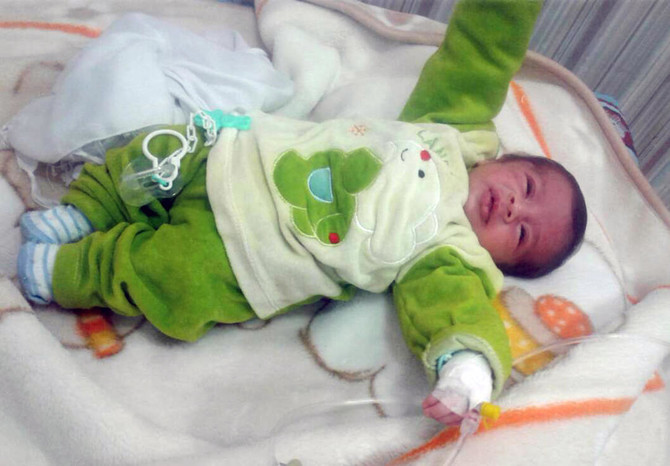
BEIRUT: One-month-old Heyim Hassan was receiving treatment for a chest infection in the Afrin general hospital in northern Syria when a shell landed a few meters (feet) away. His panicked father whisked him out of the building and spent hours looking for nebulizers to aid the infant’s breathing. No one was killed in the attack, but 30 children had to be evacuated to safety.
It was the third time Heyim’s father, Serbest, had to seek shelter for his family in the last month. Four days after the baby was born, Turkey launched an offensive in northwestern Syria, forcing them to flee their home and Serbest’s mobile phone shop to find safety in the district’s center.
Nearly a month into the offensive in Afrin, hundreds of thousands of Syrians like Hassan and his family are hiding from bombs and airstrikes in caves and basements, trapped in the Kurdish enclave while Turkey and its allies are bogged down in fierce ground battles against formidable opponents.
Crammed with 40 relatives into their new shelter, a three-bedroom apartment, the baby Heyim contracted the infection. Then the new neighborhood also got shelled while he was evacuated from the hospital.
“This is how it is in Afrin. It is not just me,” Hassan said in a series of messages to The Associated Press from inside Afrin, encircled and under attack since Jan. 20.
A slow-moving ground offensive, the assault on Afrin threatens to become a protracted standoff, deepening an already dire humanitarian situation. It could also prove costly for Turkey, diplomatically and militarily. So far, nearly 80 civilians in Afrin, according to the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights, and 31 Turkish soldiers have been killed. Turkey says it does all it can to avoid civilian casualties.
Turkey launched its offensive with more than 70 aircraft. Airstrikes were followed by a ground assault in which an estimated 10,000 allied Syrian rebel fighters took part, backed by Turkish artillery and other troops.
Fighting on six fronts, the Turkey-backed troops have met stiff resistance from the Kurdish People’s Defense Units, known as the YPG.
Turkish officials have made conflicting statements about the goals of the offensive, but have said they seek to push the Kurdish militia away from its borders.
The Kurdish fighters form the backbone of the U.S-backed Syrian Democratic Forces fighting Daesh group militants in eastern Syria, but are viewed by Turkey as an extension of its own insurgents, the Kurdistan Workers Party or the PKK.
Although Afrin is encircled from all sides by Turkey, the guerrilla fighters — with years to prepare for the defense of their 1,500-square-mile (3,885-square kilometer) district — have proven a challenge.
They targeted Turkish tanks and bases and claimed to have downed at least one helicopter. Eleven soldiers were killed in one day last week. The weather and geography have also slowed down the offensive, with fog and rain grounding jets and obstructing ground advances as fighters grappled to deal with the mountainous terrain.
The Observatory, which monitors in the war in Syria, estimates that Turkey has seized nearly 7 percent of district land along Afrin’s outer edges, including a strategic hill in the east, and Bulbul, Hassan’s hometown, in the north.
The YPG says 98 of its fighters have been killed. But the Observatory puts the toll at over 160, and estimated that over 200 Turkey-backed Syrian fighters have been killed.
YPG commanders hinted they could open new fronts against Turkey.
“We are in the first phase of the battle now,” said YPG commander Sipan Hemo. “This strategic battle will not end ... until we teach the Turkish occupation the right lessons, and they withdraw to their borders.”
