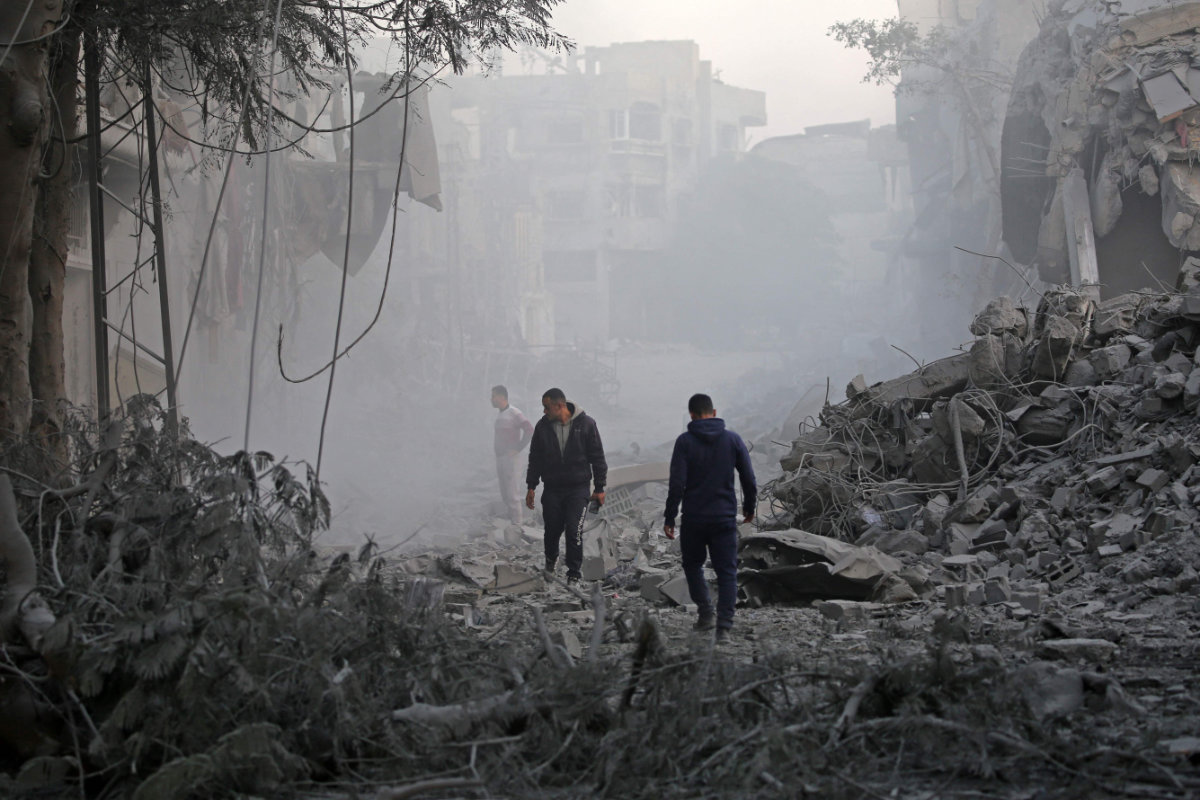

Caption
The Oct. 7 attack and the war in Gaza have done little to heal the rift. On Saturday, Fatah issued a rare statement criticizing Hamas for sacrificing Palestinian interests for Iran and causing destruction in Gaza.
The statement supports Fatah’s recent security crackdown in the Jenin refugee camp targeting Hamas, Palestinian Islamic Jihad, and other armed groups, accusing Tehran of funding these factions.