Noah Bonsey, senior analyst with the International Crisis Group who recently returned from a visit to Kurdish-controlled territories in northern Syria, said Turkey may either remain along the edges of Afrin or attempt to gain additional ground inside the enclave.
“This is when things could really turn dangerous,” he said. “I think it is unclear where things are moving from here. All eyes are on (US Secretary of State Rex) Tillerson’s visit to Ankara.”
Tillerson met Thursday with Turkey’s President Recep Tayyip Erdogan and he and Turkish Foreign Minister Melvut Cavusoglu planned a news conference Friday after meetings were concluded. Ultimately, Ankara wants Washington to halt its support for the Syrian Kurdish militia.
Meanwhile, the offensive has emboldened Washington’s adversary, the Syrian government, which with Russia’s aid, is presenting itself as the solution to the bloody, unpredictable conundrum. Russia has tried to secure the return of some form of government presence to Afrin, asking the Kurdish militia to cede control of security and borders to Damascus.
Although the YPG rejected the proposal, it remains the only idea on the table and Kurdish commanders have recently called publicly on the Syrian government to assume its role guarding Afrin’s borders.
The UN, which has no access to Afrin, said it was “extremely difficult” to verify numbers of displaced, estimating in the first week of February that between 15,000 to 30,000 people were uprooted inside the enclave.
Local Kurdish official Arefeh Bakr said it was a struggle assisting people holed up with relatives in small apartments and caves to escape airstrikes. She herself is hosting 25 people in her home, relatives displaced from nearby villages.
“We don’t want aid or help,” Bakr said. “We just want an end to the airstrikes.”
Jiwan Mohamed, director of the Afrin general hospital, said with a staff of about 250 doctors and nurses, the hospital has so far been able to cope, but it was becoming overwhelming, particularly with a lack of blood transfer products and emergency kits. The UN said there are four other facilities in the district center, including one operated by a UN partner.
Fuel and food supplies have come in through government-held areas, ensuring that prices have not gone up. A water treatment plant was damaged, temporarily affecting supply to one area in the north.
According to the UN, local authorities have prevented people from leaving the enclave, except for critical medical cases allowed out by the Syrian government and Afrin authorities.
For Hassan, the return the Syrian government to Afrin is the least bad option. Although Afrin was one of the first areas to join the protests against the Syrian government that eventually turned into the current conflic, he said the prospect of Turkey-backed rebels swarming their town is frightening.
Dozens of videos have surfaced showing Turkey-backed rebels taking hostages in Afrin, mistreating the elderly and mutilating the body of a female Kurdish fighter.
“This shows what will happen to us,” Hassan said. “We are waiting in anticipation and watching videos.”
In Turkey, the offensive in Afrin is popular, playing to nationalist and anti-Kurdish sentiments ahead of the 2019 elections. Turkish opposition lawmaker and member of the defense committee, Dursun Cicek, said the operation is progressing slowly.
“But Turkey is not in any hurry,” he said.
Civilians have no place to run as Turkey offensive drags on
Civilians have no place to run as Turkey offensive drags on
Once a beacon of hope, Tunisia’s civil society struggles to survive

- The Tunisian General Labour Union, which won the 2015 Nobel peace prize with other civil society groups and could once bring tens of thousands onto the streets, has been sapped by the arrests of junior officials on corruption charges
TUNIS: In May 2024, Tunisian activist Cherifa Riahi was arrested just two months after giving birth, accused of harboring illegal migrants. Over a year later, she is still in prison without charge.
Rights groups see Riahi’s case as a symbol of accelerating repression of civil society under President Kais Saied, who dissolved parliament in 2021 and began ruling by decree.
The crackdown marks a significant turnaround for Tunisia, where civil society groups flourished in the wake of the 2011 uprising that unseated President Zine El-Abidine Ben Ali, inspired other Arab Spring uprisings, and helped shape a democratic transition.
HIGHLIGHTS
• Activists subject to detentions, threats
• Groups report asset freezes and raids
• President accuses them of serving foreign agendas
As head of a refugee support group, Riahi had been helping sub-Saharan asylum seekers and other migrants find housing and access medicine and food. Her family says she did nothing wrong.
The forced separation from her daughter and young son has been traumatic.
“The girl doesn’t recognize her mother at all,” Riahi’s mother Farida, who is now caring for her grandchild, told Reuters at their family home in La Marsa near the capital, Tunis.
“They took her while she was breastfeeding. We didn’t even have time to understand what was happening.”
Since Saied’s power grab, at least a dozen civil society figures like Riahi have been detained on allegations activists denounce as fabricated, according to rights groups and lawyers. At least 10 civil society groups have had their assets frozen and offices raided, they say.
The Tunisian General Labour Union, which won the 2015 Nobel peace prize with other civil society groups and could once bring tens of thousands onto the streets, has been sapped by the arrests of junior officials on corruption charges.
The Tunisian government’s media office did not respond to calls and written questions seeking comment about Riahi’s case and those of other activists and civil society groups.
Saied, 67, has accused civil society groups of “serving foreign agendas” and undermining national unity.
He has said he will not be a dictator and that freedom and democracy will be preserved, but that he will not allow chaos or interference through foreign funding or organizations that represent a “tool of treason.”
Activists warn that some of Tunisia’s last surviving democratic gains are at risk as the judiciary, media and parliament have all come under tighter executive control and most opposition party leaders are in prison.
“The attack on civil society organizations is not an isolated incident,” said Romdhane Ben Amor of the Tunisian Forum for Economic and Social Rights, an independent advocacy group.
“It comes within the context of the authorities’ plan to close civic space and to end the democratic openness achieved by Tunisians after January 14, 2011.”
’SEEN AS ENEMIES’
In Tunis, the offices of I Watch, an anti-corruption watchdog founded after the 2011 revolution, used to bustle with dozens of employees, volunteers and journalists.
These days, only three employees work on-site. Dozens work remotely, some fearing raids or arrests.
Wajdi Belloumi, I Watch’s president, said its bank transfers have been hindered and official investigations into the group are piling up. Hotels have stopped renting spaces for the group’s events, citing vague instructions from authorities, Belloumi said.
Last year, the electoral commission refused for the first time to allow I Watch to monitor elections due to suspicions of foreign funding.
“We’re seen as enemies now,” Belloumi told Reuters. “Many volunteers are afraid. Whistle-blowers have gone quiet. The pressure is everywhere — legal, financial, even personal.”
Ben Amor said he had received anonymous threats and started looking over his shoulder in public spaces.
“People start saying, ‘This man must be gotten rid of’,” he said, referring to comments sent in private messages, or “’your son studies at that school, your daughter studies at that school ... I saw you on that street’.”
Foreign governments that once championed Tunisia’s democratic transition now prioritize curbing migration and short-term stability, rights groups say.
Ben Amor said he believed he had been targeted particularly after speaking out against Saied’s recent anti-migrant rhetoric.
In 2023, the same year Tunisia signed a pact with the European Union aimed at stemming migration across the Mediterranean, Saied said illegal immigration was part of a “conspiracy” to alter Tunisia’s demographics.
Since then, authorities have dismantled tents and carried out forced deportations — the campaign amid which Riahi was detained.
Though the space for civil society groups is shrinking by the day, Belloumi said he remains committed.
“We chose this path — transparency, justice, accountability,” he said. “And we’re not walking away.”
Morocco’s central bank explores digital currency cross-border payments