Fatah also condemned the Oct. 7 attack, rejecting Hamas’ strategy of armed conflict, and accused it of seeking to incite chaos in the West Bank
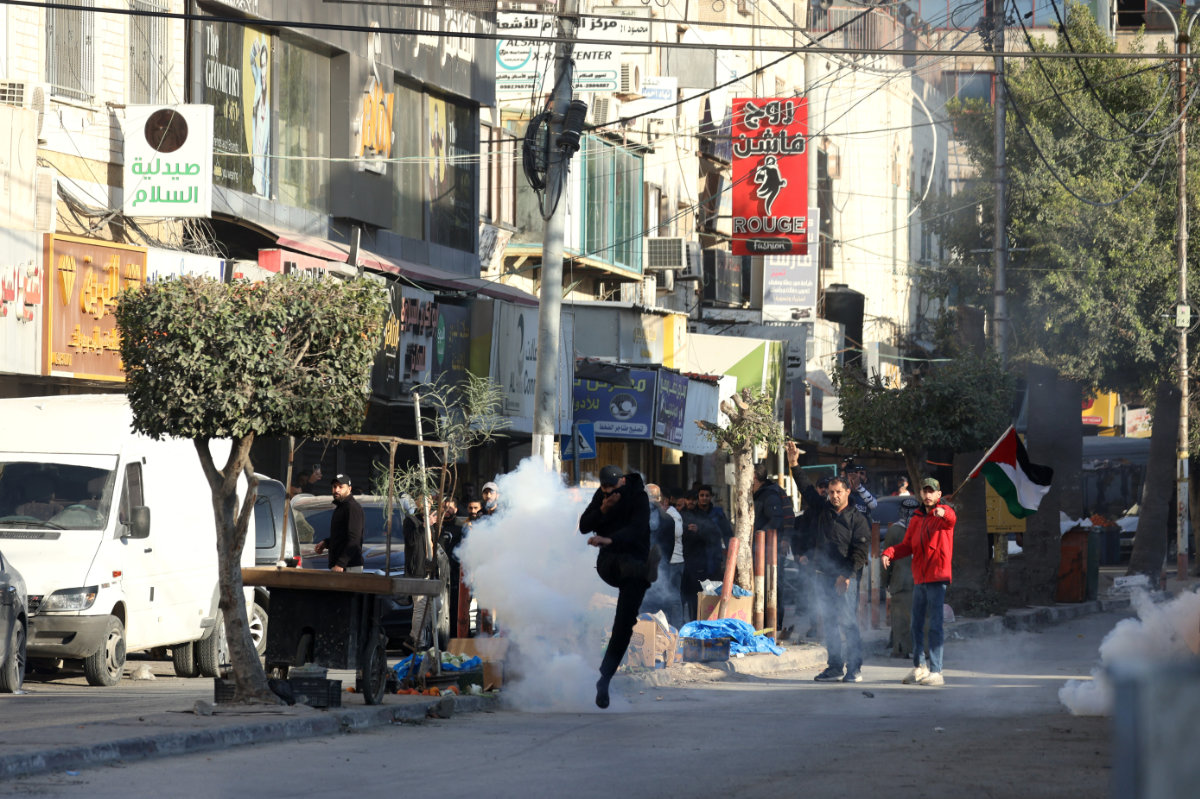

Protesters clash with members of the Palestinian Authority (PA) security forces, in Jenin in the Israel-occupied West Bank, on December 16, 2024. (AFP)
Talks in December between Fatah and Hamas about a nonpartisan Gaza administration have seen no clear progress. Meanwhile, the future governance of Gaza remains uncertain as Israeli leaders debate involving the PA following the defeat of Hamas.
Despite his long absence from the Palestinian Territories in the UAE, Mohammed Dahlan, a former Gaza security chief who was blamed by some within Fatah for the loss of Gaza, has since been tipped as a potential leader of the enclave — if Hamas were removed from power.
The Fatah Central Committee voted to expel Dahlan from the party in June 2011 after Abbas accused him of corruption and of plotting against him. Dahlan denied the allegations and accused Abbas of targeting him for his criticism of Abbas’ handling of the peace process.