- The bank has been working with the IMF and the World Bank to assess the payment system impacts of its central bank digital currency (CBDC), Jouahri told a conference in Rabat
RABAT: Morocco’s central bank was exploring the use of its own digital currency for peer-to-peer and cross border payments, bank governor Abdellatif Jouahri said on Monday.
A central bank digital currency (CBDC) is controlled by the central bank, in contrast to cryptocurrencies that are usually decentralized.
Cryptocurrencies have been banned in Morocco since 2017, but the public continues to use them underground, circumventing restrictions.
The bank has been working with the IMF and the World Bank to assess the payment system impacts of its central bank digital currency (CBDC), Jouahri told a conference in Rabat.
The Moroccan central bank, together with its Egyptian peer and the World Bank, was also exploring the use of the CBDC for cross-border transfers, he said. A draft law on crypto assets is currently under review by the finance ministry before entering the adoption process, Jouahri said last month.
WHO says staff residence in Gaza was attacked

The World Health Organization said that its staff residence and main warehouse in Gazan city of Deir Al-Balah was attacked thrice on Monday.
Two WHO staff and two family members were detained, said Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the WHO Director-General, adding that three were later released, while one staff member remained in detention.
Israeli tanks pushed into southern and eastern districts of the Gazan city of Deir Al-Balah for the first time on Monday, an area where Israeli sources said the military believes hostages may be held.
Why Lebanon’s fragile state hinges on Hezbollah’s next move

- Iran-backed group under pressure to disarm but its deep roots in armed resistance complicate peace hopes
- With Israel’s airstrikes and political paralysis, many doubt national unity can be restored without confrontation
BEIRUT: As pressure intensifies on Lebanon’s new government to resolve the question of Hezbollah’s arms, it confronts a fundamental challenge: Can the Iran-backed group relinquish its military wing and become a purely political party? And if it does, will Lebanon’s state institutions and political culture prove capable of supporting such a transition?
Earlier this month, Tom Barrack, the US ambassador to Turkiye and special envoy for Syria, telegraphed Washington’s growing impatience with the status quo in Lebanon in remarks to journalists following his visit to Beirut. He described Hezbollah’s disarmament as an essential condition for the renewal of international financial aid and long-term political stability in Lebanon.
As part of a proposal presented to Lebanese officials, the US offered support for Lebanon’s economic reform efforts in exchange for Hezbollah’s complete disarmament, Israeli withdrawal from Lebanese territory, and the release of Lebanese detainees held by Israel.
“If Lebanon doesn’t hurry up and get in line, everyone around them will,” Barrack said. He acknowledged what he described as a “spectacular” response from Beirut in a short time, but criticized the Lebanese political system’s ingrained culture of “delay, detour, and deflect,” saying time was running out for the country to adapt to a fast-changing regional order.
But disarming Hezbollah is far from straightforward. Despite suffering significant losses last year during its war with Israel, including the death of longtime leader Hassan Nasrallah and the destruction of much of its military infrastructure, Hezbollah has shown no willingness to give up its arms.

The group’s new leader, Sheikh Naim Qassem, reiterated that stance in a video address on July 19. “We will not surrender or give up to Israel; Israel will not take our weapons away from us,” he said.
According to him, any disarmament would be discussed only as part of a national defense strategy determined internally by Lebanon, and only after a complete Israeli withdrawal from Lebanese territory.
That position is tied to continued Israeli airstrikes, including recent attacks in the south that killed two individuals on July 20, as per local media reports.
Hezbollah cites these violations, along with Israel’s continued occupation of five positions seized after the November 2024 ceasefire, as justification for retaining its arms.
Although the group claims to have handed over 190 of its 265 southern military positions to the Lebanese army, it continues to maintain a significant arsenal in the region and in other strongholds.
Hezbollah emerged as Lebanon’s most powerful military force and dominant political actor in the post-civil war era, representing a significant portion of the Shiite population alongside the Amal party. Together, the two groups hold all the 27 Shiite seats in the 128-member parliament.
Analysts say that Hezbollah’s ideological foundation has long rested on armed resistance, so shifting toward civilian politics would require not only strategic recalculation but also a new political message capable of sustaining its popular base.

“For decades, the party has emphasized armed resistance against Israel as central to its appeal,” said David Wood, senior analyst on Lebanon at the International Crisis Group (ICG).
“If Hezbollah wants to transition into a normal political party, it will need to craft another electoral narrative based around how it can improve the socio-economic fortunes of its constituents.”
Such a transformation is not without precedent. Other armed movements in the region, such as the Palestinian Fatah in earlier decades, have evolved into political organizations. However, the Lebanese context is unique in many ways. Years of economic collapse, institutional paralysis and political gridlock have left the state too weak to assert its authority.
The November 2024 ceasefire, brokered by the US and France, was intended to revive the terms of UN Resolution 1701, which calls for Israeli withdrawal from all Lebanese territory, a halt to Hezbollah’s military operations near the southern border, and full control of arms by the Lebanese state. But little progress has been made.
Bilal Saab, associate fellow in the Middle East and North Africa Program at Chatham House, expressed doubt over Hezbollah’s ability to function effectively as a conventional political party. He pointed to signs of waning support in southern Lebanon and other Hezbollah strongholds.
The group’s military losses, the destruction of southern villages, and the economic suffering in Hezbollah-controlled areas are undermining its grassroots support, Saab told Arab News. “It is therefore unclear whether an unarmed Hezbollah could compete effectively in free elections, within Lebanon’s complex political system.”