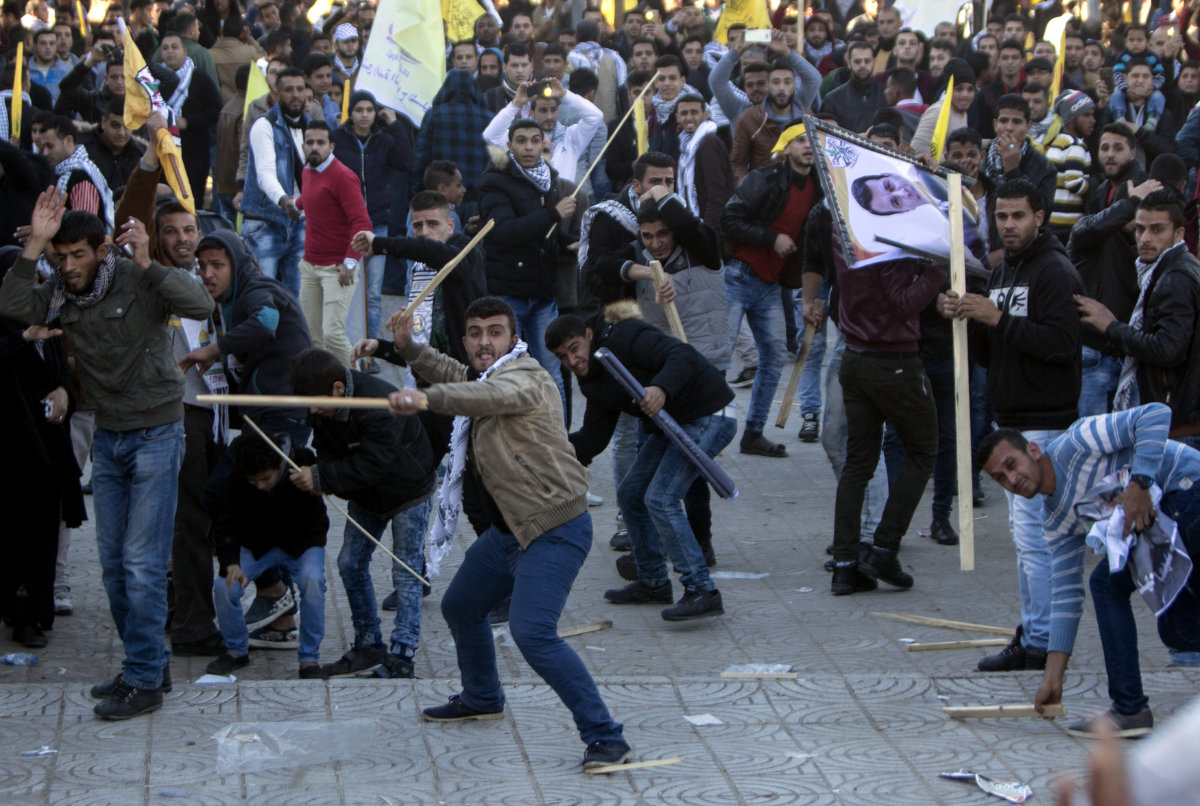

In this photo taken on December 31, 2016, supporters of Fatah's former security chief Mohammed Dahlan, an exiled rival to Mahmoud Abbas, clash with supporters of Abbas during a rally in Gaza City. (AFP file)
In spite of this history of division among the Palestinians, Abbas’ administration has achieved some notable successes on the international stage, including securing Palestine’s recognition as a non-member observer state at the UN in 2012.
This diplomatic victory underscored Abbas’ commitment to pursuing Palestinian statehood through nonviolent means and international legitimacy.
However, Abbas’ prolonged tenure has not been without controversy. Now aged 89, he has faced growing criticism for failing to hold elections since 2006, effectively extending his rule far beyond his original mandate.
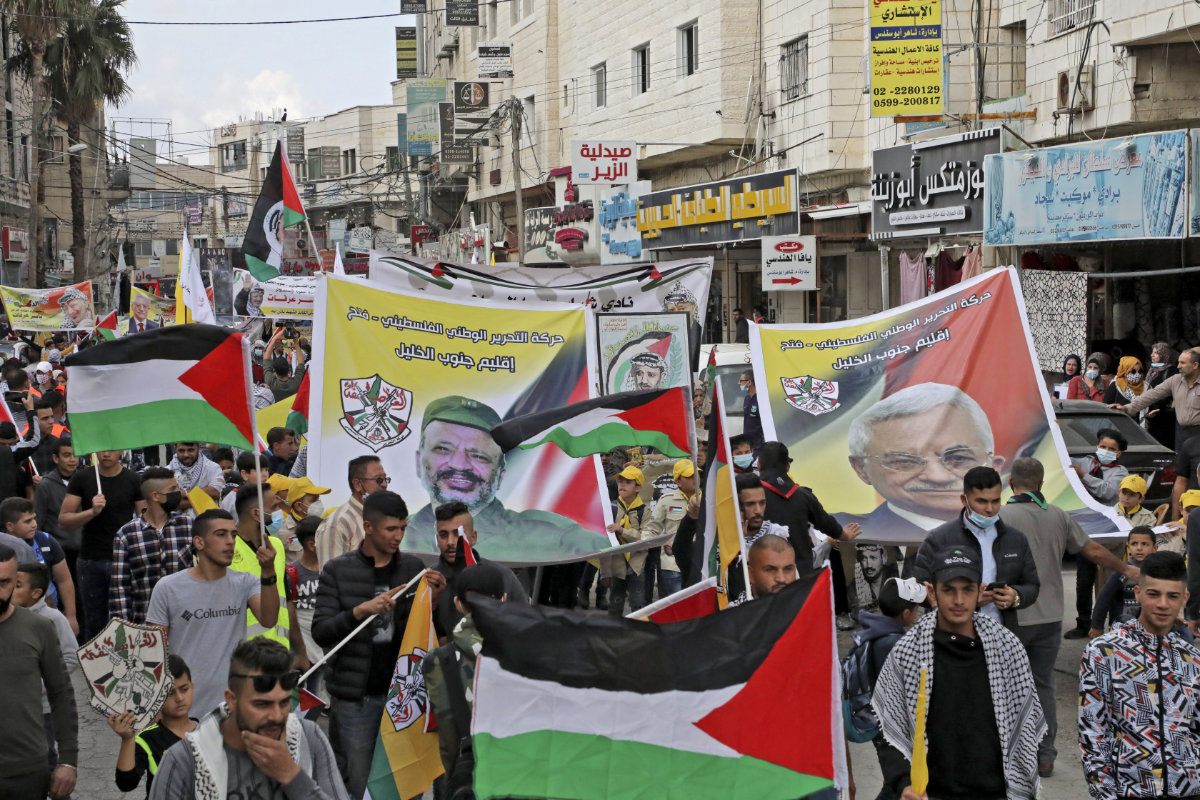

Palestinian Fatah movement supporters carry portraits of PA President Mahmud Abbas (R) and his late predecessor Yasser Arafat (L) during a march to mark the 16th anniversary of Arafat's death in the village of Dura, near the West Bank city of Hebron on November 11, 2020. (AFP file)
Many Palestinians view the PA as increasingly authoritarian, accusing it of suppressing dissent and prioritizing security coordination with Israel over the needs of its people. The PA’s reliance on international aid has also raised questions about its sustainability.
Economic dependency on donor funding has left the PA vulnerable to political pressure, particularly from the US and Israel. This dependency has fueled perceptions that the PA is complicit in managing the occupation rather than resisting it.
Meanwhile, Abbas has faced internal challenges from younger Fatah leaders and other political factions who view his leadership as out of touch. Calls for generational change have grown louder, with many Palestinians demanding a more inclusive and dynamic approach.
Despite these challenges, Abbas’ 20th year in office arrives at a moment of renewed international focus on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.

Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas (L) meeting with Saudi Arabia's Crown Prince Mohammed Bin Salman in Riyadh on August 27, 2024. (PPO/AFP)
Saudi Arabia’s emergence as a regional power broker has brought fresh hope for advancing the two-state solution. Under Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, the Kingdom has taken a proactive role in mediating conflicts and fostering dialogue, including between Israel and the Arab world.
In October 2024, Saudi Arabia announced the formation of the Global Alliance for the Implementation of the Two-State Solution. The coalition includes key players such as the US, the EU, and Arab states, with a mandate to address core issues including borders, settlements, refugees, and the status of Jerusalem.
Riyadh’s initiative has been bolstered by an ongoing Arab dialogue with Israel, which includes conditions tied to advancing Palestinian statehood in line with the 2002 Arab Peace Initiative.

Since the global alliance for the two-state solution was launched amid the Gaza war, the push for Palestinian statehood championed by Mahmoud Abbas has gained momentum. (Anadolu)
“No doubt Saudi Arabia is playing a leading role in this coalition, leveraging its regional and international influence as well as its longstanding support for the Palestinian cause,” Hani Nasira, an Egyptian writer and political expert, told Arab News.
“The Kingdom has consistently emphasized that the establishment of an independent Palestinian state is essential for peace and stability in the region and that any steps toward normalization with Israel must first secure Palestinian rights.”
This diplomatic strategy reflects Saudi Arabia’s commitment to balancing regional stability with the aspirations of the Palestinian people.
The question remains whether Abbas’ final years in power will witness the establishment of an independent Palestinian state. Much depends on the success of Saudi Arabia’s initiative and the willingness of all parties to engage in meaningful negotiations.
“Observers believe that the chances of establishing a Palestinian state under President Mahmoud Abbas remain viable, though significant challenges persist,” said Nasira.
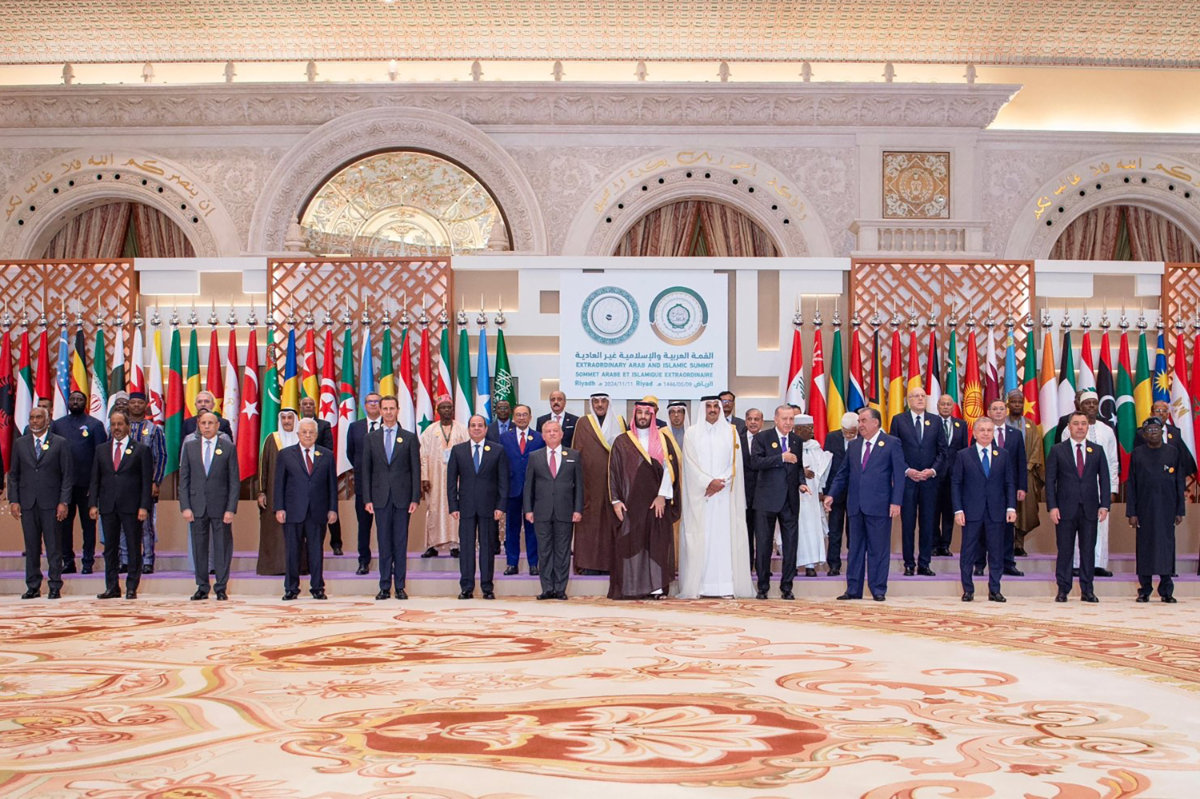
Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman (C) and leaders from member states of the Organization of Islamic Cooperation and the Arab League during their joint extraordinary summit in Riyadh on November 11, 2024 to discuss efforts at finding a peaceful solution to the question of Palestine. (SPA/AFP)
“These obstacles require internal Palestinian unity and robust Arab and international support — something Saudi Arabia is actively seeking to provide.
“Additionally, many countries and international organizations continue to support the establishment of an independent Palestinian state along the 1967 borders under the current Palestinian leadership.
“This includes the EU and most Islamic nations, as President Abbas seeks backing for a peace initiative rooted in the two-state solution and international resolutions.

“It is therefore clear that the Global Alliance reflects Saudi Arabia’s steadfast commitment to supporting the Palestinian cause and its relentless pursuit of a just and comprehensive peace in the region.
“This initiative aims to guarantee Palestinian rights and establish normalized relations among all countries in the region.”
For Abbas, the stakes are high. His legacy will ultimately be defined by whether he can translate decades of advocacy for Palestinian statehood into tangible results.