He said the obstacles ahead of the government are political willingness and “exaggerated” fears of sectarian violence. The new leaders, he said, “must recognize that the chances of sectarian tensions are higher with the status quo unchanged.”
According to Saab, lack of serious action to address the issue of Hezbollah’s arms would prompt Israel to continue its attacks and cause more damage and human casualties. “If that happens, war-weary and economically dispossessed Lebanese could blame Hezbollah for causing even more death and destruction. This would in turn increase the risk of sectarian violence and people taking up arms against Hezbollah and its supporters,” he said.
For Lebanon’s new leadership under President Joseph Aoun and Prime Minister Nawaf Salam, the challenge is to preserve national stability while dealing with an increasingly polarized domestic landscape and pressure from powerful external actors.
Though both leaders have reiterated their commitment to imposing a state monopoly on arms, they have insisted that any progress depends on Israel’s complete withdrawal from Lebanese territory and an end to violations of Lebanese sovereignty.
While Barrack’s proposal received praise for its ambition, its feasibility depends on wider geopolitical considerations. Paul Salem, senior fellow at the Middle East Institute, believes that Iran, Hezbollah’s principal backer, will have the final say.

“The key decision of disarming Hezbollah would have to be made in Iran, the group’s main backer, not in Lebanon,” he told Arab News. “For the time being, it is clear that Tehran is encouraging Hezbollah to drag its feet and not to hand over all its arms and I think that will remain the case.”
Salem emphasized the need for a coordinated domestic and international effort to encourage Hezbollah’s transition into a political entity. This, he said, would require guarantees from the US, a defined role for the LAF, and political assurances from the Arab Gulf states.
“Hezbollah, at a minimum, would need assurances about Israel’s withdrawal and protection of its operatives in Lebanon, which would have to come from the US, as well reassurances from Gulf countries of aid for reconstruction of the war-ravaged areas,” Salem said.
“They would want some of that money to come through their auspices so they could benefit politically.”
The World Bank has estimated the cost of Lebanon’s reconstruction at $11 billion. US and Gulf officials have indicated that significant portions of that aid will only be unlocked if Hezbollah agrees to disarm.

The issue of integrating Hezbollah supporters into Lebanon’s broader political and economic fabric is also paramount. Wood emphasized that the process of disarming Hezbollah should come with assurances that the Shiite community would remain part of the nation-building process in a country long paralyzed by factional politics.
“Lebanon’s leaders must think very carefully about how to fully integrate Hezbollah’s supporters into the country’s future, or else they risk creating dangerous fissures in Lebanese society,” the ICG’s Wood said.
Despite mounting pressure, few expect a quick resolution. Reports suggest Hezbollah is conducting a strategic review of its military posture, exploring possible scenarios but delaying concrete action. “Hezbollah is taking a ‘wait and see’ approach for now,” Wood said. “Perhaps it wants to know if regional circumstances might improve for it before seriously entertaining the idea of surrendering its military wing.”
Meanwhile, the Lebanese army has consolidated control over Rafik Hariri International Airport and large parts of the south, improving state authority and border security. A successful disarmament, officials argue, would boost the credibility of Lebanon’s institutions and the case for the state’s monopoly on force.
The Middle East Institute’s Salem cautioned that Hezbollah is unlikely to fully relinquish its arms without assurances that go beyond Lebanese borders. If anything, he said, the disarmament would reduce sectarian tensions “with the Sunnis, Christians, Druze and other communities that have been afraid of Hezbollah’s arms.”

The potential rewards for Lebanon are clearly substantial. Hezbollah’s disarmament would enable Lebanon to form new alliances with regional and global partners. The disarmament process could also unlock vital economic assistance, helping the country recover from years of political paralysis, financial crisis and social unrest.
However, Lebanon’s leadership remains caught between the demands of the international community and the compulsions of domestic sectarian politics. For now, a delicate balance holds. But as pressure builds, time may be running out for Lebanon’s politicians to chart the country’s future — before others do it for them.

Israeli forces push into parts of a central Gaza city that the war had largely spared

- The UN food agency, meanwhile, accused Israeli forces of firing on a crowd of Palestinians seeking humanitarian aid over the weekend
DEIR AL-BALAH, Gaza Strip: Israeli ground troops for the first time Monday pushed into areas of a central Gaza city where several aid groups are based, in what appeared to be the latest effort to carve up the Palestinian territory with military corridors.
Deir Al-Balah is the only Gaza city that has not seen major ground operations or suffered widespread devastation in 21 months of war, leading to speculation that the Hamas militant group holds large numbers of hostages there. The main group representing hostages’ families said it was “shocked and alarmed” by the incursion and demanded answers from Israeli leaders.
Israel says the seizure of territory in Gaza is aimed at pressuring Hamas to release hostages, but it is a major point of contention in ongoing ceasefire talks.
FASTFACTS
• The main group representing hostages’ families said it was ‘shocked and alarmed’ by the incursion and demanded answers from Israeli leaders.
• Israel says the seizure of territory in Gaza is aimed at pressuring Hamas to release hostages, but it is a major point of contention in ongoing ceasefire talks.
• The UN food agency has accused Israeli forces of firing on a crowd of Palestinians seeking humanitarian aid over the weekend.
The UN food agency, meanwhile, accused Israeli forces of firing on a crowd of Palestinians seeking humanitarian aid over the weekend. Gaza’s Health Ministry called it one of the deadliest attacks on aid-seekers in the war that has driven the territory to the brink of famine.
In the latest sign of international frustration, the UK, France and 23 other Western-aligned countries issued a statement saying “the war in Gaza must end now.” They harshly criticized Israel’s restrictions on humanitarian aid and called for the release of the 50 hostages remaining in Gaza.
Explosions were heard from parts of the city that were ordered evacuated on Sunday. The Israeli military official said it was the first time ground troops had operated in the area.
A man living in the evacuation zone said Israel dropped pamphlets at dawn ordering people to evacuate. Two hours later, tanks rolled into the area.
He said his 62-year-old father, who had spent the night elsewhere, fled from house to house as Israeli forces moved in and saw them flattening structures with bulldozers and tanks. Both men managed to leave the evacuation zone.
UN spokesperson Stephane Dujarric said two UN guesthouses in Deir Al-Balah were damaged by shrapnel. He said the cause was still being investigated but that heavy Israeli airstrikes had been reported in the area. Local and international staff will continue to work there, he said.
The military declined to say if it had ordered the evacuation of aid groups based in the city, saying only that it maintains continuous contact with them and facilitates their relocation when necessary.
Tens of thousands of people have sought refuge in Deir Al-Balah during repeated waves of mass displacement in Gaza.
The UN humanitarian coordinator says 87.8 percent of Gaza is now under evacuation orders or inside Israeli military zones, “leaving 2.1 million civilians squeezed into a fragmented 12 percent of the Strip, where essential services have collapsed.”
Israel has taken over large areas of Gaza and split the territory with corridors stretching from the border to the sea as it seeks to pressure Hamas to release more hostages.
In response to the Deir Al-Balah incursion, the Hostages and Missing Families Forum warned in its statement that “the people of Israel will not forgive anyone who knowingly endangered the hostages — both the living and the deceased. No one will be able to claim they didn’t know what was at stake.”
Israel blames the deaths of Palestinian civilians on Hamas because the militants operate in densely populated areas, and it accuses the group of prolonging the war because Hamas has not accepted Israel’s terms for a ceasefire.
The World Food Programme, in a rare condemnation, said the crowd surrounding its convoy in northern Gaza on Sunday “came under fire from Israeli tanks, snipers and other gunfire.” It said “countless lives” were lost. A photographer working with the AP counted 51 bodies at two hospitals.
The Gaza Health Ministry said at least 80 people were killed. Israel’s military said it fired warning shots “to remove an immediate threat” and questioned the death toll reported by the Palestinians. It declined to comment on the WFP statement.

