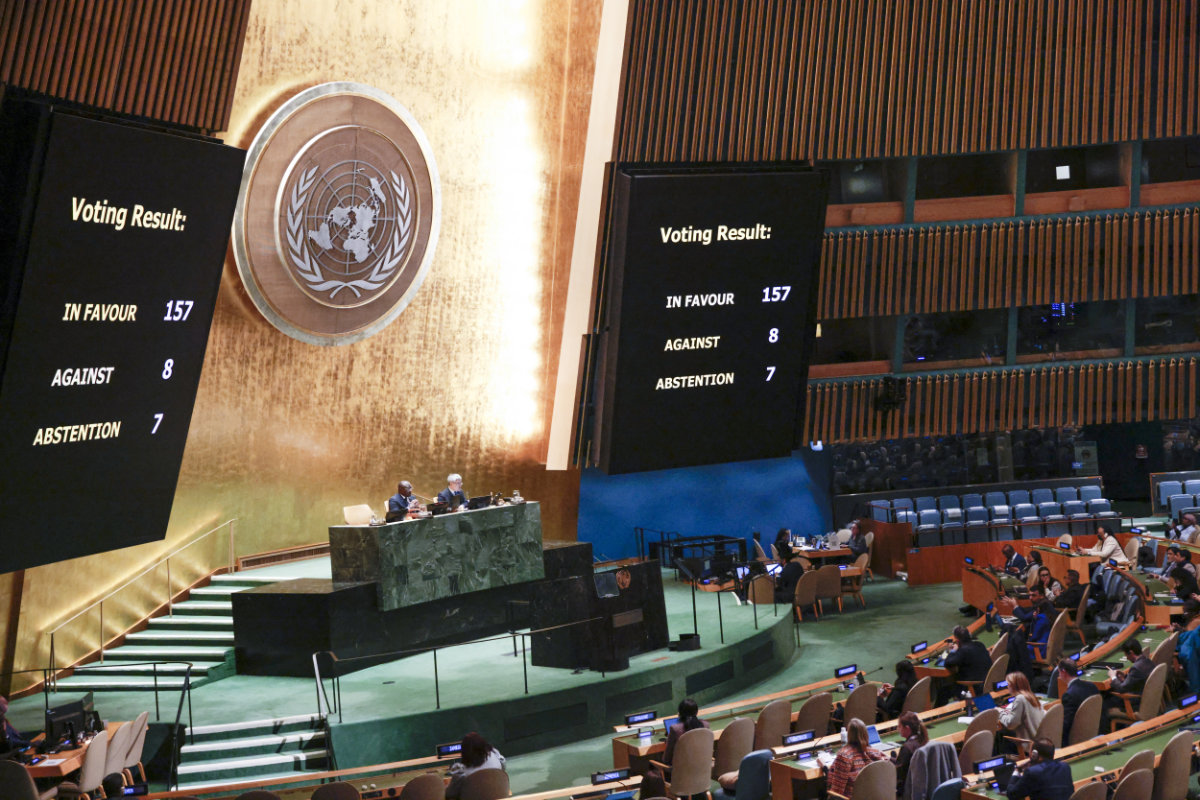

A screen shows the results of the vote on the resolution entitled "Peaceful settlement of the question of Palestine" at the General Assembly 46th plenary meeting on Dec. 3, 2024, at the UN headquarters in New York City. (AFP)
The PA has expressed cautious optimism about the Saudi-led coalition, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach that addresses historic injustices and ensures Palestinian sovereignty.
However, significant obstacles persist. Israel’s Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has shown little appetite for concessions, particularly on settlements and security issues, and has even dismissed the two-state solution out of hand.
As Abbas marks two decades in office, the Palestinians find themselves at a crossroads. While statehood remains elusive, renewed international focus on the conflict offers a glimmer of hope.

Abbas’ presidency has been a tale of resilience, missed opportunities, and unfulfilled aspirations. While his commitment to a two-state solution has earned him international respect, the lack of progress on the ground has left many Palestinians disillusioned.
“The Palestinian president remained focused on his peaceful mythology but failed to gain enough support in terms of electoral legitimization of his efforts,” Kuttab told Arab News.
“While Abbas’ direction directly reflected the recommendations of all of Palestine’s allies, they failed to engage or reward him for his rejection of violence and insistence of a politically negotiated solution to the Palestinian conflict.
“Nevertheless, President Abbas’ quest — that is, the national aspiration of Palestinians — remains to be the most logical step forward. Palestinian statehood is the best way to bring peace to the entire Middle East.”




























